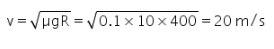All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Physics for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Circular Motion for EmSAT Achieve Exam
Centripetal force always acts at 90 degrees to the velocity, and away from the centre of the circle.- a)true
- b)cannot predict
- c)false
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Centripetal force always acts at 90 degrees to the velocity, and away from the centre of the circle.
a)
true
b)
cannot predict
c)
false
d)
none of these
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
1. The centripetal force is always towards the centre of the circle.
2. The force always acts at 90 degrees to the direction of the movement.
A model aeroplane is tethered to a post and held by a fine line. It flies in a horizontal circle. Then the line breaks. What direction will it fly in?
- a)In a circular path, as before
- b)Directly to the centre of the circle
- c)In a straight line at a tangent
- d)Directly away from the centre of the circle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A model aeroplane is tethered to a post and held by a fine line. It flies in a horizontal circle. Then the line breaks. What direction will it fly in?
a)
In a circular path, as before
b)
Directly to the centre of the circle
c)
In a straight line at a tangent
d)
Directly away from the centre of the circle
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
It is because at every point of circle an object has two acceleration (Tangential & Angular acceleration).At every point a body experience a tangential force which is perpendicular to the radius of the circle, when the string breaks the centripetal force disappear ( the radially inward force which holds a body in a circular motion) Hence the only Tangential force act on the body & it goes in that way.
Which of the following is called a fictitious force?- a)Gravitational force
- b)Frictional force
- c)Centrifugal force
- d)Centripetal force
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is called a fictitious force?
a)
Gravitational force
b)
Frictional force
c)
Centrifugal force
d)
Centripetal force
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Centrifugal force, a fictitious force, peculiar to a particle moving on a circular path, that has the same magnitude and dimensions as the force that keeps the particle on its circular path (the centripetal force) but points in the opposite direction.
Uniform circular motion is called continuously accelerated motion mainly because its :- a)direction of motion changes
- b)speed remains the same
- c)velocity remains the same
- d)direction of motion does not change
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Uniform circular motion is called continuously accelerated motion mainly because its :
a)
direction of motion changes
b)
speed remains the same
c)
velocity remains the same
d)
direction of motion does not change
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
An accelerating body is an object that is changing its velocity. And since velocity is a vector that has both magnitude and direction, a change in either the magnitude or the direction constitutes a change in the velocity.
Hence a uniform circular motion is a accelerated motion because direction of motion keeps on changing
Hence a uniform circular motion is a accelerated motion because direction of motion keeps on changing
A stone of mass 5 kg is attached to a string of 10 m length and is whirled in a horizontal circle. The string can withstand a maximum tension of 160 N. The maximum velocity of revolution that can be given to the stone without breaking the string is- a)17.88 m/s
- b)16 m/s
- c)20 m/s
- d)19.4 m/s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A stone of mass 5 kg is attached to a string of 10 m length and is whirled in a horizontal circle. The string can withstand a maximum tension of 160 N. The maximum velocity of revolution that can be given to the stone without breaking the string is
a)
17.88 m/s
b)
16 m/s
c)
20 m/s
d)
19.4 m/s
|
|
Mayank Chatterjee answered |
Given, mass of stone, m = 5 kg
Length of string, l = 10 m
Maximum tension, T = 160 N
We need to find the maximum velocity of revolution that can be given to the stone without breaking the string.
Maximum velocity of revolution:
We know that the tension in the string, T is given by:
T = (mv²) / r
where m is the mass of the stone, v is the velocity of the stone and r is the radius of the circle.
Finding the radius:
The length of the string, l is equal to the circumference of the circle, so:
l = 2πr
=> r = l / (2π)
=> r = 10 / (2π) = 1.59 m
Finding the maximum velocity:
Substituting the values in the tension equation, we get:
T = (mv²) / r
=> v² = (Tr) / m
=> v = √[(Tr) / m]
Now, substituting the given values, we get:
v = √[(160 × 1.59) / 5]
=> v = 17.88 m/s
Therefore, the maximum velocity of revolution that can be given to the stone without breaking the string is 17.88 m/s.
