All Exams >
Bank Exams >
Mock Tests for Banking Exams 2025 >
All Questions
All questions of IBPS PO Mains for Bank Exams Exam
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below-The information given below is the investment of three Venture capitalists in a partnership for the period of 1991 – 1995. The investments made by an individual are for the same period.The investment of Bikram in 1991 is 40000 and is equal is to the investment of Chandan in 1993. The total investment in 1994 is Rs. 24000 and the ratio of investments of Arjun, Bikram and Chandan are 8 : 9 : 7 respectively. The investments of Arjun in 1991, 1992 and 1993 are 32000, 48000 and 44000 respectively. The investment of Chandan in 1991 and 1992 are same i.e. Rs. 22000. The investment of Bikram in 1993 is 6000 more than the investment by him in 1992 i.e. 30000. Based on this information and extra information on the questions, answer the questions that follow.Q. Suppose all the VCs invested for one more year i.e. 1995 and the total investment of Arjun and Bikram is Rs. 56000 and invested their amounts for 24 and 16 months respectively, find for how many months C invested his amount of Rs 64, 000 so that given profits of Arjun, Bikram and Chandan are 12600, 11200 and 16800 respectively?- a)16 Months
- b)21 Months
- c)15 Months
- d)6 Months
- e)12 Months
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below-
The information given below is the investment of three Venture capitalists in a partnership for the period of 1991 – 1995. The investments made by an individual are for the same period.The investment of Bikram in 1991 is 40000 and is equal is to the investment of Chandan in 1993. The total investment in 1994 is Rs. 24000 and the ratio of investments of Arjun, Bikram and Chandan are 8 : 9 : 7 respectively. The investments of Arjun in 1991, 1992 and 1993 are 32000, 48000 and 44000 respectively. The investment of Chandan in 1991 and 1992 are same i.e. Rs. 22000. The investment of Bikram in 1993 is 6000 more than the investment by him in 1992 i.e. 30000. Based on this information and extra information on the questions, answer the questions that follow.
Q. Suppose all the VCs invested for one more year i.e. 1995 and the total investment of Arjun and Bikram is Rs. 56000 and invested their amounts for 24 and 16 months respectively, find for how many months C invested his amount of Rs 64, 000 so that given profits of Arjun, Bikram and Chandan are 12600, 11200 and 16800 respectively?
a)
16 Months
b)
21 Months
c)
15 Months
d)
6 Months
e)
12 Months
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Let A and B be the investment made by Arjun and Bikram respectively.
24A/16B = 12600/11200
12A/8B = 126/112
A/B = (126 × 8)/(12 × 112) = 3/4
Therefore, investment of Arjun = 3/7 × 56000 = 24000
So, the investment made by Bikram = 32000
Let, Chandan invested for C months
So, the ratio of Arjun and Chandan’s profit
(24000 × 24)/(64000 × C) = 12600/16800
C = 12 Months
Hence correct answer is option E.
Rohit sells a table on 40% discount on M.P and bought a table for Rs. 2400 and expect a profit of 25% then M.P of table will be-- a)Rs 4500
- b)Rs 5000
- c)Rs 6200
- d)Rs 5500
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rohit sells a table on 40% discount on M.P and bought a table for Rs. 2400 and expect a profit of 25% then M.P of table will be-
a)
Rs 4500
b)
Rs 5000
c)
Rs 6200
d)
Rs 5500
e)
None of these

|
Sharmila Yadav answered |
Given information:
- The table is sold at a 40% discount on the marked price (M.P).
- The cost price (C.P) of the table is Rs. 2400.
- The seller expects a profit of 25%.
To find:
The marked price (M.P) of the table.
Solution:
Step 1: Find the selling price (S.P) of the table.
The selling price is given by the formula:
S.P = C.P + Profit
Since the profit is 25% of the cost price, we can calculate the profit as:
Profit = (25/100) * C.P
Substituting the value of C.P = Rs. 2400, we get:
Profit = (25/100) * 2400 = Rs. 600
Therefore, the selling price (S.P) of the table is:
S.P = C.P + Profit = 2400 + 600 = Rs. 3000
Step 2: Find the M.P of the table.
The selling price is given at a 40% discount on the M.P. This means the selling price is 60% of the M.P.
Let the marked price (M.P) of the table be x.
Then, 60% of x is equal to Rs. 3000.
Mathematically, we can write:
(60/100) * x = 3000
Simplifying the equation, we get:
x = (3000 * 100) / 60 = Rs. 5000
Therefore, the marked price (M.P) of the table is Rs. 5000.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option 'B' - Rs. 5000.
- The table is sold at a 40% discount on the marked price (M.P).
- The cost price (C.P) of the table is Rs. 2400.
- The seller expects a profit of 25%.
To find:
The marked price (M.P) of the table.
Solution:
Step 1: Find the selling price (S.P) of the table.
The selling price is given by the formula:
S.P = C.P + Profit
Since the profit is 25% of the cost price, we can calculate the profit as:
Profit = (25/100) * C.P
Substituting the value of C.P = Rs. 2400, we get:
Profit = (25/100) * 2400 = Rs. 600
Therefore, the selling price (S.P) of the table is:
S.P = C.P + Profit = 2400 + 600 = Rs. 3000
Step 2: Find the M.P of the table.
The selling price is given at a 40% discount on the M.P. This means the selling price is 60% of the M.P.
Let the marked price (M.P) of the table be x.
Then, 60% of x is equal to Rs. 3000.
Mathematically, we can write:
(60/100) * x = 3000
Simplifying the equation, we get:
x = (3000 * 100) / 60 = Rs. 5000
Therefore, the marked price (M.P) of the table is Rs. 5000.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option 'B' - Rs. 5000.
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below-In each of the questions given below a sentence is given which is then divided into five parts out of which one part which is grammatically and contextually correct has been marked underlined. Out of the rest of the parts you must choose the grammatically incorrect part as your answer. If there is no error in any other part as well, choose ‘No Error’ as your option(A) Langdon recalled the first time he was fooled by senses when his young mind /(B) had been incapable of accepting that he is not in a harbor at all, but in fact /(C) he was in a cavernous underground theater that had /(D) been flooded with water to create illusion for the/(E) classic Disney World ride Pirates of the Caribbean.- a)D
- b)A
- c)C
- d)B
- e)No Error
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below-
In each of the questions given below a sentence is given which is then divided into five parts out of which one part which is grammatically and contextually correct has been marked underlined. Out of the rest of the parts you must choose the grammatically incorrect part as your answer. If there is no error in any other part as well, choose ‘No Error’ as your option
(A) Langdon recalled the first time he was fooled by senses when his young mind /(B) had been incapable of accepting that he is not in a harbor at all, but in fact /(C) he was in a cavernous underground theater that had /(D) been flooded with water to create illusion for the/(E) classic Disney World ride Pirates of the Caribbean.
a)
D
b)
A
c)
C
d)
B
e)
No Error

|
Ishani Khanna answered |
Understanding the Error in the Sentence
In the given sentence, we need to identify the part that is grammatically incorrect. Let's break down the marked parts:
Analysis of Each Part:
- (A) Langdon recalled the first time he was fooled by senses when his young mind
- This part is correct as it sets the context correctly.
- (B) had been incapable of accepting that he is not in a harbor at all, but in fact
- Here lies the error. The tense is inconsistent. "had been" suggests past perfect, but "is" is present tense. It should be "was" to maintain parallel structure.
- (C) he was in a cavernous underground theater that had
- This part is also correct as it uses the past tense consistently.
- (D) been flooded with water to create illusion for the
- This part is grammatically correct as well.
- (E) classic Disney World ride Pirates of the Caribbean.
- This part is correct and gives the specific context needed.
Conclusion:
The error in part (B) arises from the inconsistent use of tenses. To correct it, "is" should be changed to "was" for consistency with the past perfect tense established earlier in the sentence. Thus, the grammatically incorrect part is (B).
Remember to focus on tense consistency when analyzing sentences, as it is a common area where errors can occur.
In the given sentence, we need to identify the part that is grammatically incorrect. Let's break down the marked parts:
Analysis of Each Part:
- (A) Langdon recalled the first time he was fooled by senses when his young mind
- This part is correct as it sets the context correctly.
- (B) had been incapable of accepting that he is not in a harbor at all, but in fact
- Here lies the error. The tense is inconsistent. "had been" suggests past perfect, but "is" is present tense. It should be "was" to maintain parallel structure.
- (C) he was in a cavernous underground theater that had
- This part is also correct as it uses the past tense consistently.
- (D) been flooded with water to create illusion for the
- This part is grammatically correct as well.
- (E) classic Disney World ride Pirates of the Caribbean.
- This part is correct and gives the specific context needed.
Conclusion:
The error in part (B) arises from the inconsistent use of tenses. To correct it, "is" should be changed to "was" for consistency with the past perfect tense established earlier in the sentence. Thus, the grammatically incorrect part is (B).
Remember to focus on tense consistency when analyzing sentences, as it is a common area where errors can occur.
Switch to the next window from the current window ______ is used.- a)Ctrl + Tab
- b)Alt + Tab
- c)Alt + Right arrow
- d)End Key
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Switch to the next window from the current window ______ is used.
a)
Ctrl + Tab
b)
Alt + Tab
c)
Alt + Right arrow
d)
End Key
e)
None of these
|
|
Rohan Sengupta answered |
Pressing Alt + Tab lets you switch between your open Windows. With the Alt key still pressed, tap Tab again to flip between windows, and then release the Alt key to select the current window. Switch to the next window from the current window Alt + Tab used.
Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:Eight persons, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, and S are sitting in a row facing north. Each of these people earns a different amount per annum. Also, the height of each of these people is different from each other. No two people have the same salary or height.The persons in the increasing order of their salary:O (7) < p="" (9)="" />< l="" (11)="" />< m="" (15)="" />< s="" (16)="" />< q="" (25)="" />< r="" (38)="" />< n="" />The number in the bracket represents the salary of the persons in lakhs.The person sitting fourth to the left of R is 15 cm shorter than him. The person who earns the least is 3 cm shorter than the person sitting to his immediate left. The tallest person is 28 cm taller than the person sitting third to his left. M is 3 cm taller than the person who earns 16 lakh per annum. P is 11 cm shorter than the person who is sitting third to his right. Four persons are sitting between the tallest person and the person who earns the most. The highest-paid person is 2 cm shorter than the person sitting to his immediate left and their average height is 140 cm. Only one person is sitting between Q and the person who earns the least. R is sitting to the immediate left of the person who earns 15 lakhs per annum. O is taller than S. The third highest-paid person is 23 cm shorter than the person sitting to his immediate right. P, an immediate neighbour of N, is sitting on one of the extreme ends. More than one person is sitting between R and S. The height of S is more than 160 cm.What is the annual package of the person who is sitting to the immediate right of the person whose height is 152 cm?- a)15 Lakh
- b)16 Lakh
- c)14 Lakh
- d)38 Lakh
- e)11 Lakh
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given questions:
Eight persons, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, and S are sitting in a row facing north. Each of these people earns a different amount per annum. Also, the height of each of these people is different from each other. No two people have the same salary or height.
The persons in the increasing order of their salary:
O (7) < p="" (9)="" />< l="" (11)="" />< m="" (15)="" />< s="" (16)="" />< q="" (25)="" />< r="" (38)="" />< n="" />
The number in the bracket represents the salary of the persons in lakhs.
The person sitting fourth to the left of R is 15 cm shorter than him. The person who earns the least is 3 cm shorter than the person sitting to his immediate left. The tallest person is 28 cm taller than the person sitting third to his left. M is 3 cm taller than the person who earns 16 lakh per annum. P is 11 cm shorter than the person who is sitting third to his right. Four persons are sitting between the tallest person and the person who earns the most. The highest-paid person is 2 cm shorter than the person sitting to his immediate left and their average height is 140 cm. Only one person is sitting between Q and the person who earns the least. R is sitting to the immediate left of the person who earns 15 lakhs per annum. O is taller than S. The third highest-paid person is 23 cm shorter than the person sitting to his immediate right. P, an immediate neighbour of N, is sitting on one of the extreme ends. More than one person is sitting between R and S. The height of S is more than 160 cm.
What is the annual package of the person who is sitting to the immediate right of the person whose height is 152 cm?
a)
15 Lakh
b)
16 Lakh
c)
14 Lakh
d)
38 Lakh
e)
11 Lakh
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
1) Four persons are sitting between the tallest person and the person who earns the most.
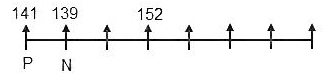
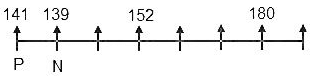
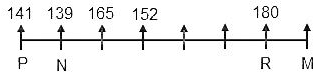
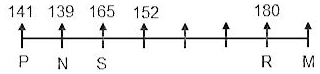
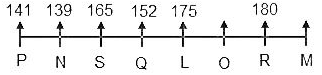
(It is clear from the given data that N earns the most.)
2) P, an immediate neighbour of N, is sitting on one of the extreme ends.
(Implies, N is sitting on the second seat from one of the ends.)
3) P is 11 cm shorter than the person who is sitting third to his right.
(Implies, P must be sitting on the leftmost seat and N must be sitting on the second seat from the left end. It further implies that the tallest person is sitting on the second seat from the right end.)
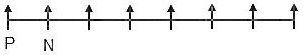
4) The highest-paid person is 2 cm shorter than the person sitting to his immediate left and their average height is 140 cm.
(Clearly, N is the highest-paid person and P is sitting to his immediate left. It further implies that the sum of their heights is 280 cm and P is taller than N by 2 cm. Hence, P is 141 cm and N is 139 cm tall. Also, according to statement 3, the person sitting third to the right of P is 152 cm tall.)
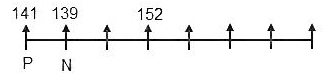
5) The tallest person is 28 cm taller than the person sitting third to his left.
(We know from the first statement that the tallest person is sitting fifth to the right of N. The person sitting third to the left of the tallest person is 152 cm tall. Hence, the tallest person is 180 cm tall.)
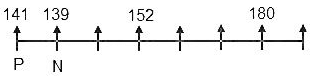
6) R is sitting to the immediate left of the person who earns 15 lakhs per annum.
(Implies, R is sitting to the immediate left of M.)
7) The person sitting fourth to the left of R is 15 cm shorter than him.
(It is only possible if we place R on the second seat from the right end. It implies, R is the tallest person and M is sitting to the immediate right of R. Also, the person sitting fourth to the left of R is 165 cm tall.)
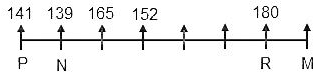
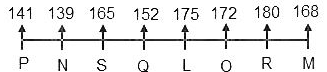
8) More than one person is sitting between R and S. The height of S is more than 160 cm.
(There is only one way for this to be possible as the height of S is more than 160 cm i.e. S must be sitting to the immediate right of N.)

9) The third highest-paid person is 23 cm shorter than the person sitting to his immediate right.
(Clearly, Q is the third highest-paid person.)
10) Only one person is sitting between Q and the person who earns the least.
(Clearly, O earns the least.)
11) O is taller than S.
(Clearly, we cannot place O to the immediate right of S as O is taller than S, implies, Q is sitting to the immediate right of S and O is sitting to the immediate left of R. Also, now that we know that the height of Q is 152 cm, implies, the height of the person sitting to the immediate right of Q is 175 cm. Now, that only L is left to be placed in the row, we can place him between Q as it is the only position left.)
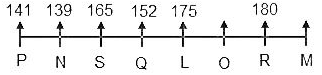
12) M is 3 cm taller than the person who earns 16 lakh per annum.
(Clearly, S earns 16 lakhs per annum and his height is 165 cm, implies, the height of M is 168 cm.)
13) The person who earns the least is 3 cm shorter than the person sitting to his immediate left.
(Clearly, O earns the least and he is 3 cm shorter than L whose height is 175 cm. Implies, the height of O is 172 cm.)

Clearly, L is sitting to the immediate right of Q whose height is 152 cm and the annual salary of L is 11 lakh.
Direction: Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.The discovery and archaeological study of Chandraketugarh, 35 kilometers north of Kolkata, provide ____(1)____ that the region in which the city ____(2)____ has been inhabited for over two millennia. Kolkata's recorded history began in 1690 with the arrival of the English East India Company, which was ____(3)____ its trade business in Bengal. Job Charnock, an ____(4)____ who worked for the company, was formerly ____(5)____as the founder of the city. In response to a public petition, the Calcutta High Court ruled in 2003 that the city does not have a founder. The area occupied by the present-day city encompassed three villages: Kalikata, Gobindapur and Sutanuti.Select the most appropriate option to fill in blank number 1.- a)stories
- b)invention
- c)evidence
- d)debunk
- e)parable
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
The discovery and archaeological study of Chandraketugarh, 35 kilometers north of Kolkata, provide ____(1)____ that the region in which the city ____(2)____ has been inhabited for over two millennia. Kolkata's recorded history began in 1690 with the arrival of the English East India Company, which was ____(3)____ its trade business in Bengal. Job Charnock, an ____(4)____ who worked for the company, was formerly ____(5)____as the founder of the city. In response to a public petition, the Calcutta High Court ruled in 2003 that the city does not have a founder. The area occupied by the present-day city encompassed three villages: Kalikata, Gobindapur and Sutanuti.
Select the most appropriate option to fill in blank number 1.
a)
stories
b)
invention
c)
evidence
d)
debunk
e)
parable
|
|
Kavya Saxena answered |
The given passage is about the history of Kolkata.
Let us read the following sentence carefully: The discovery and archaeological study of chandraketugarh, 35 kilometers north of Kolkata, provide ____(1)____ that....
From the given sentence, we can understand that the discovery of Chandraketugarh is proof of something.
The meaning of the word 'evidence' is 'proof' or 'confirmation'.
Thus, the correct word for blank number 1 is 'evidence'.
So the correct sentence is: The discovery and archaeological study of chandraketugarh, 35 kilometers north of Kolkata, provide evidence that.
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given question.In alphabetical series A-Z each letter except vowels is assigned a different number from 1-9 (for ex- B is coded as 1, C-2, L-9) and again those numbers get repeated (for ex- M-1, N-2 and so on). Also vowel is coded with different symbol viz. @, #, $, %, &.In a coded language:“Heavy new mechanic part” is coded as - 6#@82 2#9 1#26@2$2 3@57“Most pacific region war” is coded as – 1g 3@2$4$2 5#5$%2 9@5“Never beat hungry people” is coded as – 2#8#5 1#@7 6&2552 3#9#Besides the above example, following operations are to be applied for coding the words given in the questions below.I. If first letter of the word is consonant and last letter is vowel then the codes of both of them will be interchanged.II. If both first and last letter of the word are vowel then the odd numbers of the code is replaced with *.III. If first letter of the word is vowel and last letter is consonant then both are to be coded as the code of first letter.IV. If both first and last letter are consonant then the even number of the code is replaced with ^.If the word does not satisfy the conditions given above then the letters of that word are to be coded as per directions given above.What can be the code of “Related”?- a)5^9@7#3
- b)5#9^7#3
- c)5#9@7#3
- d)5#9@7^3
- e)5#9@7#^
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given question.
In alphabetical series A-Z each letter except vowels is assigned a different number from 1-9 (for ex- B is coded as 1, C-2, L-9) and again those numbers get repeated (for ex- M-1, N-2 and so on). Also vowel is coded with different symbol viz. @, #, $, %, &.
In a coded language:
“Heavy new mechanic part” is coded as - 6#@82 2#9 1#26@2$2 3@57
“Most pacific region war” is coded as – 1g 3@2$4$2 5#5$%2 9@5
“Never beat hungry people” is coded as – 2#8#5 1#@7 6&2552 3#9#
Besides the above example, following operations are to be applied for coding the words given in the questions below.
I. If first letter of the word is consonant and last letter is vowel then the codes of both of them will be interchanged.
II. If both first and last letter of the word are vowel then the odd numbers of the code is replaced with *.
III. If first letter of the word is vowel and last letter is consonant then both are to be coded as the code of first letter.
IV. If both first and last letter are consonant then the even number of the code is replaced with ^.
If the word does not satisfy the conditions given above then the letters of that word are to be coded as per directions given above.
What can be the code of “Related”?
a)
5^9@7#3
b)
5#9^7#3
c)
5#9@7#3
d)
5#9@7^3
e)
5#9@7#^

|
Mansi Mishra answered |
Understanding the Code for "Related"
To decode the word “Related” according to the provided coding rules, we need to follow the steps systematically.
Step 1: Identify Letters
- First letter: R (consonant)
- Last letter: D (consonant)
Since both the first and last letters are consonants, we apply rule IV, which states that even numbers in the code should be replaced with ^.
Step 2: Code Each Letter
Now, let’s assign codes to each letter in "Related":
- R: 5 (R is coded as 5)
- E: @ (E is a vowel, coded as @)
- L: 9 (L is coded as 9)
- A: $ (A is a vowel, coded as $)
- T: 7 (T is coded as 7)
- E: @ (E is a vowel, coded as @)
- D: 3 (D is coded as 3)
So, the initial code is: 5 @ 9 $ 7 @ 3
Step 3: Apply the Coding Rules
Now, let's transform the code according to the rules:
- The original code: 5 @ 9 $ 7 @ 3
- According to rule IV, we replace even numbers. Here, 2 (from @) is not an even number, 9 is not even, 7 is not even, and 3 is not even. Thus, there are no changes.
The even numbers in the code remain the same, so the code remains as 5 @ 9 $ 7 @ 3.
Step 4: Final Code
Now we combine the codes of the letters:
- 5 # 9 @ 7 # 3
The final code for "Related" is 5#9@7#3, which corresponds to option C.
To decode the word “Related” according to the provided coding rules, we need to follow the steps systematically.
Step 1: Identify Letters
- First letter: R (consonant)
- Last letter: D (consonant)
Since both the first and last letters are consonants, we apply rule IV, which states that even numbers in the code should be replaced with ^.
Step 2: Code Each Letter
Now, let’s assign codes to each letter in "Related":
- R: 5 (R is coded as 5)
- E: @ (E is a vowel, coded as @)
- L: 9 (L is coded as 9)
- A: $ (A is a vowel, coded as $)
- T: 7 (T is coded as 7)
- E: @ (E is a vowel, coded as @)
- D: 3 (D is coded as 3)
So, the initial code is: 5 @ 9 $ 7 @ 3
Step 3: Apply the Coding Rules
Now, let's transform the code according to the rules:
- The original code: 5 @ 9 $ 7 @ 3
- According to rule IV, we replace even numbers. Here, 2 (from @) is not an even number, 9 is not even, 7 is not even, and 3 is not even. Thus, there are no changes.
The even numbers in the code remain the same, so the code remains as 5 @ 9 $ 7 @ 3.
Step 4: Final Code
Now we combine the codes of the letters:
- 5 # 9 @ 7 # 3
The final code for "Related" is 5#9@7#3, which corresponds to option C.
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below-In the given questions, two rows are given and to find out the resultant of a particular row following rules are given.Step 1 – If an odd number is followed by a even number then the resultant comes by multiplying the numbers.Step 2 – If an even number is followed by an odd non prime number then the resultant will be the subtraction of two numbers.Step 3 – If an even number is followed by prime number (except 2) then the resultant will be the addition of two numbers.Step 4 – If an odd number is followed by a perfect cube then the resultant will be the subtraction of two numbers.Step 5 – If an odd number is followed by another odd number then the resultant will be the addition of both the numbers.Q. Find the addition of the resultant of two rows.15 10 1535 45 13- a)191
- b)195
- c)228
- d)207
- e)205
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below-
In the given questions, two rows are given and to find out the resultant of a particular row following rules are given.
Step 1 – If an odd number is followed by a even number then the resultant comes by multiplying the numbers.
Step 2 – If an even number is followed by an odd non prime number then the resultant will be the subtraction of two numbers.
Step 3 – If an even number is followed by prime number (except 2) then the resultant will be the addition of two numbers.
Step 4 – If an odd number is followed by a perfect cube then the resultant will be the subtraction of two numbers.
Step 5 – If an odd number is followed by another odd number then the resultant will be the addition of both the numbers.
Q. Find the addition of the resultant of two rows.
15 10 15
35 45 13
a)
191
b)
195
c)
228
d)
207
e)
205
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
First row – 15 10 15
According to step 1: “15 10” = 15 × 10 = 150
According to step 2: “120 15” = 150 – 15 = 135
105 is the resultant of first row.
Second row – 35 45 13
According to step 5: “35 45” = 35 + 45 = 80
According to step 3: “80 13” = 80 + 13 = 93
93 is the resultant of second row.
Addition of resultant of two rows = 135 + 93 = 228
H and K entered into a partnership by investing Rs. 7500 and Rs. 6500 respectively. After 4 months, H withdrew 1/5th of his total investment while K invested the same amount that withdrew by H. After 4 months, Q joins the business with a capital of Rs. 12500. The share of K exceeds that of Q out of the total profit of Rs. 9919 after 1 year by :- a)Rs.1820
- b)Rs.2820
- c)Rs.1720
- d)Rs.2120
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
H and K entered into a partnership by investing Rs. 7500 and Rs. 6500 respectively. After 4 months, H withdrew 1/5th of his total investment while K invested the same amount that withdrew by H. After 4 months, Q joins the business with a capital of Rs. 12500. The share of K exceeds that of Q out of the total profit of Rs. 9919 after 1 year by :
a)
Rs.1820
b)
Rs.2820
c)
Rs.1720
d)
Rs.2120
e)
None of these
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
As we know that,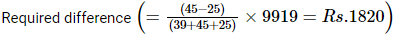
Profit is directly proportional to investment.
Ratio of total investment of H, K and Q of 1 year is
(7500 × 4 + 6000 × 8) : (6500 × 4 + 8000 × 8) : (12500 × 4)
78000 : 90000 : 50000
39 : 45 : 25
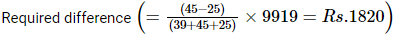
Hence correct answer is option A.
Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by three conclusions numbered I, II and III. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.Statements:I. Some bacteria are virusII. No virus is malariaIII. Only a few mosquito are bacteriaConclusions:I. No malaria is bacteriaII. Some virus is malariaIII. Some mosquito are not bacteria- a)Only conclusion I follows
- b)Only conclusion III follows
- c)Both conclusion II and III follows
- d)Only conclusion II follows
- e)All the conclusion follows
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In the question below are given three statements followed by three conclusions numbered I, II and III. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Statements:
I. Some bacteria are virus
II. No virus is malaria
III. Only a few mosquito are bacteria
Conclusions:
I. No malaria is bacteria
II. Some virus is malaria
III. Some mosquito are not bacteria
a)
Only conclusion I follows
b)
Only conclusion III follows
c)
Both conclusion II and III follows
d)
Only conclusion II follows
e)
All the conclusion follows

|
Arpita Pillai answered |
Analysis:
Statement Analysis:
- Some bacteria are virus
- No virus is malaria
- Only a few mosquitoes are bacteria
Conclusion Analysis:
I. No malaria is bacteria
II. Some virus is malaria
III. Some mosquitoes are not bacteria
Explanation:
Conclusion I: No malaria is bacteria
- Since no virus is malaria and some bacteria are virus, it is logical to conclude that no malaria is bacteria. This conclusion follows from the given statements.
Conclusion II: Some virus is malaria
- This conclusion cannot be logically inferred from the given statements. The second statement clearly states that no virus is malaria, so it contradicts this conclusion.
Conclusion III: Some mosquitoes are not bacteria
- Since only a few mosquitoes are bacteria, it is logical to conclude that some mosquitoes are not bacteria. This conclusion also follows from the given statements.
Therefore, only conclusion I (No malaria is bacteria) and conclusion III (Some mosquitoes are not bacteria) logically follow from the given statements. Hence, the correct answer is option 'B'.
Direction: In each of the questions given below, four words are given in bold. These four words may or may not be in their correct position. The sentence is then followed by options with the correct combination of words that should replace each other in order to make the sentence grammatically and contextually correct. Find the correct combination of words that replace each other. If the sentence is correct as it is, select ‘E’ as your option.Soft power can be other (A) not just by states but also by all actors (B) in international politics, such as NGOs and wielded (C) international institutions.- a)BAC
- b)BCA
- c)CAB
- d)CBA
- e)No rearrangement required
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In each of the questions given below, four words are given in bold. These four words may or may not be in their correct position. The sentence is then followed by options with the correct combination of words that should replace each other in order to make the sentence grammatically and contextually correct. Find the correct combination of words that replace each other. If the sentence is correct as it is, select ‘E’ as your option.
Soft power can be other (A) not just by states but also by all actors (B) in international politics, such as NGOs and wielded (C) international institutions.
a)
BAC
b)
BCA
c)
CAB
d)
CBA
e)
No rearrangement required
|
|
Kavya Saxena answered |
Correct Option: (D)
Observing the sentence, we see that “actors” and “other” do not make any sense at (A). Only “wielded” fits at (A).
This eliminates option A and option B.
“Actors” fits perfectly at (B). There is no need to shift it.
“Other” fits at (C) aptly.
Thus, the correct arrangement becomes: CBA
Study the following information and answer the given questions.Ten people live in three buildings namely X, Y and Z. Building X is immediate left of building Y whereas building Z is to the second right of building X. Not more than four people live in a building and immediate above or below implies that the person is not in the same building. O does not live in building Y but lives at floor number 5. P lives in that floor which is the sum of the floor number in which Q and O lives. The sum of floor number in which R and M live is 3 and both live in different building. The sum of the number of the floor in which M and S live is equal to the floor number in which N live. M lives in the even numbered floor. Equal numbers of floors are there below the floor in which T lives and above the floor in which V lives. As many floors are there below the floor in which M lives as it is above the floor in which N lives. There are four floors above the floor in which O lives. There are two floors between V and T in the same building. U lives on that floor number which is immediately below the floor number in which S lives. Only two people live in building Z. O and U live in same building. Q lives in building Y and lives at the topmost floor. M and N live in same building but they do not live in building X. Q lives immediately two floors above the floor in which O lives.Q. Who among the following lives in the same building?- a)O – S
- b)U – T
- c)Q – M
- d)M – V
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information and answer the given questions.
Ten people live in three buildings namely X, Y and Z. Building X is immediate left of building Y whereas building Z is to the second right of building X. Not more than four people live in a building and immediate above or below implies that the person is not in the same building. O does not live in building Y but lives at floor number 5. P lives in that floor which is the sum of the floor number in which Q and O lives. The sum of floor number in which R and M live is 3 and both live in different building. The sum of the number of the floor in which M and S live is equal to the floor number in which N live. M lives in the even numbered floor. Equal numbers of floors are there below the floor in which T lives and above the floor in which V lives. As many floors are there below the floor in which M lives as it is above the floor in which N lives. There are four floors above the floor in which O lives. There are two floors between V and T in the same building. U lives on that floor number which is immediately below the floor number in which S lives. Only two people live in building Z. O and U live in same building. Q lives in building Y and lives at the topmost floor. M and N live in same building but they do not live in building X. Q lives immediately two floors above the floor in which O lives.
Q. Who among the following lives in the same building?
a)
O – S
b)
U – T
c)
Q – M
d)
M – V
e)
None of these

|
Mainak Majumdar answered |
Analysis:
Given Information:
- Ten people live in buildings X, Y, and Z.
- Building X is immediately left of building Y, and building Z is the second right of building X.
- O lives on floor number 5.
- P's floor number is the sum of Q and O's floor numbers.
- The sum of R and M's floor numbers is 3, and they live in different buildings.
- The sum of M and S's floor numbers is equal to N's floor number.
- M lives on an even-numbered floor.
- The number of floors below T is equal to the number of floors above V.
- The number of floors below M is equal to the number of floors above N.
- O's floor has 4 floors above it.
- V and T have 2 floors between them in the same building.
- U lives below S.
- Only 2 people live in building Z, O and U.
- Q lives in building Y at the topmost floor.
Solution:
- Based on the given information, we can determine that M and N live in the same building but not in building X.
- Q lives in building Y, and O lives in building Z, so they do not live in the same building.
- U and O live in the same building, which is building Z.
- Therefore, the pair that lives in the same building is Q - M.
Therefore, the correct answer is:
Q - M live in the same building.
Given Information:
- Ten people live in buildings X, Y, and Z.
- Building X is immediately left of building Y, and building Z is the second right of building X.
- O lives on floor number 5.
- P's floor number is the sum of Q and O's floor numbers.
- The sum of R and M's floor numbers is 3, and they live in different buildings.
- The sum of M and S's floor numbers is equal to N's floor number.
- M lives on an even-numbered floor.
- The number of floors below T is equal to the number of floors above V.
- The number of floors below M is equal to the number of floors above N.
- O's floor has 4 floors above it.
- V and T have 2 floors between them in the same building.
- U lives below S.
- Only 2 people live in building Z, O and U.
- Q lives in building Y at the topmost floor.
Solution:
- Based on the given information, we can determine that M and N live in the same building but not in building X.
- Q lives in building Y, and O lives in building Z, so they do not live in the same building.
- U and O live in the same building, which is building Z.
- Therefore, the pair that lives in the same building is Q - M.
Therefore, the correct answer is:
Q - M live in the same building.
Each of these questions has a statement followed by three suggested courses of action numbered I, II and III. Assume everything in the statement to be true, and decide which of the given courses of action logically follows for pursuing.Statement: The Department of Education has recommended that the primary level admission to government and Government aided schools should be done purely random selection and not by admission tests. This is necessitated as the number of admission seekers are much more than the available seats.Courses of action:I. The government should instruct the private schools also to follow the same practice.II. The government should set up an independent body to regulate the primary level admissions.III. The schools should be asked to select student only from those who stay in the neighbouring areas of the school.- a)Only I follows
- b)None follows
- c)Only III follows
- d)Only I and II follow
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Each of these questions has a statement followed by three suggested courses of action numbered I, II and III. Assume everything in the statement to be true, and decide which of the given courses of action logically follows for pursuing.
Statement: The Department of Education has recommended that the primary level admission to government and Government aided schools should be done purely random selection and not by admission tests. This is necessitated as the number of admission seekers are much more than the available seats.
Courses of action:
I. The government should instruct the private schools also to follow the same practice.
II. The government should set up an independent body to regulate the primary level admissions.
III. The schools should be asked to select student only from those who stay in the neighbouring areas of the school.
a)
Only I follows
b)
None follows
c)
Only III follows
d)
Only I and II follow
e)
None of these
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Since the basic problem is that number of admission seekers are much more than the available seats hence course of action I and II will help to reduce the problem.
Direction: In the following questions out of the four/five alternatives, choose the one which is best express the meaning of the given word.Obfuscate- a)Clarify
- b)Illuminate
- c)Filter
- d)Explicate
- e)Blur
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In the following questions out of the four/five alternatives, choose the one which is best express the meaning of the given word.
Obfuscate
a)
Clarify
b)
Illuminate
c)
Filter
d)
Explicate
e)
Blur
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Obfuscate means to make something more difficult to understand. Options 1, 2 and 3 are opposite in meaning. Option 5 is the right answer. Illuminate: help to clarify or explain. Explicate: analyse (a literary work) in order to reveal its meaning. Blur: make or become unclear or less distinct.
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.The Word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of numbers rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.Input: Center Damage Empire Former Holder LosingStep I: Empire 29 Center Damage Former Holder LosingStep II: Empire 29 Damage 40 Center Former Holder LosingStep III: Empire 29 Damage 40 Losing 26 Center Former HolderStep IV: Empire 29 Damage 40 Losing 26 Holder 38 Center FormerStep V: Empire 29 Damage 40 Losing 26 Holder 38 Former 23 CenterStep VI: Empire 29 Damage 40 Losing 26 Holder 38 Former 23 Center 20Step VII: Empire Damage Losing Holder Former Center 04 04 16 22 33 58Step VII is the last step.Input: Beauty Crisis Fabric Launch Varied ServerWhat is the sum of the numbers thus formed in step VII?- a)138
- b)139
- c)143
- d)148
- e)135
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
The Word and number arrangement machine when given an input line of numbers rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.
Input: Center Damage Empire Former Holder Losing
Step I: Empire 29 Center Damage Former Holder Losing
Step II: Empire 29 Damage 40 Center Former Holder Losing
Step III: Empire 29 Damage 40 Losing 26 Center Former Holder
Step IV: Empire 29 Damage 40 Losing 26 Holder 38 Center Former
Step V: Empire 29 Damage 40 Losing 26 Holder 38 Former 23 Center
Step VI: Empire 29 Damage 40 Losing 26 Holder 38 Former 23 Center 20
Step VII: Empire Damage Losing Holder Former Center 04 04 16 22 33 58
Step VII is the last step.
Input: Beauty Crisis Fabric Launch Varied Server
What is the sum of the numbers thus formed in step VII?
a)
138
b)
139
c)
143
d)
148
e)
135
|
|
Kavya Saxena answered |
For Word Arrangement: The difference between the place value of the first and last letter in the word as per alphabetical series, depends on the resultant the words are arranged in the ascending order from the left end.
For Number Arrangement: The sum of the place value (as per the alphabetical series) of the opposite letters of the exact middle two letters of each word.
for the last step, in each number, find the sum of the unit digit of that number and the square of the difference between the digits within the number. Then arrange the final resultant in ascending order from the left to right.
E.g) SERVER→ (R + V) in reverse order→ (9 + 5) = 14→ 4 - 1 = 32 = 9 + 4(unit digit) = 13
Input: Beauty Crisis Fabric Launch Varied Server
Step I: Server 14 Beauty Crisis Fabric Launch Varied
Step II: Server 14 Fabric 34 Beauty Crisis Launch Varied
Step III: Server 14 Fabric 34 Launch 19 Beauty Crisis Varied
Step IV: Server 14 Fabric 34 Launch 19 Crisis 26 Beauty Varie
Step V: Server 14 Fabric 34 Launch 19 Crisis 26 Varied 27 Beauty
Step VI: Server 14 Fabric 34 Launch 19 Crisis 26 Varied 27 Beauty 32
Step VII: Server Fabric Launch Crisis Varied Beauty 03 05 13 22 32 73
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below-In the given questions, two rows are given and to find out the resultant of a particular row following rules are given.Step 1 – If an odd number is followed by a even number then the resultant comes by multiplying the numbers.Step 2 – If an even number is followed by an odd non prime number then the resultant will be the subtraction of two numbers.Step 3 – If an even number is followed by prime number (except 2) then the resultant will be the addition of two numbers.Step 4 – If an odd number is followed by a perfect cube then the resultant will be the subtraction of two numbers.Step 5 – If an odd number is followed by another odd number then the resultant will be the addition of both the numbers.Q. If X is the resultant of second row. Find the multiplication of the resultant of two rows?X 6 1545 33 3- a)38151
- b)38150
- c)37541
- d)38521
- e)38542
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below-
In the given questions, two rows are given and to find out the resultant of a particular row following rules are given.
Step 1 – If an odd number is followed by a even number then the resultant comes by multiplying the numbers.
Step 2 – If an even number is followed by an odd non prime number then the resultant will be the subtraction of two numbers.
Step 3 – If an even number is followed by prime number (except 2) then the resultant will be the addition of two numbers.
Step 4 – If an odd number is followed by a perfect cube then the resultant will be the subtraction of two numbers.
Step 5 – If an odd number is followed by another odd number then the resultant will be the addition of both the numbers.
Q. If X is the resultant of second row. Find the multiplication of the resultant of two rows?
X 6 15
45 33 3
a)
38151
b)
38150
c)
37541
d)
38521
e)
38542
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Second row - 45 33 3
According to step 5: “45 33” = 45 + 33 = 78
According to step 3: “78 3” = 78 + 3 = 81
81 is the resultant of second row.
First row – 81 6 15
According to step 1: “81 6” = 81 × 6 = 486
According to step 2: “486 15” = 486 – 15 = 471
471 is the resultant of first row.
Multiplication of resultant of two rows = 471 × 81 = 38151
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.In a certain code language,The consonants up to M in the English alphabetical series are coded with the first four prime numbers i.e., B = 2, C = 3, and so on (After 7, start the numbering from 2 again). The consonants from N to Z are coded with the first four composite numbers i.e., N = 4, P = 6, and so on (After 9, start the numbering from 4 again). Vowels A, E, I, O, and U are coded as @, $, %, & and # respectively.The codes are written from left to right only. If two or more condition is applicable then consider all the conditions.Condition 1: If the first and last letters are vowels, then both the codes for the vowels are to be interchanged and the vowels except them are to be coded as ‘*’. (For example ACTIVE - $36*8@)Condition 2: If the second letter of a word is a vowel, then code the letter with the corresponding code and all the vowels following it will be coded as ‘!’. (For example TECTONIC – 6$36!4!3)Condition 3: If the second letter of a word is a consonant, then code the letter with the code for the alphabet which comes after a gap of 2 letters in the given alphabet series. (i.e., the code for ‘B’ is the code for ‘E’ and so on, after Z starts with A again)Condition 4: If the first and last letters are consonants, then both consonants are to be replaced with the code for the immediate next alphabet in the given alphabet series. (For example, the code for ‘B’ will be coded with the code for ‘C’ and so on, after Z starts with A again).Condition 5: If in a word, none of the conditions follows, then code the consonants and vowels with the corresponding code and then reverse the entire code.Note:1. If conditions 2 or 3 and 1 follow, then give first priority to condition 1 and then condition 2 or 3.2. If conditions 2 or 3 and 4 follow, then give first priority to condition 4 and then condition 2 or 3.3. If more than two conditions follow between conditions 1 to condition 4, then coding will be done based on the final condition.Find the code for the phrase ‘SMART WORK EASY’ using the given conditions?- a)463@4 57&# @46!
- b)66@9# 4&92 $@46
- c)83!!3 72!6 943!
- d)7242! #54@ 83!%
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
In a certain code language,
The consonants up to M in the English alphabetical series are coded with the first four prime numbers i.e., B = 2, C = 3, and so on (After 7, start the numbering from 2 again). The consonants from N to Z are coded with the first four composite numbers i.e., N = 4, P = 6, and so on (After 9, start the numbering from 4 again). Vowels A, E, I, O, and U are coded as @, $, %, & and # respectively.
The codes are written from left to right only. If two or more condition is applicable then consider all the conditions.
Condition 1: If the first and last letters are vowels, then both the codes for the vowels are to be interchanged and the vowels except them are to be coded as ‘*’. (For example ACTIVE - $36*8@)
Condition 2: If the second letter of a word is a vowel, then code the letter with the corresponding code and all the vowels following it will be coded as ‘!’. (For example TECTONIC – 6$36!4!3)
Condition 3: If the second letter of a word is a consonant, then code the letter with the code for the alphabet which comes after a gap of 2 letters in the given alphabet series. (i.e., the code for ‘B’ is the code for ‘E’ and so on, after Z starts with A again)
Condition 4: If the first and last letters are consonants, then both consonants are to be replaced with the code for the immediate next alphabet in the given alphabet series. (For example, the code for ‘B’ will be coded with the code for ‘C’ and so on, after Z starts with A again).
Condition 5: If in a word, none of the conditions follows, then code the consonants and vowels with the corresponding code and then reverse the entire code.
Note:
1. If conditions 2 or 3 and 1 follow, then give first priority to condition 1 and then condition 2 or 3.
2. If conditions 2 or 3 and 4 follow, then give first priority to condition 4 and then condition 2 or 3.
3. If more than two conditions follow between conditions 1 to condition 4, then coding will be done based on the final condition.
Find the code for the phrase ‘SMART WORK EASY’ using the given conditions?
a)
463@4 57&# @46!
b)
66@9# 4&92 $@46
c)
83!!3 72!6 943!
d)
7242! #54@ 83!%
e)
None of these

|
Pallavi Shah answered |
Analysis:
The given phrase is 'SMART WORK EASY'.
Step-by-step solution:
- We will apply the conditions given in the question to find the code for each word in the phrase.
SMART:
- S: Consonant, so code = 4
- M: Consonant, so code = 7
- A: Vowel, so code = @
- R: Consonant, so code = 2
- T: Consonant, so code = 3
Therefore, the code for 'SMART' is 4 7 @ 2 3.
WORK:
- W: Consonant, so code = 5
- O: Vowel, so code = &
- R: Consonant, so code = 2
- K: Consonant, so code = 3
Therefore, the code for 'WORK' is 5 & 2 3.
EASY:
- E: Vowel, so code = $
- A: Vowel, so code = @
- S: Consonant, so code = 4
- Y: Consonant, so code = 9
Therefore, the code for 'EASY' is $ @ 4 9.
Combining the codes:
- SMART = 4 7 @ 2 3
- WORK = 5 & 2 3
- EASY = $ @ 4 9
Therefore, the code for the phrase 'SMART WORK EASY' is 4 7 @ 2 3 5 & 2 3 $ @ 4 9, which corresponds to option 'b) 66@9# 4&92 $@46'.
The given phrase is 'SMART WORK EASY'.
Step-by-step solution:
- We will apply the conditions given in the question to find the code for each word in the phrase.
SMART:
- S: Consonant, so code = 4
- M: Consonant, so code = 7
- A: Vowel, so code = @
- R: Consonant, so code = 2
- T: Consonant, so code = 3
Therefore, the code for 'SMART' is 4 7 @ 2 3.
WORK:
- W: Consonant, so code = 5
- O: Vowel, so code = &
- R: Consonant, so code = 2
- K: Consonant, so code = 3
Therefore, the code for 'WORK' is 5 & 2 3.
EASY:
- E: Vowel, so code = $
- A: Vowel, so code = @
- S: Consonant, so code = 4
- Y: Consonant, so code = 9
Therefore, the code for 'EASY' is $ @ 4 9.
Combining the codes:
- SMART = 4 7 @ 2 3
- WORK = 5 & 2 3
- EASY = $ @ 4 9
Therefore, the code for the phrase 'SMART WORK EASY' is 4 7 @ 2 3 5 & 2 3 $ @ 4 9, which corresponds to option 'b) 66@9# 4&92 $@46'.
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the question that follow:Eight friends A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order. All friends are facing the centre. Each person has different salaries i.e.15000, 19000, 16000, 32000, 12000, 70000, 40000, and 60000 and are of different ages 20, 26, 56, 40, 34, 54, 43 and 30 years but not necessarily in the same order. There is an angle of 135° between A and G.B’s salary is double of H’s but less than D’s salary. There is an angle of 90° between A and H. F sits at 135° clockwise direction to B. The average of B and D’s age is equal to the age of G. Salary of the one, who sits 2nd to the right of B is divisible by 4. D is not an immediate neighbour of the person who is third to the left of A. G’s salary is thousand rupees less than 1/3rd of A’s salary. There is an angle of 180° between B and the one whose age is 54 years. C’s salary is third highest salary among all the salaries. There is an angle of 180° between F and E, whose salary is divisible by 3 but not 12000. B sits at 90° clockwise direction of A. E is the youngest in the group. Only two pair is sitting diagonally opposite to each other has age difference of 6 years. The salary of C is 1000 multiple of its age. The one who have the highest salary is third youngest in the group.Who is sitting immediately left of G?- a)C
- b)D
- c)A
- d)W
- e)B
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the question that follow:
Eight friends A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order. All friends are facing the centre. Each person has different salaries i.e.15000, 19000, 16000, 32000, 12000, 70000, 40000, and 60000 and are of different ages 20, 26, 56, 40, 34, 54, 43 and 30 years but not necessarily in the same order. There is an angle of 135° between A and G.B’s salary is double of H’s but less than D’s salary. There is an angle of 90° between A and H. F sits at 135° clockwise direction to B. The average of B and D’s age is equal to the age of G. Salary of the one, who sits 2nd to the right of B is divisible by 4. D is not an immediate neighbour of the person who is third to the left of A. G’s salary is thousand rupees less than 1/3rd of A’s salary. There is an angle of 180° between B and the one whose age is 54 years. C’s salary is third highest salary among all the salaries. There is an angle of 180° between F and E, whose salary is divisible by 3 but not 12000. B sits at 90° clockwise direction of A. E is the youngest in the group. Only two pair is sitting diagonally opposite to each other has age difference of 6 years. The salary of C is 1000 multiple of its age. The one who have the highest salary is third youngest in the group.
Who is sitting immediately left of G?
a)
C
b)
D
c)
A
d)
W
e)
B

|
Shanaya Dey answered |
Given Information:
- Eight friends A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H are sitting around a circular table.
- Each person has different salaries and ages.
- Various clues are given regarding the positions, salaries, and ages of the friends.
Key Pointers:
- A and G have an angle of 135° between them.
- B's salary is double that of H's but less than D's salary.
- There is a 90° angle between A and H.
- F sits 135° clockwise from B.
- The average age of B and D is equal to G's age.
- The person sitting 2nd to the right of B has a salary divisible by 4.
- D is not an immediate neighbor of the person who is third to the left of A.
- G's salary is 1/3rd less than A's salary.
- There is a 180° angle between B and the person aged 54.
- C's salary is the third highest.
- There is a 180° angle between F and E, whose salary is divisible by 3 but not 12000.
- E is the youngest in the group.
- Only two pairs sitting diagonally opposite each other have an age difference of 6 years.
- C's salary is a multiple of 1000.
- The person with the highest salary is the third youngest.
Answer:
The person sitting immediately left of G is C. This can be deduced based on the given information and the positioning of the friends around the table.
- Eight friends A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H are sitting around a circular table.
- Each person has different salaries and ages.
- Various clues are given regarding the positions, salaries, and ages of the friends.
Key Pointers:
- A and G have an angle of 135° between them.
- B's salary is double that of H's but less than D's salary.
- There is a 90° angle between A and H.
- F sits 135° clockwise from B.
- The average age of B and D is equal to G's age.
- The person sitting 2nd to the right of B has a salary divisible by 4.
- D is not an immediate neighbor of the person who is third to the left of A.
- G's salary is 1/3rd less than A's salary.
- There is a 180° angle between B and the person aged 54.
- C's salary is the third highest.
- There is a 180° angle between F and E, whose salary is divisible by 3 but not 12000.
- E is the youngest in the group.
- Only two pairs sitting diagonally opposite each other have an age difference of 6 years.
- C's salary is a multiple of 1000.
- The person with the highest salary is the third youngest.
Answer:
The person sitting immediately left of G is C. This can be deduced based on the given information and the positioning of the friends around the table.
Direction: Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.The discovery and archaeological study of chandraketugarh, 35 kilometers north of Kolkata, provide ____(1)____ that the region in which the city ____(2)____ has been inhabited for over two millennia. Kolkata's recorded history began in 1690 with the arrival of the English East India Company, which was ____(3)____ its trade business in Bengal. Job Charnock, an ____(4)____ who worked for the company, was formerly ____(5)____as the founder of the city. In response to a public petition, the Calcutta High Court ruled in 2003 that the city does not have a founder. The area occupied by the present-day city encompassed three villages: Kalikata, Gobindapur and Sutanuti.Select the most appropriate option to fill in blank number 5.- a)contradicted
- b)heir
- c)increase
- d)precursor
- e)credited
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
The discovery and archaeological study of chandraketugarh, 35 kilometers north of Kolkata, provide ____(1)____ that the region in which the city ____(2)____ has been inhabited for over two millennia. Kolkata's recorded history began in 1690 with the arrival of the English East India Company, which was ____(3)____ its trade business in Bengal. Job Charnock, an ____(4)____ who worked for the company, was formerly ____(5)____as the founder of the city. In response to a public petition, the Calcutta High Court ruled in 2003 that the city does not have a founder. The area occupied by the present-day city encompassed three villages: Kalikata, Gobindapur and Sutanuti.
Select the most appropriate option to fill in blank number 5.
a)
contradicted
b)
heir
c)
increase
d)
precursor
e)
credited
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
The given passage is about the 'history of Kolkata'.
Let us read the following sentence carefully: was formerly ____(5)____as the founder of the city.
From the given sentence we can understand that it was believed that Job Charnock was the founder of the city.
The meaning of the word 'credited' is 'to acknowledge something publicly'.
So, the correct word for blank number 5 is 'credited'.
The correct sentence is: was formerly credited as the founder of the city.
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.Ten persons –O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, and X were born in five different months viz.- January, April, August, November, and December in two different years viz.- 2015 and 2018. All the information is not necessary in the same order. Only one person was born in each given month of the same year.S was born in November 2018. Three persons were born between W and X whereas both of them were born in different years. Neither W nor X was born adjacent to S. X was born in a month which has an odd number of days. O was born three persons after T, who was not born in the same month as W and S. Neither X nor R was born in the same month as O. The number of persons born between X and R is one less than the number of persons born after P. R was born in 2015 and was not born in the month which has an even number of days. Two persons were born between U and V. Neither U nor Q was born in the same month as R.How many persons were born between T and the one who was born in the same month as V?- a)Four
- b)As many persons born after S
- c)Three
- d)As many persons born before R
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Ten persons –O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, and X were born in five different months viz.- January, April, August, November, and December in two different years viz.- 2015 and 2018. All the information is not necessary in the same order. Only one person was born in each given month of the same year.
S was born in November 2018. Three persons were born between W and X whereas both of them were born in different years. Neither W nor X was born adjacent to S. X was born in a month which has an odd number of days. O was born three persons after T, who was not born in the same month as W and S. Neither X nor R was born in the same month as O. The number of persons born between X and R is one less than the number of persons born after P. R was born in 2015 and was not born in the month which has an even number of days. Two persons were born between U and V. Neither U nor Q was born in the same month as R.
How many persons were born between T and the one who was born in the same month as V?
a)
Four
b)
As many persons born after S
c)
Three
d)
As many persons born before R
e)
None of these
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
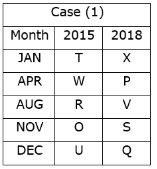
We have:
- S was born in November 2018.
- Three persons were born between W and X whereas both of them were born in different years.
- Neither W nor X was born adjacent to S.
- X was born in a month which has an odd number of days.
That means, in case (1) X was born in January 2018, and in case (2) X was born in August 2015.
Based on the above information we have:
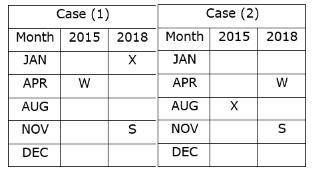
Again, we have:
- O was born three persons after T, who was not born in the same month as W and S were born.
- Neither X nor R was born in the same month as O.
That means, in case (1) & case (2) T was born in January 2015, and in case (1a) T was born in December 2015.
Based on the above information we have:
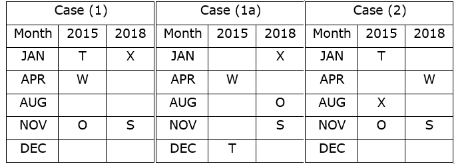
Again, we have:
- The number of persons born between X and R is one less than the number of persons born after P.
- R was born in 2015 and was not born in the month which has an even number of days.
That means, in case (1) R was born in August 2015, and in case (2) R was born in December 2015, case (1a) is not valid.
Based on the above information we have:
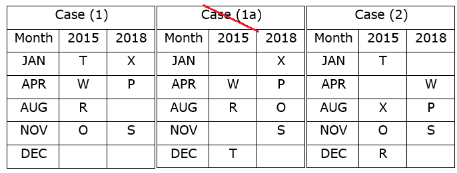
Case (1a) is not valid as R and O were not born in the same month.
Again, we have:
- Two persons were born between U and V.
- Neither U nor Q was born in the same month as R.
That means, in case (1) U was born in December 2015, case (2) is not valid.
Based on the above information we have:
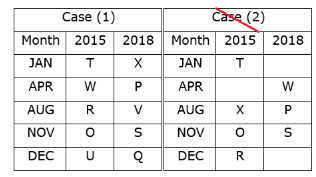
Case (2) is not valid as the number of persons born between U and R is same as the number of persons born between V and Q.
Direction: In the following questions, choose the word opposite in meaning to the given word.Ventured- a)Refrained
- b)Nudge
- c)Origin
- d)Company
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In the following questions, choose the word opposite in meaning to the given word.
Ventured
a)
Refrained
b)
Nudge
c)
Origin
d)
Company
e)
None of these

|
Tushar Das answered |
Opposite of Ventured:
Introduction:
In this question, we are asked to find the opposite word of "Ventured". To solve this, we need to understand the meaning of the word "Ventured" and then find its opposite.
Meaning of Ventured:
The word "Ventured" is a verb that means to take a risk or undertake a daring or speculative action. It refers to the act of engaging in something new or uncertain, often with the possibility of success or failure.
Opposite of Ventured:
The opposite word of "Ventured" is "Refrained". Here's why:
Explanation:
1. Refrained:
- The word "Refrained" is a verb that means to abstain or hold back from doing something.
- When someone refrains from doing something, they choose not to take a risk or engage in a particular action.
- It is the opposite of venturing, as it involves avoiding or abstaining from activities that involve risk or uncertainty.
2. Nudge, Origin, Company, None of these:
- The words "Nudge", "Origin", "Company", and "None of these" are not the opposite of "Ventured".
- "Nudge" refers to a gentle push or encouragement, which is not the opposite of taking a risk.
- "Origin" refers to the beginning or source of something, which is unrelated to the concept of venturing.
- "Company" refers to a group of people or an organization, which does not convey the opposite meaning of venturing.
- "None of these" is a generic option that does not provide an opposite word.
Conclusion:
The word opposite in meaning to "Ventured" is "Refrained". While venturing involves taking risks and engaging in uncertain actions, refraining means to abstain or hold back from such activities.
Introduction:
In this question, we are asked to find the opposite word of "Ventured". To solve this, we need to understand the meaning of the word "Ventured" and then find its opposite.
Meaning of Ventured:
The word "Ventured" is a verb that means to take a risk or undertake a daring or speculative action. It refers to the act of engaging in something new or uncertain, often with the possibility of success or failure.
Opposite of Ventured:
The opposite word of "Ventured" is "Refrained". Here's why:
Explanation:
1. Refrained:
- The word "Refrained" is a verb that means to abstain or hold back from doing something.
- When someone refrains from doing something, they choose not to take a risk or engage in a particular action.
- It is the opposite of venturing, as it involves avoiding or abstaining from activities that involve risk or uncertainty.
2. Nudge, Origin, Company, None of these:
- The words "Nudge", "Origin", "Company", and "None of these" are not the opposite of "Ventured".
- "Nudge" refers to a gentle push or encouragement, which is not the opposite of taking a risk.
- "Origin" refers to the beginning or source of something, which is unrelated to the concept of venturing.
- "Company" refers to a group of people or an organization, which does not convey the opposite meaning of venturing.
- "None of these" is a generic option that does not provide an opposite word.
Conclusion:
The word opposite in meaning to "Ventured" is "Refrained". While venturing involves taking risks and engaging in uncertain actions, refraining means to abstain or hold back from such activities.
Direction:- Below, a set of eight statements is given, out of which the first sentence, given in bold, is fixed. The rest are jumbled in any random order. Out of the remaining seven statements, one does not belong to the passage. Rearrange the remaining sentences in the correct order and then answer the questions.A. For thousands of years, the idea of God has anchored our thinking about the world.B. Nietzsche seems to think that the first response will be confusion and panic.C. But Nietzsche sees the death of God as both a great danger and a great opportunity.D. It has been especially important as a foundation for morality.E. What happens when this rug is pulled away from under us?F. Combined with industrialization in the 19th century, the growing technological power unleashed by science also gave people a sense of greater control over nature.G. The moral principles we follow had the authority of religion behind them.H. And religion provided a motive to obey these rules since it told us that virtue would be rewarded and vice punished.Which of the following sentences is FIFTH in the correct order?- a)B
- b)C
- c)E
- d)F
- e)H
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction:- Below, a set of eight statements is given, out of which the first sentence, given in bold, is fixed. The rest are jumbled in any random order. Out of the remaining seven statements, one does not belong to the passage. Rearrange the remaining sentences in the correct order and then answer the questions.
A. For thousands of years, the idea of God has anchored our thinking about the world.
B. Nietzsche seems to think that the first response will be confusion and panic.
C. But Nietzsche sees the death of God as both a great danger and a great opportunity.
D. It has been especially important as a foundation for morality.
E. What happens when this rug is pulled away from under us?
F. Combined with industrialization in the 19th century, the growing technological power unleashed by science also gave people a sense of greater control over nature.
G. The moral principles we follow had the authority of religion behind them.
H. And religion provided a motive to obey these rules since it told us that virtue would be rewarded and vice punished.
Which of the following sentences is FIFTH in the correct order?
a)
B
b)
C
c)
E
d)
F
e)
H

|
Simran Choudhury answered |
Understanding the Passage Structure
The provided statements revolve around the philosophical implications of the "death of God," particularly from Nietzsche's perspective. The fixed first statement sets the context, while the remaining statements need to be organized logically.
Correct Order of Sentences
1. A. For thousands of years, the idea of God has anchored our thinking about the world.
2. D. It has been especially important as a foundation for morality.
3. G. The moral principles we follow had the authority of religion behind them.
4. H. And religion provided a motive to obey these rules since it told us that virtue would be rewarded and vice punished.
5. B. Nietzsche seems to think that the first response will be confusion and panic.
6. C. But Nietzsche sees the death of God as both a great danger and a great opportunity.
7. E. What happens when this rug is pulled away from under us?
8. F. Combined with industrialization in the 19th century, the growing technological power unleashed by science also gave people a sense of greater control over nature.
Explanation of the Fifth Sentence
- Sentence B fits logically after establishing the impact of God on morality (D, G, H).
- It suggests that when the concept of God fades, people will feel confusion and panic – a natural reaction to losing a long-standing anchor.
- Following this, Sentence C directly addresses Nietzsche’s perspective on this event as both a danger and an opportunity.
Thus, the fifth sentence in the correct order is C, emphasizing Nietzsche’s dual view of the implications of God's death.
The provided statements revolve around the philosophical implications of the "death of God," particularly from Nietzsche's perspective. The fixed first statement sets the context, while the remaining statements need to be organized logically.
Correct Order of Sentences
1. A. For thousands of years, the idea of God has anchored our thinking about the world.
2. D. It has been especially important as a foundation for morality.
3. G. The moral principles we follow had the authority of religion behind them.
4. H. And religion provided a motive to obey these rules since it told us that virtue would be rewarded and vice punished.
5. B. Nietzsche seems to think that the first response will be confusion and panic.
6. C. But Nietzsche sees the death of God as both a great danger and a great opportunity.
7. E. What happens when this rug is pulled away from under us?
8. F. Combined with industrialization in the 19th century, the growing technological power unleashed by science also gave people a sense of greater control over nature.
Explanation of the Fifth Sentence
- Sentence B fits logically after establishing the impact of God on morality (D, G, H).
- It suggests that when the concept of God fades, people will feel confusion and panic – a natural reaction to losing a long-standing anchor.
- Following this, Sentence C directly addresses Nietzsche’s perspective on this event as both a danger and an opportunity.
Thus, the fifth sentence in the correct order is C, emphasizing Nietzsche’s dual view of the implications of God's death.
13 persons went to a hotel for taking their meals. 11 of them spent Rs. 25 each over their meals and other 2 persons spent collectively Rs. 50 more than the average expenditure of all the 13. Total money spent by them as :- a)Rs.284.02
- b)Rs.484.02
- c)Rs.384.02
- d)Rs.584.02
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
13 persons went to a hotel for taking their meals. 11 of them spent Rs. 25 each over their meals and other 2 persons spent collectively Rs. 50 more than the average expenditure of all the 13. Total money spent by them as :
a)
Rs.284.02
b)
Rs.484.02
c)
Rs.384.02
d)
Rs.584.02
e)
None of these

|
Shraddha Mehta answered |
Solution:
Let's assume the average expenditure of all 13 persons is 'x'.
According to the given information,
11 persons spent Rs. 25 each over their meals. So, the total expenditure of these 11 persons = 11 * Rs. 25 = Rs. 275.
The other 2 persons spent collectively Rs. 50 more than the average expenditure of all 13 persons. Therefore, their total expenditure = x + Rs. 50.
Total money spent by all 13 persons = Total expenditure of 11 persons + Total expenditure of 2 persons
= Rs. 275 + (x + Rs. 50)
= Rs. 275 + x + Rs. 50
= Rs. (275 + x + 50)
= Rs. (325 + x)
We know that the total money spent by all 13 persons is equal to the total money spent by them individually.
So, Rs. (325 + x) = 13x
325 = 13x - x
325 = 12x
x = 325/12
x = Rs. 27.08 (approx.)
Therefore, the average expenditure of all 13 persons is approximately Rs. 27.08.
Now, let's calculate the total money spent by all 13 persons.
Total money spent by all 13 persons = Total expenditure of 11 persons + Total expenditure of 2 persons
= Rs. 275 + (Rs. 27.08 + Rs. 50)
= Rs. 275 + Rs. 77.08
= Rs. 352.08
Hence, the total money spent by all 13 persons is Rs. 352.08.
The given options are:
a) Rs. 284.02
b) Rs. 484.02
c) Rs. 384.02
d) Rs. 584.02
e) None of these
None of the given options match the calculated total money spent by all 13 persons (Rs. 352.08).
Therefore, none of the given options is the correct answer.
Note: The correct answer may not be available in the given options.
Let's assume the average expenditure of all 13 persons is 'x'.
According to the given information,
11 persons spent Rs. 25 each over their meals. So, the total expenditure of these 11 persons = 11 * Rs. 25 = Rs. 275.
The other 2 persons spent collectively Rs. 50 more than the average expenditure of all 13 persons. Therefore, their total expenditure = x + Rs. 50.
Total money spent by all 13 persons = Total expenditure of 11 persons + Total expenditure of 2 persons
= Rs. 275 + (x + Rs. 50)
= Rs. 275 + x + Rs. 50
= Rs. (275 + x + 50)
= Rs. (325 + x)
We know that the total money spent by all 13 persons is equal to the total money spent by them individually.
So, Rs. (325 + x) = 13x
325 = 13x - x
325 = 12x
x = 325/12
x = Rs. 27.08 (approx.)
Therefore, the average expenditure of all 13 persons is approximately Rs. 27.08.
Now, let's calculate the total money spent by all 13 persons.
Total money spent by all 13 persons = Total expenditure of 11 persons + Total expenditure of 2 persons
= Rs. 275 + (Rs. 27.08 + Rs. 50)
= Rs. 275 + Rs. 77.08
= Rs. 352.08
Hence, the total money spent by all 13 persons is Rs. 352.08.
The given options are:
a) Rs. 284.02
b) Rs. 484.02
c) Rs. 384.02
d) Rs. 584.02
e) None of these
None of the given options match the calculated total money spent by all 13 persons (Rs. 352.08).
Therefore, none of the given options is the correct answer.
Note: The correct answer may not be available in the given options.
A truck after travelling a distance of 135km develops a problem in the engine and proceed at 3/5th of its former speed and arrives at the destination 90 min late. Had the problem developed 75km further on, the truck would have arrived 20 minutes sooner. Find the original speed of the truck?- a)145 km/h
- b)135 km/h
- c)150 km/h
- d)160 km/h
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A truck after travelling a distance of 135km develops a problem in the engine and proceed at 3/5th of its former speed and arrives at the destination 90 min late. Had the problem developed 75km further on, the truck would have arrived 20 minutes sooner. Find the original speed of the truck?
a)
145 km/h
b)
135 km/h
c)
150 km/h
d)
160 km/h
e)
None of these
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
As in 1st case problem is developed after travelling 135 km and in 2nd case problem is developed after travelling 210 km( i.e 135+75). It means due to difference in speed of truck in travelling 75 km, truck take 20 min. less.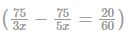
Let original speed of truck be ‘5 x’
Therefore, former speed of truck be ‘3 x’
According to question,
x = 30
Therefore, original speed of truck = 5 x = 5 X 30 = 150 km/h
Hence correct answer is option C.
Under the Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana–Gramin (PMAY-G), how many houses as of February 21, 2022, have been completed against the allocated cumulative target of 2.62 crore houses?- a)1.73 Cr houses
- b)1.62 Cr houses
- c)1.65 Cr houses
- d)1.86 Cr houses
- e)1.70 Cr houses
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Under the Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana–Gramin (PMAY-G), how many houses as of February 21, 2022, have been completed against the allocated cumulative target of 2.62 crore houses?
a)
1.73 Cr houses
b)
1.62 Cr houses
c)
1.65 Cr houses
d)
1.86 Cr houses
e)
1.70 Cr houses
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana (Gramin) PMAY-G was launched by Hon‟ by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi on November 20, 2016, to construct 2.95 Crore houses by the year 2022.
As of 21st February 2022, a total of 1.73 crores PMAY-G houses have been completed against the allocated cumulative target of 2.62 crore houses.
The cabinet extended Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana (Gramin) (PMAY-G) beyond March 2021 till March 2024 as per the existing norms to complete the remaining houses within a cumulative target of 2.95 crore houses.
In making decisions about important questions, it is desirable to be able to distinguish between “Strong” arguments and “Weak” arguments in so far as they relate to the question. “Strong” arguments are those which are both important and directly related to the question. “Weak” arguments are those which are of minor importance and also may not be directly related to the question or may be related to a trivial aspect of the question.Instructions: Each question below is followed by two arguments numbered I and II. You have to decide which of the arguments is a strong argument and which is a weak argument. Give answerStatement: Should the Indian government launch community-based programme with focus on the mother’s care?Arguments:I. Yes, the mother plays a big role in child’s good health and if the programme is community-based it will have immense impact on the poor nutritional condition of the child in IndiaII. No, it will harm the secular status of the country.- a)If neither I nor II is strong.
- b)If only argument II is strong.
- c)If either I or II is strong.
- d)If only argument I is strong.
- e)If both I and II are strong.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In making decisions about important questions, it is desirable to be able to distinguish between “Strong” arguments and “Weak” arguments in so far as they relate to the question. “Strong” arguments are those which are both important and directly related to the question. “Weak” arguments are those which are of minor importance and also may not be directly related to the question or may be related to a trivial aspect of the question.
Instructions: Each question below is followed by two arguments numbered I and II. You have to decide which of the arguments is a strong argument and which is a weak argument. Give answer
Statement: Should the Indian government launch community-based programme with focus on the mother’s care?
Arguments:
I. Yes, the mother plays a big role in child’s good health and if the programme is community-based it will have immense impact on the poor nutritional condition of the child in India
II. No, it will harm the secular status of the country.
a)
If neither I nor II is strong.
b)
If only argument II is strong.
c)
If either I or II is strong.
d)
If only argument I is strong.
e)
If both I and II are strong.
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Only I is strong because nutritional condition of a child is directly related with the role of a mother and if the programme is community-based its result will be remarkable. II is a weak argument because it is a misinterpretation of the work ‘community’.
DHCP (dynamic host configuration protocol) provides ________ to the client.- a)IP address
- b)MAC address
- c)URL
- d)Both (A) and (B)
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
DHCP (dynamic host configuration protocol) provides ________ to the client.
a)
IP address
b)
MAC address
c)
URL
d)
Both (A) and (B)
e)
None of these

|
Hridoy Sharma answered |
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) provides IP address to the client.
DHCP, which stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, is a network protocol that enables devices to obtain IP addresses and other network configuration parameters automatically. It is commonly used in local area networks (LANs) and is essential for the proper functioning of network devices.
Key Points:
- DHCP provides IP addresses to clients automatically.
- It eliminates the need for manual configuration of IP addresses on each device.
- DHCP allows for efficient and centralized management of IP addresses in a network.
- It ensures that devices on the network are assigned unique IP addresses to avoid conflicts.
- DHCP also provides other network configuration parameters, such as subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server addresses.
How DHCP works:
1. DHCP Discover: When a client device joins a network, it sends a DHCP Discover message to discover available DHCP servers on the network.
2. DHCP Offer: DHCP servers respond to the client's request with a DHCP Offer message, offering an available IP address from its pool.
3. DHCP Request: The client selects one of the offered IP addresses and sends a DHCP Request message to the chosen DHCP server, requesting the lease for that IP address.
4. DHCP Acknowledge: The DHCP server acknowledges the client's request by sending a DHCP Acknowledge message, confirming the lease of the IP address and providing other network configuration parameters.
5. IP Address Lease: The client receives the IP address and configuration parameters from the DHCP server and uses them to configure its network connection.
6. Lease Renewal: The client periodically contacts the DHCP server to renew the lease of the IP address. If the lease expires or the client disconnects from the network, the IP address is released back to the DHCP server's pool for future use.
Advantages of DHCP:
- Simplifies network administration by automating IP address assignment.
- Reduces the chances of IP address conflicts.
- Enables efficient management of IP address allocation and configuration.
- Facilitates easy addition and removal of devices from the network.
In conclusion, DHCP provides IP addresses to clients, eliminating the need for manual configuration and enabling efficient management of network resources.
DHCP, which stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, is a network protocol that enables devices to obtain IP addresses and other network configuration parameters automatically. It is commonly used in local area networks (LANs) and is essential for the proper functioning of network devices.
Key Points:
- DHCP provides IP addresses to clients automatically.
- It eliminates the need for manual configuration of IP addresses on each device.
- DHCP allows for efficient and centralized management of IP addresses in a network.
- It ensures that devices on the network are assigned unique IP addresses to avoid conflicts.
- DHCP also provides other network configuration parameters, such as subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server addresses.
How DHCP works:
1. DHCP Discover: When a client device joins a network, it sends a DHCP Discover message to discover available DHCP servers on the network.
2. DHCP Offer: DHCP servers respond to the client's request with a DHCP Offer message, offering an available IP address from its pool.
3. DHCP Request: The client selects one of the offered IP addresses and sends a DHCP Request message to the chosen DHCP server, requesting the lease for that IP address.
4. DHCP Acknowledge: The DHCP server acknowledges the client's request by sending a DHCP Acknowledge message, confirming the lease of the IP address and providing other network configuration parameters.
5. IP Address Lease: The client receives the IP address and configuration parameters from the DHCP server and uses them to configure its network connection.
6. Lease Renewal: The client periodically contacts the DHCP server to renew the lease of the IP address. If the lease expires or the client disconnects from the network, the IP address is released back to the DHCP server's pool for future use.
Advantages of DHCP:
- Simplifies network administration by automating IP address assignment.
- Reduces the chances of IP address conflicts.
- Enables efficient management of IP address allocation and configuration.
- Facilitates easy addition and removal of devices from the network.
In conclusion, DHCP provides IP addresses to clients, eliminating the need for manual configuration and enabling efficient management of network resources.
Direction: Which of the phrases A, B, C and D given below each sentence should replace the word/phrase printed in underline in the sentence to make it grammatically correct ? If the sentence is correct as it is given and no correction is required, mark E as the answer.Q. She threw caution by the wind and ran away from her own wedding, resulting in the nickname, the run-away bride.- a)threw caution to the wind
- b)threw caution in the wind
- c)threw caution in the water
- d)threw caution in the soil
- e)No correction required
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Which of the phrases A, B, C and D given below each sentence should replace the word/phrase printed in underline in the sentence to make it grammatically correct ? If the sentence is correct as it is given and no correction is required, mark E as the answer.
Q. She threw caution by the wind and ran away from her own wedding, resulting in the nickname, the run-away bride.
a)
threw caution to the wind
b)
threw caution in the wind
c)
threw caution in the water
d)
threw caution in the soil
e)
No correction required

|
Prateek Datta answered |
Understanding the Phrase
The phrase "threw caution by the wind" is incorrect and needs to be corrected for grammatical accuracy. The correct idiomatic expression is "threw caution to the wind."
Explanation of the Correct Phrase
- Meaning: The phrase "threw caution to the wind" means to abandon all concerns, worries, or hesitation in favor of taking a bold or risky action. In this context, it effectively describes the action of the bride who decided to leave her wedding despite the potential consequences.
- Usage: This idiom is often used to illustrate a moment of spontaneity or reckless abandon, which aligns perfectly with the bride's decision to run away.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
- Option B: "threw caution in the wind"
- This variation is not a recognized idiom and does not convey the intended meaning.
- Option C: "threw caution in the water"
- This phrase lacks idiomatic recognition and does not fit the context of abandoning caution.
- Option D: "threw caution in the soil"
- Similar to Option C, this phrase is not an established idiom and does not make sense in this context.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option A, "threw caution to the wind." Using this phrase enhances the clarity and impact of the sentence, effectively conveying the bride's impulsive decision.
The phrase "threw caution by the wind" is incorrect and needs to be corrected for grammatical accuracy. The correct idiomatic expression is "threw caution to the wind."
Explanation of the Correct Phrase
- Meaning: The phrase "threw caution to the wind" means to abandon all concerns, worries, or hesitation in favor of taking a bold or risky action. In this context, it effectively describes the action of the bride who decided to leave her wedding despite the potential consequences.
- Usage: This idiom is often used to illustrate a moment of spontaneity or reckless abandon, which aligns perfectly with the bride's decision to run away.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
- Option B: "threw caution in the wind"
- This variation is not a recognized idiom and does not convey the intended meaning.
- Option C: "threw caution in the water"
- This phrase lacks idiomatic recognition and does not fit the context of abandoning caution.
- Option D: "threw caution in the soil"
- Similar to Option C, this phrase is not an established idiom and does not make sense in this context.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option A, "threw caution to the wind." Using this phrase enhances the clarity and impact of the sentence, effectively conveying the bride's impulsive decision.
8 friends A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H live on 8 different floors of a building. The floors are numbered from 1 to 8. Each of these eight friends like one of the sports among chess, pogo, snooker, table-tennis, boxing, basketball, volleyball and frisbee. Further, the following information is also known
A lives on a floor which is 3 floors above B’s floor. None of them like basketball and none of them live at the highest or lowest floor. The person who likes snooker lives on the top floor and the person who lives immediately below the C’s floor likes boxing. There is exactly one person who lives between H and D. H likes table-tennis and lives on a floor whose number is lower than that of D. 2 people live between C and E and C is not a neighbour of B. Neither E nor B likes frisbee. G lives on third floor and likes volleyball. E does not like basketball. Q. Which of the following is definitely true?- a)B likes chess
- b)E likes pogo
- c)C lives on seventh floor
- d)B lives on 4th floor
- e)A likes snooker
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
8 friends A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H live on 8 different floors of a building. The floors are numbered from 1 to 8. Each of these eight friends like one of the sports among chess, pogo, snooker, table-tennis, boxing, basketball, volleyball and frisbee. Further, the following information is also known
A lives on a floor which is 3 floors above B’s floor. None of them like basketball and none of them live at the highest or lowest floor.
The person who likes snooker lives on the top floor and the person who lives immediately below the C’s floor likes boxing.
There is exactly one person who lives between H and D. H likes table-tennis and lives on a floor whose number is lower than that of D.
2 people live between C and E and C is not a neighbour of B. Neither E nor B likes frisbee.
G lives on third floor and likes volleyball. E does not like basketball.
Q. Which of the following is definitely true?
a)
B likes chess
b)
E likes pogo
c)
C lives on seventh floor
d)
B lives on 4th floor
e)
A likes snooker

|
Harsh Choudhary answered |
Understanding the Problem
To determine which statement is definitely true about the friends and their preferences, let's analyze the given clues systematically.
Key Information from Clues
- A lives 3 floors above B.
- No one lives on the highest (8th) or lowest (1st) floor.
- The person who likes snooker is on the top floor (8th floor).
- The person below C likes boxing.
- There is one person between H and D; H likes table-tennis and lives below D.
- Two people live between C and E; C is not a neighbor of B.
- E and B do not like frisbee.
- G is on the 3rd floor and likes volleyball.
Floor Assignments
1. G is confirmed on the 3rd floor.
2. Snooker is on the 8th floor.
3. Since A lives 3 floors above B, the only possible pairs are (B, A) on (4, 7) or (5, 8). However, since 8 is snooker, this limits A to the 7th floor and B to the 4th floor.
4. H must be on the 2nd floor (below D on the 5th floor).
5. C, therefore, must be on the 6th floor (boxing directly below).
6. E must be on the 1st floor, as it’s the only remaining floor.
Final Floor Assignment
- 1st: E
- 2nd: H (Table-tennis)
- 3rd: G (Volleyball)
- 4th: B
- 5th: D
- 6th: C (Boxing)
- 7th: A
- 8th: (Snooker)
Conclusion
From this analysis, we can conclude that:
- B lives on the 4th floor.
- Thus, option D is indeed correct.
This structured breakdown clarifies how we arrive at the final conclusion regarding B's floor assignment.
To determine which statement is definitely true about the friends and their preferences, let's analyze the given clues systematically.
Key Information from Clues
- A lives 3 floors above B.
- No one lives on the highest (8th) or lowest (1st) floor.
- The person who likes snooker is on the top floor (8th floor).
- The person below C likes boxing.
- There is one person between H and D; H likes table-tennis and lives below D.
- Two people live between C and E; C is not a neighbor of B.
- E and B do not like frisbee.
- G is on the 3rd floor and likes volleyball.
Floor Assignments
1. G is confirmed on the 3rd floor.
2. Snooker is on the 8th floor.
3. Since A lives 3 floors above B, the only possible pairs are (B, A) on (4, 7) or (5, 8). However, since 8 is snooker, this limits A to the 7th floor and B to the 4th floor.
4. H must be on the 2nd floor (below D on the 5th floor).
5. C, therefore, must be on the 6th floor (boxing directly below).
6. E must be on the 1st floor, as it’s the only remaining floor.
Final Floor Assignment
- 1st: E
- 2nd: H (Table-tennis)
- 3rd: G (Volleyball)
- 4th: B
- 5th: D
- 6th: C (Boxing)
- 7th: A
- 8th: (Snooker)
Conclusion
From this analysis, we can conclude that:
- B lives on the 4th floor.
- Thus, option D is indeed correct.
This structured breakdown clarifies how we arrive at the final conclusion regarding B's floor assignment.
P and Q together can complete the job in 20 days. Both started the work together and after 8 days, P worked at 80% of his efficiency and Q worked at 2/3rd of its efficiency so the remaining work completed in 4 days more than the stipulated time. If after 8 days only slower worker worked with his original efficiency then in how many days remaining work will be completed?- a)36 days
- b)28 days
- c)40 days
- d)32 days
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
P and Q together can complete the job in 20 days. Both started the work together and after 8 days, P worked at 80% of his efficiency and Q worked at 2/3rd of its efficiency so the remaining work completed in 4 days more than the stipulated time. If after 8 days only slower worker worked with his original efficiency then in how many days remaining work will be completed?
a)
36 days
b)
28 days
c)
40 days
d)
32 days
e)
None of these

|
Tanishq Sengupta answered |
Understanding the Problem:
- Let the total work be 1 unit.
- P and Q together complete the job in 20 days.
- After 8 days, P worked at 80% efficiency and Q worked at 2/3 efficiency.
- Remaining work was completed in 4 days more than the stipulated time.
Calculating Efficiencies:
- Since P and Q together complete the job in 20 days, their combined efficiency is 1/20.
- Let P's efficiency be x and Q's efficiency be y.
- Therefore, x + y = 1/20.
Calculating Work Done:
- In the first 8 days, P and Q together completed 8*(x+y) = 8/20 = 2/5 of the work.
- So, the remaining work is 1 - 2/5 = 3/5.
Calculating Work Done in the Next 4 Days:
- After 8 days, P worked at 80% efficiency and Q worked at 2/3 efficiency.
- So, the work done by P in the next 4 days = 4 * 0.8 * x = 3.2x.
- The work done by Q in the next 4 days = 4 * (2/3) * y = 8/3y.
- Combined work done by P and Q in the next 4 days = 3.2x + 8/3y.
Formulating Equations:
- Since the remaining work was completed in 4 days more than the stipulated time, the work done in the next 4 days equals the remaining work.
- Therefore, 3.2x + 8/3y = 3/5.
Solving the Equations:
- Substitute x + y = 1/20 into the equation 3.2x + 8/3y = 3/5.
- Solve for x and y.
- Once you have x and y, calculate how many more days the slower worker (Q) will take to complete the remaining work.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - 32 days.
- Let the total work be 1 unit.
- P and Q together complete the job in 20 days.
- After 8 days, P worked at 80% efficiency and Q worked at 2/3 efficiency.
- Remaining work was completed in 4 days more than the stipulated time.
Calculating Efficiencies:
- Since P and Q together complete the job in 20 days, their combined efficiency is 1/20.
- Let P's efficiency be x and Q's efficiency be y.
- Therefore, x + y = 1/20.
Calculating Work Done:
- In the first 8 days, P and Q together completed 8*(x+y) = 8/20 = 2/5 of the work.
- So, the remaining work is 1 - 2/5 = 3/5.
Calculating Work Done in the Next 4 Days:
- After 8 days, P worked at 80% efficiency and Q worked at 2/3 efficiency.
- So, the work done by P in the next 4 days = 4 * 0.8 * x = 3.2x.
- The work done by Q in the next 4 days = 4 * (2/3) * y = 8/3y.
- Combined work done by P and Q in the next 4 days = 3.2x + 8/3y.
Formulating Equations:
- Since the remaining work was completed in 4 days more than the stipulated time, the work done in the next 4 days equals the remaining work.
- Therefore, 3.2x + 8/3y = 3/5.
Solving the Equations:
- Substitute x + y = 1/20 into the equation 3.2x + 8/3y = 3/5.
- Solve for x and y.
- Once you have x and y, calculate how many more days the slower worker (Q) will take to complete the remaining work.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - 32 days.
Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given question.Eight people A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H are sitting around a circular table facing towards the table and not in the same order. Each of them likes a different color i.e. Purple, pink, red, green, blue, black, yellow, and orange but not necessarily in the same order.The one who likes red sits to the immediate left of the one who likes black. D does not like the yellow color. F sits third to the left of A, who likes purple and the person who likes purple sits to the immediate left of G. C sits to the immediate right of E and neither of them likes blue. The one who likes green and B has two people sitting in between them. C, F, and G, neither of them like green color. F and the person who likes blue has one person in between them. D sits second to the right of H. E sits opposite the person who likes yellow and the person who likes yellow sits immediately next to the one who likes orange.Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and hence form a group. Which is the one that does not belong to that group?- a)Blue, D
- b)Yellow, B
- c)Pink, A
- d)Black, C
- e)Orange, H
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information carefully to answer the given question.
Eight people A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H are sitting around a circular table facing towards the table and not in the same order. Each of them likes a different color i.e. Purple, pink, red, green, blue, black, yellow, and orange but not necessarily in the same order.
The one who likes red sits to the immediate left of the one who likes black. D does not like the yellow color. F sits third to the left of A, who likes purple and the person who likes purple sits to the immediate left of G. C sits to the immediate right of E and neither of them likes blue. The one who likes green and B has two people sitting in between them. C, F, and G, neither of them like green color. F and the person who likes blue has one person in between them. D sits second to the right of H. E sits opposite the person who likes yellow and the person who likes yellow sits immediately next to the one who likes orange.
Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and hence form a group. Which is the one that does not belong to that group?
a)
Blue, D
b)
Yellow, B
c)
Pink, A
d)
Black, C
e)
Orange, H
|
|
Dia Mehta answered |
Eight people: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H
Eight Colors: Purple, pink, red, green, blue, black, yellow, and orange
1) F sits third to the left of A, who likes purple, and the person who likes purple sits to the immediate left of G.
2) F and the person who likes blue has one person in between them.

3) C sits to the immediate right of E and neither of them likes blue.
4) E sits opposite the person who likes yellow and the person who likes yellow sits immediately next to the one who likes orange.

5) The one who likes green and B has two people sitting in between them.
6) C, F, and G, neither of them like green color.


7) D sits second to the right of H.
8) D does not like the yellow color.
This is not possible in cases II a and II b, therefore both the cases get eliminated.

9) The one who likes red sits to the immediate left of the one who likes black.

Clearly, "Black and C" does not belong to the group as all the other pairs sit adjacent to each other.
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the question that follow:Eight friends A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order. All friends are facing the centre. Each person has different salaries i.e.15000, 19000, 16000, 32000, 12000, 70000, 40000, and 60000 and are of different ages 20, 26, 56, 40, 34, 54, 43 and 30 years but not necessarily in the same order. There is an angle of 135° between A and G.B’s salary is double of H’s but less than D’s salary. There is an angle of 90° between A and H. F sits at 135° clockwise direction to B. The average of B and D’s age is equal to the age of G. Salary of the one, who sits 2nd to the right of B is divisible by 4. D is not an immediate neighbour of the person who is third to the left of A. G’s salary is thousand rupees less than 1/3rd of A’s salary. There is an angle of 180° between B and the one whose age is 54 years. C’s salary is third highest salary among all the salaries. There is an angle of 180° between F and E, whose salary is divisible by 3 but not 12000. B sits at 90° clockwise direction of A. E is the youngest in the group. Only two pair is sitting diagonally opposite to each other has age difference of 6 years. The salary of C is 1000 multiple of its age. The one who have the highest salary is third youngest in the group.Which is the correct combination?- a)D – 70000 – 30
- b)A – 15000 – 20
- c)E – 32000 – 56
- d)H – 12000 – 26
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the question that follow:
Eight friends A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order. All friends are facing the centre. Each person has different salaries i.e.15000, 19000, 16000, 32000, 12000, 70000, 40000, and 60000 and are of different ages 20, 26, 56, 40, 34, 54, 43 and 30 years but not necessarily in the same order. There is an angle of 135° between A and G.B’s salary is double of H’s but less than D’s salary. There is an angle of 90° between A and H. F sits at 135° clockwise direction to B. The average of B and D’s age is equal to the age of G. Salary of the one, who sits 2nd to the right of B is divisible by 4. D is not an immediate neighbour of the person who is third to the left of A. G’s salary is thousand rupees less than 1/3rd of A’s salary. There is an angle of 180° between B and the one whose age is 54 years. C’s salary is third highest salary among all the salaries. There is an angle of 180° between F and E, whose salary is divisible by 3 but not 12000. B sits at 90° clockwise direction of A. E is the youngest in the group. Only two pair is sitting diagonally opposite to each other has age difference of 6 years. The salary of C is 1000 multiple of its age. The one who have the highest salary is third youngest in the group.
Which is the correct combination?
a)
D – 70000 – 30
b)
A – 15000 – 20
c)
E – 32000 – 56
d)
H – 12000 – 26
e)
None of these

|
Tarun Nambiar answered |
Seating Arrangement Analysis
To solve the arrangement of the eight friends and their respective salaries and ages, we need to analyze the given clues systematically.
Key Observations:
- B's Salary Relation: B's salary is double H's but less than D's, indicating H earns less than B.
- Seating Positions: A and H have a 90° angle between them, and B is 90° clockwise from A. F is 135° clockwise from B, and there is a 180° angle between B and a person aged 54.
- Age and Salary Relationships: The average of B and D’s ages equals G’s age. C’s salary is the third highest and is a multiple of its age.
- Divisibility Conditions: The salary of the person sitting second to the right of B is divisible by 4, and E's salary is divisible by 3 but not equal to 12000.
Detailed Conclusions:
- By piecing together the clues, we deduce that D has the highest salary of 70000, making D the third youngest at age 30.
- E, being the youngest, must thus be 20 years old and earns 15000.
- H must then be 26 years old with a salary of 12000, as B's salary doubles H's and must be less than D's.
- With C being the third highest salary, we find its values and ages align with the given conditions.
Correct Combination:
Thus, the combination D – 70000 – 30 fits perfectly as it meets all the constraints provided in the clues.
This thorough analysis confirms that the correct answer is option 'A'.
To solve the arrangement of the eight friends and their respective salaries and ages, we need to analyze the given clues systematically.
Key Observations:
- B's Salary Relation: B's salary is double H's but less than D's, indicating H earns less than B.
- Seating Positions: A and H have a 90° angle between them, and B is 90° clockwise from A. F is 135° clockwise from B, and there is a 180° angle between B and a person aged 54.
- Age and Salary Relationships: The average of B and D’s ages equals G’s age. C’s salary is the third highest and is a multiple of its age.
- Divisibility Conditions: The salary of the person sitting second to the right of B is divisible by 4, and E's salary is divisible by 3 but not equal to 12000.
Detailed Conclusions:
- By piecing together the clues, we deduce that D has the highest salary of 70000, making D the third youngest at age 30.
- E, being the youngest, must thus be 20 years old and earns 15000.
- H must then be 26 years old with a salary of 12000, as B's salary doubles H's and must be less than D's.
- With C being the third highest salary, we find its values and ages align with the given conditions.
Correct Combination:
Thus, the combination D – 70000 – 30 fits perfectly as it meets all the constraints provided in the clues.
This thorough analysis confirms that the correct answer is option 'A'.
Study the following information and answer the given questions.Ten people live in three buildings namely X, Y and Z. Building X is immediate left of building Y whereas building Z is to the second right of building X. Not more than four people live in a building and immediate above or below implies that the person is not in the same building. O does not live in building Y but lives at floor number 5. P lives in that floor which is the sum of the floor number in which Q and O lives. The sum of floor number in which R and M live is 3 and both live in different building. The sum of the number of the floor in which M and S live is equal to the floor number in which N live. M lives in the even numbered floor. Equal numbers of floors are there below the floor in which T lives and above the floor in which V lives. As many floors are there below the floor in which M lives as it is above the floor in which N lives. There are four floors above the floor in which O lives. There are two floors between V and T in the same building. U lives on that floor number which is immediately below the floor number in which S lives. Only two people live in building Z. O and U live in same building. Q lives in building Y and lives at the topmost floor. M and N live in same building but they do not live in building X. Q lives immediately two floors above the floor in which O lives.Q. Who among the following lives on even numbered floor?- a)M
- b)Q
- c)U
- d)T
- e)R
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information and answer the given questions.
Ten people live in three buildings namely X, Y and Z. Building X is immediate left of building Y whereas building Z is to the second right of building X. Not more than four people live in a building and immediate above or below implies that the person is not in the same building. O does not live in building Y but lives at floor number 5. P lives in that floor which is the sum of the floor number in which Q and O lives. The sum of floor number in which R and M live is 3 and both live in different building. The sum of the number of the floor in which M and S live is equal to the floor number in which N live. M lives in the even numbered floor. Equal numbers of floors are there below the floor in which T lives and above the floor in which V lives. As many floors are there below the floor in which M lives as it is above the floor in which N lives. There are four floors above the floor in which O lives. There are two floors between V and T in the same building. U lives on that floor number which is immediately below the floor number in which S lives. Only two people live in building Z. O and U live in same building. Q lives in building Y and lives at the topmost floor. M and N live in same building but they do not live in building X. Q lives immediately two floors above the floor in which O lives.
Q. Who among the following lives on even numbered floor?
a)
M
b)
Q
c)
U
d)
T
e)
R

|
Maya Kaur answered |
Understanding the Problem
To determine who lives on an even-numbered floor, let's analyze the given information step-by-step.
Buildings and Floor Arrangement
- Buildings: X, Y, Z
- Building X is to the immediate left of Y, and Z is the second right of X.
- O lives on floor 5 (not in Y), and Q lives at the topmost floor in Y.
Floor Assignments
1. O's Floor: O is on floor 5.
2. Q's Position: If Q is on the topmost floor in Y, and O is on floor 5, Q must be on floor 6 (the topmost of 6).
3. P's Floor: P lives on a floor which is the sum of the floor numbers of Q (6) and O (5), so P is on floor 11.
4. R and M's Floors: The sum of R and M's floors is 3. Since they live in different buildings, possible pairs are (1,2) or (2,1).
5. M's Even Floor: M lives on an even-numbered floor. The only possible even-numbered floor that adds up to 3 with R (who must be on 1) is M on 2 and R on 1.
Remaining Assignments
- M is on floor 2, R is on floor 1.
- N lives in the same building as M, so N is also on floor 3.
- T and V have two floors between them; with only 6 floors total, this gives potential placements.
- U lives below S, and since M is even, the only remaining even floor is 4.
Final Identification
After organizing the data based on the constraints:
- M is on floor 2 (even).
- Q is on floor 6 (odd).
- U lives on floor 3 (odd).
- T lives on an odd floor.
- R lives on floor 1 (odd).
Thus, the only one living on an even-numbered floor is M.
Conclusion
The answer is a) M.
To determine who lives on an even-numbered floor, let's analyze the given information step-by-step.
Buildings and Floor Arrangement
- Buildings: X, Y, Z
- Building X is to the immediate left of Y, and Z is the second right of X.
- O lives on floor 5 (not in Y), and Q lives at the topmost floor in Y.
Floor Assignments
1. O's Floor: O is on floor 5.
2. Q's Position: If Q is on the topmost floor in Y, and O is on floor 5, Q must be on floor 6 (the topmost of 6).
3. P's Floor: P lives on a floor which is the sum of the floor numbers of Q (6) and O (5), so P is on floor 11.
4. R and M's Floors: The sum of R and M's floors is 3. Since they live in different buildings, possible pairs are (1,2) or (2,1).
5. M's Even Floor: M lives on an even-numbered floor. The only possible even-numbered floor that adds up to 3 with R (who must be on 1) is M on 2 and R on 1.
Remaining Assignments
- M is on floor 2, R is on floor 1.
- N lives in the same building as M, so N is also on floor 3.
- T and V have two floors between them; with only 6 floors total, this gives potential placements.
- U lives below S, and since M is even, the only remaining even floor is 4.
Final Identification
After organizing the data based on the constraints:
- M is on floor 2 (even).
- Q is on floor 6 (odd).
- U lives on floor 3 (odd).
- T lives on an odd floor.
- R lives on floor 1 (odd).
Thus, the only one living on an even-numbered floor is M.
Conclusion
The answer is a) M.
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the following questions.A, B, C and D are 4 friends. They possess some coins of different denominations of Rs. 1, Rs. 2, Rs. 5 and Rs. 10 such that the total value of money of each denomination is equal and is Rs. 120. A has 20 coins of Rs. 1 and Rs. 2 coins with A is 50% of Rs. 1 coins he has. Number of Rs. 5 coins with A is average of number of Rs. 2 and Rs. 5 coins with D. Total money with A is the average of money with B, C and D. The number of Rs. 10 coins with D is 1/4 of the total Rs. 10 coins and C has half of the total number of Rs. 1 and Rs. 10 coins. The total number of coins with A is average of the total coins with B and D. The number of Rs. 10 coins with A is same as that of D. The total number of Rs. 5 coins with B and C is half of Rs. 2 coins with B which is same as the number of Rs. 1 coins with A. Using this information answer the following questions.Find the total money D is having, if number of Rs. 1 coins with D is 15.- a)92
- b)112
- c)133
- d)97
- e)91
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the following paragraph carefully and answer the following questions.
A, B, C and D are 4 friends. They possess some coins of different denominations of Rs. 1, Rs. 2, Rs. 5 and Rs. 10 such that the total value of money of each denomination is equal and is Rs. 120. A has 20 coins of Rs. 1 and Rs. 2 coins with A is 50% of Rs. 1 coins he has. Number of Rs. 5 coins with A is average of number of Rs. 2 and Rs. 5 coins with D. Total money with A is the average of money with B, C and D. The number of Rs. 10 coins with D is 1/4 of the total Rs. 10 coins and C has half of the total number of Rs. 1 and Rs. 10 coins. The total number of coins with A is average of the total coins with B and D. The number of Rs. 10 coins with A is same as that of D. The total number of Rs. 5 coins with B and C is half of Rs. 2 coins with B which is same as the number of Rs. 1 coins with A. Using this information answer the following questions.
Find the total money D is having, if number of Rs. 1 coins with D is 15.
a)
92
b)
112
c)
133
d)
97
e)
91
|
|
Rohan Sengupta answered |
Based upon the information in the question, we can draw a table which shows the number of coins of different denominations with different people.
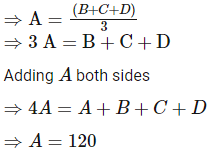

∵ In each denomination, value of money is Rs. 120
∴ Total money with all four of them is 4 × 120 = Rs. 480
A is having average money with B, C and D
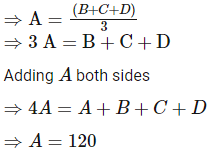
∴ Total money with A is Rs. 120
⇒ 20 × 1 + 10 × 2 + {(x + y) ÷ 2} × 5 + 3 × 10 = 120
⇒ {(x + y) ÷ 2} × 5 = 120 – 20 – 20 – 30 = 50
⇒ x + y = 20
We know the value of denomination 5 is Rs. 120
⇒ The number of coins of Rs. 5 = 24
∵ a + b = 10
⇒ (x + y) ÷ 2 + a + b + y = 24
⇒ 10 + 10 + y = 24
⇒ y = 4
⇒ x = 20 – 4 = 16
∵ Number of Rs. 1 coins is 15
∴ Total value of money with D = 15 × 1 + 16 × 2 + 4 × 5 + 3 × 10
⇒ D = 15 + 32 + 20 + 30 = 97
Direction: A, B, C, D, E and F are six family members, who were spread across three generations.Further, the following information is also known:* There are two married couples in the family.* F is the father of C.* C is the maternal uncle of D.* E is the son in law of B.* There are no single-mothers/fathers in the family.How is B related to D?- a)Grandmother
- b)Niece
- c)Mother
- d)Cousin
- e)Son-in-law
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: A, B, C, D, E and F are six family members, who were spread across three generations.
Further, the following information is also known:
* There are two married couples in the family.
* F is the father of C.
* C is the maternal uncle of D.
* E is the son in law of B.
* There are no single-mothers/fathers in the family.
How is B related to D?
a)
Grandmother
b)
Niece
c)
Mother
d)
Cousin
e)
Son-in-law
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Given the family is spread across three generation.
"F is the father of C.", "C is the maternal uncle of D." ⇒ we can say that F belongs to third generation, C belongs to second generation and D belongs to first generation.
⇒ the two married couples are F and her wife, D's parents.
"E is the son in law of B." ⇒ E is the wife of F, B is the husband of the person A.
Based on the given information the following family tree could be derived.

B is the Grandmother of D.
Hence correct answer is option A.
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the question that follow:Eight friends A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order. All friends are facing the centre. Each person has different salaries i.e.15000, 19000, 16000, 32000, 12000, 70000, 40000, and 60000 and are of different ages 20, 26, 56, 40, 34, 54, 43 and 30 years but not necessarily in the same order. There is an angle of 135° between A and G.B’s salary is double of H’s but less than D’s salary. There is an angle of 90° between A and H. F sits at 135° clockwise direction to B. The average of B and D’s age is equal to the age of G. Salary of the one, who sits 2nd to the right of B is divisible by 4. D is not an immediate neighbour of the person who is third to the left of A. G’s salary is thousand rupees less than 1/3rd of A’s salary. There is an angle of 180° between B and the one whose age is 54 years. C’s salary is third highest salary among all the salaries. There is an angle of 180° between F and E, whose salary is divisible by 3 but not 12000. B sits at 90° clockwise direction of A. E is the youngest in the group. Only two pair is sitting diagonally opposite to each other has age difference of 6 years. The salary of C is 1000 multiple of its age. The one who have the highest salary is third youngest in the group.What is B’s age?- a)56 years
- b)43 years
- c)34 years
- d)54 years
- e)26 years
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the question that follow:
Eight friends A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order. All friends are facing the centre. Each person has different salaries i.e.15000, 19000, 16000, 32000, 12000, 70000, 40000, and 60000 and are of different ages 20, 26, 56, 40, 34, 54, 43 and 30 years but not necessarily in the same order. There is an angle of 135° between A and G.B’s salary is double of H’s but less than D’s salary. There is an angle of 90° between A and H. F sits at 135° clockwise direction to B. The average of B and D’s age is equal to the age of G. Salary of the one, who sits 2nd to the right of B is divisible by 4. D is not an immediate neighbour of the person who is third to the left of A. G’s salary is thousand rupees less than 1/3rd of A’s salary. There is an angle of 180° between B and the one whose age is 54 years. C’s salary is third highest salary among all the salaries. There is an angle of 180° between F and E, whose salary is divisible by 3 but not 12000. B sits at 90° clockwise direction of A. E is the youngest in the group. Only two pair is sitting diagonally opposite to each other has age difference of 6 years. The salary of C is 1000 multiple of its age. The one who have the highest salary is third youngest in the group.
What is B’s age?
a)
56 years
b)
43 years
c)
34 years
d)
54 years
e)
26 years
|
|
Dia Mehta answered |
Eight friends: A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H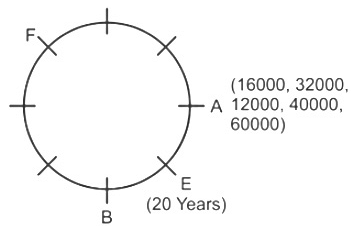
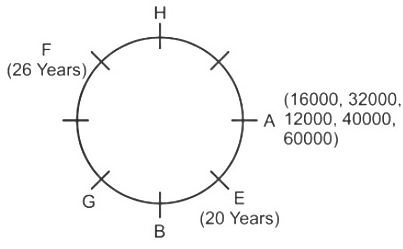
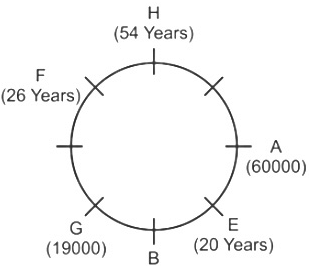
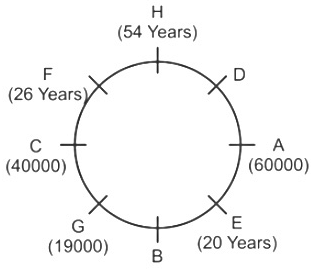
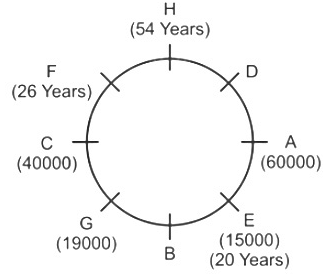
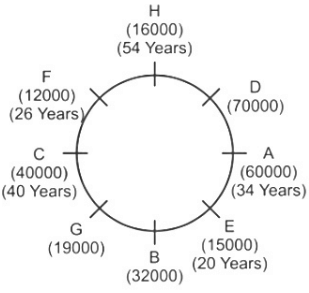
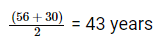
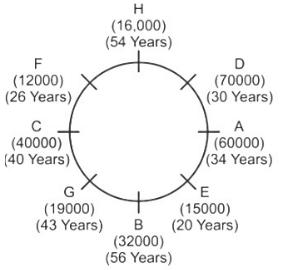
Salaries: 15000, 19000, 16000, 32000, 12000, 70000, 40000, and 60000
Ages: 20, 26, 56, 40, 34, 54, 43 and 30 years
1) F sits at 135˚ clockwise direction to B.
2) Salary of the one, who sits 2nd to right of B is divisible by 4. Here, the probabilities are (16000, 32000, 12000, 40000, 60000)
3) There is an angle of 180˚ between F and E.
4) B sits at 90˚ clockwise direction of A i.e. A is 90˚ anti-clockwise direction of B.
5) E is the youngest in the group. Therefore, E is of 20 years.

6) There is an angle of 90˚ between A and H.
7) There is an angle of 135° between A and G.
8) Only two pair is sitting diagnolly opposite to each other has age difference of 6 years.
(Such two age pairs are 20, 26 and 30, 44)

9) G’s salary is thousand rupees less than 1/3rd of A’s salary i.e. 60000/3 = 20000, 20000 – 1000 = 19000.
10) There is an angle of 180˚ between B and the one whose age is 54 years.

11) D is not an immediate neighbour of the person who is third to the left of A.
Therefore, only place left for D is between A and H and for C is between G and F.
12) C’s salary is third highest salary among all the salaries i.e. 40000.

13) E’s salary is divisible by 3 but not 12000.

14) B’s salary is double of H’s but less than D’s salary. (32,000 is double of 16000 but less than 70000, furthermore 12000 which is left is F’s salary).
15) The salary of C is 1000 multiple of its age. (Therefore, age of C is 40 years, and using point 8) the age difference of 6 to 34 is 38, therefore age of A is 34 years)

16) The one who have the highest salary is third youngest in the group. (Therefore, D is of 30 years)
17) The average of B and D’s age is equal to the age of G.
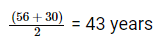

So, B’s age is 56 years.
Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on it.A survey conducted among total 180 people in three area of east of Delhi – Shahdara, Chandarlok, and Vivek Vihar about their likes among three products P, Q, and R.
Number of people belongs to Shahdara is same as difference between number of people those likes Q and those likes R. Number of people those likes product P and exactly one more product is same as number of people those likes product Q, while number of people those likes both P and R but not Q is thrice of those likes all three products. Number of people those likes R are the highest, while number of people those likes Q is least among the three given products. One – Sixth of total surveyed people don’t likes any of the product. Number of people those likes both P and Q but not R is twice of those likes both P and R but not Q. Number of people those likes all three products is multiple of three which is twice of people those likes both Q and R but not P. Find minimum possible number of people those likes only R?- a)55
- b)56
- c)78
- d)46
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on it.
A survey conducted among total 180 people in three area of east of Delhi – Shahdara, Chandarlok, and Vivek Vihar about their likes among three products P, Q, and R.
Number of people belongs to Shahdara is same as difference between number of people those likes Q and those likes R.
Number of people those likes product P and exactly one more product is same as number of people those likes product Q, while number of people those likes both P and R but not Q is thrice of those likes all three products.
Number of people those likes R are the highest, while number of people those likes Q is least among the three given products.
One – Sixth of total surveyed people don’t likes any of the product. Number of people those likes both P and Q but not R is twice of those likes both P and R but not Q.
Number of people those likes all three products is multiple of three which is twice of people those likes both Q and R but not P.
Find minimum possible number of people those likes only R?
a)
55
b)
56
c)
78
d)
46
e)
None of these
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Number of people those likes all three products is a multiple of 3, = 3a
So, number of people those likes Q and R but not P = 3a/2 = 1.5a
Number of people those likes product P and exactly one more product is same as number of people those likes product Q, while number of people those likes both P and R but not Q is thrice of those likes all three products.
(Both P and Q but not R) + (Both P and R but not Q) = (Both P and Q but not R) + All three + both Q and R but not P + only Q
Number of people those likes both P and R but not Q = 3 x 3a = 9a
Number of people those likes both P and Q but not R = 2 x 9a = 18a
Now,
9a = 3a + 1.5a + only Q
So, Only Q = 4.5a
Now,
All regions people don’t likes any of the product= 180 – 180 x 1/6 = 30
All regions people likes any one of the product = 180 - 30 = 150
Only P + 18a + 4.5a + 9a + 3a + 1.5a + only R = 150
Only P + Only R + 36a = 150
If a = 2,
Only P + Only R = 150 – 72 = 78 (possible)
If a = 4,
Only P + only R = 6
But people those likes R > those likes P >those likes Q
Those likes R = 54 + only R
Those likes P = 120 + Only P
If only P = 0, then only R = 6
So, people those likes R is less than people those likes P
So, a = 4 (not possible)
So, possible value of a = 2

Number of people those likes R = 27 + B
People those likes only P = 60 + A
We know that,
27 + B > 60 + A
B – A > 33………... (1)
Also, we know that (A + B) = 78………. (2)
We need to find the minimum possible value of B
From (1) and (2)
Value of B > (78 + 33)/2 = 55.5
So, minimum possible value of B = 56
Hence answer is option B
The passage given below carries information. Some words and phrases have been highlighted as some questions have been framed on them. Read the same carefully and choose the correct option as your answer.Monsoon rainfall over India is 8% more than what is usual for this time of the year. While this might bode well for agriculture in some regions, it also means floods and concentrated downpours with devastating consequences. At least 25 people were killed over the weekend as torrential rains triggered flash floods and landslips in Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand. Several arterial roads were blocked by debris, as currents washed away bridges and vehicles. The toll was higher in Himachal Pradesh with 21 killed and 12 injured. At least six are missing due to chaos following the downpour. Mandi, Kangra and Chamba were the worst-affected districts in the State. While death and damage to property are the surface manifestation of these rains, there are a range of secondary effects with long-term downstream impact. Schools and transport facilities, for instance, are immediately put out of action, leading to loss of productive hours. Cattle and saplings are left to perish, which in turn destroys livelihoods, debilitates family finances and strains the finances of the state exchequer. The monsoon compresses around 75% of India’s annual rainfall into four months and unevenly waters the country’s highly diverse terrain. It is, therefore, inevitable that some spots are far more vulnerable and bear a disproportionate impact of climate fury. A recent report released by Himachal Pradesh’s Department of Environment, Science and Technology underlines that mountain areas are highly vulnerable to natural disasters, where development over the years has compounded the problem by upsetting the ecological balance of various physical processes.While hill States such as Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand have certain unique challenges, the threats from the vagaries of climate are not unique to them. Monsoon rain patterns are being disrupted leading to a rise in cloudburst-like events as well as a rise in the frequency of high-energy cyclones and droughts. One strategy adopted by the government has been to improve the system of early warning forecasts. The India Meteorological Department now provides fortnightly, weekly and even three-hourly weather forecasts to districts. Within these are integrated warnings about flash floods and lightning. Not all of these are accurate and often, they are not provided early enough for authorities to prepare themselves. In recent years, improvements in early warnings for incoming cyclones have helped state agencies evacuate and rehabilitate most vulnerable, but such success has not been observed for floods. While the inherent risks of infrastructure development in hills and unstable terrain is well understood, these are often elided by authorities in the name of balancing the demands of the people for better infrastructure and services. The increased risk and cost to such projects and infrastructure should be factored in when they are tendered out by the government, and scientific advice regarding development ought to be strictly adhered to.Which of the given options is the central theme of the given passage?- a)The mountain states are used to the vagaries of the climate and do not get affected easily
- b)Development of mountain areas over the years has upset the ecological balance
- c)Our country’s diverse terrains make it difficult for us to maintain the ecological balance
- d)More than expected monsoons are bad for the country as they severely hurt the infrastructure
- e)Heavy monsoons have resulted in loss of lives in most parts of the country
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The passage given below carries information. Some words and phrases have been highlighted as some questions have been framed on them. Read the same carefully and choose the correct option as your answer.
Monsoon rainfall over India is 8% more than what is usual for this time of the year. While this might bode well for agriculture in some regions, it also means floods and concentrated downpours with devastating consequences. At least 25 people were killed over the weekend as torrential rains triggered flash floods and landslips in Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand. Several arterial roads were blocked by debris, as currents washed away bridges and vehicles. The toll was higher in Himachal Pradesh with 21 killed and 12 injured. At least six are missing due to chaos following the downpour. Mandi, Kangra and Chamba were the worst-affected districts in the State. While death and damage to property are the surface manifestation of these rains, there are a range of secondary effects with long-term downstream impact. Schools and transport facilities, for instance, are immediately put out of action, leading to loss of productive hours. Cattle and saplings are left to perish, which in turn destroys livelihoods, debilitates family finances and strains the finances of the state exchequer. The monsoon compresses around 75% of India’s annual rainfall into four months and unevenly waters the country’s highly diverse terrain. It is, therefore, inevitable that some spots are far more vulnerable and bear a disproportionate impact of climate fury. A recent report released by Himachal Pradesh’s Department of Environment, Science and Technology underlines that mountain areas are highly vulnerable to natural disasters, where development over the years has compounded the problem by upsetting the ecological balance of various physical processes.
While hill States such as Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand have certain unique challenges, the threats from the vagaries of climate are not unique to them. Monsoon rain patterns are being disrupted leading to a rise in cloudburst-like events as well as a rise in the frequency of high-energy cyclones and droughts. One strategy adopted by the government has been to improve the system of early warning forecasts. The India Meteorological Department now provides fortnightly, weekly and even three-hourly weather forecasts to districts. Within these are integrated warnings about flash floods and lightning. Not all of these are accurate and often, they are not provided early enough for authorities to prepare themselves. In recent years, improvements in early warnings for incoming cyclones have helped state agencies evacuate and rehabilitate most vulnerable, but such success has not been observed for floods. While the inherent risks of infrastructure development in hills and unstable terrain is well understood, these are often elided by authorities in the name of balancing the demands of the people for better infrastructure and services. The increased risk and cost to such projects and infrastructure should be factored in when they are tendered out by the government, and scientific advice regarding development ought to be strictly adhered to.
Which of the given options is the central theme of the given passage?
a)
The mountain states are used to the vagaries of the climate and do not get affected easily
b)
Development of mountain areas over the years has upset the ecological balance
c)
Our country’s diverse terrains make it difficult for us to maintain the ecological balance
d)
More than expected monsoons are bad for the country as they severely hurt the infrastructure
e)
Heavy monsoons have resulted in loss of lives in most parts of the country
|
|
Rohan Sengupta answered |
The passage does not boast the mountain states’ resilience and their capability to handle the consequences of climate change. Though it has been given that the impacts are not new for them, it does not mean they don’t get affected by it. So, (a) gets eliminated.
(c) has also been mentioned but in the options two different points have been merged which makes it irrelevant. (d) and (e) are impacts of rain but not the central theme as the passage does not only revolve around these.
The correct answer left to mark is hence, (b).
Direction: In the following passage, some words have been left out. Read the passage carefully and select the correct answer for the given blank out of the given alternatives.In the first two months of the New Year and a new decade, India, a climate hotspot, hosted two global leaders who believe global warming is a (1) _______ (practical joke): United States President Donald Trump and Brazil President Jair Bolsonaro. Despite their (2) _______ (unwavering) denial about the phenomenon, there is more-than- (3) _______ (plenty) scientific evidence and anecdotal confirmation that proves the (4) _______ (spread) climate crisis is becoming an urgent economic, social, and existential (5) _______ (final threat) for people across the world.Which of the following words fits the blank labelled as (4)?- a)Uploading
- b)Unfolding
- c)Upending
- d)Unloading
- e)Offloading
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In the following passage, some words have been left out. Read the passage carefully and select the correct answer for the given blank out of the given alternatives.
In the first two months of the New Year and a new decade, India, a climate hotspot, hosted two global leaders who believe global warming is a (1) _______ (practical joke): United States President Donald Trump and Brazil President Jair Bolsonaro. Despite their (2) _______ (unwavering) denial about the phenomenon, there is more-than- (3) _______ (plenty) scientific evidence and anecdotal confirmation that proves the (4) _______ (spread) climate crisis is becoming an urgent economic, social, and existential (5) _______ (final threat) for people across the world.
Which of the following words fits the blank labelled as (4)?
a)
Uploading
b)
Unfolding
c)
Upending
d)
Unloading
e)
Offloading
|
|
Dia Mehta answered |
We are looking for a word that refers to 'spread'.
Let's look at the meaning of all the words:
- Uploading: Refers to the act of transferring data from one computer to another
- Unfolding: Refers to the act of opening something or spreading it out
- Upending: Refers to the act of setting something upside down
- Unloading: Refers to the act of taking something off from something
- Offloading: Refers to the act of ridding oneself of something
Thus, the correct answer is 'unfolding'.
Each of these questions has a statement followed by three suggested courses of action numbered I, II and III. Assume everything in the statement to be true, and decide which of the given courses of action logically follows for pursuing.Statement: A sudden cloud burst over the island city resulted into unpredicted rainfall causing flood-like situation in the entire area. A large number of people were caught unaware and were stranded on the road.Courses of action:I. The local administration should immediately put in place an action plan for avoiding such a situation in future.II. The local administration should immediately deploy personnel to help the stranded people to move to safer place.III. The local administration should advice all the citizens not to venture out on the road till the situation improves.- a)Only I follows
- b)None follows
- c)Only II and III follow
- d)Only I and II follow
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Each of these questions has a statement followed by three suggested courses of action numbered I, II and III. Assume everything in the statement to be true, and decide which of the given courses of action logically follows for pursuing.
Statement: A sudden cloud burst over the island city resulted into unpredicted rainfall causing flood-like situation in the entire area. A large number of people were caught unaware and were stranded on the road.
Courses of action:
I. The local administration should immediately put in place an action plan for avoiding such a situation in future.
II. The local administration should immediately deploy personnel to help the stranded people to move to safer place.
III. The local administration should advice all the citizens not to venture out on the road till the situation improves.
a)
Only I follows
b)
None follows
c)
Only II and III follow
d)
Only I and II follow
e)
None of these

|
Mahesh Patel answered |
Statement: A sudden cloud burst over the island city resulted into unpredicted rainfall causing flood-like situation in the entire area. A large number of people were caught unaware and were stranded on the road.
Courses of action:
I. The local administration should immediately put in place an action plan for avoiding such a situation in the future.
II. The local administration should immediately deploy personnel to help the stranded people move to a safer place.
III. The local administration should advise all the citizens not to venture out on the road until the situation improves.
Explanation:
I. The local administration should immediately put in place an action plan for avoiding such a situation in the future.
This course of action logically follows from the statement. The sudden cloud burst and resulting flood-like situation caught a large number of people unaware and stranded on the road. To avoid a similar situation in the future, the local administration should develop an action plan. This plan would include measures such as improving drainage systems, implementing early warning systems, and conducting regular maintenance to prevent such disasters.
II. The local administration should immediately deploy personnel to help the stranded people move to a safer place.
This course of action also logically follows from the statement. The people who are stranded on the road due to the flood-like situation require immediate assistance to move to a safer place. The local administration should deploy personnel such as rescue teams, police, and volunteers to provide help and support to these stranded individuals. This will ensure their safety and well-being during the crisis.
III. The local administration should advise all the citizens not to venture out on the road until the situation improves.
This course of action logically follows from the statement. The flood-like situation caused by the unpredicted rainfall poses a risk to the safety of citizens. To avoid any further harm or accidents, it is essential for the local administration to advise all citizens not to venture out on the road until the situation improves. This will help prevent any additional casualties or disruptions in rescue operations.
Conclusion:
Both courses of action II and III are logical and necessary to address the immediate concerns and safety of the stranded people. Therefore, the correct answer is option C) Only II and III follow.
Courses of action:
I. The local administration should immediately put in place an action plan for avoiding such a situation in the future.
II. The local administration should immediately deploy personnel to help the stranded people move to a safer place.
III. The local administration should advise all the citizens not to venture out on the road until the situation improves.
Explanation:
I. The local administration should immediately put in place an action plan for avoiding such a situation in the future.
This course of action logically follows from the statement. The sudden cloud burst and resulting flood-like situation caught a large number of people unaware and stranded on the road. To avoid a similar situation in the future, the local administration should develop an action plan. This plan would include measures such as improving drainage systems, implementing early warning systems, and conducting regular maintenance to prevent such disasters.
II. The local administration should immediately deploy personnel to help the stranded people move to a safer place.
This course of action also logically follows from the statement. The people who are stranded on the road due to the flood-like situation require immediate assistance to move to a safer place. The local administration should deploy personnel such as rescue teams, police, and volunteers to provide help and support to these stranded individuals. This will ensure their safety and well-being during the crisis.
III. The local administration should advise all the citizens not to venture out on the road until the situation improves.
This course of action logically follows from the statement. The flood-like situation caused by the unpredicted rainfall poses a risk to the safety of citizens. To avoid any further harm or accidents, it is essential for the local administration to advise all citizens not to venture out on the road until the situation improves. This will help prevent any additional casualties or disruptions in rescue operations.
Conclusion:
Both courses of action II and III are logical and necessary to address the immediate concerns and safety of the stranded people. Therefore, the correct answer is option C) Only II and III follow.
Direction: In the following number series, one of the numbers is wrong. Find out the wrong number.465, 633, 775, 897, 993, 1065, 1113- a)465
- b)633
- c)993
- d)775
- e)1113
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In the following number series, one of the numbers is wrong. Find out the wrong number.
465, 633, 775, 897, 993, 1065, 1113
a)
465
b)
633
c)
993
d)
775
e)
1113

|
Moumita Kaur answered |
Identifying the Wrong Number
To find the wrong number in the given series, we need to observe the pattern and logic behind the numbers.
Series Analysis
- 465, 633, 775, 897, 993, 1065, 1113
Pattern Recognition
- The series seems to be increasing by different amounts in each step.
- The differences between consecutive numbers are as follows: 168, 142, 122, 96, 72, 48.
Finding the Error
- If we apply the same logic to the series, the next difference should be 24 (48 divided by 2).
- However, when we apply this logic to the last two numbers (1065 and 1113), the difference should be 24, but it is 48. This indicates an error.
Therefore, the wrong number in the series is 1065.
To find the wrong number in the given series, we need to observe the pattern and logic behind the numbers.
Series Analysis
- 465, 633, 775, 897, 993, 1065, 1113
Pattern Recognition
- The series seems to be increasing by different amounts in each step.
- The differences between consecutive numbers are as follows: 168, 142, 122, 96, 72, 48.
Finding the Error
- If we apply the same logic to the series, the next difference should be 24 (48 divided by 2).
- However, when we apply this logic to the last two numbers (1065 and 1113), the difference should be 24, but it is 48. This indicates an error.
Therefore, the wrong number in the series is 1065.
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.“A@B” means “A is either 3m or 6m north of B”.“A#B” means “A is either 9m or 15m south of B”.“A&B” means “A is either 8m or 12m west of B”.“A%B” means “A is either 4m or 6m east of B”.Condition I: C&G, B#C, B&A, D@A, D%F, H&E, F#H.Condition II: HE = BA, CG + DF = AB, CB – DA = HE, HF = 2(DF)+1What is the shortest distance between A and F?- a)2√6m
- b)4m
- c)5m
- d)√80m
- e)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
“A@B” means “A is either 3m or 6m north of B”.
“A#B” means “A is either 9m or 15m south of B”.
“A&B” means “A is either 8m or 12m west of B”.
“A%B” means “A is either 4m or 6m east of B”.
Condition I: C&G, B#C, B&A, D@A, D%F, H&E, F#H.
Condition II: HE = BA, CG + DF = AB, CB – DA = HE, HF = 2(DF)+1
What is the shortest distance between A and F?
a)
2√6m
b)
4m
c)
5m
d)
√80m
e)
None of these

|
Ashwini Chatterjee answered |
Understanding the Symbols
- “A@B” means A is either 3m or 6m north of B.
- “A#B” means A is either 9m or 15m south of B.
- “A&B” means A is either 8m or 12m west of B.
- “A%B” means A is either 4m or 6m east of B.
Analyzing the Conditions
- Condition I:
- C&G
- B#C
- B&A
- D@A
- D%F
- H&E
- F#H
- Condition II:
- HE = BA
- CG + DF = AB
- CB – DA = HE
- HF = 2(DF) + 1
Calculating Distances
1. Positioning Points:
- Start by placing points B, C, A, D, E, F, G, and H based on the relationships given by the symbols.
2. Assign Values:
- Assume B is at the origin (0,0).
- Using B#C, assume C is 9m south (0,-9).
- Next, B&A indicates A is 9m south as well (0,-18) or 15m south (0,-24).
- For D@A, place D either north of A.
3. Using Conditions:
- Plug in values from Condition II to find specific distances.
- Solve for DF, HE, and other distances accordingly.
Final Distance Calculation
- After calculating the positions based on the conditions, you will find A is at (0, -18) and F must be calculated from H and E.
- Using the equations derived from Condition II, find the exact positions of all points.
- By calculating the distance between A (0,-18) and F, you will arrive at the shortest distance of 5m.
Conclusion
The shortest distance between A and F is 5 meters, making option 'C' the correct answer.
- “A@B” means A is either 3m or 6m north of B.
- “A#B” means A is either 9m or 15m south of B.
- “A&B” means A is either 8m or 12m west of B.
- “A%B” means A is either 4m or 6m east of B.
Analyzing the Conditions
- Condition I:
- C&G
- B#C
- B&A
- D@A
- D%F
- H&E
- F#H
- Condition II:
- HE = BA
- CG + DF = AB
- CB – DA = HE
- HF = 2(DF) + 1
Calculating Distances
1. Positioning Points:
- Start by placing points B, C, A, D, E, F, G, and H based on the relationships given by the symbols.
2. Assign Values:
- Assume B is at the origin (0,0).
- Using B#C, assume C is 9m south (0,-9).
- Next, B&A indicates A is 9m south as well (0,-18) or 15m south (0,-24).
- For D@A, place D either north of A.
3. Using Conditions:
- Plug in values from Condition II to find specific distances.
- Solve for DF, HE, and other distances accordingly.
Final Distance Calculation
- After calculating the positions based on the conditions, you will find A is at (0, -18) and F must be calculated from H and E.
- Using the equations derived from Condition II, find the exact positions of all points.
- By calculating the distance between A (0,-18) and F, you will arrive at the shortest distance of 5m.
Conclusion
The shortest distance between A and F is 5 meters, making option 'C' the correct answer.
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.There are four trucks A, B, C and D. These trucks travel from one point to another point. Also, there are four points L, M, N, and O connected through a common junction.The direction of these points with respect to the junction is as follows:L is in the north direction of the junctionM is in the west direction of the junctionN is in the east direction of the junctionO is in the south direction of the junctionNote: While travelling from one point to another all the trucks must pass through the junction.The following codes are given to denote the direction of movement of the trucks.P@Q means truck P is at a certain point and moves to the north from the junction to reach point QP#Q means truck Q is at a certain point and moves to the left from the junction to reach point PP%Q means truck P is at point Q and moves to the west from the junction to reach a certain pointP&Q means truck Q is at point P and moves to the west from the junction to reach a certain pointP*Q means truck P is at point Q and moves straight through the junction to reach a certain pointP^Q means truck Q is at a certain point and moves straight through the junction to reach point PWhich of the following options denotes the final position of B is South-east of the initial position of K?- a)B*M^K
- b)B@L&K
- c)B%O#K
- d)B*L#K
- e)B*M#K
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
There are four trucks A, B, C and D. These trucks travel from one point to another point. Also, there are four points L, M, N, and O connected through a common junction.
The direction of these points with respect to the junction is as follows:
L is in the north direction of the junction
M is in the west direction of the junction
N is in the east direction of the junction
O is in the south direction of the junction
Note: While travelling from one point to another all the trucks must pass through the junction.
The following codes are given to denote the direction of movement of the trucks.
P@Q means truck P is at a certain point and moves to the north from the junction to reach point Q
P#Q means truck Q is at a certain point and moves to the left from the junction to reach point P
P%Q means truck P is at point Q and moves to the west from the junction to reach a certain point
P&Q means truck Q is at point P and moves to the west from the junction to reach a certain point
P*Q means truck P is at point Q and moves straight through the junction to reach a certain point
P^Q means truck Q is at a certain point and moves straight through the junction to reach point P
Which of the following options denotes the final position of B is South-east of the initial position of K?
a)
B*M^K
b)
B@L&K
c)
B%O#K
d)
B*L#K
e)
B*M#K
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
If all the letters of each word are arranged in alphabetical order within the words, then the third letter of each word is taken to form a meaningful word. Which of the following option will give a meaningful word?- a)GREEN, REAL, GIRL, MAKE, REST
- b)MATHS, WIFE, DICE, CAUSE, HOT
- c)FEAST, GUILT, DARE, MIST, GRAPH
- d)TALL, HEIR, LIST, WHALE, HAUL
- e)Both c and d
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
If all the letters of each word are arranged in alphabetical order within the words, then the third letter of each word is taken to form a meaningful word. Which of the following option will give a meaningful word?
a)
GREEN, REAL, GIRL, MAKE, REST
b)
MATHS, WIFE, DICE, CAUSE, HOT
c)
FEAST, GUILT, DARE, MIST, GRAPH
d)
TALL, HEIR, LIST, WHALE, HAUL
e)
Both c and d
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
A) GREEN, REAL, GIRL, MAKE, REST -> EEGNR, AELR, GILR, AEKM, ERST -> GLLKS
b) MATHS, WIFE, DICE, CAUSE, HOT -> AHMST, EFIW, CDEI, ACESU, HOT -> MIEET
c) FEAST, GUILT, DARE, MIST, GRAPH -> AEFST, GILTU, ADER, IMST, AGHPR -> FLESH
d) TALL, HEIR, LIST, WHALE, HAUL -> ALLT, EHIR, ILST, AEHLW, AHLU->LISHL-HILLS
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W are eight different people who have bought eight different cars – Santro, Renault, BMW, Swift Dzire, Nano, Nissan, Datsun and Audi on eight different days starting from Monday to Monday. The cars are of eight different colours viz. Red, Blue, White, Yellow, Black, Grey, Beige and Silver. All the information is not necessarily in the same order.Four people have bought the cars between Q and the person who has bought BMW. At least two people have bought cars after the person who has bought Datsun. Grey and Red cars have not been bought immediately before or after a Yellow car. U has bought a car immediately after W. Audi is neither in Red nor in Silver colour. Neither P nor U have bought BMW. Beige car is bought 3 days before Renault was bought. S has bought a car either immediate or on one of the days after V but before the person who has bought Datsun. Nissan is neither in a Blue nor in a White colour. Only three people have bought cars between the person who has bought Santro and the person who has bought a yellow car. Only three people have bought cars between R and T. Nano has been bought after Audi but neither immediately nor on Monday. The Blue car is bought after the Black car. Q has bought a car on one of the days before the person who has bought BMW. The number of cars bought before Nano is as same as the number of cars bought after Audi. Q has bought a Silver car. Only two people have bought the cars before S. T has not bought a car on the last day. P and S have not bought Renault nor Swift Dzire. Renault car is not in a Silver colour. Red car is bought immediately after Grey car but immediately before Black car.Red coloured car was bought by whom and on which day?- a)P, Wednesday
- b)S, Thursday
- c)S, Wednesday
- d)P, Friday
- e)U, Monday
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W are eight different people who have bought eight different cars – Santro, Renault, BMW, Swift Dzire, Nano, Nissan, Datsun and Audi on eight different days starting from Monday to Monday. The cars are of eight different colours viz. Red, Blue, White, Yellow, Black, Grey, Beige and Silver. All the information is not necessarily in the same order.
Four people have bought the cars between Q and the person who has bought BMW. At least two people have bought cars after the person who has bought Datsun. Grey and Red cars have not been bought immediately before or after a Yellow car. U has bought a car immediately after W. Audi is neither in Red nor in Silver colour. Neither P nor U have bought BMW. Beige car is bought 3 days before Renault was bought. S has bought a car either immediate or on one of the days after V but before the person who has bought Datsun. Nissan is neither in a Blue nor in a White colour. Only three people have bought cars between the person who has bought Santro and the person who has bought a yellow car. Only three people have bought cars between R and T. Nano has been bought after Audi but neither immediately nor on Monday. The Blue car is bought after the Black car. Q has bought a car on one of the days before the person who has bought BMW. The number of cars bought before Nano is as same as the number of cars bought after Audi. Q has bought a Silver car. Only two people have bought the cars before S. T has not bought a car on the last day. P and S have not bought Renault nor Swift Dzire. Renault car is not in a Silver colour. Red car is bought immediately after Grey car but immediately before Black car.
Red coloured car was bought by whom and on which day?
a)
P, Wednesday
b)
S, Thursday
c)
S, Wednesday
d)
P, Friday
e)
U, Monday
|
|
Rohan Sengupta answered |
Eight People: P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W.
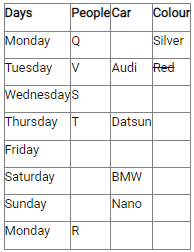
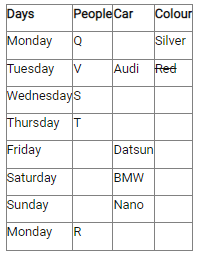
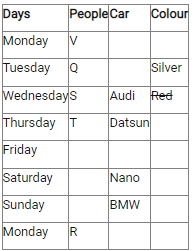
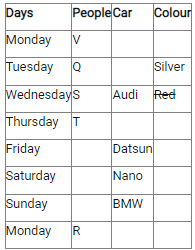
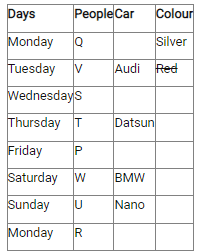
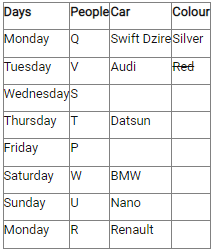
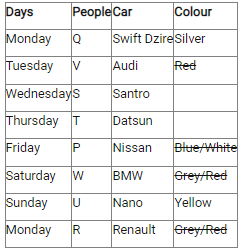
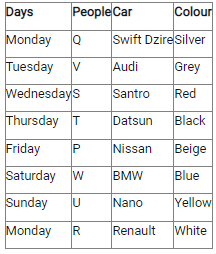
Eight Cars: Santro, Renault, BMW, Swift Dzire, Nano, Nissan, Datsun and Audi
Eight Colours: Red, Blue, White, Yellow, Black, Grey, Beige and Silver.
Eight Days: Starting from Monday to Monday.
Note: All the information is not necessarily in the same order.
1) Only two people have bought the cars before S.
2) Four people have bought the cars between Q and the person who has bought BMW.
3) Q has bought a car on one of the days before the person who has bought BMW.
4) Q has bought a Silver car.
5) The number of cars bought before Nano is as same as the number of cars bought after Audi.
6) Audi is neither in Red nor in Silver colour.
7) Nano has been bought after Audi but neither immediately nor on Monday.
Case 1

