All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Physics for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Electromotive Force for EmSAT Achieve Exam
Which among the following rules is used to determine the direction of induced emf?- a)Right-hand thumb rule
- b)Fleming’s right-hand rule
- c)Fleming’s left-hand rule
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following rules is used to determine the direction of induced emf?
a)
Right-hand thumb rule
b)
Fleming’s right-hand rule
c)
Fleming’s left-hand rule
d)
None of the above

|
Arien Instructors answered |
According to Fleming’s right-hand rule, magnetic flux is pointed by the index finger, motion of the conductor is pointed by the thumb, and induced emf is pointed by the middle finger.
A metal wheel with 20 metallic spokes each 1m long, is rotated with a speed of 180 rpm, in a plane perpendicular to the earth's field. at that place. If the magnitude of the field is 0.40 gauss, then the emf between the axle and rim of the wheel is - a)3.77× 105 V
- b)3.77× 10-5V
- c)3.77 × 104 V
- d)3.77× 10-4 V
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A metal wheel with 20 metallic spokes each 1m long, is rotated with a speed of 180 rpm, in a plane perpendicular to the earth's field. at that place. If the magnitude of the field is 0.40 gauss, then the emf between the axle and rim of the wheel is
a)
3.77× 105 V
b)
3.77× 10-5V
c)
3.77 × 104 V
d)
3.77× 10-4 V

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Given: number of spokes, n = 20 length of spokes, l = radius (r) = 1m, magnetic field (B) = 0.4 gauss = 0.4 × 10-4 tesla, and frequency (f) = 180 rpm = 3 rps
- The relation linear velocity and angular velocity is given by,
⇒ v = rω
Where ω is the angular velocity
Linear velocity of spoke at the axle = 0, and linear velocity at the rim end = rω .
Where ω is the angular velocity
Linear velocity of spoke at the axle = 0, and linear velocity at the rim end = rω .
- So the average liner velocity
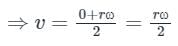
- Angular velocity (ω) of the spoke is given as
⇒ ω = 2πf = 2π × 3 = 6π
- The emf between the axle and rim of the wheel.
⇒ ε = Blv = 0.4 × 10-4 × 1 × 0.5 × 6π = 3.77× 10-4 V
- Hence option 4) is correct.
Electro motive force represents- a)Force
- b)Work
- c)Energy per unit charge
- d)Momentum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Electro motive force represents
a)
Force
b)
Work
c)
Energy per unit charge
d)
Momentum

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Electromotive force: The energy per unit electric charge that is imparted by an energy source (battery or electric generator) is called emf or electromotive force.
- Electromotive force is commonly denoted by the acronym emf, EMF or E.
- The SI unit for electromotive force is the volt.
- Electromotive force in a circuit maintains the potential difference.
- Electromotive Force (EMF) makes free electrons to flow in any closed circuit due to difference in electrical pressure or potential. Its unit is Volt.
- Volt is defined as work done per unit charge or energy consumed in bringing a charge from one point to another.
- So, the Energy per unit charge is electromotive force.
A metal wheel with 20 metallic spokes each 1m long, is rotated with a speed of 180 rpm, in a plane perpendicular to the earth's field. at that place. If the magnitude of the field is 0.40 gauss, then the emf between the axle and rim of the wheel is - a)3.77× 105 V
- b)3.77× 10-5V
- c)3.77× 104 V
- d)3.77× 10-4 V
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A metal wheel with 20 metallic spokes each 1m long, is rotated with a speed of 180 rpm, in a plane perpendicular to the earth's field. at that place. If the magnitude of the field is 0.40 gauss, then the emf between the axle and rim of the wheel is
a)
3.77× 105 V
b)
3.77× 10-5V
c)
3.77× 104 V
d)
3.77× 10-4 V

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Given: number of spokes, n = 20 length of spokes, l = radius (r) = 1m, magnetic field (B) = 0.4 gauss = 0.4 × 10-4 tesla, and frequency (f) = 180 rpm = 3 rps
The relation linear velocity and angular velocity is given by,
⇒ v = rω
Where ω is the angular velocity
Linear velocity of spoke at the axle = 0, and linear velocity at the rim end = rω .
So the average liner velocity
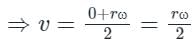
Angular velocity (ω) of the spoke is given as
⇒ ω = 2πf = 2π × 3 = 6π
The emf between the axle and rim of the wheel.
⇒ ε = Blv = 0.4 × 10-4 × 1 × 0.5 × 6π = 3.77× 10-4 V
Hence option 4) is correct.
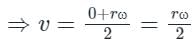
Angular velocity (ω) of the spoke is given as
⇒ ω = 2πf = 2π × 3 = 6π
The emf between the axle and rim of the wheel.
⇒ ε = Blv = 0.4 × 10-4 × 1 × 0.5 × 6π = 3.77× 10-4 V
Hence option 4) is correct.
What is the relation between the direction of motion of the conductor and the direction of induced emf?- a)Parallel to each other
- b)Equal to each other
- c)They are not related
- d)Mutually perpendicular
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the relation between the direction of motion of the conductor and the direction of induced emf?
a)
Parallel to each other
b)
Equal to each other
c)
They are not related
d)
Mutually perpendicular

