All Exams >
Humanities/Arts >
Political Science CUET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of Globalisation for Humanities/Arts Exam
With the globalisation of markets, the tastes and preferences of consumers world-wide are- a)becoming similar to the tastes and preferences of American consumers.
- b)being encouraged by multinational organizations to become increasingly similar.
- c)so different that they can be ignored by international organizations.
- d)converging upon a global norm.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
With the globalisation of markets, the tastes and preferences of consumers world-wide are
a)
becoming similar to the tastes and preferences of American consumers.
b)
being encouraged by multinational organizations to become increasingly similar.
c)
so different that they can be ignored by international organizations.
d)
converging upon a global norm.
|
|
Anjana Bose answered |
Globalisation is a continuing process of economic restructuring, which has led to an increasing cross-border flow of trade in goods, services and financial assets, along with an increasing international mobility of technology, information and individuals.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:The most visible impacts of globalization are definitely the ones affecting the economic world. Globalization has led to a sharp increase in trade and economic exchanges, but also to a multiplication of financial exchanges.In the 1970s world economies opened up and the development of free trade policies accelerated the globalization phenomenon. Between 1950 and 2010, world exports increased 33-fold. This significantly contributed to increasing the interactions between different regions of the world.This acceleration of economic exchanges has led to strong global economic growth. It fostered as well a rapid global industrial development that allowed the rapid development of many of the technologies and commodities we have available nowadays.Knowledge became easily shared and international cooperation among the brightest minds speeded things up. According to some analysts, globalization has also contributed to improving global economic conditions, creating much economic wealth.At the same time, finance also became globalized. From the 1980s, driven by neo- liberal policies, the world of finance gradually opened. Many states, particularly the US under Ronald Reagan and the UK under Margaret Thatcher introduced the famous “3D Policy”: Disintermediation, Decommissioning, and Deregulation.Q. In between which years the world’s export has increased 33-fold?- a)1970-1980
- b)1950-1990
- c)1950-2000
- d)1950-2010
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
The most visible impacts of globalization are definitely the ones affecting the economic world. Globalization has led to a sharp increase in trade and economic exchanges, but also to a multiplication of financial exchanges.
In the 1970s world economies opened up and the development of free trade policies accelerated the globalization phenomenon. Between 1950 and 2010, world exports increased 33-fold. This significantly contributed to increasing the interactions between different regions of the world.
This acceleration of economic exchanges has led to strong global economic growth. It fostered as well a rapid global industrial development that allowed the rapid development of many of the technologies and commodities we have available nowadays.
Knowledge became easily shared and international cooperation among the brightest minds speeded things up. According to some analysts, globalization has also contributed to improving global economic conditions, creating much economic wealth.
At the same time, finance also became globalized. From the 1980s, driven by neo- liberal policies, the world of finance gradually opened. Many states, particularly the US under Ronald Reagan and the UK under Margaret Thatcher introduced the famous “3D Policy”: Disintermediation, Decommissioning, and Deregulation.
Q. In between which years the world’s export has increased 33-fold?
a)
1970-1980
b)
1950-1990
c)
1950-2000
d)
1950-2010
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
In the 1970s world economies opened up and the development of free trade policies accelerated the globalization phenomenon. Between 1950 and 2010, world exports increased 33-fold. This significantly contributed to increasing the interactions between different regions of the world.
Liberalisation means:- a)integration among economies.
- b)reduced government controls and restrictions.
- c)policy of planned disinvestments.
- d)competitive market.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Liberalisation means:
a)
integration among economies.
b)
reduced government controls and restrictions.
c)
policy of planned disinvestments.
d)
competitive market.
|
|
Sahana Choudhury answered |
Liberalisation is a process whereby a state lifts restrictions on some private individual activities.
Which of the following is available in India due to globalisation?- a)Foreign TV channels
- b)Coca Cola and Pepsi
- c)Sansui brand of electronics
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is available in India due to globalisation?
a)
Foreign TV channels
b)
Coca Cola and Pepsi
c)
Sansui brand of electronics
d)
All of the above
|
|
Harshitha Basu answered |
Due to globalisation of the Indian economy, various foreign MNCs have entered the the Indian market.
Globalization has led to the flow of ideas across- a)national boundaries.
- b)state.
- c)political parties.
- d)different planets.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Globalization has led to the flow of ideas across
a)
national boundaries.
b)
state.
c)
political parties.
d)
different planets.
|
|
Shruti Joshi answered |
Globalization has led to the flow of ideas across national boundaries, e.g. spread of internet.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion: There have been left wing protests to economic liberalization voiced through political parties as well as through forums like the Indian Social Forum.Reason: The left wing believed that globalization would corrupt the politics of India.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: There have been left wing protests to economic liberalization voiced through political parties as well as through forums like the Indian Social Forum.
Reason: The left wing believed that globalization would corrupt the politics of India.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Ojasvi Mehta answered |
The left wing of India criticized globalization mainly on the issue of the entries of multinational companies and foreign investment. According to them, this would affect the trade opportunities of the local industries and products.
DIRECTION : Mark the option which is most suitable :Assertion : Local businesses may set up joint production process with MNCs and earn higher profits.Reason : MNCs can provide money for additional investments, like buying new machines for faster production.- a)If Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)If Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)If Assertion is true, but reason is false.
- d)If Both assertion and reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
DIRECTION : Mark the option which is most suitable :
Assertion : Local businesses may set up joint production process with MNCs and earn higher profits.