Case 2

8) S has bought a car either immediate or on one of the days after V but before the person who has bought Datsun.
9) At least two people have bought cars after the person who has bought Datsun.
10) Only three people have bought cars between R and T.
11) T has not bought a car on the last day.
Case 1 (a)

Case 1 (b)

Case 2 (a)

Case 2 (b)

12) U has bought a car immediately after W.
13) Neither P nor U have bought BMW.
Thus, all three cases get eliminated except case 1 (a)
Case 1 (a)

14) P and S have not bought Renault nor Swift Dzire.
15) Renault car is not in a Silver colour.
So, R has bought Renault and Q has bought Swift Dzire.
Case 1 (a)

16) Only three people have bought cars between the person who has bought Santro and the person who has bought a yellow car.
17) Nissan is neither in a Blue nor in a White colour.
18) Grey and Red cars have not been bought immediately before or after a Yellow car.
So, S has bought Santro and P has bought Nissan.
Case 1 (a)

19) The Blue car is bought after the Black car.
20) Red car is bought immediately after Grey car but immediately before Black car.
21) Beige car is bought 3 days before Renault was bought.

Thus, Red coloured car was bought by S on Wednesday.
Direction: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.The Supreme Court on Tuesday asked the Union government whether it is giving the over 40 lakh people, excluded from the National Register of Citizens (NRC) in Assam, a “second chance” to gain citizenship by allowing them to produce fresh documents to prove their Indian legacy.The court was referring to the Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) proposed by the government, which allows a claimant for Indian citizenship to “change his legacy” by submitting additional documents at the ‘claims and objections’ stage. The court asked whether this would amount to “re-doing the claims” of those left out from the draft NRC published on July 30.A Bench of Justices Ranjan Gogoi and Rohinton Nariman on Tuesday said allowing a claimant to change his legacy would amount to “tinkering with the family tree” and re-doing the verification process.“You see, a claimant submits documents to prove his legacy from his father. A family tree is drawn, which includes the claimant’s siblings, etc. The authorities verify his claim with each one of the member in the family tree before deciding his claim [for citizenship]. Now, your SOP says that a person can submit fresh documents claiming to prove his legacy from his grandfather. Now, the family tree has to be recreated. Everything has to be re-verified. This amounts to redoing the entire exercise. Why?”, Justice Gogoi asked Attorney General K.K. Venugopal.Besides, the Bench pointed out, the government, in the beginning, had specified that documents on legacy would be allowed to be filed only once. Now, it has changed tack to permit additional documents to be filed. “Are you not contradicting yourself here?” Justice Gogoi asked Mr. Venugopal.The court directed Assam State NRC Coordinator Prateek Hajela to file a report on the ramifications of the government's proposal to submit fresh documents. Mr. Hajela has to file his report before September 5, the next date of hearing.Meanwhile, the court deferred the receipt of claims and objections to a later date. This stage was supposed to start within the next days, on August 30, and would have continued till October 28.“Allowing a person to suddenly pull out an additional document, that too at the 'claims and objections' stage, will upset the apple cart,” Justice Nariman observed.Mr. Venugopal countered that the government is giving “another chance to people who risk losing all their rights”.To this, Justice Nariman agreed that the court was dealing with “human problems of a huge magnitude”.“Consequences are so severe that should they be given one more chance. Suppose a claimant has misfired once but can deliver in the next. Why should such a person not be given another chance?” Justice Nariman asked Mr. Hajela, stakeholders and petitioners in the litigation.To this, Mr. Hajela said reopening of family trees would risk the possibility of “trading of legacies or meeting of minds”. "Giving a second chance would only open trading in legacies. There may be people who are willing to sell the legacies to others,” he said.The Supreme Court further asked Mr. Hajela to submit a report with a time-frame to carry out the sample re-verification of at least 10 per cent of the names included in the final draft NRC. This is after Mr. Hajela placed before the Bench a district-wise data of the percentage of the population who have been excluded from the final draft NRC.Why has the Supreme Court observed that the new move by the government will actually make the government redo the whole exercise?- a)The government will need to verify all the documents again and then the same will have to uploaded in the database with correlation to the earlier data.
- b)The government will not understand the old data manipulation and there will be new kind of data manipulation in this new process.
- c)The government will have to draw the family tree again and the whole legacy will have to be understood again by the government.
- d)The government will need to check every single citizen in the state so that there is no duplication in the process
- e)The Supreme Court is not sure whether the government will be able to follow the whole exercise completely till the end.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
The Supreme Court on Tuesday asked the Union government whether it is giving the over 40 lakh people, excluded from the National Register of Citizens (NRC) in Assam, a “second chance” to gain citizenship by allowing them to produce fresh documents to prove their Indian legacy.
The court was referring to the Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) proposed by the government, which allows a claimant for Indian citizenship to “change his legacy” by submitting additional documents at the ‘claims and objections’ stage. The court asked whether this would amount to “re-doing the claims” of those left out from the draft NRC published on July 30.
A Bench of Justices Ranjan Gogoi and Rohinton Nariman on Tuesday said allowing a claimant to change his legacy would amount to “tinkering with the family tree” and re-doing the verification process.
“You see, a claimant submits documents to prove his legacy from his father. A family tree is drawn, which includes the claimant’s siblings, etc. The authorities verify his claim with each one of the member in the family tree before deciding his claim [for citizenship]. Now, your SOP says that a person can submit fresh documents claiming to prove his legacy from his grandfather. Now, the family tree has to be recreated. Everything has to be re-verified. This amounts to redoing the entire exercise. Why?”, Justice Gogoi asked Attorney General K.K. Venugopal.
Besides, the Bench pointed out, the government, in the beginning, had specified that documents on legacy would be allowed to be filed only once. Now, it has changed tack to permit additional documents to be filed. “Are you not contradicting yourself here?” Justice Gogoi asked Mr. Venugopal.
The court directed Assam State NRC Coordinator Prateek Hajela to file a report on the ramifications of the government's proposal to submit fresh documents. Mr. Hajela has to file his report before September 5, the next date of hearing.
Meanwhile, the court deferred the receipt of claims and objections to a later date. This stage was supposed to start within the next days, on August 30, and would have continued till October 28.
“Allowing a person to suddenly pull out an additional document, that too at the 'claims and objections' stage, will upset the apple cart,” Justice Nariman observed.
Mr. Venugopal countered that the government is giving “another chance to people who risk losing all their rights”.
To this, Justice Nariman agreed that the court was dealing with “human problems of a huge magnitude”.
“Consequences are so severe that should they be given one more chance. Suppose a claimant has misfired once but can deliver in the next. Why should such a person not be given another chance?” Justice Nariman asked Mr. Hajela, stakeholders and petitioners in the litigation.
To this, Mr. Hajela said reopening of family trees would risk the possibility of “trading of legacies or meeting of minds”. "Giving a second chance would only open trading in legacies. There may be people who are willing to sell the legacies to others,” he said.
The Supreme Court further asked Mr. Hajela to submit a report with a time-frame to carry out the sample re-verification of at least 10 per cent of the names included in the final draft NRC. This is after Mr. Hajela placed before the Bench a district-wise data of the percentage of the population who have been excluded from the final draft NRC.
Why has the Supreme Court observed that the new move by the government will actually make the government redo the whole exercise?
a)
The government will need to verify all the documents again and then the same will have to uploaded in the database with correlation to the earlier data.
b)
The government will not understand the old data manipulation and there will be new kind of data manipulation in this new process.
c)
The government will have to draw the family tree again and the whole legacy will have to be understood again by the government.
d)
The government will need to check every single citizen in the state so that there is no duplication in the process
e)
The Supreme Court is not sure whether the government will be able to follow the whole exercise completely till the end.
|
|
Kavya Saxena answered |
Refer to, ““You see, a claimant submits documents to prove his legacy from his father. A family tree is drawn, which includes the claimant’s siblings, etc. The authorities verify his claim with each one of the member in the family tree before deciding his claim [for citizenship]. Now, your SOP says that a person can submit fresh documents claiming to prove his legacy from his grandfather. Now, the family tree has to be recreated. Everything has to be re-verified. This amounts to redoing the entire exercise. Why?”, Justice Gogoi asked Attorney General K.K. Venugopal.”
From the above lines it is very clear that the Supreme Court did not understand the logic behind asking the citizens who were left out to submit the fresh documents at the claims and objections stage. It is like redoing the whole thing from the scratch without any issue.
Among the given options, only C implies the same as in the passage and all the other options can be easily eliminated since they are out of the given context of the passage. There is no reference to all such options in the passage.
It makes option C the correct choice among the given options.
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below-Seven friends I, J, K, L, M, N and O had their houses situated along a straight row facing the north. They like different colours among Golden, Silver, Purple, Grey, Violet, Indigo and Brown but not necessarily in the same order. The distance between the adjacent houses was a successive integral multiple of 5km and the distance increased from left to right.I’s house was third to the left of the friend who likes Indigo colour. J’s house was 135km to the right of the friend who likes Grey colour. K’s house was exactly between O’s house and the friend who likes brown colour. The friend who likes violet colour was to the immediate left of the friend who likes purple colour. The friend who likes purple colour was 115km to the left of L’s house. The friend who likes indigo colour was the neighbour of L’s house. The friend who likes grey colour was 85km away from M’s house. The friend who likes golden colour had house at one of the extreme ends. O did not like silver colour. The distance between any two adjacent houses was less than 80 km.Q. How many houses are there between I and the friend who likes silver colour?- a)One
- b)Two
- c)Three
- d)Four
- e)None
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below-
Seven friends I, J, K, L, M, N and O had their houses situated along a straight row facing the north. They like different colours among Golden, Silver, Purple, Grey, Violet, Indigo and Brown but not necessarily in the same order. The distance between the adjacent houses was a successive integral multiple of 5km and the distance increased from left to right.
I’s house was third to the left of the friend who likes Indigo colour. J’s house was 135km to the right of the friend who likes Grey colour. K’s house was exactly between O’s house and the friend who likes brown colour. The friend who likes violet colour was to the immediate left of the friend who likes purple colour. The friend who likes purple colour was 115km to the left of L’s house. The friend who likes indigo colour was the neighbour of L’s house. The friend who likes grey colour was 85km away from M’s house. The friend who likes golden colour had house at one of the extreme ends. O did not like silver colour. The distance between any two adjacent houses was less than 80 km.
Q. How many houses are there between I and the friend who likes silver colour?
a)
One
b)
Two
c)
Three
d)
Four
e)
None
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
1. The distance between any two houses was less than 80 km. The minimum distance mentioned in the question is 85km and so, the distance between two offices cannot be 5km as (5 + 80 = 85) which is not possible. J’s house was 135km to the right of the friend who likes Grey colour. The friend who likes grey colour was 85km away from M’s house. This is possible in only one condition when distance between J and the friend who likes grey colour is successive integral of 5 as (40 – 45 – 50).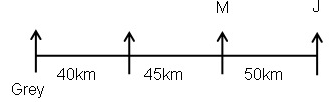
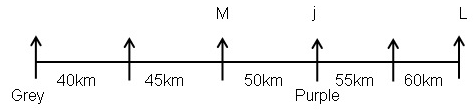
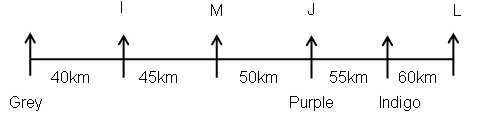
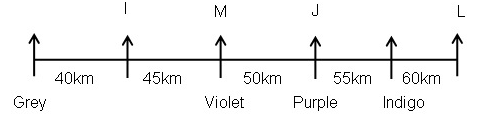

2. The friend who likes purple colour was 115km to the left of L’s house.

3- The friend who likes indigo colour was the neighbour of L’s house. I’s house was third to the left of the official who likes Indigo colour.

4- The friend who likes violet colour was to the immediate left of the friend who likes purple colour.

5- K’s house was exactly between O’s house and the friend who likes brown colour. The friend who likes golden colour had hose at one of the extreme ends. O did not like silver colour.

Hence, three houses are there between I and the friend who likes silver colour.
Under whose chairmanship the Reserve Bank of India has announced the setting up of a standing external advisory committee (SEAC) to evaluate applications for universal banks and small finance banks?- a)B Mahapatra
- b)Shyamala Gopinath
- c)T N Manoharan
- d)Revathy Iyer
- e)Usha Thorat
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Under whose chairmanship the Reserve Bank of India has announced the setting up of a standing external advisory committee (SEAC) to evaluate applications for universal banks and small finance banks?
a)
B Mahapatra
b)
Shyamala Gopinath
c)
T N Manoharan
d)
Revathy Iyer
e)
Usha Thorat
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
The Reserve Bank of India announced the setting up of a standing external advisory committee (SEAC) to evaluate applications for universal banks and small finance banks. The five-member committee will be headed by former deputy governor Shyamala Gopinath. The SEAC will have a tenure of three years and will screen applications for universal and small finance banks after the regulator first vets the proposal. The SEAC will also include four other members, Revathy Iyer, Director on the RBI central board, B Mahapatra, former executive director, RBI and presently chairman of NPCI, T N Manoharan, former chairman of Canara Bank and Hemant Contractor, former MD of State Bank of India.
Out of the given options, choose the sentence, which, in your view, is the most grammatically and structurally correct. Please note that the meaning or the context of the sentence must not change.- a)The parishioners did not know whence he will come.
- b)I always get up to very early in the morning.
- c)The women went to the river to fetching water.
- d)I bought a bag which costed me five hundred rupees.
- e)There were built around the town a small fence.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Out of the given options, choose the sentence, which, in your view, is the most grammatically and structurally correct. Please note that the meaning or the context of the sentence must not change.
a)
The parishioners did not know whence he will come.
b)
I always get up to very early in the morning.
c)
The women went to the river to fetching water.
d)
I bought a bag which costed me five hundred rupees.
e)
There were built around the town a small fence.
|
|
Kavya Saxena answered |
The most grammatically and structurally correct sentence is the parishioners did not know whence he will come.
Whence- From where, from what place or source. It is an old English adverb.
- Option 2 uses the preposition 'to' here, which is incorrect; as it lends no meaning to the sentence.
- Option 3 uses the incorrect form of a to-infinitive. Infinitives always use to, with the simple present tense form of the verb, viz, to fetch is the correct form.
- Option 4 uses the incorrect verb 'costed'. The past tense and past participle for of the verb 'to cost' is 'cost' itself.
- Option 5 uses the incorrect plural verb form 'were'. Since it is referring to a singular noun, fence, it should be in its singular form, viz, 'was'.
- Out of the given sentences, the only correct sentence is given by option 1.
Direction: In the following passage some of the words have been left out. First read the passage over and try to understand what it is about. Then fill in the blanks with the help of the alternatives given.Countless poets and lovers have declaimed over the ages that Venice is not just a city; it’s a living dream. By that same measure, irreverent others would hold that during the monsoons in India, its cities are more than just cities; they are living nightmares. Venice’s waterways are (A) all over the world and (B) of tourists descend on the city every year. In (C), the streets of India’s cities become reluctant rivers at the mere hint of rain. There’s a (D) saying in Kolkata that every time a frog wets its pants, the city goes underwater. The same goes for Mumbai, India’s shining commercial capital. A few hours of rain and the shine is smudged by knee-deep water. Chennai, which did not experience large-scale (E) even a couple of decades ago, has drastically changed since the (F) floods of 2015.Q. Choose the appropriate word pair for position D- a)Classical/ inapplicable
- b)Colloquial/ famous
- c)Particular/ permissible
- d)Infamous/ remembered
- e)Impractical/ Vague
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In the following passage some of the words have been left out. First read the passage over and try to understand what it is about. Then fill in the blanks with the help of the alternatives given.
Countless poets and lovers have declaimed over the ages that Venice is not just a city; it’s a living dream. By that same measure, irreverent others would hold that during the monsoons in India, its cities are more than just cities; they are living nightmares. Venice’s waterways are (A) all over the world and (B) of tourists descend on the city every year. In (C), the streets of India’s cities become reluctant rivers at the mere hint of rain. There’s a (D) saying in Kolkata that every time a frog wets its pants, the city goes underwater. The same goes for Mumbai, India’s shining commercial capital. A few hours of rain and the shine is smudged by knee-deep water. Chennai, which did not experience large-scale (E) even a couple of decades ago, has drastically changed since the (F) floods of 2015.
Q. Choose the appropriate word pair for position D
a)
Classical/ inapplicable
b)
Colloquial/ famous
c)
Particular/ permissible
d)
Infamous/ remembered
e)
Impractical/ Vague
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Colloquial - (of language) used in ordinary or familiar conversation; not formal or literary. Observing the sentence, we can see that B is the only correct option.
Chapter doubts & questions for IBPS PO Mains - Mock Tests for Banking Exams 2025 2025 is part of Bank Exams exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Bank Exams exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Bank Exams 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of IBPS PO Mains - Mock Tests for Banking Exams 2025 in English & Hindi are available as part of Bank Exams exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Bank Exams Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