Length of string, l = 10 m
Maximum tension, T = 160 N
We need to find the maximum velocity of revolution that can be given to the stone without breaking the string.
Maximum velocity of revolution:
We know that the tension in the string, T is given by:
T = (mv²) / r
where m is the mass of the stone, v is the velocity of the stone and r is the radius of the circle.
Finding the radius:
The length of the string, l is equal to the circumference of the circle, so:
l = 2πr
=> r = l / (2π)
=> r = 10 / (2π) = 1.59 m
Finding the maximum velocity:
Substituting the values in the tension equation, we get:
T = (mv²) / r
=> v² = (Tr) / m
=> v = √[(Tr) / m]
Now, substituting the given values, we get:
v = √[(160 × 1.59) / 5]
=> v = 17.88 m/s
Therefore, the maximum velocity of revolution that can be given to the stone without breaking the string is 17.88 m/s.
It is advised to drive along the slippery road slowly, because:- a)Normal reaction gets reduced
- b)advice is not correct
- c)water on the road opposes the motion
- d)Friction is reduced
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
It is advised to drive along the slippery road slowly, because:
a)
Normal reaction gets reduced
b)
advice is not correct
c)
water on the road opposes the motion
d)
Friction is reduced
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
It is advised to drive along the slippery road slowly, because friction is reduced and if the driver is driving at a larger speed there is a risk of skidding.
The angle through which the outer edge is raised above the inner edge is called- a)angle of inclination
- b)angle of repose
- c)angle of banking
- d)angle of declination
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle through which the outer edge is raised above the inner edge is called
a)
angle of inclination
b)
angle of repose
c)
angle of banking
d)
angle of declination
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
A banked turn (or banking turn) is a turn or change of direction in which the vehicle banks or inclines, usually towards the inside of the turn. ... The bank angle is the angle at which the vehicle is inclined about its longitudinal axis with respect to the horizontal.
In circular motion:- a)Radial acceleration is non-zero
- b)Radial velocity is zero
- c)Body is in equilibrium
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In circular motion:
a)
Radial acceleration is non-zero
b)
Radial velocity is zero
c)
Body is in equilibrium
d)
All of the above
|
|
Stuti Joshi answered |
Circular motion involves the motion of an object in a circular path. The object moves around the center of the circle with a constant speed. In circular motion, the object experiences various types of acceleration and velocity. Let’s discuss the given options to understand circular motion in detail.
Radial acceleration is non-zero:
Radial acceleration is the acceleration of an object towards the center of the circle. In circular motion, the direction of velocity changes continuously, and hence the object experiences a change in direction. This change in direction leads to the acceleration of the object towards the center of the circle, known as radial acceleration. Therefore, option ‘a’ is correct.
Radial velocity is zero:
Radial velocity is the velocity of an object in the radial direction, i.e., towards the center of the circle. In circular motion, the object moves in a circular path without any radial motion, i.e., the object moves perpendicular to the radius of the circle. Hence, radial velocity is zero in circular motion. Therefore, option ‘b’ is incorrect.
Body is in equilibrium:
Equilibrium is a state where the object is at rest or moves with a constant velocity. In circular motion, the object moves with a constant speed, but the direction of the velocity changes continuously. Therefore, the object is not at rest, but it is also not moving with a constant velocity. Hence, the body is not in equilibrium in circular motion. Therefore, option ‘c’ is incorrect.
All of the above:
From the above discussion, we can conclude that radial acceleration is non-zero, radial velocity is zero, and the body is not in equilibrium in circular motion. Therefore, option ‘d’ is the correct answer.
Conclusion:
Circular motion involves the motion of an object in a circular path. The object experiences various types of acceleration and velocity in circular motion. In circular motion, radial acceleration is non-zero, radial velocity is zero, and the body is not in equilibrium.
