All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Physics for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Electrostatic Energy for EmSAT Achieve Exam
The amount of work done in moving a charge from one point to another along an equipotential line or surface charge is- a)Zero
- b)Infinity
- c)One
- d)Two
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The amount of work done in moving a charge from one point to another along an equipotential line or surface charge is
a)
Zero
b)
Infinity
c)
One
d)
Two
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Since Potential difference between two points in equipotential surfaces is zero, the work done between two points in equipotential surface is also zero.
As shown in the figure below, an ellipsoidal cavity is carved within a perfect conductor. A positive charge Q is placed at the centre of the cavity. If points A and b are shown on the cavity surface (see figure), then which among the following choices is correct?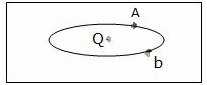
- a)Potential at A = Potential at B
- b)Charge density at A = Charge density at B
- c)Electric field near A = Electric field near B
- d)Total electric flux at the surface of the cavity = zero
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
As shown in the figure below, an ellipsoidal cavity is carved within a perfect conductor. A positive charge Q is placed at the centre of the cavity. If points A and b are shown on the cavity surface (see figure), then which among the following choices is correct?
a)
Potential at A = Potential at B
b)
Charge density at A = Charge density at B
c)
Electric field near A = Electric field near B
d)
Total electric flux at the surface of the cavity = zero
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Electric field at A is different from field at B because, E= K/r2
we know that conductor is an equipotential surface, so potential will be the same at A and B.
As charge density, σ∝1/r, then charge density is different at A and B.
we know that conductor is an equipotential surface, so potential will be the same at A and B.
As charge density, σ∝1/r, then charge density is different at A and B.
The electrostatic potential energy between two charges q1 and q2 separated by a distance by r is given by- a)
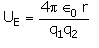
- b)
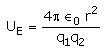
- c)
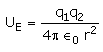
- d)
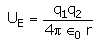
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The electrostatic potential energy between two charges q1 and q2 separated by a distance by r is given by
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Khushi Mittal answered |
Energy = force × distance U=Kq1q2/r^2 × r U=Kq1q2/r
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is
- A:
Zero
- B:
Infinity
- C:
Nonzero finite
- D:
None of the above
The answer is a.
The potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is
Zero
Infinity
Nonzero finite
None of the above

|
.mie. answered |
Answer is 0 as there are no other sources of electrostatic potential .... against which an external agent must do work.... in moving the point charge.... from infinity to its final location.... therefore correct opt is A
Electric field at the surface of a charged conductor is proportional to- a)Surface charge density
- b)Volume of the sphere
- c)Volume charge density
- d)Area of the sphere
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Electric field at the surface of a charged conductor is proportional to
a)
Surface charge density
b)
Volume of the sphere
c)
Volume charge density
d)
Area of the sphere

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Electric field at the surfaces of charged conductors is σ/ε0.n, where n is a unit vector normal to the surface.
We clearly see that the electric field is perpendicular to surface charge density (σ).
We clearly see that the electric field is perpendicular to surface charge density (σ).
In bringing an electron towards another electron, the electrostatic potential energy of the system- a)becomes zero
- b)decreases
- c)remains same
- d)increases
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In bringing an electron towards another electron, the electrostatic potential energy of the system
a)
becomes zero
b)
decreases
c)
remains same
d)
increases
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The electron has negative charge. When an electron is bringing towards another electron, then due to same negative charge repulsive force is produced between them. So, to bring them closer a work is done against this repulsive force. This work is stored in the form of electrostatic potential energy. Thus, electrostatic potential energy of system increases.
Alternative: Electrostatic potential energy of system of two electrons
U=[1/4πε0][(−e)(−e)/r] = [1/4πε0](e^2/r)
Thus, as r decreases, potential energy U increases.
If a unit charge is taken from one part to another part over an equipotential surface, then what is the change in electrostatic potential energy of the charge?- a)10 J
- b)100 J
- c)1 J
- d)0 J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If a unit charge is taken from one part to another part over an equipotential surface, then what is the change in electrostatic potential energy of the charge?
a)
10 J
b)
100 J
c)
1 J
d)
0 J

