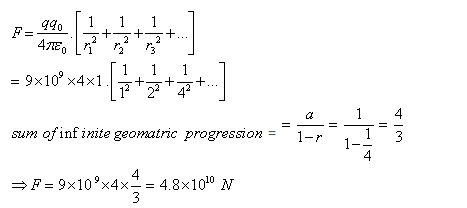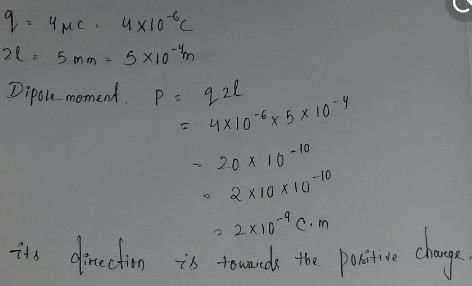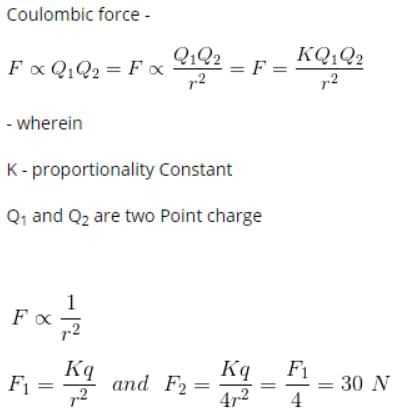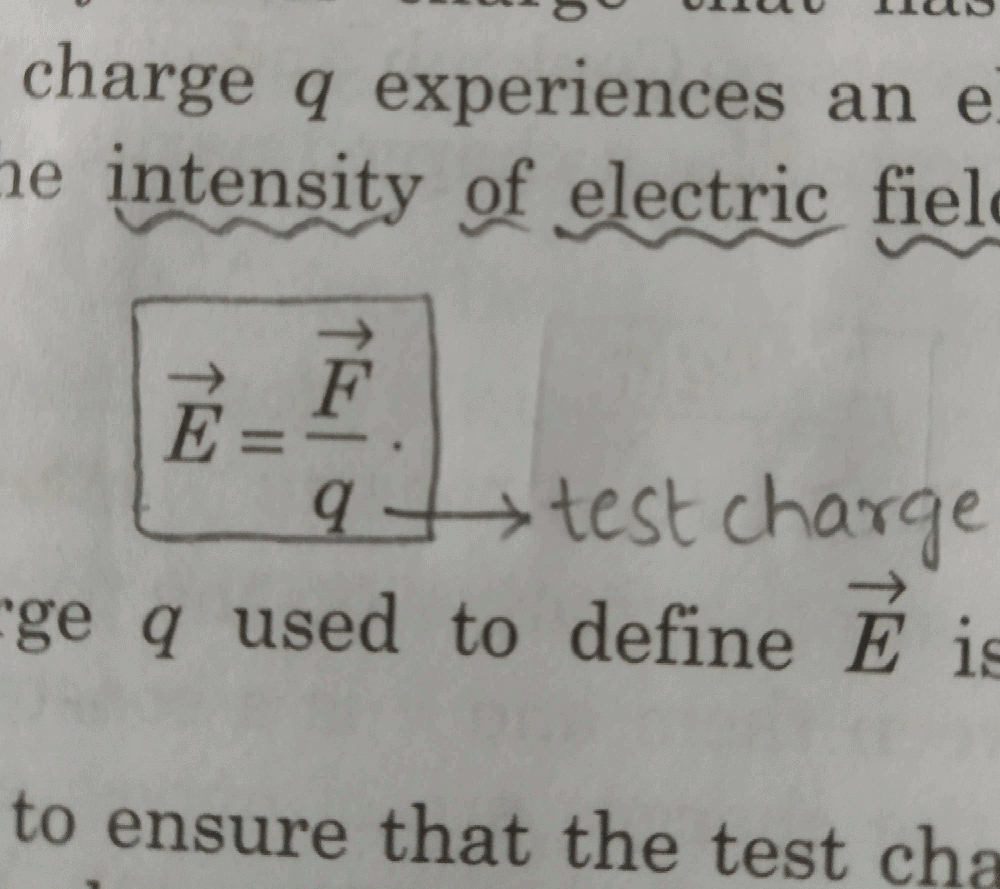All questions of Electric Charges and Fields for JEE Exam
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Charging a metal sphere by contact using a positively charged rod, followed by grounding can result in ________ charge in a metal sphere.
- A:
positive
- B:
Zero
- C:
positive or negative depending on which end is grounded
- D:
negative
The answer is b.
Charging a metal sphere by contact using a positively charged rod, followed by grounding can result in ________ charge in a metal sphere.
positive
Zero
positive or negative depending on which end is grounded
negative
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A charge q is placed at the centre of the open end of cylindrical vessel whose height is equal to its radius. The electric flux of electric field of charge q through the surface of the vessel is- A:0
- B:
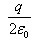
- C:
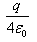
- D:
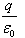
The answer is b.
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
so, when charge Q is placed at the centre of open end of a cylindrical vessel then only half of the charge will contribute to the flux, because half will lie inside the surface and half will lie outside the surface.
so, flux through the surface of vessel is q/2ε0
A uniform line charge with linear density λ lies along the y-axis. What flux crosses a spherical surface centred at the origin with r = R
- a)Rλ/ε0
- b)2Rλ/ε0
- c)λ/ε0
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
If the electric field is given by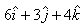 ; calculate the electric flux through as surface of area 10 units lying in y-z plane.
; calculate the electric flux through as surface of area 10 units lying in y-z plane.- a)50 units
- b)40 units
- c)60 units
- d)30 units
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
EduRev JEE answered |
Electric flux ϕ=E.A
∴ ϕ=(6i+3j+4k).(10i)
⟹ ϕ=6×10=60 unit
The force between two small charged spheres having charges 3 x 10-6C and 4 x 10-6C placed 40 cm apart in air is- a)67.5 x 10-3 N
- b)67.5 x 10-2 N
- c)6.75 x 10-1 N
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Siddharth Tiwari answered |
When two charges are placed in close proximity to each other, they exert a force on each other. This force is known as the electrostatic force. The electrostatic force between two charges is governed by Coulomb's Law, which states that the force is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
In this case, we have a positive charge of 1C and a negative charge of -4C. According to Coulomb's Law, the force between these two charges will be attractive because one charge is positive and the other is negative. The force will act along the line connecting the two charges, from the positive charge to the negative charge.
To determine the direction of the force, we can use a simple mnemonic: "like charges repel, opposite charges attract." Since the charges in this scenario are opposite (positive and negative), they will attract each other. Therefore, the force will act from the positive charge (1C) towards the negative charge (-4C).
Hence, the correct answer is option C: "From 1C to -4C."
A negative point charge placed at the point A is 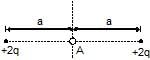
- a) In stable equilibrium along x-axis
- b)In unstable equilibrium along y-axis
- c)in stable equilibrium along y-axis
- d)in unstable equilibrium along x-axis
Correct answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
EduRev Support answered |
As along y direction no electric field, potential energy is minimum and it will be stable equilibrium along y-axis.
Along x-axis potential energy is maximum due to all charges situated along x-axis.so it will be unstable equilibrium.
Two insulated charged copper spheres A and B have their centers separated by a distance of 50 cm. What is the mutual force of electrostatic repulsion if the charge on each is 6.5×10−7 C? The radii of A and B are negligible compared to the distance of separation.- a)4.5×10−2N
- b)2.5×10−2 N
- c)1.5×10−2 N
- d)3.5×10−2 N
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Om Desai answered |

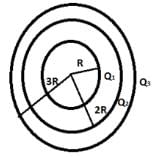
Three concentric metallic spherical shells of radii R, 2R, 3R, are given charges Q1, Q2, Q3, respectively. It is found that the surface charge densities on the outer surfaces of the shells are equal. Then, the ratio of the charges given to the shells, Q1: Q2: Q3, is - a)it is 1:03:05
- b)it is 1:02:03
- c)it is 1:04:09
- d)it is 1:08:18
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Sanaya Kumar answered |
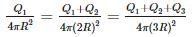
A particle of mass m and charge Q is placed in an electric field E which varies with time t ass E = E0 sinwt. It will undergo simple harmonic motion of amplitude- a)
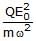
- b)
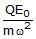
- c)
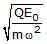
- d)
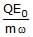
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
F=QE=QE0sinωt
at maximum amplitude A, it experience a maximum force of:-
Fmax=QE0
also, Restoring force in SHM is given by: - F=mω2x
for amplitude, x=A OR,
mω2A=QE0
⇒A= QE0/mω2
Electric flux density is a function of _______.
- a)Volume
- b)Charge
- c)Current
- d)Voltage
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Aarya Khanna answered |
Factors affecting electric flux density:
Charge:
Electric flux density is directly proportional to the amount of charge present in a given area. The higher the charge density, the higher the electric flux density.
Area:
Electric flux density is inversely proportional to the area of the surface through which the flux passes. The smaller the area, the higher the electric flux density.
Distance:
Electric flux density is inversely proportional to the distance of the charge from the surface through which the flux passes. The closer the charge, the higher the electric flux density.
Dielectric constant:
Electric flux density is affected by the dielectric constant of the material through which the flux passes. The higher the dielectric constant, the higher the electric flux density.
Conclusion:
From the above explanation, it is clear that electric flux density is a function of charge.
Which of the following molecule has permanent dipole moment?- a)HCl
- b)CO2
- c)CH4
- d)BF3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Manoj Chauhan answered |
A permanent dipole moment is created when there is an electronegativity difference between two non-identical atoms, resulting in an uneven distribution of charge. The molecule acquires a positive and negative end, creating a dipole moment.
HCl molecule has a permanent dipole moment because of the difference in electronegativity between H and Cl atoms. Chlorine has a higher electronegativity than hydrogen. Therefore, the electrons in the covalent bond are drawn closer to the chlorine atom, resulting in a partial negative charge on the chlorine atom and a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom. Thus, HCl has a dipole moment.
On the other hand, CO2, CH4, and BF3 do not have a permanent dipole moment because they are symmetrical molecules where the electronegativity of the atoms is the same. In CO2, the electronegativity of the carbon and oxygen atoms is the same, so the molecule has no dipole moment. In CH4, the four hydrogen atoms are arranged symmetrically around the carbon atom, resulting in no net dipole moment. Similarly, in BF3, the three fluorine atoms are arranged symmetrically around the boron atom, resulting in no net dipole moment.
Therefore, the correct option is A, HCl, which has a permanent dipole moment due to the difference in electronegativity between H and Cl atoms.
Two charges 4q and q are placed 30 cm. apart. At what point the value of electric field will be zero- a)10 cm. away from q and between the charge
- b)10 cm. away from 4q and out side the line joining them.
- c)20 cm. away from 4q and between the charge
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
it is the point where electric field of both charge is same
we know tha t E=kQ/r^2
here k=1/4pi€
for 4q charge
let at ''a'' distance we get E=0 which is from q charge
so distance from 4q of 'a' point is 30-a
electric field by 4q charge on a is
E=k4q/(30-a)^2
electric field by q charge on a point
E=kq/a^2
both electric field are equal so put them equal
k4q/(30-a)^2=kq/a^2
solve this we get
4a^2=(30-a)^2
2a=30-a
3a=30
a=10
so at a distance 10cm from charge q we get E=0
distance from 4q charge 30-10=20cm.
A uniform line charge with linear density λ lies along the y-axis. What flux crosses a spherical surface cantered at the origin with r = R- a)2Rλ/ε0
- b)Rλ/ε0
- c)λ/ε0
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Neha Chauhan answered |
∫E.dS = qin/ε0
So flux = 2Rλ/ε0
Hence answer is (a)
The diagram shows the electric field lines in a region of space containing two small charged spheres, Y and Z then which statement is true?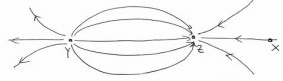
- a)Magnitude of electric field is same everywhere
- b)Y is negative & Z is positive
- c)Y and Z must have the same sign
- d)A small negatively charged body placed at X would be pushed to the right
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Divey Sethi answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:At what point is the electric field intensity due to a uniformly charged spherical shell is maximum?
- A:
at the surface of spherical shell
- B:
outside the spherical shell
- C:
inside the spherical shell
- D:
at the centre of spherical shell
The answer is a.
At what point is the electric field intensity due to a uniformly charged spherical shell is maximum?
at the surface of spherical shell
outside the spherical shell
inside the spherical shell
at the centre of spherical shell

|
Bittu Raj Bittu answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The electric field intensity due to a sphere (solid or hollow) at an external point varies as-
- A:
1/r
- B:
does not depend upon r
- C:
1/r3
- D:
1/r2
The answer is d.
The electric field intensity due to a sphere (solid or hollow) at an external point varies as-
1/r
does not depend upon r
1/r3
1/r2
|
|
Agnal Jose answered |
Electric field of a point charge extends up to r where 1/r is- a)one
- b)infinity
- c)Zero
- d)two
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Sherlin Dsouza answered |
A neutral point lies at the centre of the line joining the charges when- a)Two charges are unequal and opposite
- b)Two charges are equal and of same sign
- c)Two charges are unequal and of same sign
- d)Two charges are equal and of opposite sign
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
A certain charge Q is divided at first into two parts, (q) and (Q-q). Later on the charges are placed at a certain distance. If the force of interaction between the two charges is maximum then- a)(Q/q) = (4/1)
- b)(Q/q) = (2/1)
- c)(Q/q) = (3/1)
- d)(Q/q) = (5/1)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Om Desai answered |
F = kq(Q-q)/r²
As it is given that force between these two is Maximum....so it will be max. when dF/dq is zero
i.e, dF/dq = {k(Q-2q)}/r² = 0
so, Q = 2q
Q/q = 2/1
If an excess charge is placed on an isolated conductor, then, that amount of charge- a)gets neutralized.
- b)resides on the surface of conductor.
- c)either resides on the surface of conductor or gets neutralized.
- d)move inside the conductor
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
Ratio of the permittivity of medium to the permittivity of free space is known as
- a)Dielectric ratio
- b)Dielectric permittivity
- c)Dielectric constant
- d)Dielectric medium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:What will be the value of a charge q, such that when it is placed at the centre of two equal and like charges Q, the three charges are in equilibrium.
- A:
+Q/4
- B:
Q
- C:
-Q/4
- D:
Q/2
The answer is c.
What will be the value of a charge q, such that when it is placed at the centre of two equal and like charges Q, the three charges are in equilibrium.
+Q/4
Q
-Q/4
Q/2

|
Aiims New Delhi answered |
If the electric field is given by 6i+3j+4k calculate the electric flux through a surface of area 20 units lying in y-z plane.- a)12 units
- b)120 units
- c)260 units
- d)60 units
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
The field lines for single negative charge are:- a)Radiating outwards
- b)Radiated inwards
- c)Parallel
- d)Spheres concentric with charge
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Preethi Rajaneekanth answered |
Which one of the following statement regarding electrostatics is wrong ?- a)Charge is quantized
- b)Charge is conserved
- c)There is an electric field near an isolated charge at rest
- d)A stationary charge produces both electric and magnetic fields
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Nandita Ahuja answered |
Electrostatics is the study of electric charges at rest. It deals with the electric forces between charges, the electric field and potential, and the distribution of charges on conductors.
a) Charge is quantized:
The charge on a body or a particle is always a multiple of the elementary charge (1.6 × 10^-19 C). This means that charge is quantized, and we cannot have a fraction of an elementary charge. This is known as the law of conservation of charge.
b) Charge is conserved:
The total charge in a closed system is always conserved. This means that the net charge of a system cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transferred from one object to another.
c) There is an electric field near an isolated charge at rest:
An isolated charged object creates an electric field around it. This electric field is a vector field that exerts a force on other charged objects in the vicinity of the charged object. The electric field is proportional to the charge and inversely proportional to the distance from the charged object.
d) A stationary charge produces both electric and magnetic fields:
This statement is incorrect. A stationary charge produces only an electric field, not a magnetic field. However, a moving charge produces both electric and magnetic fields.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct option is (d), which is wrong.
The Gaussian surface for a point charge will be- a)Cube
- b)Cylinder
- c)Sphere
- d)Cuboid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
If electric field lines cross each other that would mean- a)the electric field can be in either of the two directions.
- b)the direction of the field changes at that point
- c)two directions for the electric field at one point which is not possible.
- d)the resultant electric field at a point is zero
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Tim Tim answered |
The linear charge densities of two infinitely long thin and parallel wires are 4Cm−1, 8Cm−1 and separation between them is 4 cm. Then the electric field intensity at mid point on the line joining them is- a)18 × 1011 NC−1
- b)36 × 1011NC−1
- c)9 × 1011NC−1
- d)72 × 1011 NC−1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Electric field due to an infinitely long wire:
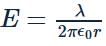
Calculate Electric Fields:
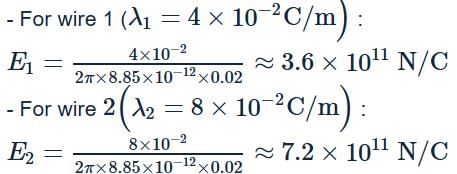
Net Electric Field at Midpoint:
- Since the fields are in opposite directions, the net field is:
E = E2 − E1 = 7.2 × 1011−3.6 × 1011 = 3.6 × 1011 N/C
In SI units, a unit of charge is called a- a)ampere
- b)milli coulomb
- c)milli ampere
- d)Coulomb
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
In space of horizontal EF(E = (mg)/q) exist as shown in figure and a mass m attached at the end of a light rod. If mass m is released from the position shown in figure find the angular velocity of the rod when it passes through the bottom most position. 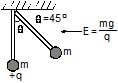
- a)
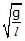
- b)
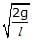
- c)
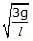
- d)
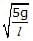
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
We+Wg=(1/2)mv2
We have work done by electrostatic force as
We=qElsinθ
and work done by the gravitational force as
Wg=mg(l−lcosθ)
Thus we get
qElsinθ+mg(l−lcosθ)=(1/2)mv2
Thus we get
mgsinθ+mgl−mglcosθ=(1/2)mv2
as θ=45o, we get
mgl=(1/2)mv2
also as v=ωl
we get
ω=√2g/l
The Gaussian surface for a line charge will be- a)Sphere
- b)Cylinder
- c)Cube
- d)Cuboid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A small circular ring has a uniform charge distribution. On a far-off axial point distance x from the centre of the ring, the electric field is proportional to
- A:
x-1
- B:
x-3/2
- C:
x-2
- D:
x5/4
The answer is C.
A small circular ring has a uniform charge distribution. On a far-off axial point distance x from the centre of the ring, the electric field is proportional to
x-1
x-3/2
x-2
x5/4
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
at point p
∣E∣= KQx /(R2+x2)3/2 Q =λ(2πr)
at a large distance, x≫R, so :- R2+x2≃x2
⇒∣E∣= K&x/(x2)3/2=KQ/x2=Eαx−2
so at a large distance, the ring behaves as a point particle.
When a negatively charged conductor is connected to earth,
- a)No charge flow occurs.
- b)Protons flow from the conductor to the earth.
- c)Electrons flow from the earth to the conductor.
- d)Electrons flow from the conductor to the earth.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
- Option A is incorrect because charge flow does occur when a negatively charged conductor is connected to the earth.
- Option B is incorrect because protons have a positive charge and they are not free to move in a conductor.
- Option C is incorrect because electrons flow from the earth to the conductor, not the other way around.
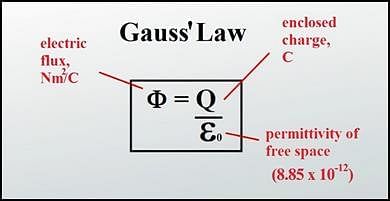
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The flux associated with a spherical surface is 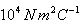 . What will be the flux, if the radius of the spherical shell is doubled?
. What will be the flux, if the radius of the spherical shell is doubled?
- A:
it will remains unchanged.
- B:
It will be the half of the previous one.
- C:
It will become zero.
- D:
It will also get doubled.
The answer is a.
The flux associated with a spherical surface is . What will be the flux, if the radius of the spherical shell is doubled?
it will remains unchanged.
It will be the half of the previous one.
It will become zero.
It will also get doubled.
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
The force between two charges is 120 N. If the distance between the charges is doubled, the force will be- a)60 N
- b)30 N
- c)40 N
- d)15 N
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
So if the distance is doubled then the force would decrease 4 times.
So the new force would be 120/4=30 Newton.
A charged particle of charge q and mass m is released from rest in an uniform electric field E. Neglecting the effect of gravity, the kinetic energy of the charged particle after time 't' seconds is- a)
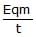
- b)
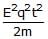
- c)
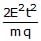
- d)
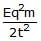
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
Hence, acceleration of particle=a=F/m=qE/m
Initial speed=u=0
Hence, final velocity=v=u+at=qEt/m
Kinetic energy=K=(1/2)mv2=(1/2)m(qEt/m)2
⟹K=E2q2t2/2m
A dipole is said to be in stable equilibrium when angle between electric field and dipole moment is:- a)0°
- b)45°
- c)180°
- d)90°
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
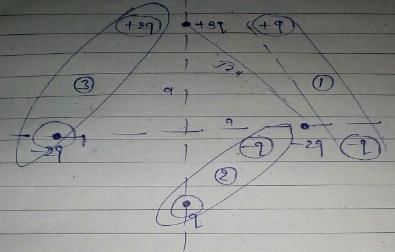
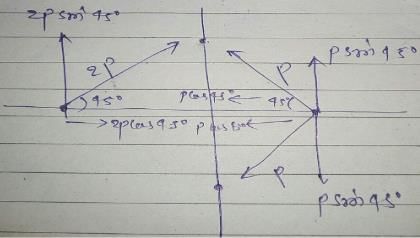
Four charges are placed each at a distance a from origin. The dipole moment of configuration is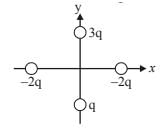
- a)
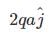
- b)
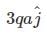
- c)
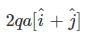
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

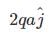
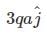
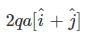

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
all four charges are placed , each at a distance 'a ' from the origin.
it means distance between two charges = √{a² + a² } = √2a
We also know, dipole moment is the system of two equal magnitude but opposite nature charges . so, we have to divide the charges as shown in the figure for making dipoles .
Hence, there are three dipoles formed.
Let P = q(√2a)
then, P₁ = P , P₂ = P and P₃ = 2P {as shown in figure.}
now resolve the vectors P₁ ,P₂ and P₃ .
as shown in figure,
vertical components of P₁ and P₂ is cancelled .
and horizontal components of P₁ and P₂ is cancelled by horizontal component of P₃ .
and rest part of dipole = vertical component of P₃ = 2Psin45° j ['j' shows direction of net dipole moment]
hence, net dipole moment = 2q(√2a) × 1/√2 j
= 2qa j
For uniform electric field, field lines are:- a)Divergent
- b)Convergent
- c)Parallel and equally spaced
- d)Convergent then divergent
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Charging a metal sphere by contact using a positively charged rod, followed by grounding can result in ________ charge in a metal sphere.- a)positive
- b)Zero
- c)positive or negative depending on which end is grounded
- d)negative
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Amrutha Pillai answered |
Chapter doubts & questions for Electric Charges and Fields - Online MCQ Tests for JEE 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Online MCQ Tests for JEE
964 tests
|