Reason : MNCs can provide money for additional investments, like buying new machines for faster production.
a)
If Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
If Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
If Assertion is true, but reason is false.
d)
If Both assertion and reason are false.
|
|
Ojasvi Mehta answered |
At times, MNCs set up production jointly with some of the local companies of the host countries. The benefit to the local company from such joint production is twofold as MNCs can provide for additional investments and can bring in newer technology of production that result in fast-paced production.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:While everything may not be known about the economic facets of globalisation, this particular dimension shapes a large part of the content and direction of contemporary debates surrounding globalisation. A part of the problem has to do with defining economic globalisation itself. The mention of economic globalisation draws our attention immediately to the role of international institutions like the IMF and the WTO and the role they play in determining economic policies across the world. Yet, globalisation must not be viewed in such narrow terms. Economic globalisation involves many actors other than these international institutions. A much broader way of understanding of economic globalisation requires us to look at the distribution of economic gains, i.e. who gets the most from globalisation and who gets less, indeed who loses from it. What is often called economic globalisation usually involves greater economic flows among different countries of the world. Some of this is voluntary and some forced by international institutions and powerful countries. As we saw in the examples at the beginning of this chapter, this flow or exchange can take various forms: commodities, capital, people and ideas. Globalisation has involved greater trade in commodities across the globe; the restrictions imposed by different countries on allowing the imports of other countries have been reduced. Similarly, the restrictions on movement of capital across countries have also been reduced. In operational terms, it means that investors in the rich countries can invest their money in countries other than their own, including developing countries, where they might get better returns.Q. Where does economic globalisation draw our attention to?- a)Declining economy
- b)Poverty in the third world countries
- c)To the role of international institutions like the IMF and the WTO
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
While everything may not be known about the economic facets of globalisation, this particular dimension shapes a large part of the content and direction of contemporary debates surrounding globalisation. A part of the problem has to do with defining economic globalisation itself. The mention of economic globalisation draws our attention immediately to the role of international institutions like the IMF and the WTO and the role they play in determining economic policies across the world. Yet, globalisation must not be viewed in such narrow terms. Economic globalisation involves many actors other than these international institutions. A much broader way of understanding of economic globalisation requires us to look at the distribution of economic gains, i.e. who gets the most from globalisation and who gets less, indeed who loses from it. What is often called economic globalisation usually involves greater economic flows among different countries of the world. Some of this is voluntary and some forced by international institutions and powerful countries. As we saw in the examples at the beginning of this chapter, this flow or exchange can take various forms: commodities, capital, people and ideas. Globalisation has involved greater trade in commodities across the globe; the restrictions imposed by different countries on allowing the imports of other countries have been reduced. Similarly, the restrictions on movement of capital across countries have also been reduced. In operational terms, it means that investors in the rich countries can invest their money in countries other than their own, including developing countries, where they might get better returns.
Q. Where does economic globalisation draw our attention to?
a)
Declining economy
b)
Poverty in the third world countries
c)
To the role of international institutions like the IMF and the WTO
d)
All of the above
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The IMF and the WTO are international organizations with about 150 members in common. While the IMF’s central focus is on the international monetary and financial system, and the WTO’s is on the international trading system, both work together to ensure a sound system for global trade and payments.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:At the most simple level, globalisation results in an erosion of state capacity, that is, the ability of government to do what they do. All over the world, the old ‘welfare state’ is now giving way to a more minimalist state that performs certain core functions such as the maintenance of law and order and the security of its citizens. However, it withdraws from many of its earlier welfare functions directed at economic and social wellbeing. In place of the welfare state, it is the market that becomes the prime determinant of economic and social priorities. The entry and the increased role of multinational companies all over the world leads to a reduction in the capacity of governments to take decisions on their own. What is important is for people in different parts of the world to recognise these interconnections with the rest of the world. Currently, we are aware of the fact that events taking place in one part of the world could have an impact on another part of the world. The Bird flu or tsunami is not confined to any particular nation. It does not respect national boundaries. Similarly, when major economic events take place, their impact is felt outside their immediate local, national or regional environment at the global level.Q. The increase in the MNCs all over the world has resulted in ....................... .- a)the governments’ inability to cater to their needs.
- b)the capacity of the nations to incorporate these MNCs.
- c)poverty to the population where these companies are set up.
- d)reduction in the capacity of governments to take decisions on their own.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
At the most simple level, globalisation results in an erosion of state capacity, that is, the ability of government to do what they do. All over the world, the old ‘welfare state’ is now giving way to a more minimalist state that performs certain core functions such as the maintenance of law and order and the security of its citizens. However, it withdraws from many of its earlier welfare functions directed at economic and social wellbeing. In place of the welfare state, it is the market that becomes the prime determinant of economic and social priorities. The entry and the increased role of multinational companies all over the world leads to a reduction in the capacity of governments to take decisions on their own. What is important is for people in different parts of the world to recognise these interconnections with the rest of the world. Currently, we are aware of the fact that events taking place in one part of the world could have an impact on another part of the world. The Bird flu or tsunami is not confined to any particular nation. It does not respect national boundaries. Similarly, when major economic events take place, their impact is felt outside their immediate local, national or regional environment at the global level.
Q. The increase in the MNCs all over the world has resulted in ....................... .
a)
the governments’ inability to cater to their needs.
b)
the capacity of the nations to incorporate these MNCs.
c)
poverty to the population where these companies are set up.
d)
reduction in the capacity of governments to take decisions on their own.
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The entry and the increased role of multinational companies all over the world leads to a reduction in the capacity of governments to make decisions on their own. At the same time, globalisation does not always reduce state capacity.
The seventh WSF meeting was held in:- a)Delhi, January 2007
- b)Nairobi, January 2007
- c)Islamabad, January 2007
- d)New York, January 2007
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The seventh WSF meeting was held in:
a)
Delhi, January 2007
b)
Nairobi, January 2007
c)
Islamabad, January 2007
d)
New York, January 2007
|
|
Akshita Saha answered |
The World Social Forum (WSF) is another global platform that brings together a wide coalition composed of human rights activists, environmentalists, labour, youth and women activists opposed to neo-liberal globalisation. The first WSF meeting was organised in Porto Alegre, Brazil in 2001. The fourth WSF meeting was held in Mumbai in 2004. The seventh WSF meeting was held in Nairobi, Kenya in January 2007.
DIRECTION : Mark the option which is most suitable :Assertion : Global production has a complex structure. Reason : Production of one good may take place in different parts of the world. For instance, an equipment may be formed by combining components produced in different countries.- a)If Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)If Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)If Assertion is true, but reason is false.
- d)If Both assertion and reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
DIRECTION : Mark the option which is most suitable :
Assertion : Global production has a complex structure. Reason : Production of one good may take place in different parts of the world. For instance, an equipment may be formed by combining components produced in different countries.
a)
If Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
If Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
If Assertion is true, but reason is false.
d)
If Both assertion and reason are false.
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Globalization leads to connectivity of different countries and goods and services can be transported across the world. Goods, components produced in different parts of the world can be used for production in any country.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:The most visible impacts of globalization are definitely the ones affecting the economic world. Globalization has led to a sharp increase in trade and economic exchanges, but also to a multiplication of financial exchanges.In the 1970s world economies opened up and the development of free trade policies accelerated the globalization phenomenon. Between 1950 and 2010, world exports increased 33-fold. This significantly contributed to increasing the interactions between different regions of the world.This acceleration of economic exchanges has led to strong global economic growth. It fostered as well a rapid global industrial development that allowed the rapid development of many of the technologies and commodities we have available nowadays.Knowledge became easily shared and international cooperation among the brightest minds speeded things up. According to some analysts, globalization has also contributed to improving global economic conditions, creating much economic wealth.At the same time, finance also became globalized. From the 1980s, driven by neo- liberal policies, the world of finance gradually opened. Many states, particularly the US under Ronald Reagan and the UK under Margaret Thatcher introduced the famous “3D Policy”: Disintermediation, Decommissioning, and Deregulation.Q. After the 1980s, which policy was introduced by US and UK?- a)4D Policy
- b)3D Policy
- c)Fair Trade Policy
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
The most visible impacts of globalization are definitely the ones affecting the economic world. Globalization has led to a sharp increase in trade and economic exchanges, but also to a multiplication of financial exchanges.
In the 1970s world economies opened up and the development of free trade policies accelerated the globalization phenomenon. Between 1950 and 2010, world exports increased 33-fold. This significantly contributed to increasing the interactions between different regions of the world.
This acceleration of economic exchanges has led to strong global economic growth. It fostered as well a rapid global industrial development that allowed the rapid development of many of the technologies and commodities we have available nowadays.
Knowledge became easily shared and international cooperation among the brightest minds speeded things up. According to some analysts, globalization has also contributed to improving global economic conditions, creating much economic wealth.
At the same time, finance also became globalized. From the 1980s, driven by neo- liberal policies, the world of finance gradually opened. Many states, particularly the US under Ronald Reagan and the UK under Margaret Thatcher introduced the famous “3D Policy”: Disintermediation, Decommissioning, and Deregulation.
Q. After the 1980s, which policy was introduced by US and UK?
a)
4D Policy
b)
3D Policy
c)
Fair Trade Policy
d)
None of the above
|
|
Sanskriti Deshpande answered |
Introduction
After the 1980s, the US and UK introduced a policy known as the "3D Policy".
Explanation
1. 3D Policy:
- The 3D Policy stands for Disintermediation, Decommissioning, and Deregulation.
- This policy was driven by neo-liberal ideologies and aimed at globalizing the world of finance.
2. Disintermediation:
- Disintermediation refers to the reduction in the use of intermediaries between producers and consumers.
- It aimed to streamline financial transactions and make them more efficient by eliminating unnecessary intermediaries.
3. Decommissioning:
- Decommissioning refers to the process of retiring or shutting down certain financial institutions or practices.
- This was done to make the financial system more competitive and responsive to market forces.
4. Deregulation:
- Deregulation involves reducing or eliminating government regulations on financial institutions and practices.
- The goal was to increase market efficiency and promote innovation in the financial sector.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the introduction of the 3D Policy by the US and UK post-1980s had a significant impact on the global financial system. It aimed to promote efficiency, competition, and innovation in the financial sector by implementing measures such as disintermediation, decommissioning, and deregulation.
After the 1980s, the US and UK introduced a policy known as the "3D Policy".
Explanation
1. 3D Policy:
- The 3D Policy stands for Disintermediation, Decommissioning, and Deregulation.
- This policy was driven by neo-liberal ideologies and aimed at globalizing the world of finance.
2. Disintermediation:
- Disintermediation refers to the reduction in the use of intermediaries between producers and consumers.
- It aimed to streamline financial transactions and make them more efficient by eliminating unnecessary intermediaries.
3. Decommissioning:
- Decommissioning refers to the process of retiring or shutting down certain financial institutions or practices.
- This was done to make the financial system more competitive and responsive to market forces.
4. Deregulation:
- Deregulation involves reducing or eliminating government regulations on financial institutions and practices.
- The goal was to increase market efficiency and promote innovation in the financial sector.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the introduction of the 3D Policy by the US and UK post-1980s had a significant impact on the global financial system. It aimed to promote efficiency, competition, and innovation in the financial sector by implementing measures such as disintermediation, decommissioning, and deregulation.
According to the rightist view in India, globalisation tends to- a)benefits the weaker section of the society.
- b)divides the State into rich and poor.
- c)weakens the State.
- d)reduces political party competition.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to the rightist view in India, globalisation tends to
a)
benefits the weaker section of the society.
b)
divides the State into rich and poor.
c)
weakens the State.
d)
reduces political party competition.
|
|
Nisha Sengupta answered |
According to rightist view, it leads to the weakening of the State. People will loose their identity and age-old values. They support protectionism and self-reliance.
DIRECTION : Mark the option which is most suitable :Assertion : MNCs can exert a strong influence on production at distant locations.Reason : MNCs set up partnerships with local companies, use local companies for supplies, compete with local companies or buy them up.- a)If Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)If Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)If Assertion is true, but reason is false.
- d)If Both assertion and reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
DIRECTION : Mark the option which is most suitable :
Assertion : MNCs can exert a strong influence on production at distant locations.
Reason : MNCs set up partnerships with local companies, use local companies for supplies, compete with local companies or buy them up.
a)
If Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
If Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
If Assertion is true, but reason is false.
d)
If Both assertion and reason are false.
|
|
Ojasvi Mehta answered |
By setting up partnerships with local companies, by using the local companies for supplies, by closely competing with the local companies or buying them up, MNCs are exerting a strong influence on production at distant locations. As a result, production in widely dispersed locations is getting interlinked.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion: In 1991, responding to a financial crisis and to the desire for higher rates of economic growth, India embarked on a programme of economic reforms that has sought increasingly to de-regulate various sectors including trade and foreign investment.Reason: This deregulation opened up the new opportunities of local as well as foreign trade. Hence, the hope of creating new employment opportunities.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: In 1991, responding to a financial crisis and to the desire for higher rates of economic growth, India embarked on a programme of economic reforms that has sought increasingly to de-regulate various sectors including trade and foreign investment.
Reason: This deregulation opened up the new opportunities of local as well as foreign trade. Hence, the hope of creating new employment opportunities.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Devanshi Choudhary answered |
Assertion: In 1991, responding to a financial crisis and to the desire for higher rates of economic growth, India embarked on a programme of economic reforms that has sought increasingly to de-regulate various sectors including trade and foreign investment.
Reason: This deregulation opened up the new opportunities of local as well as foreign trade. Hence, the hope of creating new employment opportunities.
Explanation:
The assertion states that in 1991, India implemented economic reforms to address a financial crisis and stimulate economic growth. These reforms aimed to de-regulate various sectors, including trade and foreign investment.
The reason provided supports the assertion by stating that the deregulation of these sectors created new opportunities for both local and foreign trade. As a result, it is expected that this would lead to the creation of new employment opportunities.
Analyzing the Assertion and Reason:
- The assertion is true. In 1991, India did implement a series of economic reforms known as the New Economic Policy (NEP) to address a severe balance of payments crisis and promote economic growth. These reforms focused on liberalizing and de-regulating various sectors, including trade and foreign investment.
- The reason is also true. The de-regulation of trade and foreign investment, as a part of the economic reforms, did open up new opportunities for both local and foreign trade. This led to increased trade activities, which in turn had the potential to create new employment opportunities.
- The reason provided is a correct explanation of the assertion. The de-regulation of sectors, such as trade and foreign investment, aimed to promote economic growth by enhancing trade activities. The increase in trade activities can contribute to job creation and the hope of new employment opportunities.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A: Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Reason: This deregulation opened up the new opportunities of local as well as foreign trade. Hence, the hope of creating new employment opportunities.
Explanation:
The assertion states that in 1991, India implemented economic reforms to address a financial crisis and stimulate economic growth. These reforms aimed to de-regulate various sectors, including trade and foreign investment.
The reason provided supports the assertion by stating that the deregulation of these sectors created new opportunities for both local and foreign trade. As a result, it is expected that this would lead to the creation of new employment opportunities.
Analyzing the Assertion and Reason:
- The assertion is true. In 1991, India did implement a series of economic reforms known as the New Economic Policy (NEP) to address a severe balance of payments crisis and promote economic growth. These reforms focused on liberalizing and de-regulating various sectors, including trade and foreign investment.
- The reason is also true. The de-regulation of trade and foreign investment, as a part of the economic reforms, did open up new opportunities for both local and foreign trade. This led to increased trade activities, which in turn had the potential to create new employment opportunities.
- The reason provided is a correct explanation of the assertion. The de-regulation of sectors, such as trade and foreign investment, aimed to promote economic growth by enhancing trade activities. The increase in trade activities can contribute to job creation and the hope of new employment opportunities.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A: Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion: Globalization need not always be positive; it can have negative consequences for the people.Reason: Globalization is a multidimensional concept. It has political, economic and cultural manifestations, and these must be adequately distinguished.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Globalization need not always be positive; it can have negative consequences for the people.
Reason: Globalization is a multidimensional concept. It has political, economic and cultural manifestations, and these must be adequately distinguished.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Ojasvi Mehta answered |
Globalization may have some negative consequences too. It may not be able to generate sufficient income for all; illiterate people have less knowledge about globalization. Moreover, it is a multidimensional concept and we must be acquainted about each of them and differentiate them accordingly.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion: The critics argue that contemporary globalization represents a particular phase of global capitalism that makes the rich richer (and fewer) and the poor poorer.Reason: Weakening of the state leads to a reduction in the capacity of the state to protect the interest of its poor.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: The critics argue that contemporary globalization represents a particular phase of global capitalism that makes the rich richer (and fewer) and the poor poorer.
Reason: Weakening of the state leads to a reduction in the capacity of the state to protect the interest of its poor.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Globalization leads to an increase in income inequality around the globe. This is because globalization encourages prosperous nations to outsource production to locations which provide either cheap labour or cheap raw materials or both.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion: Economic globalization involves many actors other than the international institutions. A Reason: What is often called economic globalization usually involves greater economic flows among different countries of the world.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Economic globalization involves many actors other than the international institutions. A Reason: What is often called economic globalization usually involves greater economic flows among different countries of the world.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Economic globalization is the development of trade systems within transnational actors such as corporations or NGOs; Financial globalization: can be linked with the rise of a global financial system with international financial exchanges and monetary exchanges.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:The most visible impacts of globalization are definitely the ones affecting the economic world. Globalization has led to a sharp increase in trade and economic exchanges, but also to a multiplication of financial exchanges.In the 1970s world economies opened up and the development of free trade policies accelerated the globalization phenomenon. Between 1950 and 2010, world exports increased 33-fold. This significantly contributed to increasing the interactions between different regions of the world.This acceleration of economic exchanges has led to strong global economic growth. It fostered as well a rapid global industrial development that allowed the rapid development of many of the technologies and commodities we have available nowadays.Knowledge became easily shared and international cooperation among the brightest minds speeded things up. According to some analysts, globalization has also contributed to improving global economic conditions, creating much economic wealth.At the same time, finance also became globalized. From the 1980s, driven by neo- liberal policies, the world of finance gradually opened. Many states, particularly the US under Ronald Reagan and the UK under Margaret Thatcher introduced the famous “3D Policy”: Disintermediation, Decommissioning, and Deregulation.Q. We can see “a sharp increase” due to globalisation in ................................ ?- a)employment and capital
- b)trade and economic exchanges
- c)poverty and hunger
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
The most visible impacts of globalization are definitely the ones affecting the economic world. Globalization has led to a sharp increase in trade and economic exchanges, but also to a multiplication of financial exchanges.
In the 1970s world economies opened up and the development of free trade policies accelerated the globalization phenomenon. Between 1950 and 2010, world exports increased 33-fold. This significantly contributed to increasing the interactions between different regions of the world.
This acceleration of economic exchanges has led to strong global economic growth. It fostered as well a rapid global industrial development that allowed the rapid development of many of the technologies and commodities we have available nowadays.
Knowledge became easily shared and international cooperation among the brightest minds speeded things up. According to some analysts, globalization has also contributed to improving global economic conditions, creating much economic wealth.
At the same time, finance also became globalized. From the 1980s, driven by neo- liberal policies, the world of finance gradually opened. Many states, particularly the US under Ronald Reagan and the UK under Margaret Thatcher introduced the famous “3D Policy”: Disintermediation, Decommissioning, and Deregulation.
Q. We can see “a sharp increase” due to globalisation in ................................ ?
a)
employment and capital
b)
trade and economic exchanges
c)
poverty and hunger
d)
All of the above
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Globalization has resulted in greater inter connectedness among markets around the world and increased communication and awareness of business opportunities in the far corners of the globe.
India implemented the New Economic Policy in the year- a)1980.
- b)1981.
- c)1990.
- d)1991.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
India implemented the New Economic Policy in the year
a)
1980.
b)
1981.
c)
1990.
d)
1991.
|
|
Anisha Chopra answered |
As a part of economic reforms, the Government of India announced a new industrial policy in July 1991. Through this polcy, the country moved towards the globalisation pattern.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion: Globalization results in an erosion of state capacity, that is, the ability of government to do what they do.Reason: Globalization also gives freedom to governments to act in an arbitrary manner as far as the global issues are concerned.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: Globalization results in an erosion of state capacity, that is, the ability of government to do what they do.
Reason: Globalization also gives freedom to governments to act in an arbitrary manner as far as the global issues are concerned.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Ojasvi Mehta answered |
Globalization restrains governments by inducing increased budgetary pressure. As a consequence, governments shift their expenditures in favor of transfers and subsidies and away from capital expenditures. Powerful nations curb the freedom of decision making of the weaker nations by putting indirect pressures, such as, withdrawing economic aid or using veto against them.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:Assertion: While globalization is not caused by any single factor, technology remains a critical element.Reason: The ability of ideas, capital, commodities and people to move more easily from one part of the world to another has been made possible largely by technological advances.- a)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
Assertion: While globalization is not caused by any single factor, technology remains a critical element.
Reason: The ability of ideas, capital, commodities and people to move more easily from one part of the world to another has been made possible largely by technological advances.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Anand Das answered |
Assertion (A): While globalization is not caused by any single factor, technology remains a critical element.
Reason (R): The ability of ideas, capital, commodities, and people to move more easily from one part of the world to another has been made possible largely by technological advances.
The correct answer is option 'A', which states that both the assertion and the reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Explanation:
Globalization is a complex phenomenon that involves the integration of economies, societies, cultures, and political systems across the world. It is not caused by any single factor, but rather by a combination of various factors. Technology, however, remains a critical element in facilitating and driving globalization.
Technology as a Critical Element of Globalization:
Technological advances have played a significant role in enabling and accelerating globalization. The reason states that the ability of ideas, capital, commodities, and people to move more easily from one part of the world to another has been made possible largely by technological advances. This statement is true and can be supported by several examples:
1. Communication Technology: The development of communication technologies such as the internet, mobile phones, and satellite systems has revolutionized communication and made it easier for people to connect and exchange information globally. This has facilitated the spread of ideas, knowledge, and information across borders, contributing to globalization.
2. Transportation Technology: Advances in transportation technology, including faster and more efficient modes of travel and shipping, have made it easier and cheaper to move goods, services, and people across long distances. This has facilitated international trade, investment, and migration, all of which are key components of globalization.
3. Financial Technology: The development of financial technologies, such as electronic payment systems, online banking, and global financial networks, has facilitated the flow of capital across borders. This has increased financial integration and enabled businesses and individuals to access and invest in global markets, contributing to economic globalization.
4. Production Technology: Technological advancements in production processes, such as automation, robotics, and supply chain management systems, have enabled companies to efficiently manufacture and distribute goods on a global scale. This has led to the outsourcing of production to countries with lower costs, contributing to the globalization of production networks.
Overall, technology has played a crucial role in facilitating the movement of ideas, capital, commodities, and people across the world, which are essential elements of globalization. While globalization is influenced by various other factors such as political, economic, and cultural forces, technology remains a critical and enabling element in the process. Therefore, the reason provided is a correct explanation of the assertion.
Reason (R): The ability of ideas, capital, commodities, and people to move more easily from one part of the world to another has been made possible largely by technological advances.
The correct answer is option 'A', which states that both the assertion and the reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Explanation:
Globalization is a complex phenomenon that involves the integration of economies, societies, cultures, and political systems across the world. It is not caused by any single factor, but rather by a combination of various factors. Technology, however, remains a critical element in facilitating and driving globalization.
Technology as a Critical Element of Globalization:
Technological advances have played a significant role in enabling and accelerating globalization. The reason states that the ability of ideas, capital, commodities, and people to move more easily from one part of the world to another has been made possible largely by technological advances. This statement is true and can be supported by several examples:
1. Communication Technology: The development of communication technologies such as the internet, mobile phones, and satellite systems has revolutionized communication and made it easier for people to connect and exchange information globally. This has facilitated the spread of ideas, knowledge, and information across borders, contributing to globalization.
2. Transportation Technology: Advances in transportation technology, including faster and more efficient modes of travel and shipping, have made it easier and cheaper to move goods, services, and people across long distances. This has facilitated international trade, investment, and migration, all of which are key components of globalization.
3. Financial Technology: The development of financial technologies, such as electronic payment systems, online banking, and global financial networks, has facilitated the flow of capital across borders. This has increased financial integration and enabled businesses and individuals to access and invest in global markets, contributing to economic globalization.
4. Production Technology: Technological advancements in production processes, such as automation, robotics, and supply chain management systems, have enabled companies to efficiently manufacture and distribute goods on a global scale. This has led to the outsourcing of production to countries with lower costs, contributing to the globalization of production networks.
Overall, technology has played a crucial role in facilitating the movement of ideas, capital, commodities, and people across the world, which are essential elements of globalization. While globalization is influenced by various other factors such as political, economic, and cultural forces, technology remains a critical and enabling element in the process. Therefore, the reason provided is a correct explanation of the assertion.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:At the most simple level, globalisation results in an erosion of state capacity, that is, the ability of government to do what they do. All over the world, the old ‘welfare state’ is now giving way to a more minimalist state that performs certain core functions such as the maintenance of law and order and the security of its citizens. However, it withdraws from many of its earlier welfare functions directed at economic and social wellbeing. In place of the welfare state, it is the market that becomes the prime determinant of economic and social priorities. The entry and the increased role of multinational companies all over the world leads to a reduction in the capacity of governments to take decisions on their own. What is important is for people in different parts of the world to recognise these interconnections with the rest of the world. Currently, we are aware of the fact that events taking place in one part of the world could have an impact on another part of the world. The Bird flu or tsunami is not confined to any particular nation. It does not respect national boundaries. Similarly, when major economic events take place, their impact is felt outside their immediate local, national or regional environment at the global level.Q. At the most simple level, globalisation results in an erosion of ......................... .- a)political capacity
- b)state capacity
- c)capital capacity
- d)global capacity
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
At the most simple level, globalisation results in an erosion of state capacity, that is, the ability of government to do what they do. All over the world, the old ‘welfare state’ is now giving way to a more minimalist state that performs certain core functions such as the maintenance of law and order and the security of its citizens. However, it withdraws from many of its earlier welfare functions directed at economic and social wellbeing. In place of the welfare state, it is the market that becomes the prime determinant of economic and social priorities. The entry and the increased role of multinational companies all over the world leads to a reduction in the capacity of governments to take decisions on their own. What is important is for people in different parts of the world to recognise these interconnections with the rest of the world. Currently, we are aware of the fact that events taking place in one part of the world could have an impact on another part of the world. The Bird flu or tsunami is not confined to any particular nation. It does not respect national boundaries. Similarly, when major economic events take place, their impact is felt outside their immediate local, national or regional environment at the global level.
Q. At the most simple level, globalisation results in an erosion of ......................... .
a)
political capacity
b)
state capacity
c)
capital capacity
d)
global capacity
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Globalization has had a dual effect on the sovereignty of the nation-state. Yet, simultaneously, economic integration has limited the range of policy options available to states. This has diminished their capacity to meet these obligations.
This type of globalisation refers to global markets and the flow of capital, technology & goods is- a)political globalisation.
- b)cultural globalisation.
- c)economic globalisation.
- d)opposing globalisation.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
This type of globalisation refers to global markets and the flow of capital, technology & goods is
a)
political globalisation.
b)
cultural globalisation.
c)
economic globalisation.
d)
opposing globalisation.
|
|
Arnab Gupta answered |
This includes exchanges of currencies in capital movements, technology transfer, international travel and an international flow of ideas and information.
Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows: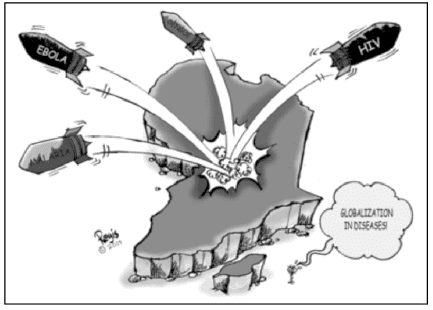 Q. What is depicted in the picture?
Q. What is depicted in the picture?- a)Spread of nuclear weapons
- b)Spread of various diseases
- c)Attacks by using biological weapons
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows:

Q. What is depicted in the picture?
a)
Spread of nuclear weapons
b)
Spread of various diseases
c)
Attacks by using biological weapons
d)
None of the above
|
|
Ojasvi Mehta answered |
Globalization, the flow of information, goods, capital, and people across political and geographic boundaries, allows infectious diseases to rapidly spread.
Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows: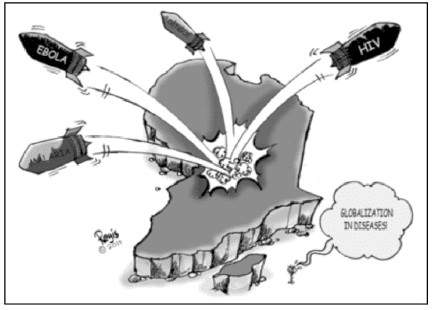 Q. How did globalization help in the medical field?
Q. How did globalization help in the medical field?- a)Exports of medicines increased.
- b)Helped in finding effective and speedy cure for the diseases with the collaboration of the medical facilities and knowledge of many countries.
- c)Inviting foreign doctors and creating employment opportunities in the various countries.
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows:

Q. How did globalization help in the medical field?
a)
Exports of medicines increased.
b)
Helped in finding effective and speedy cure for the diseases with the collaboration of the medical facilities and knowledge of many countries.
c)
Inviting foreign doctors and creating employment opportunities in the various countries.
d)
All of the above
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Although, globalization increases the risk of spreading diseases, it also helps in finding effective and speedy cure for the diseases with the collaboration of the medical facilities and knowledge of many countries. The best example can be the invention of Covid-19 vaccine.
Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows: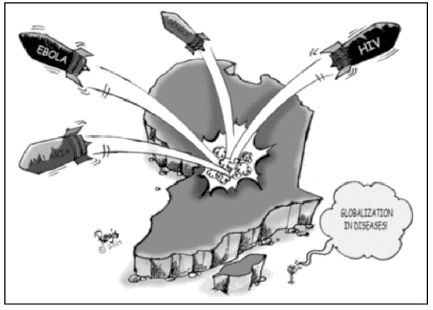 Q. Who identified the four basic aspects of globalization?
Q. Who identified the four basic aspects of globalization?- a)IMF
- b)UN
- c)EU
- d)World Bank
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows:

Q. Who identified the four basic aspects of globalization?
a)
IMF
b)
UN
c)
EU
d)
World Bank
|
|
Ojasvi Mehta answered |
In 2000, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) identified four basic aspects of globalization: trade and transactions, capital and investment movements, migration and movement of people, and the dissemination of knowledge.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:While everything may not be known about the economic facets of globalisation, this particular dimension shapes a large part of the content and direction of contemporary debates surrounding globalisation. A part of the problem has to do with defining economic globalisation itself. The mention of economic globalisation draws our attention immediately to the role of international institutions like the IMF and the WTO and the role they play in determining economic policies across the world. Yet, globalisation must not be viewed in such narrow terms. Economic globalisation involves many actors other than these international institutions. A much broader way of understanding of economic globalisation requires us to look at the distribution of economic gains, i.e. who gets the most from globalisation and who gets less, indeed who loses from it. What is often called economic globalisation usually involves greater economic flows among different countries of the world. Some of this is voluntary and some forced by international institutions and powerful countries. As we saw in the examples at the beginning of this chapter, this flow or exchange can take various forms: commodities, capital, people and ideas. Globalisation has involved greater trade in commodities across the globe; the restrictions imposed by different countries on allowing the imports of other countries have been reduced. Similarly, the restrictions on movement of capital across countries have also been reduced. In operational terms, it means that investors in the rich countries can invest their money in countries other than their own, including developing countries, where they might get better returns.Q. In terms of trade, what is the impact of globalisation?- a)Countries are divided in groups and trading with their groups only.
- b)Developing countries are not given importance in trade.
- c)Any country can receive the opportunity of trading with the other countries.
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
While everything may not be known about the economic facets of globalisation, this particular dimension shapes a large part of the content and direction of contemporary debates surrounding globalisation. A part of the problem has to do with defining economic globalisation itself. The mention of economic globalisation draws our attention immediately to the role of international institutions like the IMF and the WTO and the role they play in determining economic policies across the world. Yet, globalisation must not be viewed in such narrow terms. Economic globalisation involves many actors other than these international institutions. A much broader way of understanding of economic globalisation requires us to look at the distribution of economic gains, i.e. who gets the most from globalisation and who gets less, indeed who loses from it. What is often called economic globalisation usually involves greater economic flows among different countries of the world. Some of this is voluntary and some forced by international institutions and powerful countries. As we saw in the examples at the beginning of this chapter, this flow or exchange can take various forms: commodities, capital, people and ideas. Globalisation has involved greater trade in commodities across the globe; the restrictions imposed by different countries on allowing the imports of other countries have been reduced. Similarly, the restrictions on movement of capital across countries have also been reduced. In operational terms, it means that investors in the rich countries can invest their money in countries other than their own, including developing countries, where they might get better returns.
Q. In terms of trade, what is the impact of globalisation?
a)
Countries are divided in groups and trading with their groups only.
b)
Developing countries are not given importance in trade.
c)
Any country can receive the opportunity of trading with the other countries.
d)
None of the above
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Globalization has increased the production of goods and services. The largest companies are no longer national firms, located in one single country; they are multinational corporations with businesses in many countries.
In 1986-87, the overall fiscal deficit of India touched an all time high of- a)5% of GDP.
- b)7% of GDP.
- c)9% of GDP.
- d)10% of GDP.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In 1986-87, the overall fiscal deficit of India touched an all time high of
a)
5% of GDP.
b)
7% of GDP.
c)
9% of GDP.
d)
10% of GDP.
|
|
Simran Rane answered |
The Indian government embarked upon an expansionist policy without tackling the problem of resource mobilization, which was constrained because of the tax cuts. In 1986-87, the overall fiscal deficit touched an all time high of 9% of GDP.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:At the most simple level, globalisation results in an erosion of state capacity, that is, the ability of government to do what they do. All over the world, the old ‘welfare state’ is now giving way to a more minimalist state that performs certain core functions such as the maintenance of law and order and the security of its citizens. However, it withdraws from many of its earlier welfare functions directed at economic and social wellbeing. In place of the welfare state, it is the market that becomes the prime determinant of economic and social priorities. The entry and the increased role of multinational companies all over the world leads to a reduction in the capacity of governments to take decisions on their own. What is important is for people in different parts of the world to recognise these interconnections with the rest of the world. Currently, we are aware of the fact that events taking place in one part of the world could have an impact on another part of the world. The Bird flu or tsunami is not confined to any particular nation. It does not respect national boundaries. Similarly, when major economic events take place, their impact is felt outside their immediate local, national or regional environment at the global level.Q. What is given way recently by the old “Welfare state”?- a)More minimalist state
- b)More capitalist state
- c)More socialist state
- d)More democratic state
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
At the most simple level, globalisation results in an erosion of state capacity, that is, the ability of government to do what they do. All over the world, the old ‘welfare state’ is now giving way to a more minimalist state that performs certain core functions such as the maintenance of law and order and the security of its citizens. However, it withdraws from many of its earlier welfare functions directed at economic and social wellbeing. In place of the welfare state, it is the market that becomes the prime determinant of economic and social priorities. The entry and the increased role of multinational companies all over the world leads to a reduction in the capacity of governments to take decisions on their own. What is important is for people in different parts of the world to recognise these interconnections with the rest of the world. Currently, we are aware of the fact that events taking place in one part of the world could have an impact on another part of the world. The Bird flu or tsunami is not confined to any particular nation. It does not respect national boundaries. Similarly, when major economic events take place, their impact is felt outside their immediate local, national or regional environment at the global level.
Q. What is given way recently by the old “Welfare state”?
a)
More minimalist state
b)
More capitalist state
c)
More socialist state
d)
More democratic state
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
More minimalist state; A state with the least possible amount of powers. It is a term used in political philosophy where the duties of the state are so minimal that they cannot be reduced much further.
Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows: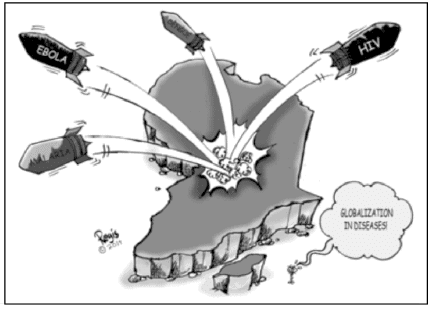 Q. Why is Africa featured in the above picture?
Q. Why is Africa featured in the above picture?- a)Because it is the centre of globalization.
- b)The diseases mentioned in the picture have their epicentre in Africa.
- c)Because Africa is a poor country.
- d)Because the world aims at developing Africa.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the cartoon carefully and give the answers to the question that follows:

Q. Why is Africa featured in the above picture?
a)
Because it is the centre of globalization.
b)
The diseases mentioned in the picture have their epicentre in Africa.
c)
Because Africa is a poor country.
d)
Because the world aims at developing Africa.
|
|
Ojasvi Mehta answered |
Africa is featured in the picture given above because it is affected with poverty the most as compared to the other countries of the world and the diseases mentioned in the picture have their epicenter in Africa.
During the colonial period, India became an- a)importer of primary goods and raw materials
- b)exporter of finished goods and also raw materials.
- c)exporter of primary goods and importer of raw materials.
- d)exporter of primary goods and raw materials.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
During the colonial period, India became an
a)
importer of primary goods and raw materials
b)
exporter of finished goods and also raw materials.
c)
exporter of primary goods and importer of raw materials.
d)
exporter of primary goods and raw materials.
|
|
Nandita Joshi answered |
India was particularly well known for its handicraft industries in the fields of cotton and silk textiles, metal and precious stone works, etc. These products enjoyed a worldwide market base.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:The most visible impacts of globalization are definitely the ones affecting the economic world. Globalization has led to a sharp increase in trade and economic exchanges, but also to a multiplication of financial exchanges.In the 1970s world economies opened up and the development of free trade policies accelerated the globalization phenomenon. Between 1950 and 2010, world exports increased 33-fold. This significantly contributed to increasing the interactions between different regions of the world.This acceleration of economic exchanges has led to strong global economic growth. It fostered as well a rapid global industrial development that allowed the rapid development of many of the technologies and commodities we have available nowadays.Knowledge became easily shared and international cooperation among the brightest minds speeded things up. According to some analysts, globalization has also contributed to improving global economic conditions, creating much economic wealth.At the same time, finance also became globalized. From the 1980s, driven by neo- liberal policies, the world of finance gradually opened. Many states, particularly the US under Ronald Reagan and the UK under Margaret Thatcher introduced the famous “3D Policy”: Disintermediation, Decommissioning, and Deregulation.Q. What is the impact of an increase in the economic exchanges between the countries of the world?- a)Strong global economic growth
- b)Sharp decline in the trade
- c)Decline in the unemployment numbers
- d)Increase in the index of poverty and hunger index
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
The most visible impacts of globalization are definitely the ones affecting the economic world. Globalization has led to a sharp increase in trade and economic exchanges, but also to a multiplication of financial exchanges.
In the 1970s world economies opened up and the development of free trade policies accelerated the globalization phenomenon. Between 1950 and 2010, world exports increased 33-fold. This significantly contributed to increasing the interactions between different regions of the world.
This acceleration of economic exchanges has led to strong global economic growth. It fostered as well a rapid global industrial development that allowed the rapid development of many of the technologies and commodities we have available nowadays.
Knowledge became easily shared and international cooperation among the brightest minds speeded things up. According to some analysts, globalization has also contributed to improving global economic conditions, creating much economic wealth.
At the same time, finance also became globalized. From the 1980s, driven by neo- liberal policies, the world of finance gradually opened. Many states, particularly the US under Ronald Reagan and the UK under Margaret Thatcher introduced the famous “3D Policy”: Disintermediation, Decommissioning, and Deregulation.
Q. What is the impact of an increase in the economic exchanges between the countries of the world?
a)
Strong global economic growth
b)
Sharp decline in the trade
c)
Decline in the unemployment numbers
d)
Increase in the index of poverty and hunger index
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Countries that are open to international trade tend to grow faster, innovate, improve productivity and provide higher income and more opportunities to their people.
Chapter doubts & questions for Globalisation - Political Science CUET Preparation 2025 is part of Humanities/Arts exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Humanities/Arts exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Humanities/Arts 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Globalisation - Political Science CUET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of Humanities/Arts exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Humanities/Arts Exam by signing up for free.
Political Science CUET Preparation
32 videos|39 docs|62 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









