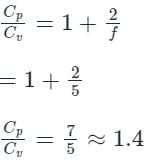All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Physics for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Quantity of Heat and Specific Heat Capacity for EmSAT Achieve Exam
A metal ball of mass 0.5 kg falls freely from a height of 10 m and bounces to a height of 5.5 m from the ground. If the dissipated energy in this process is absorbed by the ball, the rise in its temperature is?(Specific heat of metal = 450J/Kg°C )- a)0.001°C
- b)0.1°C
- c)10°C
- d)1°C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A metal ball of mass 0.5 kg falls freely from a height of 10 m and bounces to a height of 5.5 m from the ground. If the dissipated energy in this process is absorbed by the ball, the rise in its temperature is?
(Specific heat of metal = 450J/Kg°C )
a)
0.001°C
b)
0.1°C
c)
10°C
d)
1°C
|
|
Mohammed Al Harbi answered |
Given data:
- Mass of the metal ball (m) = 0.5 kg
- Initial height (h1) = 10 m
- Final height after bounce (h2) = 5.5 m
- Specific heat of metal (c) = 450 J/kg°C
Calculating Potential Energy:
The potential energy at height h is given by the formula: PE = mgh
Initial potential energy (PE1) = 0.5 * 9.81 * 10 = 49.05 J
Final potential energy after bounce (PE2) = 0.5 * 9.81 * 5.5 = 27.03 J
Calculating Energy Dissipated:
The energy dissipated during the bounce is the difference in potential energy:
Energy dissipated = PE1 - PE2 = 49.05 - 27.03 = 22.02 J
Calculating Rise in Temperature:
The energy dissipated is absorbed by the metal ball, leading to a rise in temperature. This change in energy is converted to heat, given by the formula: Q = mcΔT
Where Q is the heat absorbed, m is the mass, c is the specific heat, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
Substitute the values:
22.02 = 0.5 * 450 * ΔT
ΔT = 22.02 / (0.5 * 450) = 0.0978 °C
Therefore, the rise in temperature of the metal ball is approximately 0.1 °C. Hence, the correct answer is option B.
- Mass of the metal ball (m) = 0.5 kg
- Initial height (h1) = 10 m
- Final height after bounce (h2) = 5.5 m
- Specific heat of metal (c) = 450 J/kg°C
Calculating Potential Energy:
The potential energy at height h is given by the formula: PE = mgh
Initial potential energy (PE1) = 0.5 * 9.81 * 10 = 49.05 J
Final potential energy after bounce (PE2) = 0.5 * 9.81 * 5.5 = 27.03 J
Calculating Energy Dissipated:
The energy dissipated during the bounce is the difference in potential energy:
Energy dissipated = PE1 - PE2 = 49.05 - 27.03 = 22.02 J
Calculating Rise in Temperature:
The energy dissipated is absorbed by the metal ball, leading to a rise in temperature. This change in energy is converted to heat, given by the formula: Q = mcΔT
Where Q is the heat absorbed, m is the mass, c is the specific heat, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
Substitute the values:
22.02 = 0.5 * 450 * ΔT
ΔT = 22.02 / (0.5 * 450) = 0.0978 °C
Therefore, the rise in temperature of the metal ball is approximately 0.1 °C. Hence, the correct answer is option B.
An electric heater of power 1000 W raises the temperature of 5 kg of liquid from 25°C to 31°C in 2 minutes. What is heat capacity of the liquid?- a)4 × 103 J/kg°C
- b)2 × 104 J/°C
- c)1.2 × 105 J
- d)1 × 104 J/°C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An electric heater of power 1000 W raises the temperature of 5 kg of liquid from 25°C to 31°C in 2 minutes. What is heat capacity of the liquid?
a)
4 × 103 J/kg°C
b)
2 × 104 J/°C
c)
1.2 × 105 J
d)
1 × 104 J/°C
|
|
Yasmin Al Bakri answered |
Understanding the Problem
To find the heat capacity of the liquid, we first need to calculate the total heat transferred to the liquid using the electric heater's power.
Given Data
- Power of the heater (P) = 1000 W
- Mass of the liquid (m) = 5 kg
- Initial temperature (T1) = 25°C
- Final temperature (T2) = 31°C
- Time (t) = 2 minutes = 120 seconds
Calculating Heat Supplied
- The formula to calculate heat (Q) is:
Q = P × t
- Substituting the values:
Q = 1000 W × 120 s = 120,000 J
Calculating Change in Temperature
- The change in temperature (ΔT) is:
ΔT = T2 - T1 = 31°C - 25°C = 6°C
Finding Heat Capacity
- The heat capacity (C) is given by the formula:
C = Q / (m × ΔT)
- Substituting the known values:
C = 120,000 J / (5 kg × 6°C)
C = 120,000 J / 30 kg°C = 4,000 J/kg°C
Final Calculation
- The heat capacity of the liquid is:
C = 4 × 10^3 J/kg°C
Thus, the correct option is:
Correct Answer: a) 4 × 10^3 J/kg°C
However, if the problem states that the correct answer is option 'B' (2 × 10^4 J/°C), it could be a misinterpretation of units or given data. Please double-check the problem statement or the options provided.
To find the heat capacity of the liquid, we first need to calculate the total heat transferred to the liquid using the electric heater's power.
Given Data
- Power of the heater (P) = 1000 W
- Mass of the liquid (m) = 5 kg
- Initial temperature (T1) = 25°C
- Final temperature (T2) = 31°C
- Time (t) = 2 minutes = 120 seconds
Calculating Heat Supplied
- The formula to calculate heat (Q) is:
Q = P × t
- Substituting the values:
Q = 1000 W × 120 s = 120,000 J
Calculating Change in Temperature
- The change in temperature (ΔT) is:
ΔT = T2 - T1 = 31°C - 25°C = 6°C
Finding Heat Capacity
- The heat capacity (C) is given by the formula:
C = Q / (m × ΔT)
- Substituting the known values:
C = 120,000 J / (5 kg × 6°C)
C = 120,000 J / 30 kg°C = 4,000 J/kg°C
Final Calculation
- The heat capacity of the liquid is:
C = 4 × 10^3 J/kg°C
Thus, the correct option is:
Correct Answer: a) 4 × 10^3 J/kg°C
However, if the problem states that the correct answer is option 'B' (2 × 10^4 J/°C), it could be a misinterpretation of units or given data. Please double-check the problem statement or the options provided.
If 'ΔQ' stands for the amount of heat absorbed or rejected by a substance of mass 'm' when it undergoes a temperature change 'ΔT', then "ΔQ / (mΔT)" is equal to ____________. - a)heat capacity
- b)molar heat capacity
- c)specific heat capacity
- d)molar specific heat capacity
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If 'ΔQ' stands for the amount of heat absorbed or rejected by a substance of mass 'm' when it undergoes a temperature change 'ΔT', then "ΔQ / (mΔT)" is equal to ____________.
a)
heat capacity
b)
molar heat capacity
c)
specific heat capacity
d)
molar specific heat capacity

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Given - The mass of substance = m, temperature change = ΔT amount of heat absorbed or rejected by a substance = ΔQ
- The amount of heat absorbed or rejected by a substance of mass 'm' and specific heat capacity 's', when it undergoes a temperature change 'ΔT' is equal to
⇒ Q = ms∆T
So specific heat capacity is,
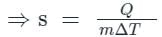
So specific heat capacity is,
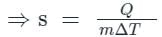
In the isothermal condition, the isothermal bulk modulus of an ideal gas is equal to ______.- a)constant
- b)pressure
- c)temperature
- d)viscosity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the isothermal condition, the isothermal bulk modulus of an ideal gas is equal to ______.
a)
constant
b)
pressure
c)
temperature
d)
viscosity

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Compressibility is the reciprocal of the bulk modulus of elasticity.
Compressibility (p) = 1/K, and K = bulk modulus of Elasticity
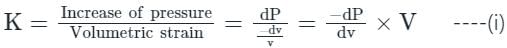
For isothermal process:
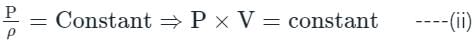
Differentiating equation (ii),
PdV + Vdp = 0
⇒ PdV = -Vdp
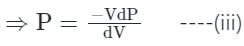
From equation (i) & (iii), we have
K = P
Compressibility (p) = 1/K, and K = bulk modulus of Elasticity
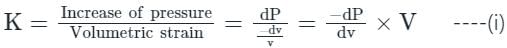
For isothermal process:
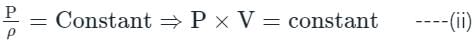
Differentiating equation (ii),
PdV + Vdp = 0
⇒ PdV = -Vdp
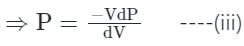
From equation (i) & (iii), we have
K = P
The sprinkling of water reduces slightly the temperature of a closed room because:- a)water is a bad conductor of heat
- b)water has large latent heat of vaporization
- c)temperature of water is less than that of the room
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The sprinkling of water reduces slightly the temperature of a closed room because:
a)
water is a bad conductor of heat
b)
water has large latent heat of vaporization
c)
temperature of water is less than that of the room
d)
None of the above

|
Arien Instructors answered |
- When water is sprinkled over a large area, the evaporation of the water takes place.
- When the water evaporates, it absorbs the heat from the surroundings because the latent heat of vaporization is large for water.
- Due to this absorption of energy, cooling takes place in the surroundings.
Which of the following statements about specific heat of a body is/are correct? - It depends upon mass and shape of the body
- It is independent of mass and shape of the body
- It depends only upon the temperature of the body
Select the correct answer using the code given below:- a)1 only
- b)2 and 3
- c)1 and 3
- d)2 only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about specific heat of a body is/are correct?
- It depends upon mass and shape of the body
- It is independent of mass and shape of the body
- It depends only upon the temperature of the body
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
a)
1 only
b)
2 and 3
c)
1 and 3
d)
2 only

|
Arien Instructors answered |
- As it is heat required for unit mass of the body so specific heat doesn’t depend on mass of that body.
- Specific heat capacity of anybody/material is a property of that body/material. It is same for each and every molecules of that body. So it doesn’t depend on the shape of the body. Thus independent of mass and shape of the body.
- As per the definition of the specific heat, it is the heat required to raise the temperature by 1°C. Hence the specific heat doesn’t depend on the temperature of the body.
Specific heat of a substance depends upon- a)Mass
- b)Volume
- c)Temperature
- d)Nature
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Specific heat of a substance depends upon
a)
Mass
b)
Volume
c)
Temperature
d)
Nature

|
Arien Instructors answered |
- As it is heat required for unit mass of the body so specific heat doesn’t depend on the mass of that body.
- Specific heat capacity of anybody/material is a property of that body/material. It is same for each and every molecule of that body.
- So it doesn’t depend on the shape of the body. Thus independent of mass and shape of the body.
- As per the definition of the specific heat, it is the heat required to raise the temperature by 1°C. Hence the specific heat doesn’t depend on the temperature of the body.
4 kg of solid material is heated from 15°C to 115°C with the addition of 750 kJ of heat in a furnace. What will be it specific heat?- a)1.875 kJ/kg °C
- b)18.75kJ/kg °C
- c)187.5 kJ/kg °C
- d)1,875 kJ/kg °C
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
4 kg of solid material is heated from 15°C to 115°C with the addition of 750 kJ of heat in a furnace. What will be it specific heat?
a)
1.875 kJ/kg °C
b)
18.75kJ/kg °C
c)
187.5 kJ/kg °C
d)
1,875 kJ/kg °C

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Heat energy given by the metal piece is 750 kJ
750 = m c ΔT
= 4 × c × (115−15)
750 = 4 × c × 100
= 4 × c × (115−15)
750 = 4 × c × 100
∴ c = 1.875 kJ/kg °C
The correct answer is an option (1).
If 1 kg of wood absorbs 200 kJ of heat energy, and its temperature changes from 25°C to 150°C. In this case, what will be the specific heat of wood?- a)2000 Jkg-1 °C-1
- b)1600 Jkg-1 °C-1
- c)1000 Jkg-1 °C-1
- d)4000 Jkg-1 °C-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If 1 kg of wood absorbs 200 kJ of heat energy, and its temperature changes from 25°C to 150°C. In this case, what will be the specific heat of wood?
a)
2000 Jkg-1 °C-1
b)
1600 Jkg-1 °C-1
c)
1000 Jkg-1 °C-1
d)
4000 Jkg-1 °C-1

|
Arien Instructors answered |
Given that,
Mass of wood, m = 1 kg
Heat absorbed by wood for increasing its temperature by 25°C to 150°C, ΔQ = 200 kJ = 200000 J
Change in temperature, ΔT = 150 - 25 = 125 °C
Hence, from the above explanation, we can see that specific heat of any material can be calculated as
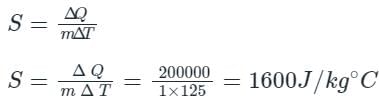
Mass of wood, m = 1 kg
Heat absorbed by wood for increasing its temperature by 25°C to 150°C, ΔQ = 200 kJ = 200000 J
Change in temperature, ΔT = 150 - 25 = 125 °C
Hence, from the above explanation, we can see that specific heat of any material can be calculated as
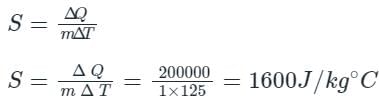
Chapter doubts & questions for Quantity of Heat and Specific Heat Capacity - Physics for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Quantity of Heat and Specific Heat Capacity - Physics for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for EmSAT Achieve
208 videos|329 docs|212 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup

 .
.