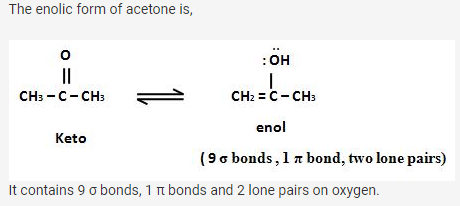All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Covalent Compounds for EmSAT Achieve Exam
In allene (C3H4), the type(s) of hybridisation of the carbon atoms is (are)
- a)sp and sp3
- b)sp and sp2
- c)Only sp2
- d)sp2 and sp3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In allene (C3H4), the type(s) of hybridisation of the carbon atoms is (are)
a)
sp and sp3
b)
sp and sp2
c)
Only sp2
d)
sp2 and sp3
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
The type(s) of hybridization of the carbon atoms in Allene (C3H4) is sp and sp2.
Which of the following is/are correct statement(s)?a)s + py→ two sp-hybrid orbitals lying in the yz planeb)s + px → two sp-hybrid orbitals lying in xz planec)(s + px + pz) → three sp2-hybrid orbitals lying in xz planed)(s + py) → two sp-hybrid orbitals lying along y-axisCorrect answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Incorrect (b)
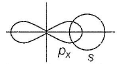
two sp-hybrid orbitals are along x-axis.
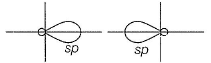
two sp-hybrid orbitals are along x-axis.
The correct order of increasing bond length of
I. C— H
II. C— O
III. C— C
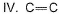
- a)I< II< III< IV
- b)I< IV < II< III
- c)Ill < IV < II < l
- d)II < I < III < IV
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of increasing bond length of
I. C— H
II. C— O
III. C— C
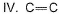
I. C— H
II. C— O
III. C— C
a)
I< II< III< IV
b)
I< IV < II< III
c)
Ill < IV < II < l
d)
II < I < III < IV

|
Amrita Sen answered |
H is smallest in size thus, (C— H)bond length is least.
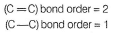
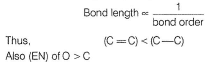
Hence, bonding pair in (C— O) is nearer to nucleus decreasing bond length as compared to (C— C).
Thus, I < IV < II < III.
Hence, bonding pair in (C— O) is nearer to nucleus decreasing bond length as compared to (C— C).
Thus, I < IV < II < III.
Expansion of octet can not take place in- a)N
- b)S
- c)Si
- d)P
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Expansion of octet can not take place in
a)
N
b)
S
c)
Si
d)
P

|
Harshad Nair answered |
N(7) = 1s22s22p3
Nitrogen does not have (2d) orbitals. Thus, (more than 8) electrons cannot be accomodated in second orbit.
Nitrogen does not have (2d) orbitals. Thus, (more than 8) electrons cannot be accomodated in second orbit.
Select the correct statement about valence bond approach.- a)Each bond is formed by maximum overlap for its maximum stability
- b)It represents localised electron model of bonding
- c)Most of the electrons retain the same orbital locations as in separated atoms
- d)All of the above are correct statements
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement about valence bond approach.
a)
Each bond is formed by maximum overlap for its maximum stability
b)
It represents localised electron model of bonding
c)
Most of the electrons retain the same orbital locations as in separated atoms
d)
All of the above are correct statements
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
(a) Hs maximum overlap - correct.
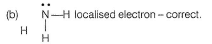
(c) Based on valence bond approach,-no prediction of change of structure due to (Ip-Ip), (Ip-bp) repulsions- correct.
(c) Based on valence bond approach,-no prediction of change of structure due to (Ip-Ip), (Ip-bp) repulsions- correct.
Polarity in a molecule and hence the dipole moment depends primarily on electronegativity of the constituent atoms and shape of a molecule. Which of the following has the highest dipole moment? - a)CO2
- b)HI
- c)H2O
- d)SO2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Polarity in a molecule and hence the dipole moment depends primarily on electronegativity of the constituent atoms and shape of a molecule. Which of the following has the highest dipole moment?
a)
CO2
b)
HI
c)
H2O
d)
SO2
|
|
Isha Kulkarni answered |
H2O will have highest dipole moment due to maximum difference in electronegativity of H and O atoms.
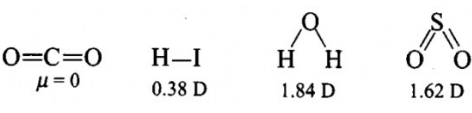
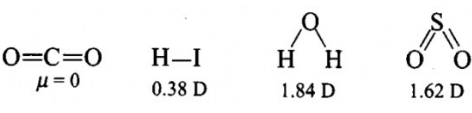
In which of the following cases, covalent bonds are cleaved?- a)Boiling of H2O
- b)Melting of KCN
- c)Boiling of CF4
- d)Melting of SiO2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following cases, covalent bonds are cleaved?
a)
Boiling of H2O
b)
Melting of KCN
c)
Boiling of CF4
d)
Melting of SiO2
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
SiO2 is a network covalent compound that has an extremely high melting and boiling point, because many silicon-oxygen bonds have to be broken in order for it to achieve the necessary freedom. To clarify, SiO2, which has a tetrahedral network lattice formation, shows that each silicon is actually bonded to 4 oxygens; each oxygen is bonded to 2 silicon. These are excess bonds aside from the ones of SiO2 which are broken.
Polarity in a molecule and hence the dipole moment depends primarily on electronegativity of the constituent atoms and shape of a molecule. Which of the following has the highest dipole moment? a)CO2b)HIc)H2Od)SO2Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
H2O will have highest dipole moment due to maximum difference in electronegativity of H and O atoms.
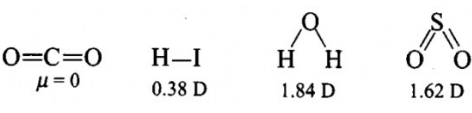
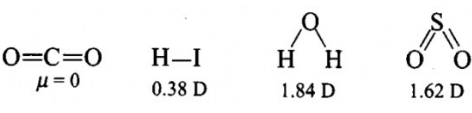
Q. Which of the following species contain at least one atom that violates the octet rule?a)O— Cl—-Ob)F— Xe— Fc)PCI5d)SF6Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
(a) Octet of Cl expanded to (9).
(b) Octet Xe expanded to (10).
(c) Octet of P expanded to (10).
(b) Octet Xe expanded to (10).
(c) Octet of P expanded to (10).
Which of the following is nonpolar?- a)CI3CCH3
- b)PCI5
- c)CH2CI2
- d)NH3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is nonpolar?
a)
CI3CCH3
b)
PCI5
c)
CH2CI2
d)
NH3
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
(b) PCI5 triangular bipyramidal, symmetrical, no lone pair.
The common features among the species CN–, CO ad NO+ are- a) Bond order three and isoelectronic
- b) Bond order three and weak field ligands
- c) Bond order two and acceptors
- d) Isoelectronic and weak field ligands
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The common features among the species CN–, CO ad NO+ are
a)
Bond order three and isoelectronic
b)
Bond order three and weak field ligands
c)
Bond order two and acceptors
d)
Isoelectronic and weak field ligands
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
According to M.O theory,
CN−,CO and NO+ are isoelectronic (14e−) and bond order is 3.
a is the correct answer.
In which of the following substances will hydrogen bond be strongest?- a)HCl
- b)H2O
- c)HI
- d)H2S
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following substances will hydrogen bond be strongest?
a)
HCl
b)
H2O
c)
HI
d)
H2S
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
HC1, HI and H2S do not from H-bonds. Only H2O forms hydrogen bonds. One H2O molecule forms four H-bonding.

The bond between B and C will be- a)Ionic
- b)Covalent
- c)Hydrogen
- d)Coordinate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The bond between B and C will be
a)
Ionic
b)
Covalent
c)
Hydrogen
d)
Coordinate
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Both B and C are non-metals and therefore, bond formed between them will be covalent.
Direction (Q. Nos. 17) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.Q. Match the orbital overlap figures shown in Column I with the description given in Column II and select the correct answer using the code given below the columns.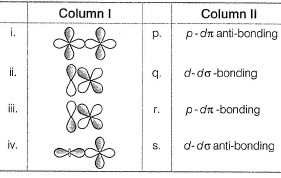
 [JEE Advanced 2014]
[JEE Advanced 2014]- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 17) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q. Match the orbital overlap figures shown in Column I with the description given in Column II and select the correct answer using the code given below the columns.
[JEE Advanced 2014]
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
(i) (d-d) σ-bonding (ii) (p-dπ bonding)
(iii) (p-dπ anti-bonding) (iv) (ddσ anti-bonding)
(iii) (p-dπ anti-bonding) (iv) (ddσ anti-bonding)
Select the correct statement(s) about NO2.- a)It is paramagnetic in nature
- b)It forms dimer and paramagnetic is lost
- c)NO2 and dimer formed have sp2-hybridised N-atom
- d)Brown colour of NO2 fades and (N— N) bond length is greater than normal (N— N) bond length
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement(s) about NO2.
a)
It is paramagnetic in nature
b)
It forms dimer and paramagnetic is lost
c)
NO2 and dimer formed have sp2-hybridised N-atom
d)
Brown colour of NO2 fades and (N— N) bond length is greater than normal (N— N) bond length
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Due to unpaired electron paramagnetic, N-atom in NO2 is electron deficie nt thus, to complete octet, dimer is formed.
In N2O4 formation, each N-atom gets
Thus, (a), (b), (c) and (d) are correct.
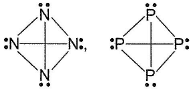
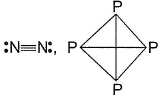
Mean bond enthalpy of different bonds are given
 Out of the given pairs, which compound is more stable than the other?
Out of the given pairs, which compound is more stable than the other?
- a)
- b)
- c)
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mean bond enthalpy of different bonds are given
Out of the given pairs, which compound is more stable than the other?
a)
b)
c)
d)
None of these

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Bond enthalpy of six (P— P) bond = 6 x 215 = 1290 k j mol-1
Bond enthalpy of six (N — N) bond = 6 x 160
= 960 kJ mol-1
Thus, P4 is more stable than N4.
Covalency of carbon in CO is three because- a)an unexcited carbon atom has two unpaired electrons
- b)the C-atom can be an acceptor of an electron pair
- c)the C-atom has four valence electrons
- d)the maximum covalency of carbon is three
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Covalency of carbon in CO is three because
a)
an unexcited carbon atom has two unpaired electrons
b)
the C-atom can be an acceptor of an electron pair
c)
the C-atom has four valence electrons
d)
the maximum covalency of carbon is three
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
In structure I, octet of oxygen is complete but octet of carbon is incomplete. Hence, carbon is an acceptor of an electron pair from oxygen. Thus, covalency of carbon is three in CO.
Select the correct statement(s) about divalent anion of orthophosphoric acid.- a)It is amphiprotic
- b)All bond length (P— O) are identical due to resonance
- c)The bond order is 1.33 for (P— O) bonds
- d)It is a base
Correct answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement(s) about divalent anion of orthophosphoric acid.
a)
It is amphiprotic
b)
All bond length (P— O) are identical due to resonance
c)
The bond order is 1.33 for (P— O) bonds
d)
It is a base
|
|
Om Desai answered |
It is a base because it presents three OH group and bond order of PO is equal to total no. of sigma and pie bond/total no of resonance structure due to which = 5/4 = 1.25 ~1.3
Considering x-axis as the internuclear axis, which out of the following will not form sigma bond.- a)1s and 1s
- b)1s and 2px
- c)2py and 2py
- d)1s and 2s
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Considering x-axis as the internuclear axis, which out of the following will not form sigma bond.
a)
1s and 1s
b)
1s and 2px
c)
2py and 2py
d)
1s and 2s
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
Sigma bond is always formed between two half-filled atomic orbitals along their internuclear axis.i.e the line joining the centres of the nuclei of two atoms(axial overlapping). 2py and 2py will not form a sigma bond because taking x-axis as the internuclear axis, there will be lateral (sideway) overlap between the two 2pv orbitals forming a straight pi bond.
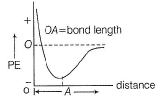
When a chemical bond is formed, there is decrease in- a)kinetic energy
- b)potential energy
- c)repulsive force
- d)attractive force
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When a chemical bond is formed, there is decrease in
a)
kinetic energy
b)
potential energy
c)
repulsive force
d)
attractive force