Radial acceleration is non-zero:
Radial acceleration is the acceleration of an object towards the center of the circle. In circular motion, the direction of velocity changes continuously, and hence the object experiences a change in direction. This change in direction leads to the acceleration of the object towards the center of the circle, known as radial acceleration. Therefore, option ‘a’ is correct.
Radial velocity is zero:
Radial velocity is the velocity of an object in the radial direction, i.e., towards the center of the circle. In circular motion, the object moves in a circular path without any radial motion, i.e., the object moves perpendicular to the radius of the circle. Hence, radial velocity is zero in circular motion. Therefore, option ‘b’ is incorrect.
Body is in equilibrium:
Equilibrium is a state where the object is at rest or moves with a constant velocity. In circular motion, the object moves with a constant speed, but the direction of the velocity changes continuously. Therefore, the object is not at rest, but it is also not moving with a constant velocity. Hence, the body is not in equilibrium in circular motion. Therefore, option ‘c’ is incorrect.
All of the above:
From the above discussion, we can conclude that radial acceleration is non-zero, radial velocity is zero, and the body is not in equilibrium in circular motion. Therefore, option ‘d’ is the correct answer.
Conclusion:
Circular motion involves the motion of an object in a circular path. The object experiences various types of acceleration and velocity in circular motion. In circular motion, radial acceleration is non-zero, radial velocity is zero, and the body is not in equilibrium.
In circular motion, the- a)Direction of motion is fixed
- b)Direction of motion changes continuously
- c)Acceleration is zero
- d)Velocity is constant
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In circular motion, the
a)
Direction of motion is fixed
b)
Direction of motion changes continuously
c)
Acceleration is zero
d)
Velocity is constant
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
When an object moves along a circular path, it is called circular motion. During such a motion, the direction of motion at any point is given by the tangent at that point which changes continuously.
The _______ circular motion describes as the motion of an object in a circular path with a _______ speed. Fill in the blank.
- a)Non-uniform, constant
- b)Uniform, constant
- c)Non-uniform, varying
- d)Uniform, Varying
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The _______ circular motion describes as the motion of an object in a circular path with a _______ speed. Fill in the blank.
a)
Non-uniform, constant
b)
Uniform, constant
c)
Non-uniform, varying
d)
Uniform, Varying
|
|
Simran Chauhan answered |
Understanding Circular Motion
Circular motion can be categorized into two types based on the speed of the object moving along the circular path: uniform and non-uniform circular motion.
Uniform Circular Motion
- Definition: This occurs when an object moves in a circular path at a constant speed.
- Key Characteristics:
- The magnitude of the velocity remains constant.
- The direction of the velocity changes continuously, which implies that the object is accelerating towards the center of the circle (centripetal acceleration).
- An example is a satellite orbiting Earth at a fixed speed.
Non-Uniform Circular Motion
- Definition: This involves an object moving in a circular path but with varying speed.
- Key Characteristics:
- The speed of the object changes; it can either accelerate or decelerate.
- The object experiences both centripetal acceleration (due to changing direction) and tangential acceleration (due to changing speed).
- An example includes a car taking a curve while speeding up or slowing down.
Correct Answer Explanation
The question allows for two correct options:
- Option B: Uniform, Constant
- This describes the scenario where an object maintains a constant speed in a circular path.
- Option C: Non-uniform, Varying
- This describes the scenario where the speed of the object changes while still moving in a circular path.
Both options reflect different characteristics of circular motion, making them valid answers depending on the context. Understanding these types is crucial for analyzing motion in physics.
Circular motion can be categorized into two types based on the speed of the object moving along the circular path: uniform and non-uniform circular motion.
Uniform Circular Motion
- Definition: This occurs when an object moves in a circular path at a constant speed.
- Key Characteristics:
- The magnitude of the velocity remains constant.
- The direction of the velocity changes continuously, which implies that the object is accelerating towards the center of the circle (centripetal acceleration).
- An example is a satellite orbiting Earth at a fixed speed.
Non-Uniform Circular Motion
- Definition: This involves an object moving in a circular path but with varying speed.
- Key Characteristics:
- The speed of the object changes; it can either accelerate or decelerate.
- The object experiences both centripetal acceleration (due to changing direction) and tangential acceleration (due to changing speed).
- An example includes a car taking a curve while speeding up or slowing down.
Correct Answer Explanation
The question allows for two correct options:
- Option B: Uniform, Constant
- This describes the scenario where an object maintains a constant speed in a circular path.
- Option C: Non-uniform, Varying
- This describes the scenario where the speed of the object changes while still moving in a circular path.
Both options reflect different characteristics of circular motion, making them valid answers depending on the context. Understanding these types is crucial for analyzing motion in physics.
Which one of the following is most probably not a case of uniform circular motion?- a)Motion of a racing car on a circular track
- b)Motion of the moon around the earth
- c)Motion of a toy train on a circular track
- d)Motion of seconds hand on the circular dial of a watch
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is most probably not a case of uniform circular motion?
a)
Motion of a racing car on a circular track
b)
Motion of the moon around the earth
c)
Motion of a toy train on a circular track
d)
Motion of seconds hand on the circular dial of a watch
|
|
Jhanvi Chakraborty answered |
Understanding Uniform Circular Motion
Uniform circular motion refers to motion along a circular path at a constant speed. In this scenario, the object’s speed remains constant, but its direction changes continuously, resulting in acceleration towards the center of the circle.
Analyzing the Options
- Motion of a racing car on a circular track
- This motion is often not uniform because a racing car changes its speed while navigating turns. Drivers accelerate or decelerate, which means the speed is not constant.
- Motion of the moon around the earth
- The moon moves in a nearly circular orbit at a constant speed, making this a classic case of uniform circular motion.
- Motion of a toy train on a circular track
- If the toy train moves at a constant speed around the track, it exemplifies uniform circular motion.
- Motion of the seconds hand on the circular dial of a watch
- The seconds hand moves at a constant speed, completing a full revolution in a fixed time, thus representing uniform circular motion.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'A' – the motion of a racing car on a circular track. This is because the car typically experiences variations in speed, unlike the other options, which maintain a constant speed while moving in a circular path.
Uniform circular motion refers to motion along a circular path at a constant speed. In this scenario, the object’s speed remains constant, but its direction changes continuously, resulting in acceleration towards the center of the circle.
Analyzing the Options
- Motion of a racing car on a circular track
- This motion is often not uniform because a racing car changes its speed while navigating turns. Drivers accelerate or decelerate, which means the speed is not constant.
- Motion of the moon around the earth
- The moon moves in a nearly circular orbit at a constant speed, making this a classic case of uniform circular motion.
- Motion of a toy train on a circular track
- If the toy train moves at a constant speed around the track, it exemplifies uniform circular motion.
- Motion of the seconds hand on the circular dial of a watch
- The seconds hand moves at a constant speed, completing a full revolution in a fixed time, thus representing uniform circular motion.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'A' – the motion of a racing car on a circular track. This is because the car typically experiences variations in speed, unlike the other options, which maintain a constant speed while moving in a circular path.
For a particle in a non- uniform accelerated circular motion
- a)Velocity is transverse and acceleration has both radial and transverse components
- b)Velocity is transverse and acceleration is radial only
- c)Velocity is radial and acceleration has both radial and transverse components
- d)Velocity is radial and acceleration is transverse only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For a particle in a non- uniform accelerated circular motion
a)
Velocity is transverse and acceleration has both radial and transverse components
b)
Velocity is transverse and acceleration is radial only
c)
Velocity is radial and acceleration has both radial and transverse components
d)
Velocity is radial and acceleration is transverse only
|
|
Sandeep Chawla answered |
Explanation:
Non-uniform circular motion is the motion of an object moving in a circular path with a varying speed. The direction of the velocity and acceleration of an object in non-uniform circular motion changes at every point on the circular path.
