All Exams >
MCAT >
Physics for MCAT >
All Questions
All questions of Force and Newton's laws of Motion for MCAT Exam
Which of the following statements best describes an object undergoing uniform circular motion?- a)The velocity and acceleration vectors are always tangential to each other.
- b)Objects in uniform circular motion tend to stay in uniform circular motion.
- c)The object moves with a constant velocity.
- d)The object would travel in a straight line if the acceleration vector goes to zero.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements best describes an object undergoing uniform circular motion?
a)
The velocity and acceleration vectors are always tangential to each other.
b)
Objects in uniform circular motion tend to stay in uniform circular motion.
c)
The object moves with a constant velocity.
d)
The object would travel in a straight line if the acceleration vector goes to zero.
|
|
Luna Howard answered |
Understanding Uniform Circular Motion
Uniform circular motion refers to the movement of an object along a circular path at a constant speed. Although the speed remains constant, the direction of the velocity vector continuously changes, leading to the presence of centripetal acceleration.
Why Option 'D' is Correct
- When an object is in uniform circular motion, it experiences a centripetal force, keeping it in a circular path.
- Acceleration Vector: This vector points towards the center of the circle, indicating that the object is continually changing direction.
- Straight-Line Movement: If the centripetal force (and thus the acceleration) were to disappear, the object would no longer have any force acting towards the center. According to Newton's first law of motion, an object in motion will continue in a straight line at constant speed if no net external force acts on it.
Other Options Explained
- Option A: Incorrect because, in uniform circular motion, the velocity vector is tangential to the circular path, while the acceleration vector is radial.
- Option B: Misleading; while an object in motion tends to stay in motion, it requires a force to maintain circular motion.
- Option C: Incorrect as "constant velocity" implies both constant speed and direction. In circular motion, the direction is continually changing.
Conclusion
In summary, option 'D' accurately reflects the behavior of an object in uniform circular motion. If the centripetal acceleration ceases, the object will move in a straight line, demonstrating the principle of inertia.
Uniform circular motion refers to the movement of an object along a circular path at a constant speed. Although the speed remains constant, the direction of the velocity vector continuously changes, leading to the presence of centripetal acceleration.
Why Option 'D' is Correct
- When an object is in uniform circular motion, it experiences a centripetal force, keeping it in a circular path.
- Acceleration Vector: This vector points towards the center of the circle, indicating that the object is continually changing direction.
- Straight-Line Movement: If the centripetal force (and thus the acceleration) were to disappear, the object would no longer have any force acting towards the center. According to Newton's first law of motion, an object in motion will continue in a straight line at constant speed if no net external force acts on it.
Other Options Explained
- Option A: Incorrect because, in uniform circular motion, the velocity vector is tangential to the circular path, while the acceleration vector is radial.
- Option B: Misleading; while an object in motion tends to stay in motion, it requires a force to maintain circular motion.
- Option C: Incorrect as "constant velocity" implies both constant speed and direction. In circular motion, the direction is continually changing.
Conclusion
In summary, option 'D' accurately reflects the behavior of an object in uniform circular motion. If the centripetal acceleration ceases, the object will move in a straight line, demonstrating the principle of inertia.
A scientist with mass m is sitting on one end of a lifeboat of uniform density with mass 3m3, m. When he spots a rescue chopper in the distance, he walks a distance of L to the other side of the lifeboat to wave for help. Which of the following statements best characterizes the motion of the lifeboat?- a)The lifeboat shifts in the same direction as the scientist’s motion with constant velocity.
- b)The lifeboat shifts by L/4 in the opposite direction of the scientist’s motion.
- c)The lifeboat does not shift forward or backward as a result of the scientist’s motion.
- d)The lifeboat shifts by the same distance traversed, but in the opposite direction of his motion.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A scientist with mass m is sitting on one end of a lifeboat of uniform density with mass 3m3, m. When he spots a rescue chopper in the distance, he walks a distance of L to the other side of the lifeboat to wave for help. Which of the following statements best characterizes the motion of the lifeboat?
a)
The lifeboat shifts in the same direction as the scientist’s motion with constant velocity.
b)
The lifeboat shifts by L/4 in the opposite direction of the scientist’s motion.
c)
The lifeboat does not shift forward or backward as a result of the scientist’s motion.
d)
The lifeboat shifts by the same distance traversed, but in the opposite direction of his motion.
|
|
Daniel Lee answered |
B) The lifeboat remains stationary
Which of the following force pairs represents an action-reaction pair?- a)Downward force of gravity on a falling object and upward force of air resistance at terminal velocity
- b)Weight of the book and normal force of the table
- c)Component of gravity along the plane of the incline on the block and static frictional force up along the plane
- d)Force of the horse on the cart and force of the cart on the horse
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following force pairs represents an action-reaction pair?
a)
Downward force of gravity on a falling object and upward force of air resistance at terminal velocity
b)
Weight of the book and normal force of the table
c)
Component of gravity along the plane of the incline on the block and static frictional force up along the plane
d)
Force of the horse on the cart and force of the cart on the horse
|
|
Olivia Johnson answered |
Force Pairs in Action
The correct answer is option D, which includes the force of the horse on the cart and the force of the cart on the horse. Let's break it down further:
Force of the horse on the cart:
- When a horse pulls a cart, it exerts a force in the forward direction on the cart to make it move.
Force of the cart on the horse:
- In response to the force exerted by the horse, the cart exerts an equal but opposite force on the horse according to Newton's third law of motion.
Therefore, the force pair of the horse on the cart and the cart on the horse represents an action-reaction pair. The action is the force of the horse on the cart, and the reaction is the force of the cart on the horse. This pair demonstrates Newton's third law, which states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Which of the following statements describes what must be true in the context of Newton’s First Law?- a)The tendency for drivers to keep moving linearly while the car makes a sharp turn on the road is an example of the concept of inertia.
- b)An object with zero acceleration and an object traveling at a constant acceleration are considered similar states.
- c)Mass is a measure of an object’s ability to resist motion or movement of any kind.
- d)The object is difficult to bring to a complete stop due to its high initial speed.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements describes what must be true in the context of Newton’s First Law?
a)
The tendency for drivers to keep moving linearly while the car makes a sharp turn on the road is an example of the concept of inertia.
b)
An object with zero acceleration and an object traveling at a constant acceleration are considered similar states.
c)
Mass is a measure of an object’s ability to resist motion or movement of any kind.
d)
The object is difficult to bring to a complete stop due to its high initial speed.
|
|
Daniel Lee answered |
Explanation:
Inertia and Newton's First Law:
- Newton's First Law states that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force. This is also known as the law of inertia.
- In the context of a car making a sharp turn, the tendency for drivers to keep moving linearly is an example of inertia. The passengers in the car will continue moving in a straight line due to their inertia, even though the car is turning.
Therefore, option 'A' is the correct statement that describes what must be true in the context of Newton's First Law.
Inertia and Newton's First Law:
- Newton's First Law states that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force. This is also known as the law of inertia.
- In the context of a car making a sharp turn, the tendency for drivers to keep moving linearly is an example of inertia. The passengers in the car will continue moving in a straight line due to their inertia, even though the car is turning.
Therefore, option 'A' is the correct statement that describes what must be true in the context of Newton's First Law.
Suppose a moving truck with mass m1 and a velocity v1 collides with a moving convertible with mass m2 and velocity v2 resulting in both coming to a complete stop, where m1 is three times the value of m2 and v2 is three times v1. The truck collides with the convertible with a force F1. Which of the following statements accurately describes the resultant force F2 of the convertible?- a)The convertible exerts the same force on the truck.
- b)The convertible exerts a smaller force because of its smaller mass.
- c)The force gets dissipated during the collision in the form of heat, sound, and deformation of the two vehicles.
- d)The convertible exerts a larger force because of its greater velocity.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Suppose a moving truck with mass m1 and a velocity v1 collides with a moving convertible with mass m2 and velocity v2 resulting in both coming to a complete stop, where m1 is three times the value of m2 and v2 is three times v1. The truck collides with the convertible with a force F1. Which of the following statements accurately describes the resultant force F2 of the convertible?
a)
The convertible exerts the same force on the truck.
b)
The convertible exerts a smaller force because of its smaller mass.
c)
The force gets dissipated during the collision in the form of heat, sound, and deformation of the two vehicles.
d)
The convertible exerts a larger force because of its greater velocity.

|
Orion Classes answered |
- Whether the convertible exerts a smaller force because of its smaller mass cannot be determined since it has a greater change in velocity and therefore, acceleration to offset its smaller mass.
- Whether the convertible exerts a larger force because of its greater velocity cannot be determined since the truck has a larger mass despite its smaller velocity. It would take more work to stop the convertible due its higher velocity.
- It is the energy of the collision that gets dissipated in the form of heat, sound, and deformation of the two vehicles, not the force.
- They exert the same force on each other is correct. Due to Newton’s Third Law, if the truck collides with force F, then the SUV collides with force -F, equal in magnitude opposite in direction.
- Additionally, their momentums are equal, so that their impulses are equal. Therefore, the time of the collision is the same for both, so the average force of impact is the same.
There is a force F acting on an object of mass m, which has an acceleration a. If the mass is doubled and the force is reduced by a factor of four, what is the acceleration of the new object?- a)a
- b)1/8 a
- c)1/2 a
- d)2a
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
There is a force F acting on an object of mass m, which has an acceleration a. If the mass is doubled and the force is reduced by a factor of four, what is the acceleration of the new object?
a)
a
b)
1/8 a
c)
1/2 a
d)
2a

|
Orion Classes answered |
- Acceleration is directly proportional to force and inversely proportional to mass: F = ma.
- If mass is doubled, acceleration would be halved: F = 2m(½a).
- If force is reduced by four, acceleration would be reduced by four: ¼F = m(¼a).
- In total, the acceleration decreases by a factor of 8: ¼F = 2m(⅛a) = ¼(ma).
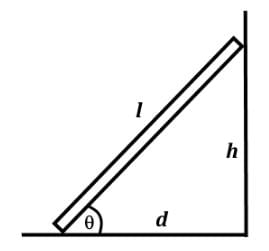
A ladder of length l of 6 meters is propped up on the wall at a height h of 5.1 meters above the ground. The bottom of the ladder is positioned at a distance d of 3 meters from the wall. There are static frictional forces at the wall and the ground that keep the ladder in place. Which of the following force components creates a positive torque if the fulcrum is placed at the bottom of the ladder? (FNW = normal force from wall, FNG = normal force from ground, FFW = friction force at wall, FFG = friction force at ground)
- a)FNW sinθ
- b)FNG cosθ
- c)W cosθ
- d)FFW sinθ
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A ladder of length l of 6 meters is propped up on the wall at a height h of 5.1 meters above the ground. The bottom of the ladder is positioned at a distance d of 3 meters from the wall. There are static frictional forces at the wall and the ground that keep the ladder in place. Which of the following force components creates a positive torque if the fulcrum is placed at the bottom of the ladder? (FNW = normal force from wall, FNG = normal force from ground, FFW = friction force at wall, FFG = friction force at ground)


a)
FNW sinθ
b)
FNG cosθ
c)
W cosθ
d)
FFW sinθ

|
Orion Classes answered |
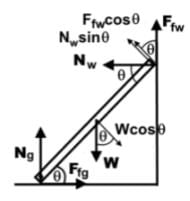
- All forces need to be resolved along the plane of the ladder such that it becomes the x-axis and the y-axis perpendicular to that, like on an inclined plane.
- Since the fulcrum is placed at the bottom of the ladder and FNG acts at the fulcrum, it is not considered to produce a torque.
- FNW points directly outward from the wall to the left. FNW cosθ is along the plane of the ladder, so FNW sin θ is the force that would create a positive or counterclockwise torque on the ladder.
- FFW points from the contact point of the ladder on the wall upwards along the wall. FNW sin θ is the force component that is along the plane of the ladder pointing into the wall. FFW cos θ would be the force that creates a counterclockwise torque.
- W points downward from the center of the ladder. Wcosθ is perpendicular to the plane of the ladder and creates a clockwise torque on the ladder.
- Here is a diagram illustrating all the forces creating the torque:
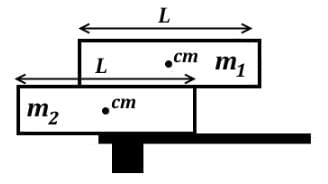
Block 1 with mass m1 sits on top of Block 2 with mass m2. While m1 is greater than m2, they have an identical length L. Which of the following statements accurately describes the torques in this two-block system?
- a)If Block 1 were shifted to the right the increasing clockwise torque on Block 1 is balanced by an increasing normal force on Block 1.
- b)If Block 2 were shifted to the left along with Block 1 without toppling off, the weight of block 2 would create a clockwise torque that is offset by the weight of Block 1 which creates a counterclockwise torque.
- c)The weight of Block 1 through its center of mass produces a clockwise torque about the right end of Block 2.
- d)The normal force on Block 1 produces a clockwise torque and the weight of Block 1 is producing a counterclockwise torque with the fulcrum at the right end of Block 1.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Block 1 with mass m1 sits on top of Block 2 with mass m2. While m1 is greater than m2, they have an identical length L. Which of the following statements accurately describes the torques in this two-block system?


a)
If Block 1 were shifted to the right the increasing clockwise torque on Block 1 is balanced by an increasing normal force on Block 1.
b)
If Block 2 were shifted to the left along with Block 1 without toppling off, the weight of block 2 would create a clockwise torque that is offset by the weight of Block 1 which creates a counterclockwise torque.
c)
The weight of Block 1 through its center of mass produces a clockwise torque about the right end of Block 2.
d)
The normal force on Block 1 produces a clockwise torque and the weight of Block 1 is producing a counterclockwise torque with the fulcrum at the right end of Block 1.

|
Orion Classes answered |
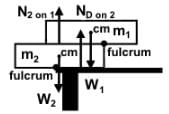
- If the force acts downwards to the left or upwards to the right of the fulcrum, then there is a counterclockwise (CCW) torque. If the force acts downwards to the right or upwards to the left of the fulcrum, then there is a clockwise (CW) torque.
- Forces will act from the center of mass if possible, and the fulcrums are the top right edge of Block 2 and the left edge of the desk.
- If Block 2 were shifted to the left, the center of mass moves to the left of the fulcrum, so the weight creates a CCW torque, not CW. The weight of Block 1 acts to the right of the same fulcrum downwards creating a CW torque, not CCW.
- If Block 1 were shifted to the right, as the center of mass moves to the right of the fulcrum, it will create a CW torque that topples off Block 1. However, the small normal force from Block 2 has been decreasing as Block 1 moved to the right.
- The weight of Block 1 acts to the left of the fulcrum downwards, and the weight will produce a CCW torque, not CW.
- There is a normal force from Block 2 on Block 1 that acts to the left of the fulcrum upwards, producing a CW torque.
- Here is a diagram indicating the forces:
Which of the following statements must additionally be true if it is determined that an object has zero acceleration?- a)The object is not moving upwards or downwards.
- b)The object has zero velocity.
- c)There are no forces acting on the object.
- d)The object has no unbalanced forces acting on it.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements must additionally be true if it is determined that an object has zero acceleration?
a)
The object is not moving upwards or downwards.
b)
The object has zero velocity.
c)
There are no forces acting on the object.
d)
The object has no unbalanced forces acting on it.

|
Orion Classes answered |
Zero acceleration means that there is no net force acting on the object according to Newton’s second law.
Zero net force does not mean there are no forces acting on the object. If there is a force, there must be an equal and opposite force to balance it.
Zero acceleration could mean two possible scenarios: zero velocity or constant velocity, and, consequently, motionless or in motion.
What must be true is that the object has no unbalanced forces acting on it.
Which of the following statements represents an example of an unbalanced force acting on an object?- a)The object is moving closer at a constant velocity.
- b)The object is moving in a straight line away.
- c)The object changes direction, but travels with the same speed.
- d)The object remains stationary.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements represents an example of an unbalanced force acting on an object?
a)
The object is moving closer at a constant velocity.
b)
The object is moving in a straight line away.
c)
The object changes direction, but travels with the same speed.
d)
The object remains stationary.

|
Orion Classes answered |
- An unbalanced force would cause an acceleration according to Newton’s second law. Change in acceleration can be due to either change in magnitude or direction.
- The object would not be stationary or traveling at a constant velocity.
- Motion in a straight line eliminates the possibility of change in direction, but there may be change in magnitude or not.
- When an object changes direction and travels with the same speed it exhibits an acceleration, in which there must be an unbalanced force.
Chapter doubts & questions for Force and Newton's laws of Motion - Physics for MCAT 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Force and Newton's laws of Motion - Physics for MCAT in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for MCAT
158 videos|21 docs|21 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









