All Exams >
MCAT >
General Chemistry for MCAT >
All Questions
All questions of Stoichiometry for MCAT Exam
Suppose that an industrial chemist wishes to obtain calcium chloride (CaCl2) by reacting calcium metal with chlorine gas. For safety reasons, she wishes to design the reaction to ensure that all of the chlorine gas is used in synthesis. Which of the following methods will ensure that the minimum amount of chlorine remains after the reaction?- a)The amount of chlorine used is independent of the relative ratios of reagents
- b)Adding less calcium in deficit of that required by stoichiometry
- c)Adding additional calcium in excess of that required by stoichiometry
- d)Adding the exact amount of calcium required by stoichiometry
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Suppose that an industrial chemist wishes to obtain calcium chloride (CaCl2) by reacting calcium metal with chlorine gas. For safety reasons, she wishes to design the reaction to ensure that all of the chlorine gas is used in synthesis. Which of the following methods will ensure that the minimum amount of chlorine remains after the reaction?
a)
The amount of chlorine used is independent of the relative ratios of reagents
b)
Adding less calcium in deficit of that required by stoichiometry
c)
Adding additional calcium in excess of that required by stoichiometry
d)
Adding the exact amount of calcium required by stoichiometry
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Even in a perfectly-balanced reaction, small amounts of unreacted reagents will remain after the reaction due to heterogeneity.
The relative amount of leftover reagents changes if one of the reagents is in excess.
If there is an excess of calcium, less chlorine will remain because any unreacted chlorine is more likely to react with the extra calcium.
The relative amount of leftover reagents changes if one of the reagents is in excess.
If there is an excess of calcium, less chlorine will remain because any unreacted chlorine is more likely to react with the extra calcium.
Suppose 1 mol of H2 completely reacts with 1 mol of O2 to form water. How many mols of water will result from the reaction?- a)2 mol
- b)4 mol
- c)1 mol
- d).5 mol
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Suppose 1 mol of H2 completely reacts with 1 mol of O2 to form water. How many mols of water will result from the reaction?
a)
2 mol
b)
4 mol
c)
1 mol
d)
.5 mol
|
|
Abigail Rodriguez answered |
Understanding the Reaction
When hydrogen gas (H2) reacts with oxygen gas (O2), they combine to form water (H2O). The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O
This equation indicates that:
- 2 moles of H2 react with 1 mole of O2 to produce 2 moles of H2O.
Reaction Stoichiometry
In this scenario, you start with:
- 1 mole of H2
- 1 mole of O2
According to the stoichiometry of the balanced equation:
- 1 mole of H2 would need 0.5 moles of O2 to react completely (since 2 moles of H2 require 1 mole of O2).
Since you have 1 mole of O2 available, it is in excess. The limiting reactant here is H2.
Water Production
From the stoichiometric ratios in the reaction:
- 1 mole of H2 produces 1 mole of H2O (as 2 moles of H2 yield 2 moles of H2O, 1 mole of H2 yields 1 mole of H2O).
Therefore, when 1 mole of H2 reacts completely with 1 mole of O2, it results in:
- 1 mole of water (H2O) produced.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is:
- 1 mole of water will result from the reaction (option C).
This understanding of stoichiometry is essential in chemistry for predicting the outcomes of reactions.
When hydrogen gas (H2) reacts with oxygen gas (O2), they combine to form water (H2O). The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O
This equation indicates that:
- 2 moles of H2 react with 1 mole of O2 to produce 2 moles of H2O.
Reaction Stoichiometry
In this scenario, you start with:
- 1 mole of H2
- 1 mole of O2
According to the stoichiometry of the balanced equation:
- 1 mole of H2 would need 0.5 moles of O2 to react completely (since 2 moles of H2 require 1 mole of O2).
Since you have 1 mole of O2 available, it is in excess. The limiting reactant here is H2.
Water Production
From the stoichiometric ratios in the reaction:
- 1 mole of H2 produces 1 mole of H2O (as 2 moles of H2 yield 2 moles of H2O, 1 mole of H2 yields 1 mole of H2O).
Therefore, when 1 mole of H2 reacts completely with 1 mole of O2, it results in:
- 1 mole of water (H2O) produced.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer is:
- 1 mole of water will result from the reaction (option C).
This understanding of stoichiometry is essential in chemistry for predicting the outcomes of reactions.
Suppose 12 × 1023, atoms of sodium metal react stoichiometrically with chlorine gas. How many grams of sodium chloride will result if the molar mass of sodium chloride is 60 g/mol?- a)100 g
- b)120 g
- c)60 g
- d)10 g
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Suppose 12 × 1023, atoms of sodium metal react stoichiometrically with chlorine gas. How many grams of sodium chloride will result if the molar mass of sodium chloride is 60 g/mol?
a)
100 g
b)
120 g
c)
60 g
d)
10 g
|
|
Violet Flores answered |
Suppose 12 is the number of students in a class.
Avogadro’s law states that one mole of an ideal gas takes up around 22 liters at standard temperature and pressure. Assuming all reagents can be treated as ideal gases, how many grams of carbon dioxide are produced in the complete reaction of 44 liters of butane (C4H10), with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide (at STP)?- a)44 g
- b)350 g
- c)10 g
- d)4400 g
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Avogadro’s law states that one mole of an ideal gas takes up around 22 liters at standard temperature and pressure. Assuming all reagents can be treated as ideal gases, how many grams of carbon dioxide are produced in the complete reaction of 44 liters of butane (C4H10), with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide (at STP)?
a)
44 g
b)
350 g
c)
10 g
d)
4400 g
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The first step is to determine the balanced combustion reaction.
The correct reaction is 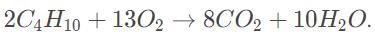
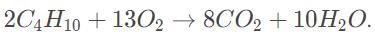
From Avogadro’s law, 44 liters of butane is 2 mol, which would produce 8 mol of carbon dioxide.
The molar mass of carbon dioxide is 12 + 2 × 16 = 44 g/mol, suggesting that 8 × 44 = 350 grams of carbon dioxide is released during the reaction.
One type of anaerobic respiration converts glucose (C6H12O6) to ethanol (C2H5OH) and carbon dioxide. If the molecular weight of glucose is 180 grams/mol and the molar mass of ethanol is 46 g/mol, how many grams of carbon dioxide are produced when 1 mol of glucose is digested via respiration?- a)88 grams
- b)0 grams
- c)40 grams
- d)100 grams
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One type of anaerobic respiration converts glucose (C6H12O6) to ethanol (C2H5OH) and carbon dioxide. If the molecular weight of glucose is 180 grams/mol and the molar mass of ethanol is 46 g/mol, how many grams of carbon dioxide are produced when 1 mol of glucose is digested via respiration?
a)
88 grams
b)
0 grams
c)
40 grams
d)
100 grams
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The first step in solving this problem is to balance the reaction.
The balanced reaction is
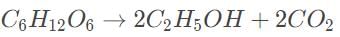
11 mol of glucose weighs 180 grams. The total weight of the products must be equal to this weight due to the conservation of mass.
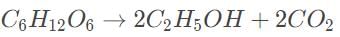
11 mol of glucose weighs 180 grams. The total weight of the products must be equal to this weight due to the conservation of mass.
Based on the balanced reaction, 2 mols of C2H5OH, are produced, weighing 92 grams.
The total weight of carbon dioxide is thus 180 − 92 = 88 grams.
In an unknown compound, the molar ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen is found to be, respectively, 1:2:1. The molar mass is separately found to be 180 grams/mol. Which of the following gives the molecular formula of the compound?- a)C1H2O1
- b)C6H12O6
- c)C6H1O8
- d)C8H8O2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In an unknown compound, the molar ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen is found to be, respectively, 1:2:1. The molar mass is separately found to be 180 grams/mol. Which of the following gives the molecular formula of the compound?
a)
C1H2O1
b)
C6H12O6
c)
C6H1O8
d)
C8H8O2
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The molecular formula gives the actual chemical structure, rather than just the minimum molar ratio given by the empirical formula.
The empirical formula, based on the mol ratio, is C1H2O1.This can be converted to a molar mass.
The empirical formula, based on the mol ratio, is C1H2O1.This can be converted to a molar mass.
The molar mass if the molecular formula was the same as the empirical formula would be (1mol × 12g/mol) + (2mol x 1g/mol) + (1mol x 16g/mol) = 30g/mol
The actual molar mass is six times the molar mass of the empirical formula; thus the molecular formula is C6H12O6
Measurements of a compound reveal that it is 36% carbon, 6% hydrogen, and 48% oxygen, with systematic error accounting for the remaining 10%. Which of the following is the most accurate empirical formula for this compound?- a)C1H1O1
- b)C1H2O1
- c)C6H12O8
- d)C6H1O8
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Measurements of a compound reveal that it is 36% carbon, 6% hydrogen, and 48% oxygen, with systematic error accounting for the remaining 10%. Which of the following is the most accurate empirical formula for this compound?
a)
C1H1O1
b)
C1H2O1
c)
C6H12O8
d)
C6H1O8
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Pick an arbitrary initial mass of 100 grams. The given analysis would suggest that this contains 36 g carbon, 6 g hydrogen, and 48 g oxygen.
Convert these masses into mols by dividing them by the known molar masses of the various elements: 36/12 = 3 mol carbon, 6/1 = 6 mol hydrogen, 48/16 = 3 mol oxygen
Divide the three mol counts by their greatest common denominator to obtain the empirical formula: C1H2O1
When an antacid tablet is used, calcium hydroxide interacts with hydrochloric acid in the stomach to form inert calcium chloride (CaCl2) and water. If the molar mass of (Ca(OH)2 is 75 grams/mol, how many mols of HCl are required to fully react with 150 g of Ca(OH)2?- a)4 mol
- b)1 mol
- c)8 mol
- d)2 mol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When an antacid tablet is used, calcium hydroxide interacts with hydrochloric acid in the stomach to form inert calcium chloride (CaCl2) and water. If the molar mass of (Ca(OH)2 is 75 grams/mol, how many mols of HCl are required to fully react with 150 g of Ca(OH)2?
a)
4 mol
b)
1 mol
c)
8 mol
d)
2 mol
|
|
Aurora Cooper answered |
Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl) in the stomach to form calcium chloride (CaCl2) and water. We are given the molar mass of Ca(OH)2 as 75 grams/mol and we need to determine the number of moles of HCl required to fully react with 150g of Ca(OH)2.
To solve this problem, we can use the concept of stoichiometry, which relates the number of moles of reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
1. Calculate the number of moles of Ca(OH)2:
Given mass of Ca(OH)2 = 150g
Molar mass of Ca(OH)2 = 75g/mol
Number of moles of Ca(OH)2 = Mass of Ca(OH)2 / Molar mass of Ca(OH)2
= 150g / 75g/mol
= 2 mol
2. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction:
Ca(OH)2 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + 2H2O
From the balanced equation, we can see that 1 mole of Ca(OH)2 reacts with 2 moles of HCl.
3. Determine the number of moles of HCl required:
Number of moles of HCl = Number of moles of Ca(OH)2 × (2 moles of HCl / 1 mole of Ca(OH)2)
= 2 mol × (2 mol HCl / 1 mol Ca(OH)2)
= 4 mol HCl
Therefore, 4 moles of HCl are required to fully react with 150g of Ca(OH)2. The correct answer is option A.
To solve this problem, we can use the concept of stoichiometry, which relates the number of moles of reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
1. Calculate the number of moles of Ca(OH)2:
Given mass of Ca(OH)2 = 150g
Molar mass of Ca(OH)2 = 75g/mol
Number of moles of Ca(OH)2 = Mass of Ca(OH)2 / Molar mass of Ca(OH)2
= 150g / 75g/mol
= 2 mol
2. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction:
Ca(OH)2 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + 2H2O
From the balanced equation, we can see that 1 mole of Ca(OH)2 reacts with 2 moles of HCl.
3. Determine the number of moles of HCl required:
Number of moles of HCl = Number of moles of Ca(OH)2 × (2 moles of HCl / 1 mole of Ca(OH)2)
= 2 mol × (2 mol HCl / 1 mol Ca(OH)2)
= 4 mol HCl
Therefore, 4 moles of HCl are required to fully react with 150g of Ca(OH)2. The correct answer is option A.
The general form of a synthesis reaction is αX + bY→ cZ, where capital letters denote reactants and lowercase letters denote balanced coefficients, a < b. Which of the following formulas gives the number of Z molecules produced when 4 mols of Y react completely? N is Avogadro’s number- a)
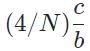
- b)
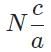
- c)
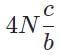
- d)
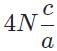
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The general form of a synthesis reaction is αX + bY→ cZ, where capital letters denote reactants and lowercase letters denote balanced coefficients, a < b. Which of the following formulas gives the number of Z molecules produced when 4 mols of Y react completely? N is Avogadro’s number
a)
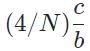
b)
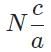
c)
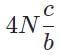
d)
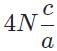

|
Orion Classes answered |
If all 4 mols of Y react completly, then X is in excess because a < b. Thus only b matters for determining the reaction yield.
The ratios of coefficients in a balanced reaction gives the ratio of moles of each reagent and product required in a perfectly stoichiometric reaction.
The number of moles of product can be converted to the number of molecules by multiplying by Avogadro’s number
The correct formula is 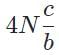
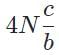
Which of the following correctly describes the relationship between an empirical formula and a molecular formula?- a)The two formulae are always identical.
- b)There are an infinite number of possible empirical formulas for a given molecular formula.
- c)At least one subscript of the empirical formula always equals one.
- d)Each subscript is equal to or greater than its counterpart in the empirical formula.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following correctly describes the relationship between an empirical formula and a molecular formula?
a)
The two formulae are always identical.
b)
There are an infinite number of possible empirical formulas for a given molecular formula.
c)
At least one subscript of the empirical formula always equals one.
d)
Each subscript is equal to or greater than its counterpart in the empirical formula.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The empirical formula is the simplest integer number of molecules that captures the molar ratio present in a sample of a compound.
This does not mean that the formula reduces until one of the subscripts is one. For example, C3D4H2 is a valid empirical formula.
The molecular formula can reduce to the empirical formula, but not vice versa.
For the molecular formula, each subscript is equal to or greater than its counterpart in the empirical formula.
Chapter doubts & questions for Stoichiometry - General Chemistry for MCAT 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Stoichiometry - General Chemistry for MCAT in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
General Chemistry for MCAT
164 videos|11 docs|16 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