Velocity:
Velocity is the rate of change of displacement with respect to time. In non-uniform circular motion, the velocity of the object is always tangent to the circular path. The magnitude of the velocity changes at every point on the circular path.
Acceleration:
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. In non-uniform circular motion, the acceleration of the object is not constant. It changes at every point on the circular path.
Now, let's discuss the given options one by one:
a) Velocity is radial and acceleration is transverse only:
In this option, the velocity is radial which means it is directed towards the center of the circular path. But the acceleration is transverse which means it is perpendicular to the velocity vector. This option is correct because the direction of the acceleration is always towards the center of the circular path in non-uniform circular motion.
b) Velocity is transverse and acceleration is radial only:
In this option, the velocity is transverse which means it is perpendicular to the radius vector. But the acceleration is radial which means it is directed towards the center of the circular path. This option is incorrect because the direction of the acceleration is not always radial in non-uniform circular motion.
c) Velocity is radial and acceleration has both radial and transverse components:
In this option, the velocity is radial which means it is directed towards the center of the circular path. But the acceleration has both radial and transverse components. This option is incorrect because the direction of the acceleration is always towards the center of the circular path in non-uniform circular motion.
d) Velocity is transverse and acceleration has both radial and transverse components:
In this option, the velocity is transverse which means it is perpendicular to the radius vector. But the acceleration has both radial and transverse components. This option is incorrect because the direction of the acceleration is not always radial in non-uniform circular motion.
Hence, the correct option is 'a' - Velocity is radial and acceleration is transverse only.
Non-uniform circular motion is the motion of an object moving in a circular path with a varying speed. The direction of the velocity and acceleration of an object in non-uniform circular motion changes at every point on the circular path.
Velocity:
Velocity is the rate of change of displacement with respect to time. In non-uniform circular motion, the velocity of the object is always tangent to the circular path. The magnitude of the velocity changes at every point on the circular path.
Acceleration:
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. In non-uniform circular motion, the acceleration of the object is not constant. It changes at every point on the circular path.
Now, let's discuss the given options one by one:
a) Velocity is radial and acceleration is transverse only:
In this option, the velocity is radial which means it is directed towards the center of the circular path. But the acceleration is transverse which means it is perpendicular to the velocity vector. This option is correct because the direction of the acceleration is always towards the center of the circular path in non-uniform circular motion.
b) Velocity is transverse and acceleration is radial only:
In this option, the velocity is transverse which means it is perpendicular to the radius vector. But the acceleration is radial which means it is directed towards the center of the circular path. This option is incorrect because the direction of the acceleration is not always radial in non-uniform circular motion.
c) Velocity is radial and acceleration has both radial and transverse components:
In this option, the velocity is radial which means it is directed towards the center of the circular path. But the acceleration has both radial and transverse components. This option is incorrect because the direction of the acceleration is always towards the center of the circular path in non-uniform circular motion.
d) Velocity is transverse and acceleration has both radial and transverse components:
In this option, the velocity is transverse which means it is perpendicular to the radius vector. But the acceleration has both radial and transverse components. This option is incorrect because the direction of the acceleration is not always radial in non-uniform circular motion.
Hence, the correct option is 'a' - Velocity is radial and acceleration is transverse only.
A particles revolves along a circle with a uniform speed. The motion of the particle is ____ .- a)one dimensional
- b)two dimensional.
- c)translatory
- d)oscillatory
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particles revolves along a circle with a uniform speed. The motion of the particle is ____ .
a)
one dimensional
b)
two dimensional.
c)
translatory
d)
oscillatory
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
To describe the motion of a particle along a circle with a uniform speed. We need two variable, either x and y, or r and θ. Therefore, the motion of the particle is two-dimensional.
In a uniform circular motion - - a)Both velocity and acceleration are constant.
- b)Both speed and velocity constant
- c)Both Acceleration and speed changes
- d)Both acceleration and velocity changes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a uniform circular motion -
a)
Both velocity and acceleration are constant.
b)
Both speed and velocity constant
c)
Both Acceleration and speed changes
d)
Both acceleration and velocity changes

|
Stepway Academy answered |
CONCEPT:
- Uniform motion is the type of motion where a moving object traces equal distances in equal intervals of time.
- Since the distance and time intervals are the same, speed is constant in uniform motion.
- Uniform circular motion is where a moving object traces a circular path with constant speed.
- A circle is assumed to be a polygon with infinitely many sides such that each side approximates to a point.
- So, if the object moving on a circular path undergoes a change in direction at every point.
- Since direction changes and speed remains constant, velocity is varying.
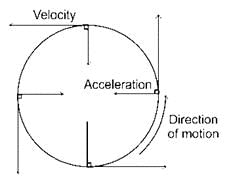
EXPLANATION:
- Velocity is changing in a uniform circular motion as the direction of the object keeps changing at every point.
- Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. Since velocity keeps changing at every instant, acceleration also changes.
Therefore, both acceleration and velocity changes in a uniform circular motion.
Railway tracks are banked at the curves so that the necessary centripetal force may be obtained from the horizontal component of the reaction on the train.
- a)true
- b)false
- c)cannot predict
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Railway tracks are banked at the curves so that the necessary centripetal force may be obtained from the horizontal component of the reaction on the train.
a)
true
b)
false
c)
cannot predict
d)
none of these
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Railway tracks are banked at curves to help the train negotiate the curve safely. The banking of the tracks ensures that the necessary centripetal force is provided by the horizontal component of the normal reaction force from the track. This reduces the reliance on friction between the train wheels and the track, allowing trains to travel safely around curves at higher speeds.
Uniform circular motion is called continuously accelerated motion mainly because- a)direction of motion changes
- b)speed remains the same
- c)velocity remains the same
- d)direction of motion does not change
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Uniform circular motion is called continuously accelerated motion mainly because
a)
direction of motion changes
b)
speed remains the same
c)
velocity remains the same
d)
direction of motion does not change
|
|
Anoushka Basu answered |
**Uniform Circular Motion**
Uniform circular motion refers to the motion of an object traveling in a circular path at a constant speed. In this type of motion, the object moves along the circumference of the circle, maintaining a fixed distance from the center.
**Acceleration in Uniform Circular Motion**
While the speed of the object remains constant in uniform circular motion, it is important to note that the object is still experiencing acceleration. This may seem counterintuitive since we typically associate acceleration with a change in speed. However, in uniform circular motion, the acceleration is directed towards the center of the circle and is known as centripetal acceleration.
**Direction of Motion Changes**
The correct answer to why uniform circular motion is called continuously accelerated motion is that the direction of motion changes. In uniform circular motion, an object continuously changes its direction as it moves along the circular path. This change in direction implies that the object is experiencing acceleration.
**Velocity Remains the Same**
While the object is undergoing acceleration in uniform circular motion, its velocity remains constant. Velocity is a vector quantity that includes both magnitude (speed) and direction. In uniform circular motion, the speed of the object remains constant, but its direction changes. Therefore, the velocity of the object remains the same in terms of magnitude, but the direction of the velocity vector continually changes.
**Centripetal Acceleration**
The centripetal acceleration is the acceleration experienced by an object undergoing uniform circular motion. It is directed towards the center of the circle and is responsible for continuously changing the direction of the object's motion. The magnitude of the centripetal acceleration can be calculated using the formula:
a = v^2 / r
where a is the centripetal acceleration, v is the velocity of the object, and r is the radius of the circular path.
**Conclusion**
In conclusion, uniform circular motion is called continuously accelerated motion because the direction of motion of the object undergoing circular motion continually changes. Although the speed (magnitude of velocity) remains constant, the object experiences centripetal acceleration directed towards the center of the circle. This acceleration is responsible for continuously changing the direction of the object's motion, making it an example of accelerated motion.
Uniform circular motion refers to the motion of an object traveling in a circular path at a constant speed. In this type of motion, the object moves along the circumference of the circle, maintaining a fixed distance from the center.
**Acceleration in Uniform Circular Motion**
While the speed of the object remains constant in uniform circular motion, it is important to note that the object is still experiencing acceleration. This may seem counterintuitive since we typically associate acceleration with a change in speed. However, in uniform circular motion, the acceleration is directed towards the center of the circle and is known as centripetal acceleration.
**Direction of Motion Changes**
The correct answer to why uniform circular motion is called continuously accelerated motion is that the direction of motion changes. In uniform circular motion, an object continuously changes its direction as it moves along the circular path. This change in direction implies that the object is experiencing acceleration.
**Velocity Remains the Same**
While the object is undergoing acceleration in uniform circular motion, its velocity remains constant. Velocity is a vector quantity that includes both magnitude (speed) and direction. In uniform circular motion, the speed of the object remains constant, but its direction changes. Therefore, the velocity of the object remains the same in terms of magnitude, but the direction of the velocity vector continually changes.
**Centripetal Acceleration**
The centripetal acceleration is the acceleration experienced by an object undergoing uniform circular motion. It is directed towards the center of the circle and is responsible for continuously changing the direction of the object's motion. The magnitude of the centripetal acceleration can be calculated using the formula:
a = v^2 / r
where a is the centripetal acceleration, v is the velocity of the object, and r is the radius of the circular path.
**Conclusion**
In conclusion, uniform circular motion is called continuously accelerated motion because the direction of motion of the object undergoing circular motion continually changes. Although the speed (magnitude of velocity) remains constant, the object experiences centripetal acceleration directed towards the center of the circle. This acceleration is responsible for continuously changing the direction of the object's motion, making it an example of accelerated motion.
A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude. Which is always perpendicular to the velocity of the particle ? The motion of the particle takes place in a plane. It follow that that- a)its velocity is constant
- b)its acceleration is constant
- c)its kinetic energy is constant
- d)it moves in a circular path
Correct answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude. Which is always perpendicular to the velocity of the particle ? The motion of the particle takes place in a plane. It follow that that
a)
its velocity is constant
b)
its acceleration is constant
c)
its kinetic energy is constant
d)
it moves in a circular path
|
|
Shail Majumdar answered |
Perpendicular Force on a Particle in a Plane
When a particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude that is always perpendicular to its velocity, the following can be observed:
Circular Motion
The particle moves in a circular path because the force acts as a centripetal force, pulling the particle towards the center of the circle.
Constant Kinetic Energy
Since the force is always perpendicular to the velocity of the particle, it does not do any work on the particle. Therefore, the kinetic energy of the particle remains constant.
Variable Speed
Although the particle moves in a circular path, its speed is not constant. This is because the force only changes the direction of the particle, not its speed. Therefore, the particle will move faster when it is farther away from the center of the circle and slower when it is closer to the center.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when a particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude that is always perpendicular to its velocity, it will move in a circular path with variable speed while maintaining constant kinetic energy.
When a particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude that is always perpendicular to its velocity, the following can be observed:
Circular Motion
The particle moves in a circular path because the force acts as a centripetal force, pulling the particle towards the center of the circle.
Constant Kinetic Energy
Since the force is always perpendicular to the velocity of the particle, it does not do any work on the particle. Therefore, the kinetic energy of the particle remains constant.
Variable Speed
Although the particle moves in a circular path, its speed is not constant. This is because the force only changes the direction of the particle, not its speed. Therefore, the particle will move faster when it is farther away from the center of the circle and slower when it is closer to the center.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when a particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude that is always perpendicular to its velocity, it will move in a circular path with variable speed while maintaining constant kinetic energy.
Chapter doubts & questions for Circular Motion - Physics for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Circular Motion - Physics for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for EmSAT Achieve
208 videos|329 docs|212 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup