All Exams >
Class 9 >
Science Class 9 >
All Questions
All questions of Atoms and Molecules for Class 9 Exam
Which constituent of air is monoatomic?- a)Argon
- b)Water vapour
- c)Oxygen
- d)Nitrogen
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which constituent of air is monoatomic?
a)
Argon
b)
Water vapour
c)
Oxygen
d)
Nitrogen
|
|
Avinash Patel answered |
Argon is a Noble gas. Noble gases are not very reactive since they have a very stable electron configuration. It is only about 1% of the air in the atmosphere but it is more abundant than any other element on the Periodic Table behind Nitrogen and Oxygen.
Which one of the following is the modern symbol of Gold?- a)Gl
- b)Go
- c)Si
- d)Au
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the modern symbol of Gold?
a)
Gl
b)
Go
c)
Si
d)
Au
|
|
Arvind Singh answered |
Gold is a chemical element with symbol Au (from Latin: aurum) and atomic number 79, making it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. In its purest form, it is a bright, slightly reddish yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Which is the smallest particle of an element that can take part in a chemical reaction?
- A:
Molecule
- B:
Mixture
- C:
Compound
- D:
Atom
The answer is d.
Which is the smallest particle of an element that can take part in a chemical reaction?
Molecule
Mixture
Compound
Atom
|
|
Arvind Singh answered |
The basic unit of matter is the atom. It is the smallest particle of an element which can take part in chemical reactions and may or may not exist separately. It consists of sub-atomic particles, i.e., protons, neutrons and electrons.
The number of moles for 52g of He is:
(Atomic Mass of He: 4u)- a) 6.022 × 1023
- b)13
- c)52
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of moles for 52g of He is:
(Atomic Mass of He: 4u)
(Atomic Mass of He: 4u)
a)
6.022 × 1023
b)
13
c)
52
d)
1

|
Learners Habitat answered |
Gram atomic mass of He = 4u
Therefore 52 g of He contains :
= 52 / 4
= 13 moles
Therefore 52 g of He contains :
= 52 / 4
= 13 moles
The number of atoms present in one molecule of an element is called as:- a)Empirical formula
- b)Molecule
- c)Atomicity
- d)Compound
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of atoms present in one molecule of an element is called as:
a)
Empirical formula
b)
Molecule
c)
Atomicity
d)
Compound
|
|
Ananya Sharma answered |
Atomicity is the total number of atoms present in one molecule of an element or a compound.
For example: one molecule of hydrogen (H2) contains two atoms of hydrogen. Therefore, atomicity of hydrogen is 2. Similarly, 1 molecule of O3 contains 3 atoms. Therefore, its atomicity is 3. molecule of Argon exist as Ar and hence its a monoatomic compound.
One atomic mass unit is a mass unit equal to exactly one twelfth (1/12th) the mass of one atom of ___________.- a)Carbon-12
- b)Nitrogen -14
- c)Carbon-1
- d)4.Silicon-14
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One atomic mass unit is a mass unit equal to exactly one twelfth (1/12th) the mass of one atom of ___________.
a)
Carbon-12
b)
Nitrogen -14
c)
Carbon-1
d)
4.Silicon-14
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
An atomic mass unit (symbolized AMU or amu) is defined as precisely 1/12 the mass of an atom of carbon-12. The carbon-12 (C-12) atom has six protons and six neutrons in its nucleus. In imprecise terms, one AMU is the average of the proton rest mass and the neutron rest mass.
NaCl molecule is made of which of the following ions?- a)Na cation and Cl anion
- b)Cl cation and Na anion
- c)Both Na and Cl cation
- d)Both Na and Cl anion
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
NaCl molecule is made of which of the following ions?
a)
Na cation and Cl anion
b)
Cl cation and Na anion
c)
Both Na and Cl cation
d)
Both Na and Cl anion
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
An oxygen molecule (O2) is a good example of a molecule with a covalent bond. Ionic bonds occur when electrons are donated from one atom to another. Table salt (NaCl) is a common example of a compound with an ionic bond.
Valency of Calcium element is:- a)4
- b)5
- c)2
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Valency of Calcium element is:
a)
4
b)
5
c)
2
d)
3
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
The valency of Calcium of 2+. Calcium has 2 electrons in its outermost shell, its electronic configuration being (2,8,8,2). In order to attain stability it loses 2 electrons to become stable according to the octet rule.
The reaction used in the experiment to verify the law of conservation of masses is included in which of the following categories?
AgNO3(aqueous) + KCl(aqueous) —–AgCl(precipitate) + KNO3(aqueous)
- a)Precipitation reaction
- b)Double displacement reaction
- c)Neutralization reaction
- d)Both A and B
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction used in the experiment to verify the law of conservation of masses is included in which of the following categories?
AgNO3(aqueous) + KCl(aqueous) —–AgCl(precipitate) + KNO3(aqueous)
AgNO3(aqueous) + KCl(aqueous) —–AgCl(precipitate) + KNO3(aqueous)
a)
Precipitation reaction
b)
Double displacement reaction
c)
Neutralization reaction
d)
Both A and B