|
Utsav Srivastava answered |
Equipotential surface means the potential on every. point on that surface is constant. it means the change in potential on equipotential surface is zero we know that... ( electrostatic potential energy = change in potential × charge.)... ... according to this electrostatic potential energy is zero
Find the band gap energy when a light of wavelength 1240nm is incident on it.- a)1eV
- b)2eV
- c)3eV
- d)4eV
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the band gap energy when a light of wavelength 1240nm is incident on it.
a)
1eV
b)
2eV
c)
3eV
d)
4eV
|
|
Khushi Singh answered |
Find the band gap energy when a light of wavelength 1240nm is incident on it. Explanation: The band gap energy in electron volt when wavelength is given is, Eg = 1.24(μm)/λ = 1.24 x 10-6/1240 x 10-9 = 1eV.
The potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is
- a)Zero
- b)Infinity
- c)Non zero finite
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is
a)
Zero
b)
Infinity
c)
Non zero finite
d)
None of the above
|
|
Manoj Chauhan answered |
Explanation:
Potential energy is defined as the work done by an external force in bringing a system from infinity to its position. Hence, the potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is given by -
U = qV
where, q is the charge of the point charge and V is the potential at its position.
Now, let's consider the two cases -
Case 1: When the point charge is at infinity
At infinity, the potential is zero as the electric field due to a point charge decreases as we move away from it. Hence, the potential energy of the system containing only one point charge at infinity is zero.
U = qV = q x 0 = 0
Case 2: When the point charge is at a finite distance from infinity
In this case, the potential energy of the system will be non-zero finite as the potential at the position of the point charge will be non-zero.
U = qV ≠ 0
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option 'A' i.e. zero as the potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is zero when the point charge is at infinity.
Potential energy is defined as the work done by an external force in bringing a system from infinity to its position. Hence, the potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is given by -
U = qV
where, q is the charge of the point charge and V is the potential at its position.
Now, let's consider the two cases -
Case 1: When the point charge is at infinity
At infinity, the potential is zero as the electric field due to a point charge decreases as we move away from it. Hence, the potential energy of the system containing only one point charge at infinity is zero.
U = qV = q x 0 = 0
Case 2: When the point charge is at a finite distance from infinity
In this case, the potential energy of the system will be non-zero finite as the potential at the position of the point charge will be non-zero.
U = qV ≠ 0
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option 'A' i.e. zero as the potential energy of a system containing only one point charge is zero when the point charge is at infinity.
A charge q = 1.0 C moves distance of 1.5 m in the direction of a uniform electric field E of magnitude 2.0 N/C. Find its change in electrostatic potential energy.- a)2 J
- b)3 J
- c)4 J
- d)1 J
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A charge q = 1.0 C moves distance of 1.5 m in the direction of a uniform electric field E of magnitude 2.0 N/C. Find its change in electrostatic potential energy.
a)
2 J
b)
3 J
c)
4 J
d)
1 J

|
Anchal Maurya answered |
Force (F)=E•q=2×1=2,. Energy (E)=F•d=2×1.5=3 joule
Negative mutual potential energy corresponds to attraction between two charges- a)False
- b)True
- c)Can’t predict
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Negative mutual potential energy corresponds to attraction between two charges
a)
False
b)
True
c)
Can’t predict
d)
None of the above

|
Soham Rastogi answered |
The formula for electric potential energy of system of 2 charges is (kq1q2)/r, if the result comes out to be negative,one of the charges has to be negative and one has to be positive, because there can be no other case in which it comes out to be negative. Since opposite charges attract each other,hence the answer is True.
Some charge is being given to a conductor. Then its potential:- a)is maximum somewhere between surface and centre.
- b)is maximum at surface
- c)is maximum at centre
- d)remains same throughout the conductor
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Some charge is being given to a conductor. Then its potential:
a)
is maximum somewhere between surface and centre.
b)
is maximum at surface
c)
is maximum at centre
d)
remains same throughout the conductor

|
Om Rana answered |
Because what charge is given to the conductor spread on its surface evenly such that electric field throughout the conductor remains zero.
So as dV/dt=E and E is zero inside the conductor,
V would be same throughout the conductor.
So as dV/dt=E and E is zero inside the conductor,
V would be same throughout the conductor.
How does the charge densities of conductors vary on an irregularly shaped conductor?- a)High at sharp and less at flat portion
- b)Less at sharp and high at flat portion
- c)Remains constant
- d)Zero at sharp and high at flat portion
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How does the charge densities of conductors vary on an irregularly shaped conductor?
a)
High at sharp and less at flat portion
b)
Less at sharp and high at flat portion
c)
Remains constant
d)
Zero at sharp and high at flat portion

|
Tinku Kumar answered |
Because at sharp portion there is very less area for charges . so they accumulate very close to each other and this increases their charge densities... But in flat portion there is much more area than the sharp portion , so charges distributed over the whole area . this is the reason for less charge density at flat portion
Inside a conductor, electrostatic field is:- a)infinity
- b)zero
- c)maximum
- d)minimum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Inside a conductor, electrostatic field is:
a)
infinity
b)
zero
c)
maximum
d)
minimum
|
|
Harsh Singhal answered |
Bcz all charge appears on surface
Two spherical conductors B and C having equal radii and carrying equal charges repel each other witha force F when kept apart at some distance. A third spherical conductor having same radius as that of B but uncharged is brought in contact with B, then brought in contact with C and finally removed awayfrom both. The new force of repulsion between B and C- a)F/4
- b)3F/4
- c)F/8
- d)3F/8
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two spherical conductors B and C having equal radii and carrying equal charges repel each other witha force F when kept apart at some distance. A third spherical conductor having same radius as that of B but uncharged is brought in contact with B, then brought in contact with C and finally removed awayfrom both. The new force of repulsion between B and C
a)
F/4
b)
3F/4
c)
F/8
d)
3F/8
|
|
Soumya Nair answered |
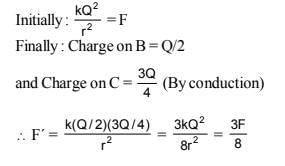
Two spherical conductors A and B of radii 1 mm and 2 mm are separated by a distance of 5 cm and are uniformly charged. If the spheres are connected by a conducting wire then in equilibrium condition, the ratio of the magnitude of the electric fields at the surface of spheres A and B is ?
- a)2:1
- b)4:1
- c)1:2
- d)1:4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two spherical conductors A and B of radii 1 mm and 2 mm are separated by a distance of 5 cm and are uniformly charged. If the spheres are connected by a conducting wire then in equilibrium condition, the ratio of the magnitude of the electric fields at the surface of spheres A and B is ?
a)
2:1
b)
4:1
c)
1:2
d)
1:4
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Potential of sphere A = Potential of sphere B, as they are joined by a conducting wire, which makes both sphere`s potential same. VA = VB.Implies , Kq1/R1 = kq2/R2Implies q1/q2= R1/R2.E1/E2 = (Kq1/R1^2) / kq2/R2^2 = (q1/q2)X R2^2/R1^2 = R2/ R1 as( q1/q2=R1/R2) = 2:1.
The value of electric potential throughout the volume of a conductor is- a)Either infinite or zero
- b)Constant
- c)Zero
- d)Infinite
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of electric potential throughout the volume of a conductor is
a)
Either infinite or zero
b)
Constant
c)
Zero
d)
Infinite
|
|
Gauri Datta answered |
Since the electric field inside the conductor is zero and has no tangential component on its surface, therefore, no work is done in moving a test charge within the conductor or on its surface. It means the potential difference between any two points inside or on the surface is zero. Hence, electrostatic potential is constant throughout the volume of the charged conductor and has the same value on its surface as inside it.
Consider a neutral conducting sphere. A positive point charge is placed outside the sphere. The net charge on the sphere is then,- a)Negative and distributed non–uniformly over the entire surface of the sphere
- b)Negative and distributed uniformly over the surface of the sphere
- c)Negative and appears only at the point on the sphere closest to the point charge
- d)Zero
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a neutral conducting sphere. A positive point charge is placed outside the sphere. The net charge on the sphere is then,
a)
Negative and distributed non–uniformly over the entire surface of the sphere
b)
Negative and distributed uniformly over the surface of the sphere
c)
Negative and appears only at the point on the sphere closest to the point charge
d)
Zero
|
|
Rishika Patel answered |
If a charge q is placed outside than the electric field lines incident on the conducting sphere , if some charge is developed due to thee lines than opposite surface becomes oppositely charge and the total charge becomes zero
Two conductors having same type of charges are connected by a conducting wire. There would not be any amount of charges on them if:- a)they have the same capacity
- b)they have the same amount of charge
- c)they have the same potential
- d)they have the same shape
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Two conductors having same type of charges are connected by a conducting wire. There would not be any amount of charges on them if:
a)
they have the same capacity
b)
they have the same amount of charge
c)
they have the same potential
d)
they have the same shape
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Electric potential I know is Work done per charge in bringing it from infinity to a point .
Electric potential is Like gravitational potential it The closer a test charge is to a electric field source more potential energy it has and thus more Electric potential .
Electrons flow from higher to lower potential thats what makes electricity flow
V(a) - V(b) = integral from a to b E.dl
E = -dV/dr
V = E.d
Due to a point charge at a distance R the electric potential is Q/4 pi Epsilno0 R
Positive mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges corresponds to- a)Repulsion
- b)Attraction
- c)Can’t predict
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Positive mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges corresponds to
a)
Repulsion
b)
Attraction
c)
Can’t predict
d)
None of the above
|
|
Kiran Khanna answered |
Explanation:
The mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges is given by,
U = (1/4πε0) * (q1q2/r)
where q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the charges, r is the distance between them, and ε0 is the permittivity of free space.
If the charges are of the same sign, i.e., both positive or both negative, then the product q1q2 is positive. As a result, the mutual potential energy U will also be positive. This means that the charges will experience a repulsive force, and will tend to move away from each other.
On the other hand, if the charges are of opposite sign, i.e., one positive and the other negative, then the product q1q2 will be negative. As a result, the mutual potential energy U will also be negative. This means that the charges will experience an attractive force, and will tend to move towards each other.
Therefore, we can conclude that a positive mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges corresponds to repulsion between the charges.
The mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges is given by,
U = (1/4πε0) * (q1q2/r)
where q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the charges, r is the distance between them, and ε0 is the permittivity of free space.
If the charges are of the same sign, i.e., both positive or both negative, then the product q1q2 is positive. As a result, the mutual potential energy U will also be positive. This means that the charges will experience a repulsive force, and will tend to move away from each other.
On the other hand, if the charges are of opposite sign, i.e., one positive and the other negative, then the product q1q2 will be negative. As a result, the mutual potential energy U will also be negative. This means that the charges will experience an attractive force, and will tend to move towards each other.
Therefore, we can conclude that a positive mutual potential energy of a system containing two charges corresponds to repulsion between the charges.
A particle of mass 1 kg and charge 1/3μC is projected towards a non conducting fixed spherical shell having the same charge uniformly distributed on its surface. The minimum initial velocity V0 of projection of particle required if the particle just grazes the shell is
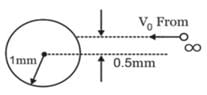
- a)
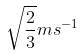
- b)
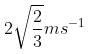
- c)2/3 ms-1
- d)1 ms-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle of mass 1 kg and charge 1/3μC is projected towards a non conducting fixed spherical shell having the same charge uniformly distributed on its surface. The minimum initial velocity V0 of projection of particle required if the particle just grazes the shell is


a)
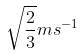
b)
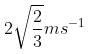
c)
2/3 ms-1
d)
1 ms-1
|
|
Amar Shah answered |
From conservation of angular momentum,

from conservation of energy,
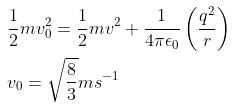

from conservation of energy,
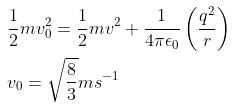
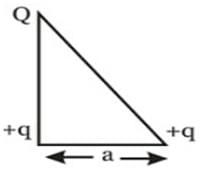
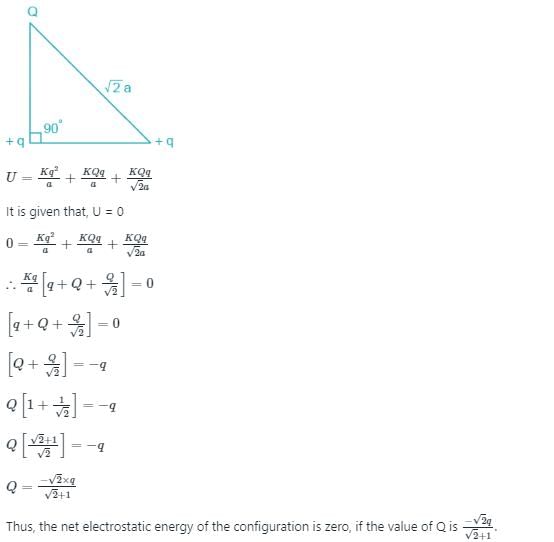
Three point charges Q, +q and +q are placed at the vertices of a right-angled isosceles triangle as shown in the figure. If the net electrostaic energy of the configuration is zero, find the value Q\q is [Take √2 = 1.4]
- a)-2q
- b)+q
- c)
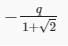
- d)
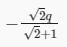
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Three point charges Q, +q and +q are placed at the vertices of a right-angled isosceles triangle as shown in the figure. If the net electrostaic energy of the configuration is zero, find the value Q\q is [Take √2 = 1.4]

a)
-2q
b)
+q
c)
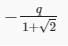
d)
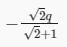
|
|
Raghavendra Rane answered |
Given,
The distance between them when the electrostatic energy between two charges q1 and q2 is given as 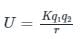
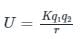
According to the principle of superposition, total energy of the charge system as shown in the figure below is
Electrostatic field is zero_____ the conductor.- a)At the edge
- b)On surface
- c)outside
- d)Inside
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Electrostatic field is zero_____ the conductor.
a)
At the edge
b)
On surface
c)
outside
d)
Inside

|
Navina Rajavelu answered |
As electrostatic field is a surface property it is zero inside the conductor.
Chapter doubts & questions for Electrostatic Energy - Physics for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Electrostatic Energy - Physics for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for EmSAT Achieve
208 videos|329 docs|212 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