|
Arpita Nambiar answered |
When two atoms approach to form a bond, there is decrease in potential energy (PE). After bond formation, at a minimum distance (called bond length). PE further increases.
Malleability and ductility of metals can be accounted due to- a)the presence of electrostatic force
- b)the crystalline structure in metal
- c)the capacity of layers of metal ions to slide over the other
- d)the interaction of electrons with metal ions in the lattice
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Malleability and ductility of metals can be accounted due to
a)
the presence of electrostatic force
b)
the crystalline structure in metal
c)
the capacity of layers of metal ions to slide over the other
d)
the interaction of electrons with metal ions in the lattice
|
|
Vishnu Sankar answered |
In metallic bonds, the valence shell electrons are delocalised and shared between many atoms. These delocalised electrons allow the metal atoms to slide past one another without being subjected to strong repulsive forces. The malleability and ductility of metals is due to this sliding capacity of the delocalised electrons.
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-19) This section contains 2 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE Then ONE is correct.Peroxide ion ______.
a) is diamagnetic.b) has five completely filled antibonding molecular orbitals.c) is isoelectronic with neon.d) has bond order one.Which one of these is correct?- a)a), b) and d)
- b)d) and c)
- c)a) and d)
- d)a), b) and c)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-19) This section contains 2 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE Then ONE is correct.
Peroxide ion ______.
a) is diamagnetic.
a) is diamagnetic.
b) has five completely filled antibonding molecular orbitals.
c) is isoelectronic with neon.
d) has bond order one.
Which one of these is correct?
a)
a), b) and d)
b)
d) and c)
c)
a) and d)
d)
a), b) and c)
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
Peroxide ion (O2^2-) doesn't have any unpaired electrons and is diamagnetic.
Peroxide ion is O2^−2.
O2^2-(18)=σ1s2, σ∗1s2, σ2s2, σ∗2s2, σ2pz2, π2px^2 ≈ π2py2,π∗2px2 ≈ π∗2py2
Bond order = Nb−Na/2 =(10−8)/2 = 1
Hyperconjugation involve overlap of the following orbitals- a)σ-σ
- b)σ-π
- c)p-p
- d)π-π
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hyperconjugation involve overlap of the following orbitals
a)
σ-σ
b)
σ-π
c)
p-p
d)
π-π

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Hyperconjugation takes place in allylic compounds in which alkyl group (having at least one H) is attached to 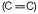 bond .
bond .
σ-bond of (— CH3) and π -bond of (ene) are involved, π-bond is formed due to overlapping of p-orbitals. Thus, σ-orbital and p-orbital are involved.
Maximum covalency is equal to the number- a)paired p-electrons
- b)unpaired s-electrons
- c)unpaired s and p-electrons
- d)s-and p-electrons in the valence shells
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Maximum covalency is equal to the number
a)
paired p-electrons
b)
unpaired s-electrons
c)
unpaired s and p-electrons
d)
s-and p-electrons in the valence shells

|
Kaavya Mukherjee answered |
s-and p-electrons have generally low energy than d-and f-electrons thus take part in chemical bonding.
Maximum covalency = (s + p) valence electrons,
covalency of C =4, valence electrons = 4 S = 6 valence electrons = 6
Maximum covalency = (s + p) valence electrons,
covalency of C =4, valence electrons = 4 S = 6 valence electrons = 6
Ratio of σ and π-bonds is equal to 1 in
- a)benzene
- b)tetracyanomethane
- c)allene(C3H4)
- d)CO2
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ratio of σ and π-bonds is equal to 1 in
a)
benzene
b)
tetracyanomethane
c)
allene(C3H4)
d)
CO2
|
|
Jithin Saini answered |
Correct Answer : B
Explanation : Tetracyanomethane, where σ bond =8, ratio = 1, π bond = 8.
Carbon dioxide, O=C=O
σ = 2, π = 2
Ratio = 1.
Passage IIConsider the following structure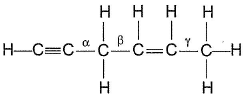
Q. Shortest (C— H) bond is- a)
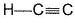
- b)
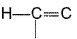
- c)
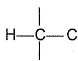
- d)all (C— H) bonds are of equal length.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage II
Consider the following structure
Q.
Shortest (C— H) bond is
a)
b)
c)
d)
all (C— H) bonds are of equal length.

|
Ruchi Basak answered |
Greater the electronegativity of carbon atom
(sp3 < sp2 < sp)
Greater the attraction for (C— H) bonding pair hence, shorter the (C— H)bond.
(sp3 < sp2 < sp)
Greater the attraction for (C— H) bonding pair hence, shorter the (C— H)bond.
The bond between two identical nonmetal atoms has a pair of electrons:- a) unequally shared between the two.
- b) transferred fully from one atom to another
- c) with identical spins
- d) equally shared between them
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The bond between two identical nonmetal atoms has a pair of electrons:
a)
unequally shared between the two.
b)
transferred fully from one atom to another
c)
with identical spins
d)
equally shared between them
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
When bond is formed between identical atoms, it is a perfectly covalent bond. Electrons will be shared equally among them.
Direction (Q. Nos. 21-25) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)
Passage I
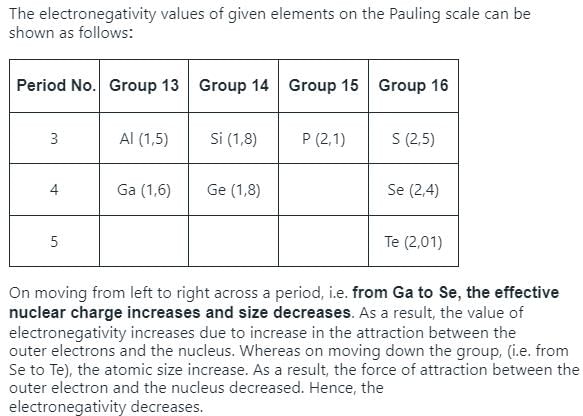
Electronegativity values (EN) of elements have been given (in Pauling’s scale)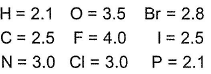
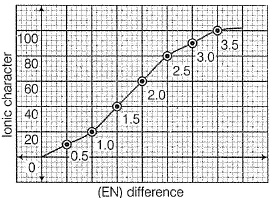
Graph shows variation of percentage ionic character with (EN) difference of two elements.
Q. Which of the following bonds is most polar?- a)H— Br
- b)N— H
- c)N— O
- d)P— H
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 21-25) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)
Passage I
Electronegativity values (EN) of elements have been given (in Pauling’s scale)
Passage I
Electronegativity values (EN) of elements have been given (in Pauling’s scale)
Graph shows variation of percentage ionic character with (EN) difference of two elements.
Q. Which of the following bonds is most polar?
a)
H— Br
b)
N— H
c)
N— O
d)
P— H
|
|
Simran Chauhan answered |
The compound (NH3, BF3)can be easily separated into its individual components because- a)BF3 is highly reactive
- b)NH3 is highly reactive
- c)ESF3 is a Lewis base
- d)BF3 and NH3 are joined by weak coordinate bond and have independent existence
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound (NH3, BF3)can be easily separated into its individual components because
a)
BF3 is highly reactive
b)
NH3 is highly reactive
c)
ESF3 is a Lewis base
d)
BF3 and NH3 are joined by weak coordinate bond and have independent existence

|
Rahul Chaudhary answered |
The compound (NH3, BF3) can be easily separated into its individual components because:
Explanation:
1. Weak Coordinate Bond:
The compound (NH3, BF3) can be easily separated into its individual components because BF3 and NH3 are joined by a weak coordinate bond. A coordinate bond is a type of covalent bond in which one atom donates both electrons to form a bond with another atom. In this case, the nitrogen atom in NH3 donates a pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond with the boron atom in BF3.
2. Independent Existence:
BF3 and NH3 have independent existence, which means they can exist separately without being chemically bonded. BF3 is a Lewis acid, meaning it can accept a pair of electrons, while NH3 is a Lewis base, meaning it can donate a pair of electrons. Due to their independent existence, it is possible to separate them from each other.
3. Reactivity:
Neither BF3 nor NH3 is highly reactive. BF3 is a strong Lewis acid, but it is not highly reactive in terms of chemical reactivity. NH3, on the other hand, is not highly reactive either. Both compounds are stable and have relatively low reactivity compared to highly reactive compounds.
Conclusion:
The compound (NH3, BF3) can be easily separated into its individual components because BF3 and NH3 are joined by a weak coordinate bond and have independent existence. This means that the bond between them can be broken relatively easily, allowing the individual components to be separated. Additionally, the low reactivity of both compounds further facilitates their separation.
Explanation:
1. Weak Coordinate Bond:
The compound (NH3, BF3) can be easily separated into its individual components because BF3 and NH3 are joined by a weak coordinate bond. A coordinate bond is a type of covalent bond in which one atom donates both electrons to form a bond with another atom. In this case, the nitrogen atom in NH3 donates a pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond with the boron atom in BF3.
2. Independent Existence:
BF3 and NH3 have independent existence, which means they can exist separately without being chemically bonded. BF3 is a Lewis acid, meaning it can accept a pair of electrons, while NH3 is a Lewis base, meaning it can donate a pair of electrons. Due to their independent existence, it is possible to separate them from each other.
3. Reactivity:
Neither BF3 nor NH3 is highly reactive. BF3 is a strong Lewis acid, but it is not highly reactive in terms of chemical reactivity. NH3, on the other hand, is not highly reactive either. Both compounds are stable and have relatively low reactivity compared to highly reactive compounds.
Conclusion:
The compound (NH3, BF3) can be easily separated into its individual components because BF3 and NH3 are joined by a weak coordinate bond and have independent existence. This means that the bond between them can be broken relatively easily, allowing the individual components to be separated. Additionally, the low reactivity of both compounds further facilitates their separation.
Direction (Q. Nos. 27 and 28) This section contains 2 question. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)Q. In acidic medium,H2O2 changes Cr2O72- to CrO5 which has two (-O-O-) bonds. Oxidation state of Cr in CrO3 is
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 27 and 28) This section contains 2 question. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. In acidic medium,H2O2 changes Cr2O72- to CrO5 which has two (-O-O-) bonds. Oxidation state of Cr in CrO3 is
|
|
Sparsh Datta answered |
When H2O2 is added to an acidified solution of a dichromate, Cr2O72-, aO deep blue coloured complex, chromic peroxide, CrO5 [ or CrO(O2)2] is formed.
Cr2O72- +2H++4H2O2 ---> 2CrO(O2)2 +5H2O
This deep blue coloured complex.
Oxidation state of Cr is +6 due to the presence of two peroxide linkages which can be calculated as Cr peroxide normal
x+(-1)4+(-2) =0
x-6 =0
x=+6
Cr2O72- +2H++4H2O2 ---> 2CrO(O2)2 +5H2O
This deep blue coloured complex.
Oxidation state of Cr is +6 due to the presence of two peroxide linkages which can be calculated as Cr peroxide normal
x+(-1)4+(-2) =0
x-6 =0
x=+6
Bond order of (B— H) x and y bonds in diborane are respectively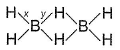
- a)1, 1
- b)0, 0.5
- c)0.5, 0.5
- d)1, 0.5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Bond order of (B— H) x and y bonds in diborane are respectively
a)
1, 1
b)
0, 0.5
c)
0.5, 0.5
d)
1, 0.5

|
Sankar Bose answered |
In allene (C3H4), the type(s) of hybridisation of the carbon atoms is (are) - a)sp and sp3
- b)sp and sp2
- c)Only sp2
- d)sp2 and sp3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In allene (C3H4), the type(s) of hybridisation of the carbon atoms is (are)
a)
sp and sp3
b)
sp and sp2
c)
Only sp2
d)
sp2 and sp3
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
In allene, hybridization of C-atoms:
The two C-atoms H2-C=C=C-H2 at terminal have sp2 while the middle have sp .
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-16) This section contains 16 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. Octet rule is not followed in- a)CCI4, N2O4, N2O5
- b)BF3, BeCI3, NO2
- c)NaCI, MgCI2, MgO
- d)PCI3, NH3, H2O
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-16) This section contains 16 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Octet rule is not followed in
a)
CCI4, N2O4, N2O5
b)
BF3, BeCI3, NO2
c)
NaCI, MgCI2, MgO
d)
PCI3, NH3, H2O

|
Sinjini Datta answered |
Octet rule violation in BF3, BeCl3, NO2:
The octet rule states that atoms tend to combine in such a way that each atom has a full outer shell of 8 electrons. However, there are certain molecules where the octet rule is violated due to the presence of an odd number of electrons or an incomplete octet.
BF3 (Boron Trifluoride):
- Boron has 3 valence electrons, and in BF3, it forms 3 single bonds with fluorine atoms. As a result, boron has only 6 electrons in its outer shell, violating the octet rule.
BeCl3 (Beryllium Chloride):
- Beryllium also has 2 valence electrons, and in BeCl3, it forms 3 single bonds with chlorine atoms. This results in beryllium having only 6 electrons in its outer shell, again violating the octet rule.
NO2 (Nitrogen Dioxide):
- In NO2, nitrogen forms a double bond with one oxygen atom and a single bond with another oxygen atom. This results in nitrogen having 7 electrons in its outer shell, violating the octet rule.
In contrast, the other options provided (a, c, d) follow the octet rule:
- Option (a) contains compounds like CCl4, N2O4, N2O5 which satisfy the octet rule.
- Option (c) contains compounds like NaCl, MgCl2, MgO which also satisfy the octet rule.
- Option (d) contains compounds like PCl3, NH3, H2O which follow the octet rule as well.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option B, as BF3, BeCl3, and NO2 do not follow the octet rule due to the specific bonding arrangements in these molecules.
Following is the dot structure of XY4
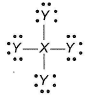 Q. X and Y can be
Q. X and Y can be- a)Cl, F
- b)I, Br
- c)Xe, F
- d)Si, Cl
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Following is the dot structure of XY4
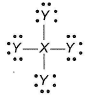
Q. X and Y can be
a)
Cl, F
b)
I, Br
c)
Xe, F
d)
Si, Cl

|
Mansi Chopra answered |
There are three lone pairs on Y and four σ - bonds between X and Y.
Thus, octets of X and Y are complete.
X has four electrons in valence shell.
Y has seven electrons in valence shell.
Thus, X = Si (group 14), y = Cl (group 17)
Thus, octets of X and Y are complete.
X has four electrons in valence shell.
Y has seven electrons in valence shell.
Thus, X = Si (group 14), y = Cl (group 17)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-15) This section contains 15 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. By Lewis structure NO has following fact- a)Dot Lewis structure is

- b)Bond order is 2.5 since, five electrons are shared between N and O-atom
- c)There is one unpaired electron hence, NO is paramagnetic
- d)All are correct facts
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-15) This section contains 15 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. By Lewis structure NO has following fact
a)
Dot Lewis structure is 

b)
Bond order is 2.5 since, five electrons are shared between N and O-atom
c)
There is one unpaired electron hence, NO is paramagnetic
d)
All are correct facts
|
|
Anand Kapoor answered |
To complete octet, N shares 2 electrons and oxygen shares 3 electrons.
Thus, (a) is correct.
Electron-seeking species are called electrophiles. Which of the following sets consists of electrophiles only?- a)
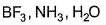
- b)
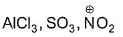
- c)
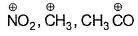
- d)
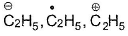
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Electron-seeking species are called electrophiles. Which of the following sets consists of electrophiles only?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Puja Das answered |
AICI3-Octet of Al is incomplete; thus electrophile.
SO3—It has positive charge on sulphur due to resonance.
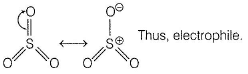
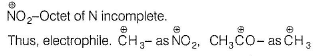
SO3—It has positive charge on sulphur due to resonance.
Direction (Q. Nos. 26) Choice for the correct combination of elements from coloumn I and Coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which one is correct.Match the species in Column I with their properties in Column II.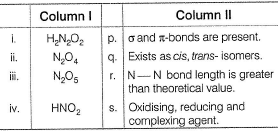

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 26) Choice for the correct combination of elements from coloumn I and Coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which one is correct.
Match the species in Column I with their properties in Column II.
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Madhavan Chatterjee answered |
α and π bonds exist.
Oxidation number of N = + 3 it can be increased to +5 (maximum) and decreased to -3 (minimum) HNO2 is also a ’ligand.
HNO2 is also the complexing agent
Chapter doubts & questions for Covalent Compounds - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Covalent Compounds - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve
191 videos|265 docs|160 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup