All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Physics for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Pascal’s Principle for EmSAT Achieve Exam
Find the force required at the plunger which has 3 cm diameter, and the diameter of the hydraulic press is 30 cm. It is used for lifting a weight of 30 kN.- a)200 N
- b)150 N
- c)100 N
- d)300 N
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the force required at the plunger which has 3 cm diameter, and the diameter of the hydraulic press is 30 cm. It is used for lifting a weight of 30 kN.
a)
200 N
b)
150 N
c)
100 N
d)
300 N

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Concept:
Pascal’s Law:
- It was given by Blaise pascal
- It is also known as the principle of transmission of fluid pressure
- It states that the pressure change at any point in a confined incompressible fluid is transmitted throughout the fluid such that the same change occurs everywhere.
- Alternate definition:- The pressure applied to any part of the enclosed liquid will be transmitted equally in all directions through the liquid.
Applications:
- The underlying principle of hydraulic jack and hydraulic press.
- Force amplification in the braking system of most motor vehicles.
- Used in artesian wells, water towers, and dams.
Calculation:
Given:
Diameter of plunger, d = 3 cm, Diameter of ram, D = 30 cm, Force required at the plunger = ?, Weight = 30 kN
According to pascals law,
Pressure applied at ram = Pressure exerted on the plunger
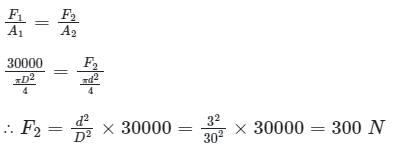
Here, F2 = force required on the plunger
As per Pascal’s law:- a)intensity of pressure at a point in a moving fluid is equal in the direction of applied force.
- b)intensity of pressure at a point in a static fluid is equal in all directions.
- c)intensity of pressure at a point in a moving fluid is equal in all directions
- d)intensity of pressure at a point in a static fluid is equal in the direction of applied force.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
As per Pascal’s law:
a)
intensity of pressure at a point in a moving fluid is equal in the direction of applied force.
b)
intensity of pressure at a point in a static fluid is equal in all directions.
c)
intensity of pressure at a point in a moving fluid is equal in all directions
d)
intensity of pressure at a point in a static fluid is equal in the direction of applied force.

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Concept:
- Pascal’s principle: Pascal’s Law is the principle of transmission of fluid-pressure.
- It says that "a pressure exerted anywhere in a point of the confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions throughout the fluid”.
EXPLANATION:
- Centrifuge: Centrifugation is used to separate the contents of mixtures according to their size and density. The centrifuge works on the principle of sedimentation.
- Hydraulic Lift: The lift that uses pascal's law and used to lift objects with the help of fluid is called hydraulic lift. It works on Pascal's law. So option 2 is correct.
- Motor: A motor is an electrical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It works on the principle that a current-carrying conductor experiences a mechanical force when it is placed in a magnetic field.
- Lever: A lever is a simple machine that is made up of two load arms and a fulcrum. The distance from the fulcrum can be used to determine how the input and output forces are related to each other.
A hydraulic lift has two pistons with area 1 m2 and 0.25 m2. What is the force exerted by the smaller piston when 40 N is placed on the larger piston?- a)160 N
- b)10 N
- c)40 N
- d)Cannot be determined
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A hydraulic lift has two pistons with area 1 m2 and 0.25 m2. What is the force exerted by the smaller piston when 40 N is placed on the larger piston?
a)
160 N
b)
10 N
c)
40 N
d)
Cannot be determined

|
Arien Instructors answered |
CONCEPT:
- Pascals Law: In a fluid at rest in a closed container, the external static pressure applied on a confined liquid is transmitted without loss to every portion of the fluid and to the walls of the container.
- In Pascal's law, the effect of gravity is neglected.
CALCULATION:
Given that A1 = 0.25 m2 and A2 = 1 m2; F2 = 40N F1 = ?
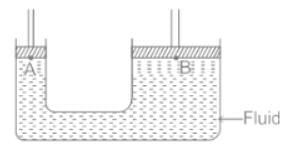
From Pascal's Law, the pressure inside the liquid will be equal at every place. So the pressure at A and B will be equal.
PA = PB

So the correct answer is option 2.
An air bubble of radius 'r' doubles its radius as it rises from a depth 'h' to the surface of the lake at a constant temperature. If the atmospheric pressure is equal to 10 m height of the water column, neglecting surface tension the value of 'h' is:- a)90 m
- b)70 m
- c)60 m
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An air bubble of radius 'r' doubles its radius as it rises from a depth 'h' to the surface of the lake at a constant temperature. If the atmospheric pressure is equal to 10 m height of the water column, neglecting surface tension the value of 'h' is:
a)
90 m
b)
70 m
c)
60 m
d)
None of these
|
|
Sameer Al Mazroui answered |
Understanding the Problem
An air bubble rises from a depth h in a lake and doubles its radius as it reaches the surface. We need to find the depth h, given that atmospheric pressure is equivalent to a 10 m water column.
Key Principles
- Boyle's Law: This law states that the pressure and volume of a gas are inversely proportional at a constant temperature (P1V1 = P2V2).
- Pressure Change: As the bubble rises, the pressure decreases from the pressure at depth h (P1) to atmospheric pressure (P2).
Initial Conditions
- Initial Radius: r
- Initial Volume: V1 = (4/3)πr^3
Final Conditions
- Final Radius: 2r
- Final Volume: V2 = (4/3)π(2r)^3 = (32/3)πr^3
Pressure Calculations
1. At Depth h:
- The pressure at depth h can be calculated as:
P1 = ρgh + Patm
Where ρ (density of water) ≈ 1000 kg/m³ and g (acceleration due to gravity) ≈ 10 m/s².
2. At the Surface:
- The pressure at the surface is simply atmospheric pressure:
P2 = Patm
Applying Boyle's Law
Using Boyle's Law:
P1V1 = P2V2
Substituting the volumes:
(ρgh + Patm)(4/3)πr^3 = Patm(32/3)πr^3
The π and (4/3) can be canceled out:
(ρgh + Patm)r^3 = 8Patm
Final Steps
Rearranging gives:
ρgh = 8Patm - Patm
ρgh = 7Patm
Substituting Patm = 1000 kg/m³ × 10 m:
ρgh = 7 × 1000 × 10
Solving for h:
h = (7 × 1000 × 10) / (1000 × 10) = 70 m
Conclusion
Therefore, the value of h is 70 m, confirming option B as the correct answer.
An air bubble rises from a depth h in a lake and doubles its radius as it reaches the surface. We need to find the depth h, given that atmospheric pressure is equivalent to a 10 m water column.
Key Principles
- Boyle's Law: This law states that the pressure and volume of a gas are inversely proportional at a constant temperature (P1V1 = P2V2).
- Pressure Change: As the bubble rises, the pressure decreases from the pressure at depth h (P1) to atmospheric pressure (P2).
Initial Conditions
- Initial Radius: r
- Initial Volume: V1 = (4/3)πr^3
Final Conditions
- Final Radius: 2r
- Final Volume: V2 = (4/3)π(2r)^3 = (32/3)πr^3
Pressure Calculations
1. At Depth h:
- The pressure at depth h can be calculated as:
P1 = ρgh + Patm
Where ρ (density of water) ≈ 1000 kg/m³ and g (acceleration due to gravity) ≈ 10 m/s².
2. At the Surface:
- The pressure at the surface is simply atmospheric pressure:
P2 = Patm
Applying Boyle's Law
Using Boyle's Law:
P1V1 = P2V2
Substituting the volumes:
(ρgh + Patm)(4/3)πr^3 = Patm(32/3)πr^3
The π and (4/3) can be canceled out:
(ρgh + Patm)r^3 = 8Patm
Final Steps
Rearranging gives:
ρgh = 8Patm - Patm
ρgh = 7Patm
Substituting Patm = 1000 kg/m³ × 10 m:
ρgh = 7 × 1000 × 10
Solving for h:
h = (7 × 1000 × 10) / (1000 × 10) = 70 m
Conclusion
Therefore, the value of h is 70 m, confirming option B as the correct answer.
According to _______, the intensity of pressure in a liquid at rest is constant in all directions.- a)Newton's law
- b)Boyles law
- c)hydrostatic law
- d)Pascal's law
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
According to _______, the intensity of pressure in a liquid at rest is constant in all directions.
a)
Newton's law
b)
Boyles law
c)
hydrostatic law
d)
Pascal's law

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Pascal’s principle:
- Pascal’s Law is the principle of transmission of fluid pressure.
- It says that "a pressure exerted anywhere in a point of the confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions throughout the fluid”.
A hydraulic press has a ram of 15 cm diameter and plunger of 1.5 cm. It is required to lift a weight of 1000 kg. The force required on the plunger is equal to:- a)10 kg
- b)100 kg
- c)1000 kg
- d)10,000 kg
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A hydraulic press has a ram of 15 cm diameter and plunger of 1.5 cm. It is required to lift a weight of 1000 kg. The force required on the plunger is equal to:
a)
10 kg
b)
100 kg
c)
1000 kg
d)
10,000 kg

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Concept:
Pascal’s Law:
- It was given by Blaise pascal
- It is also known as principle of transmission of fluid pressure
- It states that the pressure change at any point in a confined incompressible fluid is transmitted throughout the fluid such that the same change occurs everywhere.
- Alternate definition:- The pressure applied to any part of the enclosed liquid will be transmitted equally in all directions through the liquid.
Applications:
- The underlying principle of hydraulic jack and hydraulic press.
- Force amplification in the braking system of most motor vehicles.
- Used in artesian wells, water towers and dams.
Calculation:
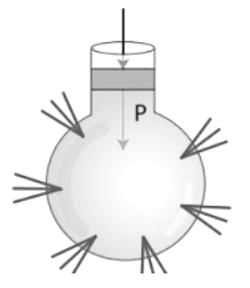
Given:
Diameter of plunger, d = 1.5 cm, Diameter of ram, D = 15 cm, weight exerted on the ram, F1 = 1000 kg
According to pascals law,
Pressure applied at plunger = Pressure exerted on the ram
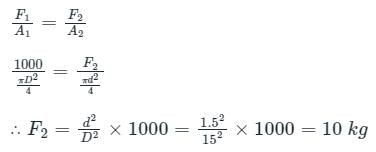
Here, F2 = force required on the plunger
At what depth from surface of water, the pressure will be equal to three times the atmosphere pressure? Given atmospheric pressure = 10 N/cm2 and g = 9.8 m/s2.- a)20.4 m
- b)5.6 m
- c)2.8 m
- d)10.2 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At what depth from surface of water, the pressure will be equal to three times the atmosphere pressure? Given atmospheric pressure = 10 N/cm2 and g = 9.8 m/s2.
a)
20.4 m
b)
5.6 m
c)
2.8 m
d)
10.2 m

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Concept:
- Gauge pressure inside the water at the depth of ℎ m will be:
Pgauge = ρgh N/m2
- Derived using Bernoulli's equation
Calculation:
Given: Patm = 10 N/cm2 = 10× 104 N/ m2 , ρ = 1000 kg/m3, g = 9.8m/s2
Patm= 105Pa
- Now Pgauge should be equal to three times Patm
Pabs = Patm + Pgauge
⇒ 3 × Patm = Patm + ρgh
⇒ ρgh = 2× Patm
⇒ 1000 × 9.8 × h = 2 × 105
⇒ h = 20.4m
- Hence at the depth of 20.4m the pressure inside the water will be three times the atmospheric pressure.
Additional Information
- Gauge pressure or relative pressure (Pg) is the difference between the measured pressure and the local atmospheric pressure.
- Absolute pressure is the actual pressure at a point measured with respect to vacuum pressure i.e. zero pressure.
The resultant pressure on a body submerged in a fluid due to the fluid acts at which of the following points in the body?- a)Centre of pressure
- b)Centre of mass
- c)Centre of buoyancy
- d)Metacentre
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The resultant pressure on a body submerged in a fluid due to the fluid acts at which of the following points in the body?
a)
Centre of pressure
b)
Centre of mass
c)
Centre of buoyancy
d)
Metacentre

|
Arien Instructors answered |
CONCEPT:
- When a body is submerged in a fluid, it experiences pressure due to the surrounding fluid.
- The resultant of the pressure due to the fluid acts at a point in the body.
- Centre of pressure: The point where the total sum of (or resultant) pressure due to the fluid acts on a body submerged inside it.
EXPLANATION:
- The resultant pressure on a body submerged in a fluid acts on a point on a body called the centre of pressure.
Additional Information
- Centre of mass: The point where all the mass of a body is assumed to be concentrated.
- Centre of buoyancy: The centre of gravity of the volume of fluid displaced by the body submerged in the fluid is called the centre of buoyancy.
- Metacentre: The point at which an imaginary vertical line passing through the centre of buoyancy and centre of gravity intersects the imaginary vertical line through a new centre of buoyancy created when the body is displaced, or tipped, in the fluid.
Which one of the following laws is applicable to a hydraulic lift?- a)Kirchhoff's law
- b)Pascal's Law
- c)Archimedes’ principle
- d)Archimedes' Law
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following laws is applicable to a hydraulic lift?
a)
Kirchhoff's law
b)
Pascal's Law
c)
Archimedes’ principle
d)
Archimedes' Law

|
Arien Instructors answered |
The correct answer is Pascal's law.
- The Pascal's law states that in a fluid which is at rest in a container, the pressure applied to one part of the fluid is uniformly transmitted to all the parts of the fluid.
Key Points
- A hydraulic lift employs this principle to lift heavy objects.
- When pressure is applied to a fluid through one piston, it results in an equivalent pressure on another piston in the system which is then able to lift objects.
- With the increase in the area of the second piston, the force exerted by it also increases thus enabling lifting of heavier objects.
Additional Information
- Hooke's law states that force needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance is directly proportional to that distance.
- Newton's first law of motion - A body at rest remains at rest, or if in motion, remains in motion at constant velocity unless acted on by a net external force.
- Archimedes' principle states that the upward buoyant force that is exerted on a body immersed in a fluid, whether fully or partially submerged, is equal to the weight of the fluid that the body displaces.
Which of the following laws states that pressure or intensity of pressure at a point in static fluid is equal in all directions?- a)Darcy's law
- b)Newton's law
- c)Hydrostatic law
- d)Pascal's law
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following laws states that pressure or intensity of pressure at a point in static fluid is equal in all directions?
a)
Darcy's law
b)
Newton's law
c)
Hydrostatic law
d)
Pascal's law

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Pascal’s law: Pascal’s Law is the principle of transmission of fluid-pressure, It says that "a pressure exerted anywhere in a point of the confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions throughout the fluid”.

A liquid is filled in a large cylindrical container. The pressure exerted by the liquid on the wall of the container depends on- a)Density of liquid
- b)Gravity
- c)Depth of liquid
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A liquid is filled in a large cylindrical container. The pressure exerted by the liquid on the wall of the container depends on
a)
Density of liquid
b)
Gravity
c)
Depth of liquid
d)
All of these

|
Arien Instructors answered |
CONCEPT:
- Pressure: Pressure is defined as the physical force exerted on an object. The unit of pressure is Pascal.
The basic formula for pressure is given by:
P = F/A, Where P is pressure, F = force, A = area.
The pressure exerted by a liquid on the wall of container can be given by
P = ρ h g, Where ρ = density of liquid, h = height of the liquid, g = gravity.
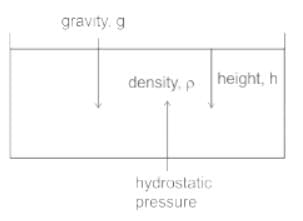
EXPLANATION:
- The pressure exerted by a liquid on the wall of container can be given by
P = ρ h g, Where ρ = density of liquid, h = height of the liquid, g = gravity.
- Thus it depends on the density of the liquid, height of the liquid in the container, and the acceleration due to gravity. So option 4 is correct.
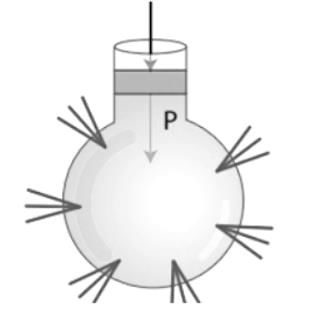
Which of the following is based on Pascal's law? - a)Centrifuge
- b)Hydraulic Lift
- c)Motor
- d)More than one of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is based on Pascal's law?
a)
Centrifuge
b)
Hydraulic Lift
c)
Motor
d)
More than one of the above

|
Arien Instructors answered |
CONCEPT:
- Pascal’s principle: Pascal’s Law is the principle of transmission of fluid-pressure.
- It says that "a pressure exerted anywhere in a point of the confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions throughout the fluid”.
EXPLANATION:
- Centrifuge: Centrifugation is used to separate the contents of mixtures according to their size and density. The centrifuge works on the principle of sedimentation.
- Hydraulic Lift: The lift that uses pascal's law and used to lift objects with the help of fluid is called hydraulic lift. It works on Pascal's law. So option 2 is correct.
- Motor: A motor is an electrical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It works on the principle that a current-carrying conductor experiences a mechanical force when it is placed in a magnetic field.
- Lever: A lever is a simple machine that is made up of two load arms and a fulcrum. The distance from the fulcrum can be used to determine how the input and output forces are related to each other.
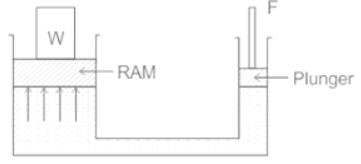
A hydraulic press has a ram of cross-section area 30 × 30 cm and a plunger of cross-section area 4 × 4 cm as shown in figure. Find the force 'F' required to lift the weight 'W' = 30 KN.
- a)232.88 N
- b)533.33 N
- c)589.58 N
- d)481.22 N
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A hydraulic press has a ram of cross-section area 30 × 30 cm and a plunger of cross-section area 4 × 4 cm as shown in figure. Find the force 'F' required to lift the weight 'W' = 30 KN.


a)
232.88 N
b)
533.33 N
c)
589.58 N
d)
481.22 N

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Concept:
The ratio of force applied in ram to the area of ram is equal to ratio of force applied in plunger to the area of plunger, as the pressure intensity is same.
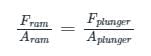
Calculation:
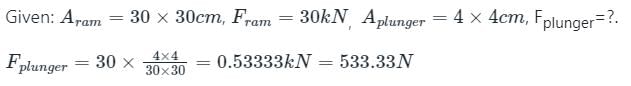
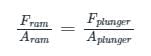
Calculation:
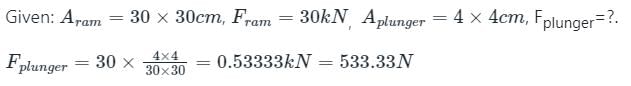
A stream of water flowing horizontally with a speed of 20 m/s pushes out of a tube of cross-sectional area 10-1m2 and hits at a vertical wall nearby. Find the force exerted on the wall by the impact of water, assuming that it does not rebound? - a)40000 N
- b)400 N
- c)2250 N
- d)4000 N
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A stream of water flowing horizontally with a speed of 20 m/s pushes out of a tube of cross-sectional area 10-1m2 and hits at a vertical wall nearby. Find the force exerted on the wall by the impact of water, assuming that it does not rebound?
a)
40000 N
b)
400 N
c)
2250 N
d)
4000 N

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Given:
Speed of stream of water (v) = 20 m/s
Area of cross-section of tube (A)= 10-1m2 (or 0.1 m2)
Concept:
Force exerted on the wall = Rate of loss in momentum of the water
Formula:
The volume rate of flow of water: dV/dt = Av
The mass rate of flow of water: dm/dt = ρAv
Rate of loss in momentum of water = (dm/dt)v
Calculation:
Mass rate of flow of water : dm/dt = ρAv
⇒ dm/dt = 1000 × 0.1 × 20
= 2000 kg/s
Rate of loss in momentum of water = (dm/dt)v
⇒ (dm/dt)v = 2000 × 20
= 40000 N
∴ Force exerted = 40000 N
A hydraulic press has a ram of 20 cm diameter and a plunger of 3 cm diameter. It is used for lifting a weight of 30 kN. Find the force required at the plunger.- a)975 N
- b)1075 N
- c)875 N
- d)675 N
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A hydraulic press has a ram of 20 cm diameter and a plunger of 3 cm diameter. It is used for lifting a weight of 30 kN. Find the force required at the plunger.
a)
975 N
b)
1075 N
c)
875 N
d)
675 N

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Concept:
Pascal’s Law:
- It was given by Blaise pascal
- It is also known as the principle of transmission of fluid pressure
- It states that the pressure change at any point in a confined incompressible fluid is transmitted throughout the fluid such that the same change occurs everywhere.
- Alternate definition:- The pressure applied to any part of the enclosed liquid will be transmitted equally in all directions through the liquid.
Applications:
- The underlying principle of hydraulic jack and hydraulic press.
- Force amplification in the braking system of most motor vehicles.
- Used in artesian wells, water towers, and dams.
Calculation:
Given:
Diameter of plunger, d = 3 cm, Diameter of ram, D = 20 cm, Force required at the plunger = ?, Weight = 30 kN
According to pascals law,
Pressure applied at ram = Pressure exerted on the plunger
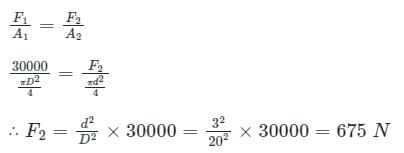
Here, F2 = force required on the plunger
The pressure exerted by a liquid column at the bottom of the liquid container is- a)Dependent on the density of the liquid
- b)Equal in all directions
- c)Not dependent on the area of cross-section of container
- d)All the above are true
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The pressure exerted by a liquid column at the bottom of the liquid container is
a)
Dependent on the density of the liquid
b)
Equal in all directions
c)
Not dependent on the area of cross-section of container
d)
All the above are true

|
Arien Instructors answered |
- Pressure in liquids is the multiplication of three quantities i.e.
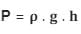
- Where:
- P is the pressure at the depth,
- ρ is the density of the fluid,
- g is the acceleration due to gravity, and
- h is the depth or height of the fluid column.
- Option 1 - Dependent on the density of the liquid
- Pressure is directly proportional to the density (ρ) of the liquid.
- As the density increases, the pressure at a given depth also increases.
- Option 2 - Equal in all directions
- Pascal's Law states that when there is an increase in pressure at any point in a confined fluid, there is an equal increase in pressure throughout the fluid in all directions.
- In the context of a liquid in a container, this means that the pressure at the bottom of the container is transmitted equally in all directions to the sides and top of the container.
- Option 3 - Not dependent on the area of cross-section of container
- As per the formula, the pressure (P) is not directly dependent on the area of cross-section (A) of the container.
- The pressure is primarily influenced by the height, density, and acceleration due to gravity.
A glass bottle filled with liquid will break at the bottom if a stopper is forced into its open end as per- a)Hydrostatic law
- b)Pascal’s law
- c)Gravitational law
- d)Bernoulli’s law
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A glass bottle filled with liquid will break at the bottom if a stopper is forced into its open end as per
a)
Hydrostatic law
b)
Pascal’s law
c)
Gravitational law
d)
Bernoulli’s law

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Pascal’s principle: Pascal’s Law is the principle of transmission of fluid-pressure.
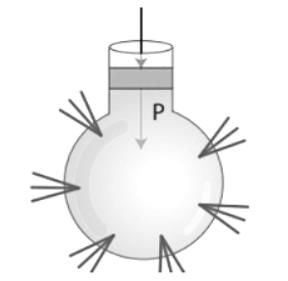
- It says that "a pressure exerted anywhere in a point of the confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions throughout the fluid”.
Hydrostatic Law
The law states that the rate of increase of pressure in a vertically downward direction must be equal to the specific weight of the fluid at that point.
From the adjacent figure, the correct observation is ______
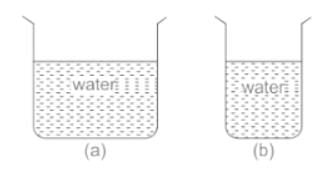
- a)The pressure on the bottom of tank (a) is greater than at the bottom of (b)
- b)The pressure on the bottom of tank (a) is smaller than at the bottom of (b)
- c)The pressure depend on the shape of the container
- d)The pressure on the bottom of (a) and (b) is the same
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
From the adjacent figure, the correct observation is ______


a)
The pressure on the bottom of tank (a) is greater than at the bottom of (b)
b)
The pressure on the bottom of tank (a) is smaller than at the bottom of (b)
c)
The pressure depend on the shape of the container
d)
The pressure on the bottom of (a) and (b) is the same

|
Arien Instructors answered |
CONCEPT:
- The normal force exerted by liquid at rest on a given surface in contact with it is called the thrust of liquid on that surface.
- The normal force (or thrust) exerted by liquid at rest per unit area of the surface in contact with it, is called pressure of liquid or hydrostatic pressure.
- If Po is the atmospheric pressure then for a point at depth h below the surface of a liquid of density ρ,
- Hydrostatic pressure P is given by
P = Po + ρgh
EXPLANATION:
- Hydrostatic pressure depends on the depth of the point below the surface (h), nature of the liquid (ρ), and acceleration due to gravity (g).
- Hydrostatic pressure is independent of the amount of liquid, the shape of the container, or the cross-sectional area.
- If a given liquid is filled in vessels of different shapes to the same height, the pressure at the base in each vessel's will be the same, though the volume or weight of the liquid in different vessels will be different. Therefore option 4 is correct.
Which is the law states that the intensity of pressure at a point in a fluid at rest is the same in all directions.- a)Bernoulli’s law
- b)Darcy’s law
- c)Pascal’s law
- d)Newton’s law
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the law states that the intensity of pressure at a point in a fluid at rest is the same in all directions.
a)
Bernoulli’s law
b)
Darcy’s law
c)
Pascal’s law
d)
Newton’s law

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Pascal Law:
Pascal's law states that a pressure change occurring anywhere in a confined incompressible fluid is transmitted throughout the fluid such that the same change occurs everywhere.
This follows that pressure at any point in a fluid at rest has the same magnitude in all directions.
Uses: This law is used in hydraulic lifts and hydraulic brakes in cars.
For a fluid in motion, pressure at a point is same in all directions, then the fluid is:- a)Real fluid
- b)Newtonian fluid
- c)Ideal fluid
- d)Non-Newtonian fluid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For a fluid in motion, pressure at a point is same in all directions, then the fluid is:
a)
Real fluid
b)
Newtonian fluid
c)
Ideal fluid
d)
Non-Newtonian fluid

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Newtonian fluids:
- Newtonian fluids defined as fluids for which the shear stress is linearly proportional to the shear strain rate
- Newtonian fluids are analogous to elastic solids (Hooke’s law: stress proportional to strain)
- Any common fluids, such as air and other gases, water, kerosene, gasoline, and other oil-based liquids, are Newtonian fluids
Non-Newtonian fluid:
- Fluids for which the shear stress is not linearly related to the shear strain rate are called non-Newtonian fluids examples include slurries and colloidal suspensions, polymer solutions, blood, paste, and cake batter
Ideal fluid:
- Fluids which don’t have viscosity and are incompressible are termed as an ideal fluid such fluid do not offer shear resistance i.e no resistance is encountered as the fluid moves. In ideal fluid, the pressure at a point is the same in all direction.
Real fluid:
- Fluids which do possess viscosity are termed as real fluids. These fluids always offer shear resistance i.e. Certain amount of resistance is always offered by these fluids as they move.
Hence in practical life, ideal fluid does not exist. It is an imaginary fluid taken into consideration to compare with all other fluids to check how close they are to the ideal fluid.
Chapter doubts & questions for Pascal’s Principle - Physics for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Pascal’s Principle - Physics for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for EmSAT Achieve
208 videos|329 docs|212 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