|
Imk Pathshala answered |
The correct answer is D: Both A and B.
- Precipitation Reaction: AgNO3(aq) + KCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + KNO3(aq) forms a solid precipitate.
- Double Displacement Reaction: AgNO3(aq) + KCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + KNO3(aq) involves the exchange of ions between two compounds.
- Explanation: The given reaction demonstrates both characteristics, forming a precipitate (A) and involving double displacement of ions (B), making it both a precipitation and a double displacement reaction.
- Precipitation Reaction: AgNO3(aq) + KCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + KNO3(aq) forms a solid precipitate.
- Double Displacement Reaction: AgNO3(aq) + KCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + KNO3(aq) involves the exchange of ions between two compounds.
- Explanation: The given reaction demonstrates both characteristics, forming a precipitate (A) and involving double displacement of ions (B), making it both a precipitation and a double displacement reaction.
5 grams of compound A reacts with 10 grams of compound B to produce a new compound C. What should be the mass of C according to law of conservation of mass?- a)15 g
- b)5 g
- c)50 g
- d)10 g
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
5 grams of compound A reacts with 10 grams of compound B to produce a new compound C. What should be the mass of C according to law of conservation of mass?
a)
15 g
b)
5 g
c)
50 g
d)
10 g
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
As from law of conservation of mass:-mass of reactants=mass of productTherefore, mass of compound A + mass of compound B=mass of compound CSo, 5g + 10g= 15g
Cl2 stands for:- a)2 molecules of chlorine
- b)2 atoms of chlorine
- c)2 ions of chlorine
- d)3 molecule of chlorine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cl2 stands for:
a)
2 molecules of chlorine
b)
2 atoms of chlorine
c)
2 ions of chlorine
d)
3 molecule of chlorine
|
|
Ravi Verma answered |
Cl’ represents one chlorine atom. It is found in nature in diatomic form as a molecule I.E. ,Cl2.
Which atom is the smallest atom of all?- a)Lithium
- b)Helium
- c)Hydrogen
- d)Carbon
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which atom is the smallest atom of all?
a)
Lithium
b)
Helium
c)
Hydrogen
d)
Carbon
|
|
Gayatri Deshpande answered |
Explanation:
Factors Affecting Atomic Radius:
Comparison of Atomic Radii:
Conclusion:
The size of an atom is determined by its atomic radius, which is the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost electron. Therefore, the smallest atom will have the smallest atomic radius.
Factors Affecting Atomic Radius:
- Number of protons in the nucleus
- Number of energy levels or electron shells
- Effective nuclear charge
Comparison of Atomic Radii:
Based on the factors affecting atomic radius, we can compare the atomic radii of the four given elements:
- Hydrogen has only one proton and one electron, making it the smallest atom.
- Helium has two protons and two electrons, making it slightly larger than hydrogen.
- Lithium has three protons and electrons, and is larger than both hydrogen and helium.
- Carbon has six protons and electrons, and is larger than all three previous elements.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the smallest atom of all is Hydrogen, with only one proton and one electron.
How do atoms usually exist in nature?- a)In the form of molecules
- b)In the form of ions
- c)In the free state
- d)In the form of molecules and Ions
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How do atoms usually exist in nature?
a)
In the form of molecules
b)
In the form of ions
c)
In the free state
d)
In the form of molecules and Ions

|
Khushi answered |
Most of the elements in environment do not have 8
electrons in their valance shells(because of which they are more or less reactive and unstable ) so they react with the atoms of other metals to form molecules or ion to achieve noble gas configuration and become stable. The atoms of only a few elements like helium , Neon ..etc have their valance shells already filled with 8 electrons.so they can exist in free state. But matter mostly exist in the form of molecules and ions.
The atomic masses and chemical properties of Sulphur and Phosphorus are different. This can be explained on the basis of:- a)Law of conservation of mass
- b)Laws of Chemical combination
- c)Law of constant proportions
- d)Dalton’s Atomic theory
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The atomic masses and chemical properties of Sulphur and Phosphorus are different. This can be explained on the basis of:
a)
Law of conservation of mass
b)
Laws of Chemical combination
c)
Law of constant proportions
d)
Dalton’s Atomic theory

|
Let's Tute answered |
The differences in atomic masses and chemical properties of sulphur and phosphorus can be explained by:
- Dalton’s Atomic Theory suggests that elements are made of atoms, each with a specific mass. This theory helps explain why different elements, like sulphur and phosphorus, have different atomic masses.
- According to Dalton, atoms of different elements have distinct properties, which explains the variation in their chemical behaviour.
Who gave the Law of constant proportions?
- a) Cavendish
- b) Proust
- c) Dalton
- d) Lavoisier
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who gave the Law of constant proportions?
a)
Cavendishb)
Proustc)
Daltond)
Lavoisier|
|
Arvind Singh answered |
A molecule of water will always have two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, meaning that in a bottle of pure water the hydrogen to oxygen atom ratio will always be 2:1. This seems very logical to us today. But 300 years ago, scientists didn't understand compounds this way. However, in 1794, Joseph Proust published the Law of Constant Proportions, which says that a chemical molecule will always contains the same elements in the same proportion.
There are two parts to the law of constant proportions: 1) there will always be the same elements that make up a compound, and 2) the mass of these compounds will always be in the same proportion.
Which of the following is anion?
A. Magnesium
B. Sulphate
C. Oxalate
D. Ammonium- a)(a) and (b) are correct
- b)(a), (b) and (c) are correct
- c)(b) and (c) are correct
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is anion?
A. Magnesium
B. Sulphate
C. Oxalate
D. Ammonium
A. Magnesium
B. Sulphate
C. Oxalate
D. Ammonium
a)
(a) and (b) are correct
b)
(a), (b) and (c) are correct
c)
(b) and (c) are correct
d)
All of these

|
Aditi Uppal answered |
Anions means negatively charged ions .Therefore , (c) is the correct option .
Valency of hydrogen is 1 and that of sulphur is 2. What should be the formula of hydrogen sulphide?- a)HS
- b)H2S2
- c)HS2
- d)H2S
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Valency of hydrogen is 1 and that of sulphur is 2. What should be the formula of hydrogen sulphide?
a)
HS
b)
H2S2
c)
HS2
d)
H2S
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Hydrogen sulfide is the chemical compound with the chemical formula H2S. It is a colorless gas with the characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. It is very poisonous, corrosive, and flammable.
Molecules can exist in free state because:- a)They are very stable.
- b)They are electrically charged.
- c)They are very reactive.
- d)They are bigger in size as compared to atoms.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Molecules can exist in free state because:
a)
They are very stable.
b)
They are electrically charged.
c)
They are very reactive.
d)
They are bigger in size as compared to atoms.

