All questions of Verification of Accounting Records for Grade 9 Exam
The credit balance of Rs. 2,000 in the bank column of the cash book was carried forwarded as its debit balance. When overdraft as per pass book is starting point: - a)Rs. 2,000 will be deducted
- b)Rs. 2,000 will be added
- c)Rs. 4,000 will be deducted
- d)Rs. 4,000 will be added
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Sonal Patel answered |
When the credit balance of Rs. 2,000 in the bank column of the cash book was carried forward as its debit balance, it means that the cash book shows an overdraft balance of Rs. 2,000 instead of a credit balance.
Now, we need to compare this balance with the balance as per pass book. If the pass book shows an overdraft balance, then we need to deduct it from the cash book balance. If the pass book shows a credit balance, then we need to add it to the cash book balance.
In this question, the starting point is given as the pass book showing an overdraft balance. Therefore, we need to deduct this balance from the cash book balance.
So, the calculation would be:
Cash book balance (overdraft) = Rs. 2,000 (debit balance)
Pass book balance (overdraft) = Given
Overdraft as per pass book = Pass book balance - Cash book balance
Since the pass book balance is an overdraft balance, it would be higher than the cash book balance (overdraft). Therefore, we need to deduct the cash book balance from the pass book balance.
Overdraft as per pass book = Pass book balance - Cash book balance
Overdraft as per pass book = (Given) - Rs. 2,000
Overdraft as per pass book = Rs. (Given - 2,000)
Hence, option C. Rs. 4,000 will be deducted is the correct answer.
The Cash book showed an overdraft of Rs.1,500 but the pass book made up to same date should that cheques of Rs. 100, Rs. 50 and Rs. 125 had not been presented for payment and a cheque of Rs. 400 had not been cleared. The balance as per the Cash Book will be:
- a)Rs. 1,100
- b)Rs. 1,625
- c)Rs. 2,175
- d)Rs. 1,375
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Rithika Nair answered |
Overdraft in Cash Book = Rs. 1,500
Cheques not presented for payment = Rs. 100 + Rs. 50 + Rs. 125 = Rs. 275
Cheque not cleared = Rs. 400
To find: Balance as per Cash Book
Solution:
Step 1: Adjust the cheques not presented for payment
Cash Book balance = Overdraft - Cheques not presented for payment
Cash Book balance = Rs. 1,500 - Rs. 275 = Rs. 1,225
Step 2: Adjust the cheque not cleared
Cash Book balance = Cash Book balance - Cheque not cleared
Cash Book balance = Rs. 1,225 - Rs. 400 = Rs. 825
Step 3: Compare with Pass Book balance
As per the Pass Book, there are no transactions that have not been recorded in the Cash Book. Therefore, the balance as per Pass Book is the actual balance.
Pass Book balance = Cash Book balance + Overdraft
Pass Book balance = Rs. 825 + Rs. 1,500 = Rs. 2,325
Therefore, the balance as per Cash Book is Rs. 825 and the correct option is (b) Rs. 1,625.
Balance as per pass book Rs. 20,000 Rs. 4,000 were directly deposited by a customer into the bank. Then the balance as per cash book is:
- a)Rs. 24,000
- b)Rs. 18,000
- c)Rs. 16,000
- d)Rs. 22,000
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
KP Classes answered |
- Balance as per pass book: Rs. 20,000
- Direct deposit by customer: Rs. 4,000
Calculation for balance as per cash book:
- Balance as per pass book: Rs. 20,000
- Direct deposit: Rs. 4,000
- Total balance: Rs. 20,000 (from pass book) + Rs. 4,000 (direct deposit) = Rs. 24,000
Therefore, the balance as per cash book is Rs. 24,000.
The Trial Balance of M/S RAM & Co. shows closing Stock of Rs. 30,000. It will be recorded in : - a)Trading account
- b)Profit and Loss account
- c)Balance sheet
- d)Both (a) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Harshad Nair answered |
The credit balance as per pass book of Mr. X was Rs. 65,600. Cheques issued but not presented for payment Rs. 75,800. Cheques deposited by one of the customers of the bank but wrongly credited in Mr. X account Rs. 20,600. The balance as per cash book will be:-- a)Rs. 30,800 Debit
- b)Rs. 30,800 overdraft
- c)Rs. 1,20,800 Debit
- d)Rs. 10,400 overdraft.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Raghavendra Choudhury answered |
Credit balance as per pass book = Rs. 65,600
Cheques issued but not presented for payment = Rs. 75,800
Cheques deposited by a customer but wrongly credited in Mr. X account = Rs. 20,600
To calculate the balance as per cash book, we need to adjust the above items in the credit balance as per pass book.
Step 1: Adjust the cheques issued but not presented for payment
Credit balance as per pass book = Rs. 65,600
Less: Cheques issued but not presented for payment = Rs. 75,800
Adjusted balance = Rs. (10,200) (overdraft)
Step 2: Adjust the cheques deposited by a customer but wrongly credited in Mr. X account
Credit balance as per pass book = Rs. (10,200) (overdraft)
Add: Cheques deposited by a customer but wrongly credited in Mr. X account = Rs. 20,600
Adjusted balance = Rs. 10,400 (overdraft)
Therefore, the balance as per cash book will be Rs. 10,400 (overdraft).
Favourable balance as per Cash Book Rs. 5,000. Debit side of Cash Book under cast by Rs. 2.000. Cheque deposited into bank Rs. 3,000 dishonoured but no entry for dishonour is made in cash book. Balance as per Pass Book is :- a)Rs. 4,000
- b)Rs. 10,000
- c)Rs. 6,000
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Subhankar Sen answered |
Favourable balance as per Cash Book = Rs. 5,000
Debit side of Cash Book under cast by Rs. 2,000.
Therefore, the revised balance as per Cash Book = Rs. (5,000 - 2,000) = Rs. 3,000.
Cheque deposited into bank Rs. 3,000 dishonoured but no entry for dishonour is made in cash book.
Hence, the balance as per Cash Book should be further reduced by Rs. 3,000.
Therefore, the actual balance as per Cash Book = Rs. (3,000 - 3,000) = Rs. 0.
Now, we need to reconcile the Pass Book balance with the actual balance as per Cash Book.
The Pass Book balance will only reflect the amount of Rs. 3,000 that was deposited into the bank and not the dishonour.
Hence, the Pass Book balance will be Rs. (5,000 + 3,000) = Rs. 8,000.
However, since the actual balance as per Cash Book is Rs. 0, the correct balance as per Pass Book will be reduced by Rs. 8,000.
Therefore, the correct balance as per Pass Book = Rs. (8,000 - 8,000) = Rs. 4,000.
Hence, the correct answer is option 'A' - Rs. 4,000.
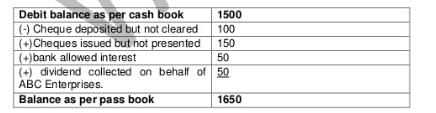
Debit balance as per Cash Book of ABC Enterprises as on 31.3.2006 is Rs. 1,500.Cheques deposited but not cleared amounts to Rs. 100 and Cheques issued but not presented of Rs. 150. The bank allowed interest amounting Rs. 50 and collected dividend Rs. 50 on behalf of ABC Enterprises. Balance as per pass book should be- a)1,600.
- b)1,450.
- c)1,850.
- d)1,650.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Freedom Institute answered |
When drawing up a Bank Reconciliation Statement, if you start with a debit balance as per the Bank Statement, the unpresented cheques should be:- a)Added;
- b)Deducted;
- c)Not required to be adjusted.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Devanshi Rane answered |
Bank Reconciliation Statement is a statement that reconciles the bank balance as per the company's books with the bank balance as per the bank statement. The statement helps in identifying the discrepancies and errors between the two balances.
Debit Balance occurs when the bank balance as per the bank statement is more than the bank balance as per the company's books. In this case, the company owes money to the bank.
Unpresented Cheques
Unpresented Cheques are the cheques issued by the company but not yet presented to the bank for payment. These cheques are included in the company's books, but not in the bank statement, resulting in a difference between the two balances.
Adjustment of Unpresented Cheques
When drawing up a Bank Reconciliation Statement with a debit balance as per the Bank Statement, the unpresented cheques should be added to the bank balance as per the company's books. This adjustment will increase the bank balance, bringing it closer to the bank balance as per the bank statement.
Reason for Adding Unpresented Cheques
Unpresented Cheques represent the company's liabilities, and hence, should be added to the bank balance as per the company's books. The company owes money to the bank for these cheques, and hence, the bank balance should be increased accordingly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when drawing up a Bank Reconciliation Statement with a debit balance as per the Bank Statement, the unpresented cheques should be added to the bank balance as per the company's books. This adjustment will bring the bank balance closer to the bank balance as per the bank statement, helping the company identify any discrepancies and errors.
Credit balance as per cash Book Rs. 10,000
Bank charged interest Rs. 150
Cheques issued but not presented for payment Rs. 2,500
Balance as per pass Book will be :
- a)Rs. 7,650
- b)Rs. 12,350
- c)Rs. 12,650
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bank charged interest Rs. 150
Cheques issued but not presented for payment Rs. 2,500
Balance as per pass Book will be :
|
|
Pj Commerce Academy answered |
- Credit balance as per Cash Book: Rs. 10,000
- Bank charged interest: Rs. 150
- Cheques issued but not presented for payment: Rs. 2,500
Calculation:
- Opening balance (Credit balance as per Cash Book): Rs. 10,000
- Add: Bank charged interest: Rs. 150
- Less: Cheques issued but not presented for payment: Rs. 2,500
Balance as per Pass Book:
10,000 + 150 - 2,500
= Rs. 7,650
Therefore, the correct answer is A: Rs. 7,650.
Which type of error occurs when credit sales is wrongly posted to Purchase Day Book:- a)Error of omission
- b)Error of commission
- c)Compensatory error
- d)Error of principle
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Live To answered |
such that new expense (debit) balance and liability (credit) is created at the same time.
Bank Overdraft as per cash book is Rs. 10,500. Interest debited by bank Rs. 3,500 for which advice was not received by account holder. Cheques deposited but not credited by bank Rs. 7,500. Cheques issued but not yet presented Rs. 9,500. What is the Overdraft amount as per Pass Book?- a)Rs. 12,000
- b)Rs. 16,000
- c)Rs. 5,000
- d)Rs. 9,000
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Nipun Tuteja answered |
- Adjust for Bank Interest: The bank debited Rs. 3,500 for interest not known to the account holder. This increases the overdraft, so add Rs. 3,500.
- Adjust for Deposited but Uncredited Cheques: Cheques amounting to Rs. 7,500 are deposited but not yet credited by the bank. This also increases the overdraft, so add Rs. 7,500.
- Adjust for Issued but Unpresented Cheques: Cheques issued but not yet presented amount to Rs. 9,500. This reduces the overdraft, so subtract Rs. 9,500.
- Calculate Overdraft as per Pass Book:
\[
\text{Overdraft as per Pass Book} = 10,500 + 3,500 + 7,500 - 9,500 = 12,000
\]
- Correct Answer: A: Rs. 12,000
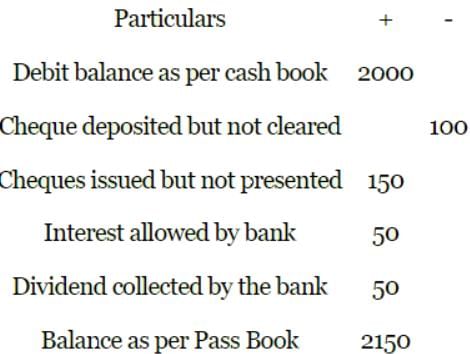
Debit balance as per cash book Rs.2000
Cheques deposited but not cleared Rs. 100
Cheques issued but not presented Rs. 150
Bank allowed interest Rs. 50
Bank collected dividend Rs. 50
Balance as per Pass Book will be:
- a)Rs. 2,100
- b)Rs. 1,950
- c)Rs. 2,350
- d)Rs. 2,150
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cheques deposited but not cleared Rs. 100
Cheques issued but not presented Rs. 150
Bank allowed interest Rs. 50
Bank collected dividend Rs. 50
Balance as per Pass Book will be:

|
Niharika Chavan answered |
Debit balance as per cash book = Rs. 2000
Cheques deposited but not cleared = Rs. 100
Cheques issued but not presented = Rs. 150
Bank allowed interest = Rs. 50
Bank collected dividend = Rs. 50
Adding the above transactions:
2000 + 100 - 150 + 50 + 50 = Rs. 2,050
Adjustment for Cheques:
Cheques issued but not presented = Rs. 150
Cheques deposited but not cleared = Rs. 100
Net adjustment for cheques = Rs. 50 (150 - 100)
Adding net adjustment for cheques to the balance as per pass book:
Rs. 2,050 + Rs. 50 = Rs. 2,100
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - Rs. 2,150.
Debit balance as per cash book Rs.2000
Cheques deposited but not cleared Rs. 100
Cheques issued but not presented Rs. 150
Bank allowed interest Rs. 50
Bank collected dividend Rs. 50
Balance as per Pass Book will be:
- a)Rs. 2,100
- b)Rs. 1,950
- c)Rs. 2,350
- d)Rs. 2,150
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cheques deposited but not cleared Rs. 100
Cheques issued but not presented Rs. 150
Bank allowed interest Rs. 50
Bank collected dividend Rs. 50
Balance as per Pass Book will be:

|
KP Classes answered |
Opening and Closing Balance of Debtors A/c were Rs. 30,000 and 40,000 respectively cash collected from the debtors during the year was Rs. 2,40,000. Discount allowed to debtors for timely payment amounted to Rs. 15,000 and bad debts written off were Rs. 10,00. Goods sold on credit were:- a)Rs. 2,55,000
- b)Rs. 2,45,000
- c)Rs. 2,95,000
- d)Rs. 2,75,000
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Rithika Mukherjee answered |
Cash collected from debtors during the year = Rs. 2,40,000
Discount allowed to debtors = Rs. 15,000
Bad debts written off = Rs. 10,000
Total amount received from debtors = Rs. 2,40,000 + Rs. 15,000 - Rs. 10,000 = Rs. 2,45,000
Closing balance of Debtors A/c = Opening balance + Goods sold on credit - Total amount received from debtors
Closing balance of Debtors A/c = Rs. 30,000 + Goods sold on credit - Rs. 2,45,000
Closing balance of Debtors A/c = Goods sold on credit - Rs. 2,15,000
Since the closing balance of Debtors A/c is Rs. 40,000,
Goods sold on credit = Rs. 40,000 + Rs. 2,15,000 = Rs. 2,55,000
Therefore, the correct option is D) Rs. 2,75,000
The goods sold for Rs. 900 but the amount was entered in the sales Account as Rs. 1080. On Rectification, suspense account will be:- a)Debited by Rs. 180
- b)Credited by Rs. 180
- c)Debited by Rs. 1080
- d)Credited by Rs. 1080
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Meera Basak answered |
Rectification of errors is an important aspect of accounting. It involves identifying and correcting errors made in the books of accounts. There are two types of errors in accounting:
1. Clerical errors: These are errors made due to mistakes in recording transactions. They can be corrected by making the necessary adjustments in the books of accounts.
2. Substantive errors: These are errors that affect the financial statements. They require a more detailed analysis to correct.
In this question, we are given that the goods were sold for Rs. 900 but the amount was entered in the sales account as Rs. 1080. This is a clerical error and can be rectified by making the necessary adjustment in the books of accounts.
Suspense Account
A suspense account is a temporary account used to hold transactions that cannot be immediately identified. It is created when there is uncertainty about the correct accounting treatment for a transaction. The transactions are then later identified and transferred to their appropriate accounts.
In this question, the difference between the amount sold and the amount recorded in the sales account is Rs. 180. This amount needs to be transferred to the correct account. Since the amount was recorded in excess, the suspense account needs to be credited with Rs. 180.
Answer
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - Suspense account will be credited by Rs. 180.
The payment side of Cash Book is under cast by Rs. 250. If the starting point of BRS is the Overdraft Balance as per Pass Book, then what would be the treatment to reach to Overdraft Balance of Cash Book ?
- a)Less 250
- b)Add 250
- c)Add 500
- d)Less 500
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
An amount of Rs. 6,000 due from Anshul, which had been written off as a bad debt in a previous year, was unexpectedly recovered and had been posted to his personal account. The rectification entry is :
- a)Anshul A/c Dr. Rs. 6,000
To Suspense A/c Rs. 6,000
- b)Suspense A/c Dr. Rs. 6,000
To Bad Debts
Recovered A/c Rs. 6,000
- c)No entry will be made
- d)Anshul A/c Dr. Rs. 6,000
To Bad Debts
Recovered A/c Rs. 6,000
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
To Suspense A/c Rs. 6,000
To Bad Debts
Recovered A/c Rs. 6,000
To Bad Debts
Recovered A/c Rs. 6,000

|
Nipun Tuteja answered |
When an amount previously written off as a bad debt is unexpectedly recovered, the rectification entry in the accounting records is as follows:
- Bad Debts Recovered A/c Dr. Rs. 6,000: This account is debited to record the recovery of the bad debt. It increases the amount of income or reduction in expense related to bad debts.
- Anshul A/c Cr. Rs. 6,000: Anshul's personal account is credited to reinstate the amount that had been previously written off as a bad debt. This reduces the accounts receivable balance from Anshul.
To Anshul A/c 6,000
A cheque for Rs. 500 received from Yuvraj & Co. was dishonoured and debited to discount Account. Due to rectification of this error, net profit will :- a)Decrease by Rs. 1,000
- b)Increase by Rs. 500
- c)Increase by Rs. 1,000
- d)No change
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Nipuns Institute answered |
When the balance as per Cash Book is the starting point, direct deposits by customers are.- a)Added
- b)Subtracted
- c)Not required to be adjusted
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Harjindra Singh answered |
When the balance as per Cash Book is the starting point, direct deposits by customers are:- a)added
- b)subtracted;
- c)not required to be adjusted
- d)neither of the two
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Rajveer Jain answered |
Direct deposits by customers are added when the balance as per Cash Book is the starting point. This is because direct deposits by customers are an inflow of cash into the business, which increases the cash balance. Adding these deposits to the starting balance of the Cash Book reflects the actual cash position of the business.
To understand this concept in detail, let's break down the answer:
**1. Cash Book:**
The Cash Book is a subsidiary book that records all cash and bank transactions of a business. It serves as a record of all cash inflows and outflows, including cash received from customers and cash paid to suppliers, employees, etc.
**2. Starting Point:**
The starting point refers to the opening balance of the Cash Book. It is the balance of cash on hand or in the bank at the beginning of a particular accounting period. This balance is carried forward from the previous period's closing balance.
**3. Direct Deposits by Customers:**
Direct deposits by customers refer to cash payments made directly into the business's bank account by its customers. These deposits could be in the form of payments for goods or services, loan repayments, or any other form of cash inflow from customers.
**4. Adding Direct Deposits:**
When the balance as per Cash Book is the starting point, direct deposits by customers are added. This means that the amount of direct deposits made by customers is added to the starting balance of the Cash Book.
Adding these deposits increases the cash balance in the Cash Book, reflecting the actual inflow of cash into the business. It ensures that the Cash Book accurately represents the cash position of the business at the beginning of the accounting period.
**5. Purpose of Adjustment:**
The purpose of this adjustment is to reconcile the Cash Book balance with the bank statement balance. By adding the direct deposits made by customers, the Cash Book balance will match the bank statement balance, which also includes these deposits.
**Conclusion:**
In summary, when the balance as per Cash Book is the starting point, direct deposits by customers are added. This adjustment ensures that the Cash Book accurately reflects the cash position of the business and reconciles it with the bank statement balance.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:If balance as per Pass Book is the starting point, then uncollected cheques are:
- A:
Added in BRS
- B:
Subtracted in BRS
- C:
Ignored while preparing BRS
- D:
None of these
The answer is a.
If balance as per Pass Book is the starting point, then uncollected cheques are:
Added in BRS
Subtracted in BRS
Ignored while preparing BRS
None of these

|
Jyoti Nair answered |
When preparing a Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS), the starting point is the balance as per Pass Book, which is the balance shown in the bank statement. However, this balance may not be the same as the balance in the company's Cash Book due to various reasons, such as outstanding cheques, bank charges, interest, etc.
One of the reasons for the difference between the balances is uncollected cheques, which are cheques issued by the company but have not yet been presented for payment by the recipients. These cheques are also known as outstanding cheques or uncleared cheques.
When preparing a BRS, uncollected cheques are added to the balance as per Pass Book because they have already been recorded in the company's Cash Book but have not yet been debited by the bank. Therefore, they are part of the company's bank balance that is not reflected in the bank statement.
For example, if the balance as per Pass Book is Rs. 50,000 and there are uncollected cheques worth Rs. 10,000, the adjusted bank balance would be Rs. 60,000 (Rs. 50,000 + Rs. 10,000).
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A', i.e., uncollected cheques are added in BRS.
The balance as per Cash Book (overdraft ) is 1,500. Cheques for Rs. 400 were deposited but were not collected. The cheques issued but not presented were Rs. 100, Rs. 125, Rs. 50. Balance as per Pass Book is :
- a)Rs. 1,100
- b)Rs. 1,625
- c)Rs. 12,000
- d)Rs. 1,375
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
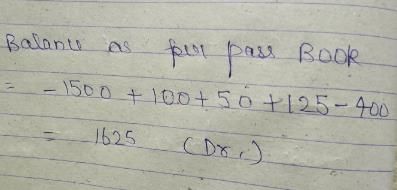
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Balance as per Cash Book is Rs. 5,000. Cheques issued but not presented for payment Rs. 2,000 and Cheques sent for collection but not collected Rs. 1,500. The Bank had wrongly debited the account of firm by Rs. 20. Balance as per pass book will be:
- A:
Rs. 5,580
- B:
Rs. 5,480
- C:
Rs. 4,520
- D:
Rs. 5,520
The answer is b.
Balance as per Cash Book is Rs. 5,000. Cheques issued but not presented for payment Rs. 2,000 and Cheques sent for collection but not collected Rs. 1,500. The Bank had wrongly debited the account of firm by Rs. 20. Balance as per pass book will be:
Rs. 5,580
Rs. 5,480
Rs. 4,520
Rs. 5,520

|
Sai Joshi answered |
Sale of old furniture is wrongly transferred to Sales Account. Which type of error is this ?- a)Error of Principle
- b)Compensating Error
- c)Error of Omission
- d)Error of Commission
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
Which of these types of errors are not detected during Bank Reconciliation’:
- a)Cash embezzlement by cashier
- b)Cheques deposited but not credited by bank
- c)Casting mistakes in bank column of cash book
- d)Interest or commission charged by the bank not accounted in cash book
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Devanshi Rane answered |
1. Errors in recording transactions in the bank statement: Bank reconciliation only compares the bank statement with the company's records. If there are errors in recording transactions in the bank statement, such as duplicate entries or incorrect amounts, they will not be detected during bank reconciliation.
2. Errors in recording transactions in the company's books: Bank reconciliation compares the bank statement with the company's records to identify any discrepancies. However, if there are errors in recording transactions in the company's books, such as incorrect amounts or incorrect accounts, they may not be detected during bank reconciliation.
3. Errors in timing: Bank reconciliation compares the timing of transactions recorded in the bank statement with the company's records. However, if there are errors in timing, such as recording a transaction in the wrong period or recording a transaction on the wrong date, they may not be detected during bank reconciliation.
4. Errors in reconciliation process: Bank reconciliation is a process that involves comparing the bank statement with the company's records to identify any discrepancies. However, if there are errors in the reconciliation process itself, such as incorrect calculations or incorrect matching of transactions, they may not be detected during bank reconciliation.
Debit balance as per Cash Book of ABC Enterprises as on 31.3.2011 is Rs. 1,500. Cheques deposited but not cleared amounts to Rs. 100 and Cheques issued but not presented of Rs. 150. The bank allowed interest amounting Rs. 50 and collected dividend Rs. 50 on behalf of ABC Enterprises. Balance as per pass book should be- a)Rs.1,600.
- b)Rs.1,450.
- c)Rs.1,850.
- d)Rs.1,650.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
Which of the following in Trial Balance is contradictory to each other? __________.- a)Inventory and Drawings
- b)Sales and Purchase Return
- c)Carriage Inward and Outward
- d)Trade Receivable and Liability
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Freedom Institute answered |
Trial Balance is a :- a)Statement
- b)Account
- c)Summary
- d)Ledger
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
K Srivastava answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A Bank Reconciliation Statement is a
- A:
part of Cash Book;
- B:
part of Bank Account;
- C:
part of financial statements,
- D:
none of the above.
The answer is c.
A Bank Reconciliation Statement is a
part of Cash Book;
part of Bank Account;
part of financial statements,
none of the above.

|
Lakshya Raj answered |
The beginning stock of the current year is overstated by Rs. 500 and closing stock is overstated by Rs. 1200. Effect on profit:
- a)Rs. 1700 (overstated)
- b)Rs. 1200 (understated)
- c)Rs. 1700 (understated)
- d)Rs. 700 (overstated)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Siddharth Sen answered |
Explanation:
Overstating the beginning stock and closing stock will have an impact on the calculation of cost of goods sold (COGS) and gross profit.
Impact on COGS:
COGS is calculated as Beginning Stock + Purchases - Closing Stock. If the beginning stock is overstated, it will lead to an increase in COGS, and if the closing stock is overstated, it will lead to a decrease in COGS.
Impact on Gross Profit:
Gross profit is calculated as Sales - COGS. If COGS is overstated due to an overstated beginning stock or understated closing stock, it will lead to a decrease in gross profit.
Answer:
In this case, the beginning stock is overstated by Rs. 500 and closing stock is overstated by Rs. 1200.
Impact on COGS:
COGS = Beginning Stock + Purchases - Closing Stock
Overstated Beginning Stock = Rs. 500
Overstated Closing Stock = Rs. 1200
COGS = Rs. 500 + Purchases - Rs. 1200
COGS is understated by Rs. 700 (Rs. 1200 - Rs. 500)
Impact on Gross Profit:
Gross Profit = Sales - COGS
Assuming Sales remain the same,
Gross Profit is overstated by Rs. 700.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - Rs. 700 (overstated).
Balance as per Cash Book is Rs. 5,000. Cheques issued but not presented for payment Rs. 2,000 and Cheques sent for collection but not collected Rs. 1,500. The Bank had wrongly debited the account of firm by Rs. 20. Balance as per pass book will be:- a)Rs. 5,580
- b)Rs. 5,480
- c)Rs. 4,520
- d)Rs. 5,520
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
User12742372 answered |
Which of these types of errors are not detected during Bank Reconciliation’ :- a)Cash embezzlement by cashier
- b)Cheques deposited but not credited by bank
- c)Casting mistakes in bank column of cash book
- d)Interest or commission charged by the bank not accounted in cash book
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Raghavendra Choudhury answered |
When drawing up a Bank Reconciliation Statement, if you start with a debit balance as per the Bank Statement, the unpresented cheques should be:- a)Added
- b)Deducted
- c)Not required to be adjusted
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Aditi Joshi answered |
| Bank Reconciliation Statement |
Introduction to Bank Reconciliation Statement
A Bank Reconciliation Statement is a statement prepared by a business to reconcile the difference between the bank balance as per the company's records and the bank balance as per the bank statement. It ensures that both balances are in agreement by comparing the financial transactions recorded by the business with those recorded by the bank.
Debit Balance as per the Bank Statement
When starting with a debit balance as per the bank statement, it means that the bank statement shows a higher balance than the company's records. This can happen due to various reasons such as outstanding checks, deposits in transit, bank errors, or other reconciling items.
Unpresented Cheques
Unpresented cheques refer to checks issued by the company that have not yet been presented to the bank for payment. These checks are recorded in the company's books as payments but have not yet been deducted from the bank balance.
Addition of Unpresented Cheques
To reconcile the difference between the bank balance as per the company's records and the bank statement, the unpresented cheques need to be added to the bank balance as per the bank statement. This adjustment is made because the bank statement does not reflect the deduction of these checks, resulting in a higher balance.
Reasoning behind Adding Unpresented Cheques
The reason for adding the unpresented cheques is to align the bank balance as per the bank statement with the company's records. Since the company has already recorded these checks as payments, they need to be added to the bank balance to reflect the correct position.
Example
Let's say the bank balance as per the bank statement is $10,000, and there are unpresented cheques of $3,000. When preparing the bank reconciliation statement, the unpresented cheques of $3,000 will be added to the bank balance, resulting in a reconciled balance of $13,000.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when starting with a debit balance as per the bank statement, the unpresented cheques should be added to the bank balance to reconcile the difference between the bank balance as per the company's records and the bank statement. This adjustment ensures that both balances are in agreement and reflects the correct financial position of the business.
The bank charged Rs. 1,000 as bank charges to a client and communicates the same to him. The accountant records it in the bank account in books. Later on the bank realizes that the charges were wrongly charged and reverses the same, but forgot to communicate the same to the client. If the accountant is starting with the bank balance as per bank account in books, what will be the treatment in Bank Reconciliation statement to arrive at balance as per Bank statement:- a)Reduce Rs. 1,000
- b)Add Rs. 1,000
- c)Add Rs. 2,000
- d)No treatment
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Mihir Banerjee answered |
When preparing a Bank Reconciliation Statement, the accountant must reconcile the bank balance as per the bank statement with the bank balance as per the books of accounts. In this scenario, the bank charged Rs. 1,000 as bank charges to a client, which was recorded in the books. However, the bank later realized the error and reversed the charges without informing the client.
To arrive at the balance as per the bank statement, the following treatment must be applied:
Add Rs. 1,000
- The bank charges were reversed by the bank, which means that the bank balance as per the bank statement will be higher by Rs. 1,000.
- However, since the reversal was not communicated to the client, the bank balance as per the books of accounts will not reflect this change.
- Therefore, to reconcile the two balances, the accountant must add Rs. 1,000 to the bank balance as per the books of accounts.
- This will result in the balance as per the bank statement and the balance as per the books of accounts being reconciled.
In summary, when bank charges are reversed but not communicated to the client, the accountant must add the amount of the reversal to the bank balance as per the books of accounts to arrive at the balance as per the bank statement.
Rs. 200 paid as wages for erecting a machine should be debited to - a)Repair account.
- b)Machine account
- c)Capital account.
- d)Furniture account
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
KP Classes answered |
Hari charges 10% depreciation on plant and machinery. On 1st April 2011 he debited Rs. 7,520 paid on installation of plant and machinery to profit and loss account. At the time of preparing final accounts on 31st March, 2012 due to this error,
- a)Net Profit will decrease by Rs. 6,768
- b)Net Profit will decrease by Rs. 7,520
- c)Net Profit will decrease by Rs. 8,272
- d)Net Profit will increase by Rs. 6,768
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Pranav Gupta answered |
- Hari charges 10% depreciation on plant and machinery.
- Depreciation is a non-cash expense that reduces the value of an asset over its useful life.
- It is charged to the profit and loss account.
Error in Debit Entry
- On 1st April 2011, Hari debited Rs. 7,520 paid on installation of plant and machinery to the profit and loss account.
- This entry should have been debited to the plant and machinery account.
- As a result, the profit and loss account was overstated by Rs. 7,520.
Impact on Final Accounts
- At the time of preparing final accounts on 31st March 2012, the error is discovered.
- The amount of Rs. 7,520 should be debited to the plant and machinery account and credited to the profit and loss account to rectify the error.
- The effect of this correction on the profit and loss account will be to decrease the profit by Rs. 6,768 (i.e., 10% of Rs. 7,520).
- The correct amount of depreciation for the year ending 31st March 2012 will be Rs. 752 (i.e., 10% of Rs. 7,520).
- Therefore, the net profit will decrease by Rs. 6,768 due to this error.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:When overdraft as per Cash Book is the starting point, a cheque of Rs. 500 deposited into bank but not recorded in cash book will be :
- A:
Added by Rs. 500
- B:
Deducted by Rs. 500
- C:
Added by Rs. 1,000
- D:
Deducted by Rs. 1,000
The answer is b.
When overdraft as per Cash Book is the starting point, a cheque of Rs. 500 deposited into bank but not recorded in cash book will be :
Added by Rs. 500
Deducted by Rs. 500
Added by Rs. 1,000
Deducted by Rs. 1,000
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
The balance as per Cash Book is Rs. 10,000 Cheques for Rs. 2,000 were issued but not presented for payment. What would be the balance as per Pass Book?- a)Rs. 10,000
- b)Rs. 2,000
- c)Rs. 12,000
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Monica D answered |
Add: cheques issued but not presented =2,000
.•. bal. as per passbook = 12,000
If the balance as per Pass Book is the starting point, so the treatment of undercasting of receipt side of Cash Book will be :- a)Added
- b)Deducted
- c)No treatment
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Prasenjit Kapoor answered |
When the balance as per Pass Book is the starting point, the treatment of undercasting of receipt side of Cash Book will be deducted from the balance as per Pass Book. This is because undercasting of receipt side of Cash Book means that some of the cash received has not been recorded in the Cash Book, resulting in a lower balance as per Cash Book. As a result, when we start with the balance as per Pass Book, we need to adjust it for the undercast amount so that the correct balance is reflected.
Steps for Deducting Undercasting of Receipt Side of Cash Book
The following steps can be followed to deduct the undercasting of receipt side of Cash Book:
Step 1: Identify the undercast amount
The first step is to identify the undercast amount on the receipt side of the Cash Book. This can be done by comparing the entries in the Cash Book with the bank statement or Pass Book.
Step 2: Deduct the undercast amount from the balance as per Pass Book
Once the undercast amount has been identified, it should be deducted from the balance as per Pass Book. This will give us the correct balance as per Cash Book.
Step 3: Record the adjustment in the Cash Book
The adjustment for the undercast amount should be recorded in the Cash Book. This can be done by writing a narration explaining the adjustment and the reason for it.
Example
Suppose the balance as per Pass Book is Rs. 50,000. On comparing the Cash Book with the Pass Book, it is found that a receipt of Rs. 5,000 has been undercast in the Cash Book. The treatment of undercasting of receipt side of Cash Book will be as follows:
- Deduct the undercast amount of Rs. 5,000 from the balance as per Pass Book:
Balance as per Pass Book = Rs. 50,000 - Rs. 5,000 = Rs. 45,000
- Record the adjustment in the Cash Book with a narration:
Cash Book:
Receipt side
To adjust undercast of Rs. 5,000
By deducting the undercast amount, the correct balance as per Cash Book of Rs. 45,000 is reflected, and the adjustment is recorded in the Cash Book.
The cash book showed an overdraft of Rs. 2,000 as cash at bank but the pass book upto the same date showed that cheques of Rs. 100, Rs. 150 and Rs. 175 have not been presented for payments; and the cheque of Rs. 600 deposited into account has not been cleared. The overdraft as per pass book will be:- a)Rs. 2,150
- b)Rs. 2,175
- c)Rs. 1,475
- d)Rs. 1,925
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Puja Singh answered |
Bank column of a cash book of a trader shows a credit balance of Rs. 7,900 and the bank statement shows a debit balance of Rs. 10,300 on a particular date after payments made by the bank as per the standing orders. In the statement of affairs, the bank balance will be shown on:- a)Assets side Rs. 7,900
- b)Liabilities side Rs. 10,300
- c)Liabilities side Rs. 2,400
- d)Assets side Rs. 10,300
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Ritika Iyer answered |
The bank column of a cash book shows the balance of the trader's account with the bank. On a particular date, the bank column of the cash book shows a credit balance of Rs. 7,900. This means that the trader has deposited Rs. 7,900 in the bank account.
However, the bank statement shows a debit balance of Rs. 10,300. This means that the bank has paid out Rs. 10,300 from the trader's account as per the standing orders.
Therefore, the actual balance of the trader's account with the bank on that particular date is a debit balance of Rs. 10,300. This balance will be shown on the liabilities side of the statement of affairs because it represents an amount that the trader owes to the bank.
Hence, the correct answer is option B, i.e., the bank balance will be shown on the liabilities side of the statement of affairs as Rs. 10,300.
Closing stock in the trial balance implies that.- a)It is already adjusted in the opening stock.
- b)It is adjusted in sales a/c
- c)It is adjusted in the purchase a/c
- d)None of these.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Balances of the accounts are transferred to : - a)Trial Balance
- b)Trading Account
- c)Profit & Loss Account
- d)Balance sheet
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
Trial Balance under balance method is known as :- a)Gross Trial Balance
- b)Net Trial Balance
- c)Simple Trial balance
- d)Trial Balance Appropriation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
Goods of Rs. 1,000 purchased from Mr. “A” were recorded in sales book, the rectification of this error will?- a)Increase the gross profit
- b)Reduce the gross profit
- c)Have no effect on gross Profit
- d)None of the given options
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Raghav Ghoshal answered |
Sales of Rs. 1,540 to Mr. X was posted to his account as Rs. 1450. To rectify the error, Rs. 90 will be _________to X ‘s Account :- a)Debited
- b)Credited
- c)ignored
- d)Either (a) or (b)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Nipun Tuteja answered |
What will be the effect when return inward is wrongly entered as return outward?- a)Gross Profit is increased by Rs. 100
- b)Gross Profit is decreased by Rs. 100.
- c)Gross Profit is increased by Rs. 200.
- d)Gross Profit is decreased by Rs. 200.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Nipuns Institute answered |
- Return Inward as Return Outward: If sales returns are mistakenly recorded as purchase returns, it affects both sales and purchase figures:
- Sales: They are overstated because the returns that should have reduced the sales are not recorded.
- Purchases: They are understated because the entries increase the amount of returns, which decreases the net purchases.
- Net Effect on Gross Profit: Gross Profit (G.P.) is calculated as Sales minus Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). Here’s the impact:
- Sales are higher by the amount of the return (let's assume Rs. 100).
- Purchases are lower by the same amount (Rs. 100), which implies COGS is also lower by Rs. 100.
- Combined Impact:
- The sales not decreasing by Rs. 100 (when they should have due to returns) effectively increases the G.P. by Rs. 100.
- The purchases being reduced by Rs. 100 (mistakenly increasing returns) further reduces the COGS, increasing the G.P. by another Rs. 100.
Bill accepted by Govinda was discounted with the bank for Rs. 2000. On the due date the bill was dishonoured. However, there is error of Omission towards Bills dishonoured. Journal Entry for rectification will be:-- a)B/R A/c Dr.
To Bank A/c - b)Govinda’s A/c Dr.
To Bank B/R A/c - c)Govinda’s A/c Dr.
To Bank A/c - d)Bank A/c Dr.
To B/R A/c
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
To Bank A/c
To Bank B/R A/c
To Bank A/c
To B/R A/c

|
Anuj Roy answered |
Explanation:
The correct journal entry for rectification of the error of omission towards bills dishonoured would be:
B/R A/c Dr. To Govinda A/c
Explanation:
When the bill accepted by Govinda was discounted with the bank, the following journal entry would have been passed:
Bank A/c Dr. To B/R A/c
On the due date, when the bill was dishonoured, the following journal entry would have been passed:
B/R A/c Dr. To Govinda A/c
However, the error of omission towards bills dishonoured was made and the above journal entry was not passed. Therefore, to rectify the error, the correct journal entry would be:
B/R A/c Dr. To Govinda A/c
This entry will increase the B/R account, which was reduced when the bill was discounted with the bank. It will also increase the liability of Govinda towards the bill, which was reduced when the bill was discounted with the bank.
The overdraft as per cash book of Mr. X is Rs. 20,500. One of the customer of Mr. X residing in Mumbai directly remitted Rs. 50,000 into Mr. X’s account, about which Mr. X was not aware. One of the cheques deposited into bank for Rs. 25,000 was returned unpaid and the advice in this regard is yet to be received by Mr. X. The balance as per Pass book was:- a)Rs. 4,500 credit
- b)Rs. 4,500 overdraft
- c)Rs. 45,500 credit
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Srsps answered |
Chapter doubts & questions for Verification of Accounting Records - Accounting for Grade 9 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Accounting for Grade 9
60 videos|76 docs|34 tests
|

Contact Support
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|










