All Exams >
MCAT >
Physics for MCAT >
All Questions
All questions of Fluids at Rest for MCAT Exam
When the gauge pressure is doubled, what happens to the absolute pressure?- a)It increases by a factor less than 2.
- b)It stays the same.
- c)It is halved.
- d)It doubles.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When the gauge pressure is doubled, what happens to the absolute pressure?
a)
It increases by a factor less than 2.
b)
It stays the same.
c)
It is halved.
d)
It doubles.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Absolute pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure plus gauge pressure.
- Atmospheric pressure is 101,300 Pa, while a typical gauge pressure for a tire is 30 psi or 207 Pa.
- Since atmospheric pressure is relatively large compared to most gauge pressures, doubling the gauge pressure would not end up doubling the absolute pressure.
- To use the tire example, if the gauge is 414 Pa, then absolute pressure would be 101,314 Pa. Absolute pressure increase by a factor less than 2.
A patient is scheduled to receive an intravenous injection of medication that must be at least 109.3 kilopascals at the injection point before going into surgery. If the patient is lying on a bed 0.9 meters high, what is the minimum height above the ground that the nurse must suspend the bag to achieve that pressure at the injection point?
(ρfluid = 1020 kg/m3)- a)2.0 m
- b)0.80 m
- c)1.7 m
- d)2.3 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A patient is scheduled to receive an intravenous injection of medication that must be at least 109.3 kilopascals at the injection point before going into surgery. If the patient is lying on a bed 0.9 meters high, what is the minimum height above the ground that the nurse must suspend the bag to achieve that pressure at the injection point?
(ρfluid = 1020 kg/m3)
(ρfluid = 1020 kg/m3)
a)
2.0 m
b)
0.80 m
c)
1.7 m
d)
2.3 m
|
|
Ava Brown answered |
Given Data:
- Pressure required at the injection point = 109.3 kPa
- Height of the bed = 0.9 meters
- Density of the fluid (ρ) = 1020 kg/m³
Formula:
Pressure at a certain height in a fluid is given by the formula:
P = ρgh
Where:
P = Pressure
ρ = Density of the fluid
g = Acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s²)
h = Height
Calculation:
Given P = 109.3 kPa = 109300 Pa
ρ = 1020 kg/m³
g = 9.81 m/s²
h = ?
Convert kPa to Pa:
109.3 kPa = 109.3 * 1000 = 109300 Pa
Using the formula P = ρgh, we can solve for h:
h = P / (ρg)
h = 109300 / (1020 * 9.81)
h ≈ 11.18 meters
Since the bed is 0.9 meters high, the bag must be suspended at a height above the ground that is the difference between the total height required and the height of the bed:
Height above the ground = 11.18 - 0.9 ≈ 10.28 meters
Therefore, the minimum height above the ground that the nurse must suspend the bag to achieve the required pressure at the injection point is approximately 10.28 meters, which is closest to option C (1.7 m).
A 30 kilogram object is dropped into acetic acid, which has a specific gravity of 1.06. Once it is immersed in acetic acid, the object has an apparent weight of 240 N. What is the object’s specific gravity?- a)8.5
- b)5.3
- c)0.17
- d)1.3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A 30 kilogram object is dropped into acetic acid, which has a specific gravity of 1.06. Once it is immersed in acetic acid, the object has an apparent weight of 240 N. What is the object’s specific gravity?
a)
8.5
b)
5.3
c)
0.17
d)
1.3
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Convert 30 kg to Newtons, which would be 300 N. With an apparent weight of 240 N, the buoyant force gives it an upward push of 60 N.
- The buoyant force of 60 N accounts for the displaced volume of acetic acid, and we know the object weighs 300 N.
- Setup a ratio of FB(aceticacid)/Wobject = paceticacid/pobject
- 60/300 = 1.06/x, so 60·5 = 300 and 1.06·5 must equal x, which is 5.3.
A gold crown recently acquired is suspected to be brass covered in gold. The crown weighs 25.0 N in air and has an apparent weight of 22.5 N in fresh water. Based on these results, which of the following conclusions is correct?
(ρgold = 19,300 kg/m3, ρbrass = 8300-8700 kg/m3)- a)It is likely that the crown is made of gold only.
- b)It is likely that the crown is made of half brass and half gold.
- c)It is likely that the crown is made of brass covered in gold.
- d)It is likely that the crown is made of brass only.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A gold crown recently acquired is suspected to be brass covered in gold. The crown weighs 25.0 N in air and has an apparent weight of 22.5 N in fresh water. Based on these results, which of the following conclusions is correct?
(ρgold = 19,300 kg/m3, ρbrass = 8300-8700 kg/m3)
(ρgold = 19,300 kg/m3, ρbrass = 8300-8700 kg/m3)
a)
It is likely that the crown is made of gold only.
b)
It is likely that the crown is made of half brass and half gold.
c)
It is likely that the crown is made of brass covered in gold.
d)
It is likely that the crown is made of brass only.
|
|
Jack Reed answered |
The crown weighs less in water than in air, indicating that it experiences an upward buoyant force in water. This means that the crown displaces a volume of water equal to its own volume. Since the crown is suspected to be brass covered in gold, and brass is denser than gold, it is likely that the crown is not made entirely of gold.
Therefore, the correct conclusion is that the crown is not made entirely of gold.
Therefore, the correct conclusion is that the crown is not made entirely of gold.
There is a 1-liter container filled with 500 milliliters of water placed on top of a scale displaying 80 pounds. When a metal cube is submerged tied to a string end into the container, which of the following statements accurately describes the result?- a)The cube’s density must be provided to predict what will happen.
- b)The scale will remain at 80 pounds until the cube is floating on top of the water fully submerged.
- c)The scale will register a weight greater than 80 pounds due to Newton’s Third Law.
- d)The scale will remain at 80 pounds unless the cube touches the bottom of the bowl.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
There is a 1-liter container filled with 500 milliliters of water placed on top of a scale displaying 80 pounds. When a metal cube is submerged tied to a string end into the container, which of the following statements accurately describes the result?
a)
The cube’s density must be provided to predict what will happen.
b)
The scale will remain at 80 pounds until the cube is floating on top of the water fully submerged.
c)
The scale will register a weight greater than 80 pounds due to Newton’s Third Law.
d)
The scale will remain at 80 pounds unless the cube touches the bottom of the bowl.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- When the cube is submerged, the object floats in equilibrium.
- There must be a buoyant force keeping the object afloat pushing upward.
- According to Newton’s Third Law, there should be an equal and opposite force downwards.
- That additional force will cause the scale to register a weight greater than 80 pounds.
What property of a fluid allows it to exert pressure equally in all directions?- a)Viscosity
- b)Surface tension
- c)Compressibility
- d)Incompressibility
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What property of a fluid allows it to exert pressure equally in all directions?
a)
Viscosity
b)
Surface tension
c)
Compressibility
d)
Incompressibility

|
Orion Classes answered |
Incompressibility is the property of a fluid that allows it to exert pressure equally in all directions. Since the fluid cannot be compressed, any force applied to it is transmitted equally in all directions, resulting in equal pressure distribution.
On which of the following does the buoyant force on an object floating on the surface of a liquid most directly depend?- a)viscosity of the liquid
- b)volume of the object
- c)density of the liquid
- d)mass of the liquid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
On which of the following does the buoyant force on an object floating on the surface of a liquid most directly depend?
a)
viscosity of the liquid
b)
volume of the object
c)
density of the liquid
d)
mass of the liquid
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- The buoyant force is the upward force by the fluid that opposes the downward force of gravity, and in the case of a floating object, the two forces are equal and opposite.
- The formula for buoyant force is FB = pVg, where V is the volume of the object submerged. So the buoyant force does not depend on the volume of the object.
- The buoyant force does not depend on the viscosity of the liquid since viscosity refers to fluids in motion and is the resistance to shearing flows.
- In the formula for buoyant force, the density in question is that of the liquid, so to reiterate:
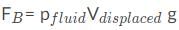
Which of the following scenarios most accurately represents Pascal’s law?- a)A person pushes the brake with a small area with a small force over a short distance to produce an equivalent force to stop the car.
- b)The volume displaced by piston 1 is equal to the volume displaced by piston 2 in a hydraulic lift.
- c)When you push down on the stopper of a big water jug with 10 N, the same force of 10 N is transmitted undiminished to the larger bottom surface of the jug.
- d)When a pregnant mother is riding in a car that crashes, the fluid surrounding the fetus will help to dissipate any force from the crash.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following scenarios most accurately represents Pascal’s law?
a)
A person pushes the brake with a small area with a small force over a short distance to produce an equivalent force to stop the car.
b)
The volume displaced by piston 1 is equal to the volume displaced by piston 2 in a hydraulic lift.
c)
When you push down on the stopper of a big water jug with 10 N, the same force of 10 N is transmitted undiminished to the larger bottom surface of the jug.
d)
When a pregnant mother is riding in a car that crashes, the fluid surrounding the fetus will help to dissipate any force from the crash.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Pascal’s Law states that pressure is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and to the walls of the container.
- This allows us to write the equation P1 = P2, and then F1/A1 = F2/A2, as well as F1d1 = F2d2.
- As a result, we can explorate that a small force applied on a small area over a long distance will produce a large force applied on a large area over a short distance.
- We also can deduce that W1/V1 = W2/V2. Since work is the same on both sides, the volume displaced by one side will be equal to the volume displaced on the other side in a hydraulic lift.
Which of the following graphs represents the hydrostatic pressure for an incompressible fluid in a container open to the atmosphere on the surface of the Moon? (P0 = atmospheric pressure on Earth’s surface, h = height above Moon’s surface)- a)
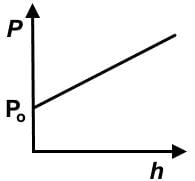
- b)
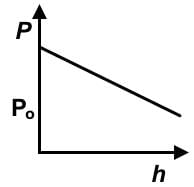
- c)
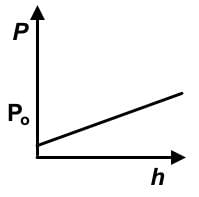
- d)
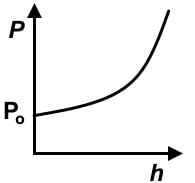
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following graphs represents the hydrostatic pressure for an incompressible fluid in a container open to the atmosphere on the surface of the Moon? (P0 = atmospheric pressure on Earth’s surface, h = height above Moon’s surface)
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Recall the hydrostatic pressure equation, P = Po + gh. Recognize that it is a manifestation of y = mx +b, which is the formula for a linear function.
- y is P, and x is h. Po start subscript, o, end subscript would be b, and ρg together represents m. Eliminate any choices that are not showing a linear or straight line function.
- On the moon, there is less atmospheric pressure due to its much smaller mass and would be less than Po, specifically defined as atmospheric pressure on Earth. The y-intercept would start below Po.
- This is the correct graph:
Which of the following statements about fluids at rest is true?- a)Fluids always flow at a constant speed.
- b)The pressure in a fluid increases with depth.
- c)Liquids cannot exert pressure on their containers.
- d)Gases have a fixed volume and shape.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about fluids at rest is true?
a)
Fluids always flow at a constant speed.
b)
The pressure in a fluid increases with depth.
c)
Liquids cannot exert pressure on their containers.
d)
Gases have a fixed volume and shape.

|
Orion Classes answered |
According to Pascal's law, the pressure in a fluid increases with depth. This is because the weight of the fluid above exerts a force on the fluid below, resulting in an increase in pressure as we move deeper into the fluid.
Chapter doubts & questions for Fluids at Rest - Physics for MCAT 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Fluids at Rest - Physics for MCAT in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for MCAT
158 videos|21 docs|21 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