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Fleming’s right-hand rule says that the motion of the conductor, the induced emf and the magnetic flux are mutually perpendicular to each other.
A wire of length 3m is moving with a speed of 50m/s in a direction perpendicular to a magnetic field of 4.5 Wb/m2. The induced emf in the wire is- a)675 × 102 V
- b)675 V
- c)675 mV
- d)675 × 105V
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A wire of length 3m is moving with a speed of 50m/s in a direction perpendicular to a magnetic field of 4.5 Wb/m2. The induced emf in the wire is
a)
675 × 102 V
b)
675 V
c)
675 mV
d)
675 × 105V

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Motional emf: The emf induced due to motion relative to a magnetic field is called the motional emf.
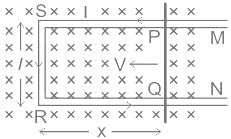
- Consider a straight conductor PQ moving perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B.
- Assume the motion of the rod to be uniform with a constant velocity of (v m/s).
- The rectangle PQRS forms a closed circuit enclosing a changing area due to the motion of the rod PQ.
- The magnetic flux ϕ enclosed by the loop PQRS can be given as:
⇒ ϕ = B × area = B × (l.x)
- Since the conductor is moving, there is a change in the rate of area moving. This causes a rate of change of flux which induces an emf.
- This induced emf is given by:
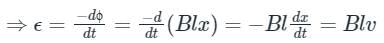
Where - dx/dt = v is the speed of the conductor PQ
Consider the following statement for a circular conductor moving in and out of the magnetic field: - The polarity of induced motional EMF is such that it supports the change in magnetic flux responsible for its production.
- Magnetic flux is independent of the area of the circular conductor.
- If the coil is cut somewhere and then moved in and out of the magnetic field, EMF will be generated.
- The basic cause of induced emf is the change in magnetic flux.
Which of the following statements are correct - a)1) and 2) only
- b)2) and 4 only
- c)3) and 4) only
- d)More than one of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statement for a circular conductor moving in and out of the magnetic field:
- The polarity of induced motional EMF is such that it supports the change in magnetic flux responsible for its production.
- Magnetic flux is independent of the area of the circular conductor.
- If the coil is cut somewhere and then moved in and out of the magnetic field, EMF will be generated.
- The basic cause of induced emf is the change in magnetic flux.
Which of the following statements are correct
a)
1) and 2) only
b)
2) and 4 only
c)
3) and 4) only
d)
More than one of the above

|
Arien Instructors answered |
- According to Lenz law, the polarity of induced EMF is such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux responsible for its production.
- Magnetic flux depends on the area of the circular conductor. The magnetic flux (ϕ) enclosed by the circular loop can be given as ϕ = B × area
- If the coil is cut somewhere and then moved in and out of the magnetic field, EMF will be generated.
- The basic cause of induced emf is the change in magnetic flux.
- When a conductor is moved in and out of the magnetic field, magnetic flux across it changes. this causes the generation of EMF in the direction such that it opposes the change. Hence option 4) is correct.
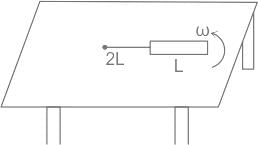
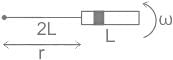
A metallic rod of length l is tied to a string of length 2l and made to rotate with angular speed ω on horizontal table with one end of the string fixed. If the induced emf across the ends of the rod is e, then the vertical magnetic field in the region is.
- a)
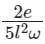
- b)
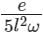
- c)
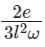
- d)
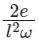
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A metallic rod of length l is tied to a string of length 2l and made to rotate with angular speed ω on horizontal table with one end of the string fixed. If the induced emf across the ends of the rod is e, then the vertical magnetic field in the region is.


a)
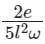
b)
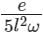
c)
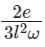
d)
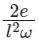

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Given, the length of the rod = L, length of the string = 2L, induced emf across the ends of the rod = e
Then L1 = 2L, L2 = 2L + L = 3L
Let the vertical magnetic field in the region is B, then from equation 1,
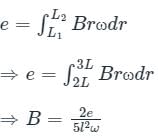
Then L1 = 2L, L2 = 2L + L = 3L
Let the vertical magnetic field in the region is B, then from equation 1,

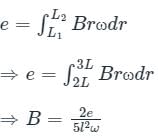
If an accelerating magnet is moved inside a current-carrying coil, then what will happen to the current inside it?- a)Current increases
- b)Current decreases
- c)Current remains constant
- d)Reverse current flows
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If an accelerating magnet is moved inside a current-carrying coil, then what will happen to the current inside it?
a)
Current increases
b)
Current decreases
c)
Current remains constant
d)
Reverse current flows

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Since an emf is induced by the change in the magnetic field, there should be a current when there is an emf. Due to this reason, the current inside the coil increases when the magnet is moved inside it.
A circular ring containing n number of spokes, parallel to each other, is rotated in a plane that is perpendicular to the earth's magnetic field. This generates EMF between the center and circular rim. If we increase the number of spokes of the ring then the induce emf - a)increases
- b)decreases
- c)goes to infinity
- d)remain same
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A circular ring containing n number of spokes, parallel to each other, is rotated in a plane that is perpendicular to the earth's magnetic field. This generates EMF between the center and circular rim. If we increase the number of spokes of the ring then the induce emf
a)
increases
b)
decreases
c)
goes to infinity
d)
remain same

|
Arien Instructors answered |
- The EMF induced across the spokes of the ring is the same as the spokes are parallel to each other. So the net EMF will be equal to that generated in a single spoke.
- Hence the number of spokes will not affect the total EMF induced. Hence option 4) is correct.
Chapter doubts & questions for Electromotive Force - Physics for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Electromotive Force - Physics for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for EmSAT Achieve
208 videos|329 docs|212 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