|
Raghavendra Jain answered |
The answer to the given question is option 'A': Molecules can exist in a free state because they are very stable.
Explanation:
Molecules are formed when two or more atoms chemically combine by sharing electrons or through other types of bonding. These atoms can be from the same element or different elements. The resulting molecule has a stable structure due to the sharing or transfer of electrons, which allows the atoms to achieve a more stable electron configuration. Here is a detailed explanation of why molecules are stable and can exist in a free state:
1. Stable electron configuration:
Molecules are formed when atoms combine in such a way that they achieve a stable electron configuration. This stability is achieved by filling or emptying their outermost energy level, also known as the valence shell. By sharing or transferring electrons, atoms can achieve a full valence shell, which is a highly stable configuration. This stable electron configuration contributes to the stability of molecules.
2. Strong chemical bonds:
Molecules are held together by strong chemical bonds, such as covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, while ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. These bonds are formed through the attraction between positively charged nuclei and negatively charged electrons. The strength of these bonds contributes to the stability of molecules.
3. Low potential energy:
Molecules have lower potential energy compared to individual atoms. When atoms combine to form a molecule, the resulting structure has a lower energy state. This decrease in potential energy is due to the formation of chemical bonds, which release energy. The lower potential energy of molecules makes them more stable and allows them to exist in a free state.
4. Balanced forces:
In a molecule, the attractive forces between atoms (chemical bonds) are balanced by repulsive forces between electrons and between nuclei. This balance of forces helps maintain the structure of the molecule and prevents it from easily breaking apart. The balanced forces contribute to the stability of molecules in a free state.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, molecules can exist in a free state because they are very stable. This stability is due to their stable electron configuration, strong chemical bonds, low potential energy, and balanced forces. These factors work together to maintain the integrity of the molecule and prevent it from easily dissociating into its constituent atoms.
Explanation:
Molecules are formed when two or more atoms chemically combine by sharing electrons or through other types of bonding. These atoms can be from the same element or different elements. The resulting molecule has a stable structure due to the sharing or transfer of electrons, which allows the atoms to achieve a more stable electron configuration. Here is a detailed explanation of why molecules are stable and can exist in a free state:
1. Stable electron configuration:
Molecules are formed when atoms combine in such a way that they achieve a stable electron configuration. This stability is achieved by filling or emptying their outermost energy level, also known as the valence shell. By sharing or transferring electrons, atoms can achieve a full valence shell, which is a highly stable configuration. This stable electron configuration contributes to the stability of molecules.
2. Strong chemical bonds:
Molecules are held together by strong chemical bonds, such as covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, while ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. These bonds are formed through the attraction between positively charged nuclei and negatively charged electrons. The strength of these bonds contributes to the stability of molecules.
3. Low potential energy:
Molecules have lower potential energy compared to individual atoms. When atoms combine to form a molecule, the resulting structure has a lower energy state. This decrease in potential energy is due to the formation of chemical bonds, which release energy. The lower potential energy of molecules makes them more stable and allows them to exist in a free state.
4. Balanced forces:
In a molecule, the attractive forces between atoms (chemical bonds) are balanced by repulsive forces between electrons and between nuclei. This balance of forces helps maintain the structure of the molecule and prevents it from easily breaking apart. The balanced forces contribute to the stability of molecules in a free state.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, molecules can exist in a free state because they are very stable. This stability is due to their stable electron configuration, strong chemical bonds, low potential energy, and balanced forces. These factors work together to maintain the integrity of the molecule and prevent it from easily dissociating into its constituent atoms.
Which of the following can be used to see atoms?- a)Scanning tunneling microscope
- b)Microscope
- c)Most powerful microscope
- d)Optical microscope
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following can be used to see atoms?
a)
Scanning tunneling microscope
b)
Microscope
c)
Most powerful microscope
d)
Optical microscope
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
A scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is an instrument for imaging surfaces at the atomic level. Its development in 1981 earned its inventors, Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer (at IBM Zrich), the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986. For an STM, good resolution is considered to be 0.1 nm lateral resolution and 0.01 nm (10 pm) depth resolution.With this resolution, individual atoms within materials are routinely imaged and manipulated. The STM can be used not only in ultra-high vacuum but also in air, water, and various other liquid or gas ambients, and at temperatures ranging from near zero kelvin to over 1000 DEGC.
Calculate the formula unit mass of ZnCl2?
- a)136.3 u
- b)124 u
- c)123 u
- d)111 u
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the formula unit mass of ZnCl2?
a)
136.3 u
b)
124 u
c)
123 u
d)
111 u

|
Kavya Nambiar answered |
Formula mass unit is calculatedin same way as molecular mass.
so,zncl2= 65.3+35.5 x 2
= 65.3+71
=136.3
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Which of the following is correct pair of elements and its symbol?
- A:
Silver – Si
- B:
Sodium – So
- C:
Potassium – Pt
- D:
Sulphur – S
The answer is d.
Which of the following is correct pair of elements and its symbol?
Silver – Si
Sodium – So
Potassium – Pt
Sulphur – S

|
Prachi Rathore answered |
Here are the righ pairs .......... ... silver-Ag ....... sodium-Na ...... potassium- K...... and sulphur - s so in the given options (D) sulphur - s. is right answer
9 grams of water decompose to give:- a)4g oxygen and 16g hydrogen
- b)2g hydrogen and 1g oxygen
- c)8g oxygen and 1g hydrogen
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
9 grams of water decompose to give:
a)
4g oxygen and 16g hydrogen
b)
2g hydrogen and 1g oxygen
c)
8g oxygen and 1g hydrogen
d)
none

|
Imk Pathshala answered |
The decomposition of water (H₂O) into its constituent gases yields 1 gram of hydrogen (H₂) and 8 grams of oxygen (O₂) from 9 grams of water, which aligns with the law of conservation of mass.
A student heats 25g of reactant ‘A’ with 50g of reactant ‘B’. He obtains 50g of product ‘C’ and recovers 25 g of unreacted ‘B’. Which of the following law is confirmed in the following reaction?- a)Law of constant proportion
- b)Law of conservation of mass
- c)Law of conservation of mass and Law of constant proportion
- d)Law of multiple proportion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A student heats 25g of reactant ‘A’ with 50g of reactant ‘B’. He obtains 50g of product ‘C’ and recovers 25 g of unreacted ‘B’. Which of the following law is confirmed in the following reaction?
a)
Law of constant proportion
b)
Law of conservation of mass
c)
Law of conservation of mass and Law of constant proportion
d)
Law of multiple proportion
|
|
Arvind Singh answered |
Two laws are followed in this question.
First law is Law of definite proportion as follows:
Here 25 g of reactant A reacts with 50 g of reactant B to produce 50 g of product C. That means 25 g of A consumes only 25 g of B. The ratio is 1:1. Even if there would have been say 75 g B is present, still only 25 g of B will react with 25 g of A. Or if 10 g of B is present then only 10 g of A will react and remaining 15 g of A will remain unreacted.
Second law is Law of conservation of mass as follows :
There is 25 g of A and 50 g of B. That means total 75 g of reactant is present. On product side 50 g of C and 25 g of unreacted B is present. That means total 75 g of product is present. Hence, the correct option will be " Law of conservation of mass and Law of constant proportion ".
The balancing of chemical equation is based upon:- a)Law of conservation of mass
- b)Law of multiple proportions
- c)Law of definite proportion
- d)Law of combining volumes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The balancing of chemical equation is based upon:
a)
Law of conservation of mass
b)
Law of multiple proportions
c)
Law of definite proportion
d)
Law of combining volumes

|
Nikhil Mehra answered |
A chemical equation consists of reactants, products and an arrow showing the direction of reaction. The equation in which number of atoms of all the molecules is equal on both sides of the equation is known as balanced chemical equation. Law of conservation of mass governs the balancing of a chemical equation.
If all the reactants in a chemical reaction are completely used, which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between the reactants and the products?- a)The reactants must contain more complex molecules than the products do.
- b)The products must have different physical state than the reactants.
- c)The total mass of the reactants must equal the total mass of the products.
- d)The density of the reactants must equal the density of the products.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If all the reactants in a chemical reaction are completely used, which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between the reactants and the products?
a)
The reactants must contain more complex molecules than the products do.
b)
The products must have different physical state than the reactants.
c)
The total mass of the reactants must equal the total mass of the products.
d)
The density of the reactants must equal the density of the products.
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
According to the Law of Conservation of mass, the total mass of the Reactants must equal the total mass of the products.
Which of the following is not a postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory?
- a)The number of atoms in a given compound is fixed.
- b)Atoms of the same elements cannot combine in more than one ratio to form more than one compound.
- c)Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed.
- d)Atoms cannot be divided.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory?
a)
The number of atoms in a given compound is fixed.
b)
Atoms of the same elements cannot combine in more than one ratio to form more than one compound.
c)
Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed.
d)
Atoms cannot be divided.
|
|
Nishi Kumari answered |
B is the correct answer
Which of the following statements is true about the law of conservation of mass?- a)In a chemical reaction, efforts should be made to preserve rare elements without changing them.
- b)In a chemical reaction, the final mass of the products is always greater than the starting mass of the reactants.
- c)In a chemical reaction, matter is not created or destroyed, but is conserved.
- d)Matter can be created and destroyed but does not change forms.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is true about the law of conservation of mass?
a)
In a chemical reaction, efforts should be made to preserve rare elements without changing them.
b)
In a chemical reaction, the final mass of the products is always greater than the starting mass of the reactants.
c)
In a chemical reaction, matter is not created or destroyed, but is conserved.
d)
Matter can be created and destroyed but does not change forms.
|
|
Himangshu Das answered |
Law of conservation of mass states that in a chemical reaction, matter is neither created nor destroyed as it is always conserved.
Hence the option 'c' is correct.
Hence the option 'c' is correct.
Which of the following statement is not in accordance with Dalton’s atomic theory?- a)All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms.
- b)Atoms can be divided into proton, neutron and electrons.
- c)Atoms of given element are identical in mass and chemical properties.
- d)Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is not in accordance with Dalton’s atomic theory?
a)
All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms.
b)
Atoms can be divided into proton, neutron and electrons.
c)
Atoms of given element are identical in mass and chemical properties.
d)
Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Dalton’s Atomic Theory was given by John Dalton.
According to this theory: -
(a) Matter is made up of invisible particles known as atoms.
(b) The properties of all the atoms of a given element are the same including mass.
(c) Atoms of different elements combine in fixed ratios to form compounds.
(d) Atoms are neither created nor destroyed.
(e) The formation of new products results from the rearrangements of existing atoms.
(f) Atoms of an element are identical in mass, size and properties.
According to this theory: -
(a) Matter is made up of invisible particles known as atoms.
(b) The properties of all the atoms of a given element are the same including mass.
(c) Atoms of different elements combine in fixed ratios to form compounds.
(d) Atoms are neither created nor destroyed.
(e) The formation of new products results from the rearrangements of existing atoms.
(f) Atoms of an element are identical in mass, size and properties.
Match the following with correct response. 
- a)1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
- b)1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A
- c)1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
- d)1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following with correct response.

a)
1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
b)
1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A
c)
1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
d)
1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C

|
Nk Classes answered |
The Law of Definite Proportions states that a compound always contains the same elements in certain fixed proportions by mass, regardless of its source or how it was prepared.
Law of conservation of mass can be derived from which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory?- a)Atoms of a given element have same mass and chemical properties.
- b)Matter is made of tiny particles.
- c)Atom can neither be created nor destroyed.
- d)The relative number and kind of atoms are constant in a given compound.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Law of conservation of mass can be derived from which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory?
a)
Atoms of a given element have same mass and chemical properties.
b)
Matter is made of tiny particles.
c)
Atom can neither be created nor destroyed.
d)
The relative number and kind of atoms are constant in a given compound.

|
Ankit Saha answered |
According to the law of conservation of mass, mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Which is not true about H2SO4?
A. It is composed of 2 Hydrogen, 1 Sulpher and 4 Oxygen atoms
B. It relative molecular mass is 98
C. It is composed of one molecule of H2 One atom S and two molecules O2
D. Its relative molecular mass is 108 - a)(c) and (d) are incorrect
- b)Only (d) is incorrect
- c)(a), (b) and (c) are incorrect
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is not true about H2SO4?
A. It is composed of 2 Hydrogen, 1 Sulpher and 4 Oxygen atoms
B. It relative molecular mass is 98
C. It is composed of one molecule of H2 One atom S and two molecules O2
D. Its relative molecular mass is 108
A. It is composed of 2 Hydrogen, 1 Sulpher and 4 Oxygen atoms
B. It relative molecular mass is 98
C. It is composed of one molecule of H2 One atom S and two molecules O2
D. Its relative molecular mass is 108
a)
(c) and (d) are incorrect
b)
Only (d) is incorrect
c)
(a), (b) and (c) are incorrect
d)
All of these

|
Dishani Sarkar answered |
Understanding Formula Mass of ZnO
To determine the formula mass of zinc oxide (ZnO), we must consider the atomic masses of its constituent elements: zinc (Zn) and oxygen (O).
Atomic Mass of Zinc (Zn)
- The atomic mass of zinc is approximately 65.38 u.
Atomic Mass of Oxygen (O)
- The atomic mass of oxygen is about 16.00 u.
Calculating the Formula Mass of ZnO
- To find the total formula mass of ZnO, add the atomic masses of zinc and oxygen together:
- Formula Mass = Atomic Mass of Zn + Atomic Mass of O
- Formula Mass = 65.38 u + 16.00 u
Summing the Values
- When you perform the addition, you get:
- Formula Mass = 81.38 u
- For simplicity in many contexts, this value is often rounded to 81 u.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the formula mass of ZnO is closest to 81 u, which corresponds to option 'B'. This is how we arrive at the correct answer for the formula mass of zinc oxide in chemistry.
To determine the formula mass of zinc oxide (ZnO), we must consider the atomic masses of its constituent elements: zinc (Zn) and oxygen (O).
Atomic Mass of Zinc (Zn)
- The atomic mass of zinc is approximately 65.38 u.
Atomic Mass of Oxygen (O)
- The atomic mass of oxygen is about 16.00 u.
Calculating the Formula Mass of ZnO
- To find the total formula mass of ZnO, add the atomic masses of zinc and oxygen together:
- Formula Mass = Atomic Mass of Zn + Atomic Mass of O
- Formula Mass = 65.38 u + 16.00 u
Summing the Values
- When you perform the addition, you get:
- Formula Mass = 81.38 u
- For simplicity in many contexts, this value is often rounded to 81 u.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the formula mass of ZnO is closest to 81 u, which corresponds to option 'B'. This is how we arrive at the correct answer for the formula mass of zinc oxide in chemistry.
An atom has atomic number 11. The number of protons are ________.- a)11
- b)12
- c)23
- d)44
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An atom has atomic number 11. The number of protons are ________.
a)
11
b)
12
c)
23
d)
44

|
Imk Pathshala answered |
- The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons in its nucleus.
- An atom with an atomic number of 11 has 11 protons.
- The correct answer is A: 11.
- An atom with an atomic number of 11 has 11 protons.
- The correct answer is A: 11.
A sample of CaCO3 conatins 3.01×1023 ions of Ca2+ and (CO3)2-.The mass of the sample is- a)100g
- b)5g
- c)200g
- d)50g
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A sample of CaCO3 conatins 3.01×1023 ions of Ca2+ and (CO3)2-.The mass of the sample is
a)
100g
b)
5g
c)
200g
d)
50g
|
|
Maheshwar Choudhary answered |
The mass of one mole of CaCO3 is equal to 100 g. one mole of is equal to 6.022 × 1023ions. Therefore, mass of 3.01×1023 ions = 50 g
What is the mass of 0.2 mole of lead nitrate? (N=14, O=16, Pb=207)- a)33.1 g
- b)3.31 g
- c)66.2 g
- d)6.62 g
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the mass of 0.2 mole of lead nitrate? (N=14, O=16, Pb=207)
a)
33.1 g
b)
3.31 g
c)
66.2 g
d)
6.62 g
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Gram Molecular weight of Pb(NO3)2
= 207 + (2 × 14) + 2 (16 × 3)
= 207 + 28 + 96
= 331
1 mole of Pb(NO3)2 is 331g
Therefore 0.2 mole of Pb(NO3)2 is 331 × 0.2
= 66.2 g
Match the following with correct response. 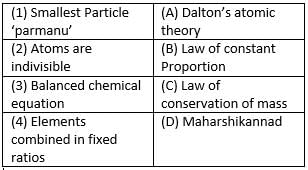
- a)1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
- b)1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
- c)1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
- d)1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following with correct response.

a)
1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
b)
1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
c)
1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
d)
1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A

|
Amrit Raj answered |
Please read ncert ch atoms introduction
Which of the following is correct for the ‘Law of Conservation of Mass’?- a)Mass can neither be created nor destroyed.
- b)The rate of reaction is directly proportional to the active mass of the reactants.
- c)Mass can either be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- d)The elements are always present in a constant proportion in a chemical substance
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is correct for the ‘Law of Conservation of Mass’?
a)
Mass can neither be created nor destroyed.
b)
The rate of reaction is directly proportional to the active mass of the reactants.
c)
Mass can either be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
d)
The elements are always present in a constant proportion in a chemical substance
|
|
Himaja Ammu answered |
Law of conservation of mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction....
It was proposed by Antoine lavoisier but experimentally proved by landolt
It was proposed by Antoine lavoisier but experimentally proved by landolt
The atomic number of an element X is 13. What will be the number of electrons in its ion X3+?- a)11
- b)16
- c)15
- d)10
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The atomic number of an element X is 13. What will be the number of electrons in its ion X3+?
a)
11
b)
16
c)
15
d)
10
|
|
Sarika Singh answered |
Atomic Number and Number of Electrons
The atomic number of an element represents the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element. Since atoms are electrically neutral, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons orbiting the nucleus.
Ion Formation
An ion is formed when an atom gains or loses electrons. If an atom gains electrons, it becomes negatively charged and is called an anion. If an atom loses electrons, it becomes positively charged and is called a cation.
Determining the Number of Electrons in an Ion
To determine the number of electrons in an ion, we need to know the charge of the ion. The charge of an ion is indicated by a superscript after the element symbol. For example, X3 indicates that the ion has a charge of +3.
Calculation
In this case, the element X has an atomic number of 13. This means it has 13 protons and 13 electrons in its neutral state. The ion X3 has a charge of +3, indicating that it has lost 3 electrons.
To find the number of electrons in the ion X3, we subtract the charge of the ion from the number of electrons in the neutral atom.
Number of electrons in ion X3 = Number of electrons in neutral atom - Charge of ion
Number of electrons in ion X3 = 13 electrons - 3 electrons
Number of electrons in ion X3 = 10 electrons
Therefore, the correct answer is option D) 10. The ion X3 has 10 electrons.
The atomic number of an element represents the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element. Since atoms are electrically neutral, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons orbiting the nucleus.
Ion Formation
An ion is formed when an atom gains or loses electrons. If an atom gains electrons, it becomes negatively charged and is called an anion. If an atom loses electrons, it becomes positively charged and is called a cation.
Determining the Number of Electrons in an Ion
To determine the number of electrons in an ion, we need to know the charge of the ion. The charge of an ion is indicated by a superscript after the element symbol. For example, X3 indicates that the ion has a charge of +3.
Calculation
In this case, the element X has an atomic number of 13. This means it has 13 protons and 13 electrons in its neutral state. The ion X3 has a charge of +3, indicating that it has lost 3 electrons.
To find the number of electrons in the ion X3, we subtract the charge of the ion from the number of electrons in the neutral atom.
Number of electrons in ion X3 = Number of electrons in neutral atom - Charge of ion
Number of electrons in ion X3 = 13 electrons - 3 electrons
Number of electrons in ion X3 = 10 electrons
Therefore, the correct answer is option D) 10. The ion X3 has 10 electrons.
The formula of a compound is X3Y. The valencies of elements X and Y will be, respectively- a)1 and 3
- b)3 and 1
- c)2 and 3
- d)3 and 2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The formula of a compound is X3Y. The valencies of elements X and Y will be, respectively
a)
1 and 3
b)
3 and 1
c)
2 and 3
d)
3 and 2

|
Harsh Datta answered |
Explanation:
When we are given the formula of a compound, X3Y, we can determine the valencies of elements X and Y by analyzing the subscript numbers.
The subscript number after element X is 3, which indicates that there are three atoms of element X present in the compound. Similarly, the subscript number after element Y is 1, which indicates that there is only one atom of element Y present in the compound.
From this information, we can determine the valencies of elements X and Y.
Valency of element X:
The valency of an element is defined as the combining capacity of an element with other elements. In this case, since there are three atoms of element X present in the compound, we can determine the valency of X as follows:
Valency of X = Total number of electrons in the outermost shell of X - Number of electrons required to complete its octet
To determine the total number of electrons in the outermost shell of X, we need to know the electronic configuration of X. Since the question does not provide this information, we cannot determine the exact valency of X. However, based on the given options, option A (1 and 3) is the most likely answer.
Valency of element Y:
Since there is only one atom of element Y present in the compound, we can determine the valency of Y as follows:
Valency of Y = Total number of electrons in the outermost shell of Y - Number of electrons required to complete its octet
Similar to element X, we need to know the electronic configuration of Y to determine its valency accurately. However, based on the given options, option A (1 and 3) is the most likely answer.
Therefore, based on the given formula X3Y, the valencies of elements X and Y are most likely 1 and 3, respectively.
When we are given the formula of a compound, X3Y, we can determine the valencies of elements X and Y by analyzing the subscript numbers.
The subscript number after element X is 3, which indicates that there are three atoms of element X present in the compound. Similarly, the subscript number after element Y is 1, which indicates that there is only one atom of element Y present in the compound.
From this information, we can determine the valencies of elements X and Y.
Valency of element X:
The valency of an element is defined as the combining capacity of an element with other elements. In this case, since there are three atoms of element X present in the compound, we can determine the valency of X as follows:
Valency of X = Total number of electrons in the outermost shell of X - Number of electrons required to complete its octet
To determine the total number of electrons in the outermost shell of X, we need to know the electronic configuration of X. Since the question does not provide this information, we cannot determine the exact valency of X. However, based on the given options, option A (1 and 3) is the most likely answer.
Valency of element Y:
Since there is only one atom of element Y present in the compound, we can determine the valency of Y as follows:
Valency of Y = Total number of electrons in the outermost shell of Y - Number of electrons required to complete its octet
Similar to element X, we need to know the electronic configuration of Y to determine its valency accurately. However, based on the given options, option A (1 and 3) is the most likely answer.
Therefore, based on the given formula X3Y, the valencies of elements X and Y are most likely 1 and 3, respectively.
The atoms of which of the following pair of elements are most likely to exist in free state?- a)Hydrogen and helium
- b)Helium and neon
- c)Argon and carbon
- d)Neon and nitrogen
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The atoms of which of the following pair of elements are most likely to exist in free state?
a)
Hydrogen and helium
b)
Helium and neon
c)
Argon and carbon
d)
Neon and nitrogen
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
The atoms of which are most likely to exist in free state are Helium and neon being inert gases having octet filled.
How many litres of ammonia are present in 3.4 kg of it? (N = 14, H = 1)- a)22.4 litres
- b)44.8 litres
- c)4480 litres
- d)2240 litres
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many litres of ammonia are present in 3.4 kg of it? (N = 14, H = 1)
a)
22.4 litres
b)
44.8 litres
c)
4480 litres
d)
2240 litres
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
Gram molecular weight of NH3 = 14 + (1 × 3) = 17 g
17 g of NH3= 22.4 litres
∴ 3.4 × 103g of NH = 22.4/17 × 3.4 × 103
= 76160/17 = 4480 litres
The anion of an element has- a)Less electrons than the normal atom
- b)More electrons than the normal atom
- c)More protons than the normal atom
- d)Same number of electrons as normal atom
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The anion of an element has
a)
Less electrons than the normal atom
b)
More electrons than the normal atom
c)
More protons than the normal atom
d)
Same number of electrons as normal atom
|
|
Sravya Chauhan answered |
The anion of an element has more electrons than the normal atom.
An atom is made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons carry a positive charge, neutrons carry no charge, and electrons carry a negative charge. The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number and identifies the element.
An atom is considered neutral when the number of protons and electrons is equal. In this state, the positive charge of the protons cancels out the negative charge of the electrons, resulting in a net charge of zero. However, when an atom gains or loses electrons, it becomes an ion.
Anions:
An anion is a negatively charged ion formed when an atom gains one or more electrons. When an atom gains electrons, its negative charge increases. This results in the formation of an anion with more electrons than the normal atom. The extra electrons are attracted to the positively charged protons in the atom's nucleus, creating a net negative charge.
For example, let's consider the element chlorine (Cl) which has an atomic number of 17, meaning it has 17 protons and 17 electrons in its neutral state. However, when chlorine gains one electron, it becomes a chloride ion (Cl-). In this ion, there are now 18 electrons (one more than the normal atom) and 17 protons. The extra electron gives the ion a net negative charge.
Key Points:
- An anion is a negatively charged ion.
- Anions are formed when atoms gain one or more electrons.
- The extra electrons in an anion give it a negative charge.
- Anions have more electrons than the normal atom.
- The number of protons in an anion remains the same as the normal atom.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B': Anions have more electrons than the normal atom.
An atom is made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons carry a positive charge, neutrons carry no charge, and electrons carry a negative charge. The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number and identifies the element.
An atom is considered neutral when the number of protons and electrons is equal. In this state, the positive charge of the protons cancels out the negative charge of the electrons, resulting in a net charge of zero. However, when an atom gains or loses electrons, it becomes an ion.
Anions:
An anion is a negatively charged ion formed when an atom gains one or more electrons. When an atom gains electrons, its negative charge increases. This results in the formation of an anion with more electrons than the normal atom. The extra electrons are attracted to the positively charged protons in the atom's nucleus, creating a net negative charge.
For example, let's consider the element chlorine (Cl) which has an atomic number of 17, meaning it has 17 protons and 17 electrons in its neutral state. However, when chlorine gains one electron, it becomes a chloride ion (Cl-). In this ion, there are now 18 electrons (one more than the normal atom) and 17 protons. The extra electron gives the ion a net negative charge.
Key Points:
- An anion is a negatively charged ion.
- Anions are formed when atoms gain one or more electrons.
- The extra electrons in an anion give it a negative charge.
- Anions have more electrons than the normal atom.
- The number of protons in an anion remains the same as the normal atom.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B': Anions have more electrons than the normal atom.
Which postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory gives laws of conservation of mass- a)Atom can neither be created nor be destroyed
- b)Atoms of same elements are similar
- c)Atoms of different elements are different
- d)Atom combine in fixed ratio to form compound
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory gives laws of conservation of mass
a)
Atom can neither be created nor be destroyed
b)
Atoms of same elements are similar
c)
Atoms of different elements are different
d)
Atom combine in fixed ratio to form compound
|
|
Nandini Ahuja answered |
Dalton’s Atomic Theory and the Law of Conservation of Mass
Dalton’s atomic theory was proposed by John Dalton in the early 19th century and it laid the foundation for modern atomic theory. It consisted of several postulates that explained the behavior and properties of atoms. One of these postulates is the idea that atoms can neither be created nor destroyed, which is closely related to the law of conservation of mass.
Explanation of the Law of Conservation of Mass
The law of conservation of mass states that in a chemical reaction, matter is neither created nor destroyed. This means that the total mass of the reactants must be equal to the total mass of the products. In other words, the total amount of mass before a chemical reaction is the same as the total amount of mass after the reaction. This principle was first stated by Antoine Lavoisier in the late 18th century and is a fundamental concept in chemistry.
Dalton’s Postulate and the Law of Conservation of Mass
Dalton’s atomic theory included the postulate that atoms can neither be created nor destroyed. This postulate is in line with the law of conservation of mass. If atoms could be created or destroyed, then the total mass before and after a reaction would not be conserved.
When a chemical reaction occurs, the atoms of the reactants rearrange to form new compounds. However, the total number of atoms of each element remains constant. This means that the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products.
Example
Let's consider the reaction between hydrogen gas (H2) and oxygen gas (O2) to form water (H2O). According to the law of conservation of mass, the total mass of hydrogen and oxygen before the reaction should be equal to the total mass of water formed.
Before the reaction:
2 moles of H2 (2 x 2g/mol = 4g)
1 mole of O2 (1 x 32g/mol = 32g)
Total mass = 36g
After the reaction:
2 moles of H2O (2 x 18g/mol = 36g)
Total mass = 36g
As we can see, the total mass before and after the reaction is the same, confirming the law of conservation of mass. This example illustrates how Dalton’s postulate that atoms can neither be created nor destroyed is consistent with the law of conservation of mass.
Conclusion
The postulate of Dalton's atomic theory that atoms can neither be created nor destroyed aligns with the law of conservation of mass. This principle states that in a chemical reaction, the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products. By adhering to this postulate, Dalton's theory provides a foundation for understanding the behavior of atoms and the conservation of mass in chemical reactions.
Dalton’s atomic theory was proposed by John Dalton in the early 19th century and it laid the foundation for modern atomic theory. It consisted of several postulates that explained the behavior and properties of atoms. One of these postulates is the idea that atoms can neither be created nor destroyed, which is closely related to the law of conservation of mass.
Explanation of the Law of Conservation of Mass
The law of conservation of mass states that in a chemical reaction, matter is neither created nor destroyed. This means that the total mass of the reactants must be equal to the total mass of the products. In other words, the total amount of mass before a chemical reaction is the same as the total amount of mass after the reaction. This principle was first stated by Antoine Lavoisier in the late 18th century and is a fundamental concept in chemistry.
Dalton’s Postulate and the Law of Conservation of Mass
Dalton’s atomic theory included the postulate that atoms can neither be created nor destroyed. This postulate is in line with the law of conservation of mass. If atoms could be created or destroyed, then the total mass before and after a reaction would not be conserved.
When a chemical reaction occurs, the atoms of the reactants rearrange to form new compounds. However, the total number of atoms of each element remains constant. This means that the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products.
Example
Let's consider the reaction between hydrogen gas (H2) and oxygen gas (O2) to form water (H2O). According to the law of conservation of mass, the total mass of hydrogen and oxygen before the reaction should be equal to the total mass of water formed.
Before the reaction:
2 moles of H2 (2 x 2g/mol = 4g)
1 mole of O2 (1 x 32g/mol = 32g)
Total mass = 36g
After the reaction:
2 moles of H2O (2 x 18g/mol = 36g)
Total mass = 36g
As we can see, the total mass before and after the reaction is the same, confirming the law of conservation of mass. This example illustrates how Dalton’s postulate that atoms can neither be created nor destroyed is consistent with the law of conservation of mass.
Conclusion
The postulate of Dalton's atomic theory that atoms can neither be created nor destroyed aligns with the law of conservation of mass. This principle states that in a chemical reaction, the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products. By adhering to this postulate, Dalton's theory provides a foundation for understanding the behavior of atoms and the conservation of mass in chemical reactions.
Which of the following is the correct IUPAC symbol for the element Cobalt?- a)Co
- b)Cb
- c)C
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct IUPAC symbol for the element Cobalt?
a)
Co
b)
Cb
c)
C
d)
none of these
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
The wrong thing in writing cobalt as CO is that we can't write o as O because O represent Oxygen and symbols representing an element with two letters have first one as capital and next one should be in small letter.
Therefore we should always write cobalt as..Co not CO!
If the number of electrons in an ion Z3– is 10, the atomic number of element Z will be- a)7
- b)5
- c)10
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the number of electrons in an ion Z3– is 10, the atomic number of element Z will be
a)
7
b)
5
c)
10
d)
8
|
|
Niyati Shah answered |
Explanation:
An ion is formed when an atom gains or loses electrons. In the case of the ion Z3–, the negative superscript indicates that the ion has gained 3 extra electrons.
To determine the atomic number of element Z, we need to find the number of protons in the nucleus, which is equal to the atomic number.
Step 1: Find the number of electrons in the neutral atom
Since the ion Z3– has gained 3 extra electrons, the number of electrons in the neutral atom is 10 - 3 = 7.
Step 2: Identify the atomic number
The atomic number represents the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. In a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons. Therefore, the atomic number of element Z is 7, which is option A.
Summary:
In the ion Z3–, the number of electrons is 10. To find the atomic number of element Z, we subtract the number of extra electrons from the total number of electrons. In this case, the atomic number is 7, which corresponds to option A.
An ion is formed when an atom gains or loses electrons. In the case of the ion Z3–, the negative superscript indicates that the ion has gained 3 extra electrons.
To determine the atomic number of element Z, we need to find the number of protons in the nucleus, which is equal to the atomic number.
Step 1: Find the number of electrons in the neutral atom
Since the ion Z3– has gained 3 extra electrons, the number of electrons in the neutral atom is 10 - 3 = 7.
Step 2: Identify the atomic number
The atomic number represents the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. In a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons. Therefore, the atomic number of element Z is 7, which is option A.
Summary:
In the ion Z3–, the number of electrons is 10. To find the atomic number of element Z, we subtract the number of extra electrons from the total number of electrons. In this case, the atomic number is 7, which corresponds to option A.
A particle P has 18 electrons, 20 neutrons and 19 protons. This particle must be- a)A molecule
- b)A cation
- c)An anion
- d)A binary compound
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle P has 18 electrons, 20 neutrons and 19 protons. This particle must be
a)
A molecule
b)
A cation
c)
An anion
d)
A binary compound
|
|
Shilpa Choudhury answered |
No. of electron = No. of proton but in this case electron is less than proton. In cation also less
electrons are present than a neutral atom.
Which is the smallest particle of an element that can take part in a chemical reaction?- a)Molecule
- b)Mixture
- c)Compound
- d)Atom
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the smallest particle of an element that can take part in a chemical reaction?
a)
Molecule
b)
Mixture
c)
Compound
d)
Atom
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
An atom can be defined as the smallest particle of an element, which can take part in chemical change or reaction and still retain the identity of the element. Notice that the atom is not the smallest particle of an element, as there are electrons, protons and neutrons which are smaller, but, it is the smallest which can be involved in chemical change and still retain the chemical properties of the element.
Certain mass of carbon burns with a given mass of oxygen to form certain mass of carbon mass of carbon dioxide, which law of chemical combination is used in this process of formation of compound- a)Law of conservation of mass
- b)Law of constant proportion
- c)Law of multiple proportion
- d)Gay Lussac’s law
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Certain mass of carbon burns with a given mass of oxygen to form certain mass of carbon mass of carbon dioxide, which law of chemical combination is used in this process of formation of compound
a)
Law of conservation of mass
b)
Law of constant proportion
c)
Law of multiple proportion
d)
Gay Lussac’s law
|
|
Abhishek Rane answered |
The correct answer is option 'B', the Law of constant proportion.
The Law of constant proportion, also known as the Law of definite proportions, states that a given compound always contains the same elements in the same proportion by mass. This means that no matter how the compound is formed, the ratio of the masses of the elements in the compound will always be the same.
When carbon burns with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, the Law of constant proportion is followed because the mass ratio of carbon to oxygen to carbon dioxide remains constant.
Let's break down the process and see how the Law of constant proportion applies:
1. Carbon burns with oxygen:
In this step, carbon reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide. The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
C + O2 → CO2
2. Mass of carbon:
Let's assume that a certain mass of carbon is burned. The mass of carbon is constant and does not change during the reaction.
3. Mass of oxygen:
To completely react with the given mass of carbon, a specific mass of oxygen is required. The ratio of the mass of oxygen to carbon is fixed and determined by the stoichiometry of the balanced equation.
4. Formation of carbon dioxide:
The carbon and oxygen react to form carbon dioxide. The mass of carbon dioxide formed is determined by the Law of constant proportion. The ratio of the masses of carbon and oxygen in the carbon dioxide is always constant, regardless of the mass of carbon burned.
In conclusion, the Law of constant proportion is used in the formation of carbon dioxide from the burning of carbon with oxygen because the masses of carbon and oxygen combine in a fixed ratio to form carbon dioxide, as stated by the Law of constant proportion.
The Law of constant proportion, also known as the Law of definite proportions, states that a given compound always contains the same elements in the same proportion by mass. This means that no matter how the compound is formed, the ratio of the masses of the elements in the compound will always be the same.
When carbon burns with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, the Law of constant proportion is followed because the mass ratio of carbon to oxygen to carbon dioxide remains constant.
Let's break down the process and see how the Law of constant proportion applies:
1. Carbon burns with oxygen:
In this step, carbon reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide. The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
C + O2 → CO2
2. Mass of carbon:
Let's assume that a certain mass of carbon is burned. The mass of carbon is constant and does not change during the reaction.
3. Mass of oxygen:
To completely react with the given mass of carbon, a specific mass of oxygen is required. The ratio of the mass of oxygen to carbon is fixed and determined by the stoichiometry of the balanced equation.
4. Formation of carbon dioxide:
The carbon and oxygen react to form carbon dioxide. The mass of carbon dioxide formed is determined by the Law of constant proportion. The ratio of the masses of carbon and oxygen in the carbon dioxide is always constant, regardless of the mass of carbon burned.
In conclusion, the Law of constant proportion is used in the formation of carbon dioxide from the burning of carbon with oxygen because the masses of carbon and oxygen combine in a fixed ratio to form carbon dioxide, as stated by the Law of constant proportion.
Which of the following is the correct pair of atom and its atomic symbol?- a)Sulphur – Su
- b)Potassium – P
- c)Phosphorus -P
- d)Sodium- S
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct pair of atom and its atomic symbol?
a)
Sulphur – Su
b)
Potassium – P
c)
Phosphorus -P
d)
Sodium- S

|
EduRev Class 9 answered |
Ans: (c)
Solution: The correct pair of atom and its atomic symbol is Phosphorus -P
Match the following with correct response. 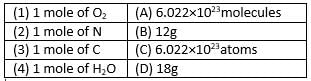
- a)1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
- b)1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
- c)1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
- d)1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following with correct response.

a)
1-D, 2-A, 3-C, 4-B
b)
1-A, 2-C, 3-B, 4-D
c)
1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C
d)
1-C, 2-B, 3-D, 4-A

|
Imk Pathshala answered |
Molecular mass is the sum of the atomic masses of all atoms in a molecule, compared to the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
Chapter doubts & questions for Atoms and Molecules - Science Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Atoms and Molecules - Science Class 9 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Science Class 9
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily










