All Exams >
JEE >
Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced >
All Questions
All questions of General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals for JEE Exam
Bauxite is the chief ore of:- a)Iron
- b)Zinc
- c)Copper
- d)Aluminium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Bauxite is the chief ore of:
a)
Iron
b)
Zinc
c)
Copper
d)
Aluminium
|
|
Shreya Singh answered |
Aluminum....(it's given in Metallurgy chapter)...
Calamine is an ore of- a)Lead
- b)Calcium
- c)Magnesium
- d)Zinc
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Calamine is an ore of
a)
Lead
b)
Calcium
c)
Magnesium
d)
Zinc

|
Gauri Chauhan answered |
Calamine is ore of zinc.
The purpose of adding cryolite is- a)to increase the electrical conductivity of pure aluminium
- b)to lower the melting point of Al2O3
- c)to remove the impurities as slag
- d)to increase the Al% in the yield
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The purpose of adding cryolite is
a)
to increase the electrical conductivity of pure aluminium
b)
to lower the melting point of Al2O3
c)
to remove the impurities as slag
d)
to increase the Al% in the yield
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Cryolite is used in the electrolysis of aluminium oxide. The mixture of cryolite and aluminium oxide has a lower melting point than pure aluminium oxide. This means a lower amount of energy is required to establish effective conditions for electrolysis and thus makes it more cost effective.
When a metal is to be extracted from its ore and if the gangue associated with the ore is silica ,then- a)Both acidic and basic fluxes are used
- b)Neither of them is needed.
- c)An acidic flux is used
- d)A basic flux is used
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When a metal is to be extracted from its ore and if the gangue associated with the ore is silica ,then
a)
Both acidic and basic fluxes are used
b)
Neither of them is needed.
c)
An acidic flux is used
d)
A basic flux is used
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
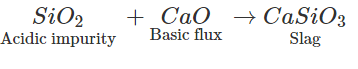
When a metal is to be extracted from its ore and the gangue associated with the silica, then a basic flux is needed.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Which of the following contains both copper and iron?
- A:
Cuprite
- B:
Chalcocite
- C:
Chalcopyrite
- D:
Malachite
The answer is c.
Which of the following contains both copper and iron?
Cuprite
Chalcocite
Chalcopyrite
Malachite
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Chalcopyrite is a brass-yellow mineral with a chemical composition of CuFeS2. It occurs in most sulfide mineral deposits throughout the world and has been the most important ore of copper for thousands of years.
› Chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) is the ore contains both copper and iron.
› The largest deposit of nearly pure chalcopyrite ever discovered in Canada was at the southern end of the Temagami Greenstone Belt where Copperfield Mine extracted the high-grade copper.
Liquation method is used for the metals which have- a)Low boiling points
- b)High melting points
- c)High boiling points
- d)Low melting points
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Liquation method is used for the metals which have
a)
Low boiling points
b)
High melting points
c)
High boiling points
d)
Low melting points

|
Sankar Gupta answered |
Liquification is purification technique used for metals having low melting points.
Only One Option Correct TypeThis section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctQ. Which represents the correct abundance order of elements in the earth crust?- a)O > Si > Fe > Al
- b)O > Si > AI > Fe
- c)O > C > Si > AI
- d)AI > Fe > 0 > Si
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
Q.
Which represents the correct abundance order of elements in the earth crust?
a)
O > Si > Fe > Al
b)
O > Si > AI > Fe
c)
O > C > Si > AI
d)
AI > Fe > 0 > Si
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The mass-abundance of the nine most abundant elements in the Earth's crust is approximately: oxygen 46%, silicon 28%, aluminum 8.3%, iron 5.6%, calcium 4.2%, sodium 2.5%, magnesium 2.4%, potassium 2.0%, and titanium 0.61%.
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 5 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q. Which of the following is the correct combination?
- a)Borax = Na2B4O7 . 5H2O
- b)Colemanite = Ca2Br6O11 . 5H2O
- c)Anglesite = PbCO3
- d)Chile saltpeter = NaNO3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 5 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q. Which of the following is the correct combination?
a)
Borax = Na2B4O7 . 5H2O
b)
Colemanite = Ca2Br6O11 . 5H2O
c)
Anglesite = PbCO3
d)
Chile saltpeter = NaNO3
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Sodium nitrate is the chemical compound with the formula NaNO3. This alkali metal nitrate salt is also known as Chile saltpeter (large deposits of which were historically mined in Chile) to distinguish it from ordinary saltpeter, potassium nitrate. The mineral form is also known as nitratine, nitratite or soda niter.
Gravity separation technique is mainly applicable to- a)Halide ore
- b)Sulphide ore
- c)Carbonate ore
- d)Oxide ore
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Gravity separation technique is mainly applicable to
a)
Halide ore
b)
Sulphide ore
c)
Carbonate ore
d)
Oxide ore

|
Asha Nair answered |
Gavity separation is done maily for oxide ores.
Regarding cryolite incorrect statement is
- a)It is an ore of Al
- b)The non-metal is fluorine
- c)It is used in aluminium extraction from bauxite
- d)Its formula is 3NaF. AIF3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Regarding cryolite incorrect statement is
a)
It is an ore of Al
b)
The non-metal is fluorine
c)
It is used in aluminium extraction from bauxite
d)
Its formula is 3NaF. AIF3
|
|
Anisha Bose answered |
Cryolite is an important ore of aluminum that is used in the extraction of aluminum from bauxite. It is a rare mineral that occurs in small quantities in Greenland, and its chemical formula is Na3AlF6.
Which metal is used in paints and lacquers?- a)Cu
- b)Zn
- c)Al
- d)Fe
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which metal is used in paints and lacquers?
a)
Cu
b)
Zn
c)
Al
d)
Fe

|
Bhavana Banerjee answered |
Al is generally used in paints and lacquers.
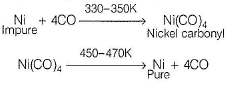
Formation of Ni(CO)4 and subsequent its decomposition into Ni and CO (recycled) makes basis of Mond's processNi + 4CO 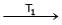 Ni (CO)4
Ni (CO)4 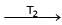 Ni + 4COT1 and T2 are :
Ni + 4COT1 and T2 are :- a)100ºC, 50ºC
- b)50ºC, 100ºC
- c)50ºC, 230ºC
- d)230ºC, 50ºC
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Formation of Ni(CO)4 and subsequent its decomposition into Ni and CO (recycled) makes basis of Mond's process
Ni + 4CO 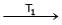 Ni (CO)4
Ni (CO)4 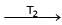 Ni + 4CO
Ni + 4CO
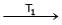 Ni (CO)4
Ni (CO)4 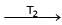 Ni + 4CO
Ni + 4COT1 and T2 are :
a)
100ºC, 50ºC
b)
50ºC, 100ºC
c)
50ºC, 230ºC
d)
230ºC, 50ºC
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Ni + 4CO 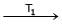 Ni (CO)4
Ni (CO)4 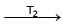 Ni + 4CO
Ni + 4CO
T1 = 50ºC
T2 = 230ºC
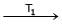 Ni (CO)4
Ni (CO)4 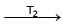 Ni + 4CO
Ni + 4COT1 = 50ºC
T2 = 230ºC
2CuCO3 . Cu(OH)2 is the formula of- a)Malachite
- b)Azurite
- c)Siderite
- d)Chalcopyrite
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
2CuCO3 . Cu(OH)2 is the formula of
a)
Malachite
b)
Azurite
c)
Siderite
d)
Chalcopyrite
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Azurite is an copper Ore [2CuCO3⋅Cu(OH)2]
Which of the following statements is correct?
a) In Hall-Heroult process, the electrolyte used is a molten mixture of alumina, sodium hydroxide and cryolite.
b) Lead is extracted form its chief ore by both carbon reduction and self reduction.
c) Tin is extracted from its chief ore by carbon monoxide reduction.
d) Siderite, cassiterite and argentite are carbonate ores.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Sinjini Tiwari answered |
One Integer Value Correct TypeThis section contains 5 questions, when worked out will result in an integer value from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)Q. The number of carbonate minerals among the followingCassiterite , Siderite , Anglesite , Azurite , Calamine , Cryolite ,Calcite ,Magnetite, Magnesite
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
One Integer Value Correct Type
This section contains 5 questions, when worked out will result in an integer value from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. The number of carbonate minerals among the following
Cassiterite , Siderite , Anglesite , Azurite , Calamine , Cryolite ,Calcite ,Magnetite, Magnesite
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The carbonate ores are siderite, azurite. calamine, calcite, magnesite.
The common impurity present in most of the ores is- a)SnO2
- b)PbS
- c)ZnS
- d)SiO2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The common impurity present in most of the ores is
a)
SnO2
b)
PbS
c)
ZnS
d)
SiO2
|
|
Saanvi Bose answered |
Impurities in Ores
Ores are naturally occurring rocks that contain minerals or metal compounds in sufficient amounts to make it economically viable to extract the metal. However, these ores also contain impurities, which are substances that are not desired and need to be removed before the metal can be extracted.
Common Impurities in Ores
The most common impurity present in most ores is silica (SiO2). This is because silica is a very common mineral that is found in many rocks and soils. When the metal ore is formed, it is often in close association with silica and other minerals, which become mixed with the metal during the mining process.
Other common impurities found in ores include:
- Iron oxide (Fe2O3)
- Aluminium oxide (Al2O3)
- Calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
- Magnesium carbonate (MgCO3)
- Sulfur (S)
- Phosphorus (P)
Importance of Removing Impurities
The presence of impurities in the metal can have a negative effect on its properties and performance. For example, impurities can make the metal weaker, less ductile, less resistant to corrosion, and more prone to cracking or failure. Therefore, it is important to remove these impurities before the metal can be used in various applications.
Methods of Removing Impurities
There are several methods for removing impurities from ores, depending on the type and nature of the impurities and the metal being extracted. Some of the commonly used methods include:
- Gravity separation
- Froth flotation
- Magnetic separation
- Leaching
- Roasting
In conclusion, silica (SiO2) is the most common impurity present in most ores, and it needs to be removed before the metal can be extracted and used in various applications.
Ores are naturally occurring rocks that contain minerals or metal compounds in sufficient amounts to make it economically viable to extract the metal. However, these ores also contain impurities, which are substances that are not desired and need to be removed before the metal can be extracted.
Common Impurities in Ores
The most common impurity present in most ores is silica (SiO2). This is because silica is a very common mineral that is found in many rocks and soils. When the metal ore is formed, it is often in close association with silica and other minerals, which become mixed with the metal during the mining process.
Other common impurities found in ores include:
- Iron oxide (Fe2O3)
- Aluminium oxide (Al2O3)
- Calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
- Magnesium carbonate (MgCO3)
- Sulfur (S)
- Phosphorus (P)
Importance of Removing Impurities
The presence of impurities in the metal can have a negative effect on its properties and performance. For example, impurities can make the metal weaker, less ductile, less resistant to corrosion, and more prone to cracking or failure. Therefore, it is important to remove these impurities before the metal can be used in various applications.
Methods of Removing Impurities
There are several methods for removing impurities from ores, depending on the type and nature of the impurities and the metal being extracted. Some of the commonly used methods include:
- Gravity separation
- Froth flotation
- Magnetic separation
- Leaching
- Roasting
In conclusion, silica (SiO2) is the most common impurity present in most ores, and it needs to be removed before the metal can be extracted and used in various applications.
Which one of the following is not a method of concentration of ore?- a)Gravity separation
- b)Froth floatation process
- c)Electromagnetic separation
- d)Smelting
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a method of concentration of ore?
a)
Gravity separation
b)
Froth floatation process
c)
Electromagnetic separation
d)
Smelting
|
|
Vama Shah answered |
Hey mate...Answer is smelting as it is the process of applying heat to the ore in order to extract the ore metal and the concn of ore is purely different than smelting so yah that's d reason behind hope it helped uh...!!!!!:)
For which oxide formation ΔG° is more negative than Gr2O3?- a)FeO
- b)ZnO
- c)Al2O3
- d)MgO
Correct answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
For which oxide formation ΔG° is more negative than Gr2O3?
a)
FeO
b)
ZnO
c)
Al2O3
d)
MgO
|
|
Anuj Unni answered |
Introduction:
The question asks us to determine which oxide formation has a more negative value of standard Gibbs free energy of formation (ΔG°f) compared to Gr2O3. The standard Gibbs free energy of formation is a measure of the thermodynamic stability of a compound, with more negative values indicating greater stability.
Analysis:
To compare the ΔG°f values of different oxides, we need to refer to the standard Gibbs free energy of formation data. By comparing the values, we can determine which oxide formation is more stable (i.e., has a more negative ΔG°f value) than Gr2O3.
Options:
a) FeO:
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation for FeO is -272.8 kJ/mol. Since FeO has a more negative ΔG°f value than Gr2O3, it is more stable.
b) ZnO:
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation for ZnO is -318.3 kJ/mol. Since ZnO has a more negative ΔG°f value than Gr2O3, it is more stable.
c) Al2O3:
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation for Al2O3 is -1582.3 kJ/mol. Since Al2O3 has a more negative ΔG°f value than Gr2O3, it is more stable.
d) MgO:
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation for MgO is -601.6 kJ/mol. Since MgO has a more negative ΔG°f value than Gr2O3, it is more stable.
Conclusion:
Based on the comparison of the standard Gibbs free energy of formation values, the oxide formations with more negative ΔG°f values than Gr2O3 are Al2O3 and MgO. Therefore, the correct answer is option C and D.
The question asks us to determine which oxide formation has a more negative value of standard Gibbs free energy of formation (ΔG°f) compared to Gr2O3. The standard Gibbs free energy of formation is a measure of the thermodynamic stability of a compound, with more negative values indicating greater stability.
Analysis:
To compare the ΔG°f values of different oxides, we need to refer to the standard Gibbs free energy of formation data. By comparing the values, we can determine which oxide formation is more stable (i.e., has a more negative ΔG°f value) than Gr2O3.
Options:
a) FeO:
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation for FeO is -272.8 kJ/mol. Since FeO has a more negative ΔG°f value than Gr2O3, it is more stable.
b) ZnO:
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation for ZnO is -318.3 kJ/mol. Since ZnO has a more negative ΔG°f value than Gr2O3, it is more stable.
c) Al2O3:
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation for Al2O3 is -1582.3 kJ/mol. Since Al2O3 has a more negative ΔG°f value than Gr2O3, it is more stable.
d) MgO:
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation for MgO is -601.6 kJ/mol. Since MgO has a more negative ΔG°f value than Gr2O3, it is more stable.
Conclusion:
Based on the comparison of the standard Gibbs free energy of formation values, the oxide formations with more negative ΔG°f values than Gr2O3 are Al2O3 and MgO. Therefore, the correct answer is option C and D.
In froth-floatation process, palm oil functions as :- a)Activator
- b)Frother
- c)Collector
- d)Agitator
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In froth-floatation process, palm oil functions as :
a)
Activator
b)
Frother
c)
Collector
d)
Agitator

|
Surbhi Sengupta answered |
Palm oil function as frother. It decreases the surface tension of the total solution, by which the formation of froth becomes easier.
Statement TypeThis section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct anser from the codes given below.Q. Statement I : The copper pyrite (CuFeS2) is the ore of copper.Statement II : The clay (Al2O3 . 2SiO2 . 2H2O) is the ore of aluminium.- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement Type
This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct anser from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : The copper pyrite (CuFeS2) is the ore of copper.
Statement II : The clay (Al2O3 . 2SiO2 . 2H2O) is the ore of aluminium.
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
Aluminium cannot be extracted from clay profitably.
Which metal is also found in sea beds ?- a)Magnesium
- b)Calcium
- c)Manganese
- d)Aluminium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which metal is also found in sea beds ?
a)
Magnesium
b)
Calcium
c)
Manganese
d)
Aluminium
|
|
Kavita Joshi answered |
Many thousands of square kilometres of the deep-sea floor are covered by metal-bearing nodules. They contain primarily manganese, but also nickel, cobalt and copper, which makes them economically promising.
Statement- 1: In the Hoop’s process of aluminium purification, the fused materials remain in three different layers. These layers remain intact even in electrolytic reduction.
Statement-2 : This is an oxidation reaction and leads to the formation of a soluble complex.- a)Statement- 1 is True, Statement- 2 is True; Statement- 2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
- b)Statement- 1 is True, Statement- 2 is True; Statement- 2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
- c)Statement- 1 is True, Statement- 2 is False
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement- 1: In the Hoop’s process of aluminium purification, the fused materials remain in three different layers. These layers remain intact even in electrolytic reduction.
Statement-2 : This is an oxidation reaction and leads to the formation of a soluble complex.
Statement-2 : This is an oxidation reaction and leads to the formation of a soluble complex.
a)
Statement- 1 is True, Statement- 2 is True; Statement- 2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
b)
Statement- 1 is True, Statement- 2 is True; Statement- 2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
c)
Statement- 1 is True, Statement- 2 is False
d)
none of these
|
|
Priyanshu Intelligent answered |
A is correct
Which of the following is the correct combination?- a)Calamine, siderite
- b)Magnesite , dolomite
- c)Malachite , azurite
- d)Calcite , witherite
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct combination?
a)
Calamine, siderite
b)
Magnesite , dolomite
c)
Malachite , azurite
d)
Calcite , witherite

|
Naani Mahesh answered |
B becoz they have same carbonates MAGNESITE IS MgCO3 and DOLOMITE is CaCO3.MgCO3.......
Comprehension TypeThis section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
PassageThe natural substances in which metals occur in the earth are called minerals. A mineral has a definite composition. It may be a single compound or a complex mixture . It is usually associated with number of impurities. The minerals from which the metals can be conveniently extracted are called ores .Thus, all ores are minerals but all minerals are not ores. Depending on the composition ores are classified into different types such as oxides, sulphides, carbonates, halides, silicates etc.Q. The impurities associated with minerals are called.- a)Gangue
- b)Flux
- c)Slag
- d)Depressant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Comprehension Type
This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Passage
Passage
The natural substances in which metals occur in the earth are called minerals. A mineral has a definite composition. It may be a single compound or a complex mixture . It is usually associated with number of impurities. The minerals from which the metals can be conveniently extracted are called ores .Thus, all ores are minerals but all minerals are not ores. Depending on the composition ores are classified into different types such as oxides, sulphides, carbonates, halides, silicates etc.
Q. The impurities associated with minerals are called.
a)
Gangue
b)
Flux
c)
Slag
d)
Depressant
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
The correct answer is option A
The impurities associated with minerals used in metallurgy are collectively called Gangue.
The impurities associated with minerals used in metallurgy are collectively called Gangue.
Copper can be extracted from (1978)- a)Kupfernical
- b)Dolomite
- c)Malachite
- d)Galena
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Copper can be extracted from (1978)
a)
Kupfernical
b)
Dolomite
c)
Malachite
d)
Galena
|
|
Abhijeet Ingle answered |
Malachite is a green copper carbonate hydroxide mineral with a chemical composition of cu2( co3)(oh)2
it was used as an ore of copper but is of minor importance today because of presence of copper in small quantities
it was used as an ore of copper but is of minor importance today because of presence of copper in small quantities
. Malachite is an ore of:- a)Copper
- b)Magnesium
- c)Calcium
- d)Both magnesium and calcium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
. Malachite is an ore of:
a)
Copper
b)
Magnesium
c)
Calcium
d)
Both magnesium and calcium
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
The distinctive bright-green hydrous CARBONATE MINERAL malachite is a common but minor ore of copper. It is usually found in copper deposits associated with LIMESTONE, occurring with AZURITE as the weathering product of other copper ore minerals.
Extraction process of Bauxite is known as- a)Cynanide process
- b)Hall – Heroult process
- c)Van – Arkel – de Boer process
- d)Mond’s process
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Extraction process of Bauxite is known as
a)
Cynanide process
b)
Hall – Heroult process
c)
Van – Arkel – de Boer process
d)
Mond’s process

|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Hall – Heroult process of extraction of Al from Bauxite.
One or More than One Options Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. Purification of alumina is called- a)Baeyer’s proces
- b)Hall process
- c)Mond’s proces
- d)Hoope’s proces
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Purification of alumina is called
a)
Baeyer’s proces
b)
Hall process
c)
Mond’s proces
d)
Hoope’s proces

|
Universe Mystery answered |
Baeyer's process is used to obtain pure alumina. as sodium silicate, leaving behind the impurities. The resulting solution is filtered, and cooled and neutralized with carbon dioxide to get aluminium hydroxide as precipitate leaving sodium silicate in the solution.
Which one of the following ores is concentrated by chemical leaching method?- a)Galena
- b)Copper pyrite
- c)CaO + SiO3
- d)SiO2 and CaSiO3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following ores is concentrated by chemical leaching method?
a)
Galena
b)
Copper pyrite
c)
CaO + SiO3
d)
SiO2 and CaSiO3
|
|
Sreemoyee Choudhury answered |
In this process the finely divided powdered argentite or the native silver or gold is treated with a dilute solution (0.5%) of sodium or potassium cyanide while a current of air is continuously passed. As a result silver pass into solution forming their respective soluble complex cyanides while the impurities remain unaffected which are filtered off.
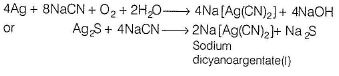
Cryolite is the chief ore of- a)Aluminium
- b)Zink
- c)Iron
- d)Copper
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cryolite is the chief ore of
a)
Aluminium
b)
Zink
c)
Iron
d)
Copper

|
M. Vishnu answered |
The cryolite mine Ivigtut, Greenland, summer 1940.It was historically used as an ore of aluminium and later in the electrolyticprocessing of the aluminium-rich oxide ore bauxite (itself a combination of aluminium oxide minerals such as gibbsite, boehmite and diaspore).
Match the method of concentration of the ore in column I with the ore in column II and select the correct alternate: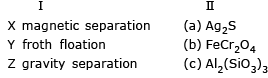
- a)
- b)
- c)

- d)
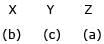
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the method of concentration of the ore in column I with the ore in column II and select the correct alternate:
a)
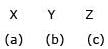
b)
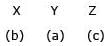
c)

d)
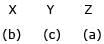
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Magnete seperation → FeCr2O4
froath floatation → Ag2S
gravity separation → Al2 (SiO3)2
froath floatation → Ag2S
gravity separation → Al2 (SiO3)2
(I) FeCr2O4 + NaOH + air → (A) + Fe2O3(II) (A) + (B) → Na2Cr2O7(III) Na2Cr2O7 + X 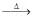 Cr2O3(IV) Cr2O3 + Y
Cr2O3(IV) Cr2O3 + Y 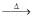 CrQ. Compounds (A) and (B) are :
CrQ. Compounds (A) and (B) are :- a)Na2CrO4, H2SO4
- b)Na2Cr2O7, HCl
- c)Na2CrO5, H2SO4
- d)Na4[Fe(OH)6], H2SO4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
(I) FeCr2O4 + NaOH + air → (A) + Fe2O3
(II) (A) + (B) → Na2Cr2O7
(III) Na2Cr2O7 + X 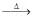 Cr2O3
Cr2O3
(IV) Cr2O3 + Y 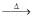 Cr
Cr
Q.
Compounds (A) and (B) are :
a)
Na2CrO4, H2SO4
b)
Na2Cr2O7, HCl
c)
Na2CrO5, H2SO4
d)
Na4[Fe(OH)6], H2SO4
|
|
Deepak Kapoor answered |
A → Na2CrO4
B → H2SO4
B → H2SO4
Refining of silver is done by- a)Cupellation
- b)Poling
- c)Liquation
- d)Zone refining
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Refining of silver is done by
a)
Cupellation
b)
Poling
c)
Liquation
d)
Zone refining
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Electrolysis. Electrolysis uses currents to give the energy needed to help a chemical reaction occur to break apart chemical bonds between metals and impurities. This method was first used in the late 18th century to separate tin and zinc from their salts. This method is also used for purifying aluminum.
Which one of the following ores is best concentrated by froath-flotation method ?[AIEEE-2004]- a)Magnetite
- b)Cassiterite
- c)Galena
- d)Malachite
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following ores is best concentrated by froath-flotation method ?
[AIEEE-2004]
a)
Magnetite
b)
Cassiterite
c)
Galena
d)
Malachite
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Froth flotation method is used for the concentration of sulphide ores. The method is based on the preferential wetting properties with the frothing agent and water. In the given options, Galena (PbS) is the only sulphide ore. CORRECT OPTION IS C.
One or More than One Options Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. In the following processes, which are not sulphatising roasting ?- a)2ZnS + 3O2 → 2ZnO + 2SO2
- b)ZnS + 2O2 → ZnSO4
- c)2Cu2S + 3O2 → 2Cu2O + 2SO4
- d)Ag2S + 2NaCI + 2O2 → 2AgCl + Na2SO4
Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
In the following processes, which are not sulphatising roasting ?
a)
2ZnS + 3O2 → 2ZnO + 2SO2
b)
ZnS + 2O2 → ZnSO4
c)
2Cu2S + 3O2 → 2Cu2O + 2SO4
d)
Ag2S + 2NaCI + 2O2 → 2AgCl + Na2SO4
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
22ZnS + 3O2 → 2ZnO + 2SO2,
2CU2S + 3O2 → 2Cu2O + 2SO2
Ag2S + 2NaCI + O2 → 2AgCI + Na 2SO4
2CU2S + 3O2 → 2Cu2O + 2SO2
Ag2S + 2NaCI + O2 → 2AgCI + Na 2SO4
In which of the following isolations no reducing agent is required :- a)Iron from haematite
- b)Aluminium from bauxite
- c)Mercury from cinnabar
- d)Zinc from zinc blends
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following isolations no reducing agent is required :
a)
Iron from haematite
b)
Aluminium from bauxite
c)
Mercury from cinnabar
d)
Zinc from zinc blends
|
|
Suhana Agrawal answered |
Extraction of mercury from cinnabar does takes place by electrolysis hence no R.A is required.
Aluminium is industrially prepared by - [AIEEE-2002]- a) Fused cryolite
- b)Bauxite ore
- c)Alumina
- d)Alumina mixed with molten cryolite
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Aluminium is industrially prepared by -
[AIEEE-2002]
a)
Fused cryolite
b)
Bauxite ore
c)
Alumina
d)
Alumina mixed with molten cryolite
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
The Hall–Héroult process is the major industrial process for smelting aluminium. It involves dissolving aluminium oxide (alumina) (obtained most often from bauxite, aluminium's chief ore, through the Bayer process) in molten cryolite, and electrolysing the molten salt bath, typically in a purpose-built cell.
The Hall–Héroult process is the major industrial process for smelting aluminium. It involves dissolving aluminium oxide (alumina) (obtained most often from bauxite, aluminium's chief ore, through the Bayer process) in molten cryolite, and electrolysing the molten salt bath, typically in a purpose-built cell.
In the froth floatation process for benefaction of the ores, the ore particles float because- a)They are light
- b)Their surface is not easily wetted by water
- c)They are insoluble
- d)They bear electric charge
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the froth floatation process for benefaction of the ores, the ore particles float because
a)
They are light
b)
Their surface is not easily wetted by water
c)
They are insoluble
d)
They bear electric charge
|
|
Kiran Khanna answered |
Introduction:
The froth flotation process is a widely used method for the benefaction of ores. It is based on the principle of difference in the wetting properties of the ore and gangue particles with water and oil. In this process, the ore is finely ground and mixed with water and a suitable collector, such as pine oil or xanthates. Air is then passed through the mixture to produce a froth containing the ore particles, which can be collected and separated from the gangue.
Explanation:
The reason why the ore particles float in the froth flotation process is because their surface is not easily wetted by water. This is due to the hydrophobic nature of the ore particles, which means they have a tendency to repel or resist wetting by water. On the other hand, the gangue particles, which are usually made up of minerals that are hydrophilic or easily wetted by water, sink to the bottom.
Hydrophobic nature of ore particles:
The hydrophobic nature of the ore particles is attributed to their surface properties. These particles usually have a thin film of adsorbed collector molecules on their surface, which makes them hydrophobic. The collector molecules are attracted to the surface of the ore particles and form a monolayer, which reduces the surface energy and makes the particles repel water.
Formation of froth:
When air is passed through the mixture of ground ore and water, it creates bubbles that carry the ore particles to the surface. The collector molecules on the surface of the ore particles act as a bridge between the particles and the air bubbles. They attach to the air bubbles, causing them to become hydrophobic and carry the ore particles to the surface, forming a froth.
Separation of ore and gangue:
The froth containing the ore particles is collected and separated from the gangue particles. This can be done by skimming off the froth or by using mechanical devices to scrape off the froth. The separated froth is then further processed to obtain the desired ore concentrate.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the reason why the ore particles float in the froth flotation process is because their surface is not easily wetted by water. This is due to the hydrophobic nature of the ore particles, which is attributed to the presence of collector molecules on their surface. The formation of froth and the subsequent separation of ore and gangue particles allow for the benefaction of ores in this process.
The froth flotation process is a widely used method for the benefaction of ores. It is based on the principle of difference in the wetting properties of the ore and gangue particles with water and oil. In this process, the ore is finely ground and mixed with water and a suitable collector, such as pine oil or xanthates. Air is then passed through the mixture to produce a froth containing the ore particles, which can be collected and separated from the gangue.
Explanation:
The reason why the ore particles float in the froth flotation process is because their surface is not easily wetted by water. This is due to the hydrophobic nature of the ore particles, which means they have a tendency to repel or resist wetting by water. On the other hand, the gangue particles, which are usually made up of minerals that are hydrophilic or easily wetted by water, sink to the bottom.
Hydrophobic nature of ore particles:
The hydrophobic nature of the ore particles is attributed to their surface properties. These particles usually have a thin film of adsorbed collector molecules on their surface, which makes them hydrophobic. The collector molecules are attracted to the surface of the ore particles and form a monolayer, which reduces the surface energy and makes the particles repel water.
Formation of froth:
When air is passed through the mixture of ground ore and water, it creates bubbles that carry the ore particles to the surface. The collector molecules on the surface of the ore particles act as a bridge between the particles and the air bubbles. They attach to the air bubbles, causing them to become hydrophobic and carry the ore particles to the surface, forming a froth.
Separation of ore and gangue:
The froth containing the ore particles is collected and separated from the gangue particles. This can be done by skimming off the froth or by using mechanical devices to scrape off the froth. The separated froth is then further processed to obtain the desired ore concentrate.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the reason why the ore particles float in the froth flotation process is because their surface is not easily wetted by water. This is due to the hydrophobic nature of the ore particles, which is attributed to the presence of collector molecules on their surface. The formation of froth and the subsequent separation of ore and gangue particles allow for the benefaction of ores in this process.
Which method of purification is represented by the following equation ? [2012]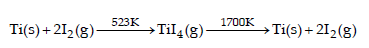
- a)Zone refining
- b)Cupellation
- c)Polling
- d)Van Arkel
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which method of purification is represented by the following equation ? [2012]
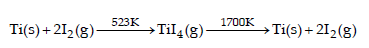
a)
Zone refining
b)
Cupellation
c)
Polling
d)
Van Arkel
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
Van Arkel is a method in which heat treatment is used to purify metal in this process metals are converted into other metal compound for loosly coupled like as iodine to make metal iodide which are easily decomposed and give pure metal.
The process is known as Van Arkel method.
The process is known as Van Arkel method.
Pb and Sn are extracted from their chief ore by:- a)carbon reduction and self reduction respectively.
- b)self reduction and carbon reduction respectively.
- c)electrolysis and self reduction respectively.
- d)self reduction and self reduction respectively
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Pb and Sn are extracted from their chief ore by:
a)
carbon reduction and self reduction respectively.
b)
self reduction and carbon reduction respectively.
c)
electrolysis and self reduction respectively.
d)
self reduction and self reduction respectively
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Which of the following chemicals are involved in froth floatation process?- a)Collectors
- b)Depressant
- c)Flux
- d)Activators
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following chemicals are involved in froth floatation process?
a)
Collectors
b)
Depressant
c)
Flux
d)
Activators
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
In froth flotation the effectiveness of an air bubble to adhere to a particle is based on how hydrophobic the particle is. Hydrophobic particles have an affinity to air bubbles, leading to adsorption. Collectors are the main additives used to improve particle surfaces.
The substance not likely to contain CaCO3 is – [AIEEE-2003]- a)Sea shells
- b)Dolomite
- c)A marble statue
- d)Calcined gypsum
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The substance not likely to contain CaCO3 is – [AIEEE-2003]
a)
Sea shells
b)
Dolomite
c)
A marble statue
d)
Calcined gypsum
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The correct answer is option D
A) On heating, gypsum loses water and gives the hemihydrate (CaSO4. 1/2H2O) or the anhydrite. The hemihydrate known as Calcined gypsum/ Plaster of Paris / stucco is an important building material.
B) Seashells are the exoskeletons of mollusks such as snails, clams, oysters and many others. Such shells have three distinct layers and are composed mostly of calcium carbonate(CaCO3).
C) Dolomite is an anhydrous carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate, ideally CaMg(CO3)2.
D) A marble statue typically consists of calcium carbonate.
So Calcined gypsum does not have calcium carbonate.
A) On heating, gypsum loses water and gives the hemihydrate (CaSO4. 1/2H2O) or the anhydrite. The hemihydrate known as Calcined gypsum/ Plaster of Paris / stucco is an important building material.
B) Seashells are the exoskeletons of mollusks such as snails, clams, oysters and many others. Such shells have three distinct layers and are composed mostly of calcium carbonate(CaCO3).
C) Dolomite is an anhydrous carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate, ideally CaMg(CO3)2.
D) A marble statue typically consists of calcium carbonate.
So Calcined gypsum does not have calcium carbonate.
A mineral is called an ore if- a)the percentage of metal content is more than 50 %
- b)it is possible to isolate metal from it
- c)a metal can be profitably extracted from it
- d)if it is free from any earthly impurities
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A mineral is called an ore if
a)
the percentage of metal content is more than 50 %
b)
it is possible to isolate metal from it
c)
a metal can be profitably extracted from it
d)
if it is free from any earthly impurities

|
Anisha Deshpande answered |
The Definition of an Ore
An ore is a type of mineral that contains a valuable metal or metal compound. It is a naturally occurring solid material from which a metal or valuable mineral can be profitably extracted. The classification of a mineral as an ore depends on certain criteria.
Criteria for Classifying a Mineral as an Ore
To be classified as an ore, a mineral must meet the following criteria:
1. Metal Content Percentage
The percentage of metal content in a mineral does not determine whether it is classified as an ore. Some ores may have a metal content of less than 50%, while some non-ores may have a higher metal content. Therefore, option A is incorrect.
2. Ability to Isolate Metal
For a mineral to be classified as an ore, it must be possible to isolate the metal from it. This means that the metal should be extractable from the mineral in a relatively straightforward manner. If it is not possible to isolate the metal from the mineral, it cannot be classified as an ore. Therefore, option B is correct.
3. Profitable Extraction
The extraction of metal from an ore should be economically viable. This means that the cost of extracting the metal should be lower than the value of the metal obtained. If the extraction process is not profitable, the mineral cannot be classified as an ore. Therefore, option C is correct.
4. Absence of Earthly Impurities
The presence of earthly impurities does not determine whether a mineral is classified as an ore. Ores often contain impurities that need to be removed during the extraction process. Therefore, option D is incorrect.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a mineral is called an ore if it is possible to isolate a metal from it, and if the extraction of the metal is economically viable. The percentage of metal content or the absence of earthly impurities are not determining factors for classifying a mineral as an ore.
An ore is a type of mineral that contains a valuable metal or metal compound. It is a naturally occurring solid material from which a metal or valuable mineral can be profitably extracted. The classification of a mineral as an ore depends on certain criteria.
Criteria for Classifying a Mineral as an Ore
To be classified as an ore, a mineral must meet the following criteria:
1. Metal Content Percentage
The percentage of metal content in a mineral does not determine whether it is classified as an ore. Some ores may have a metal content of less than 50%, while some non-ores may have a higher metal content. Therefore, option A is incorrect.
2. Ability to Isolate Metal
For a mineral to be classified as an ore, it must be possible to isolate the metal from it. This means that the metal should be extractable from the mineral in a relatively straightforward manner. If it is not possible to isolate the metal from the mineral, it cannot be classified as an ore. Therefore, option B is correct.
3. Profitable Extraction
The extraction of metal from an ore should be economically viable. This means that the cost of extracting the metal should be lower than the value of the metal obtained. If the extraction process is not profitable, the mineral cannot be classified as an ore. Therefore, option C is correct.
4. Absence of Earthly Impurities
The presence of earthly impurities does not determine whether a mineral is classified as an ore. Ores often contain impurities that need to be removed during the extraction process. Therefore, option D is incorrect.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a mineral is called an ore if it is possible to isolate a metal from it, and if the extraction of the metal is economically viable. The percentage of metal content or the absence of earthly impurities are not determining factors for classifying a mineral as an ore.
The different number of non-metals present in fluorapatite are
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
The different number of non-metals present in fluorapatite are
|
|
Sankar Singh answered |
Fluorapatite is a mineral that belongs to the apatite group. It has the chemical formula Ca5(PO4)3F and is composed of calcium, phosphorus, oxygen, and fluorine. The number of non-metals present in fluorapatite can be determined by analyzing its chemical formula.
Chemical Formula of Fluorapatite
- The chemical formula of fluorapatite is Ca5(PO4)3F.
- The formula can be broken down into its constituent elements as follows:
- Calcium (Ca)
- Phosphorus (P)
- Oxygen (O)
- Fluorine (F)
Non-Metals Present in Fluorapatite
- Non-metals are elements that lack metallic properties such as malleability, ductility, and conductivity.
- In the chemical formula of fluorapatite, the non-metals present are phosphorus, oxygen, and fluorine.
- Calcium is a metal, and therefore, it is not considered a non-metal.
Conclusion
- Fluorapatite contains three non-metals, which are phosphorus, oxygen, and fluorine.
Chemical Formula of Fluorapatite
- The chemical formula of fluorapatite is Ca5(PO4)3F.
- The formula can be broken down into its constituent elements as follows:
- Calcium (Ca)
- Phosphorus (P)
- Oxygen (O)
- Fluorine (F)
Non-Metals Present in Fluorapatite
- Non-metals are elements that lack metallic properties such as malleability, ductility, and conductivity.
- In the chemical formula of fluorapatite, the non-metals present are phosphorus, oxygen, and fluorine.
- Calcium is a metal, and therefore, it is not considered a non-metal.
Conclusion
- Fluorapatite contains three non-metals, which are phosphorus, oxygen, and fluorine.
Comprehension Type Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageImpure metals are purified by different methods in order to remove the undesired impurities. These methods depend on the nature of metal and nature of impurities. Liquation is used for purifying metals with low melting points like Bi, Sn, Pb, Hg etc. Distillation is used for volatile metals like Zn, Cd, Hg. Cupellation is used to purify silver metal with lead impurities. Electrolytic refining (Cu, Ag, Mg, Al) Zone refining (Si, Ge, Ga) Mond’s process (Ni) van Arkel process (Zr, Ti).Q. In the extraction of nickel by Mond’s process, the metal is obtained by- a)electrochemical reduction
- b)thermal decomposition
- c)chemical reduction by aluminium
- d)chemical reduction by carbon
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
Impure metals are purified by different methods in order to remove the undesired impurities. These methods depend on the nature of metal and nature of impurities. Liquation is used for purifying metals with low melting points like Bi, Sn, Pb, Hg etc. Distillation is used for volatile metals like Zn, Cd, Hg. Cupellation is used to purify silver metal with lead impurities. Electrolytic refining (Cu, Ag, Mg, Al) Zone refining (Si, Ge, Ga) Mond’s process (Ni) van Arkel process (Zr, Ti).
Q.
In the extraction of nickel by Mond’s process, the metal is obtained by
a)
electrochemical reduction
b)
thermal decomposition
c)
chemical reduction by aluminium
d)
chemical reduction by carbon

|
Asha Nair answered |
The metal is obtained by thermal decomposition. Impure nickel is heated in a current of CO at 330-350 K. It forms volatile nickel carbonyl leaving behind the impurities.
Chapter doubts & questions for General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals - Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals - Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup