All Exams >
A Level >
Biology A-Level >
All Questions
All questions of Transport in Mammals for A Level Exam
Which of the following engulfs pathogens rapidly?- a)Basophils
- b)Acidophils
- c)Monocytes
- d)Neutrophils
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following engulfs pathogens rapidly?
a)
Basophils
b)
Acidophils
c)
Monocytes
d)
Neutrophils
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Neutrophils are the type of WBCs which can engulf the pathogen rapidly. Neutrophils are more in number i.e. upto 60% of Total Leukocyte Count. They immediately engulf bacteria and viruses to destroy them by phagocytosis.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
How many contraction nodes are found in heart of Human :-- a)One
- b)Two
- c)Many
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many contraction nodes are found in heart of Human :-
a)
One
b)
Two
c)
Many
d)
None
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
Two contraction nodes...SAN and AVN..option B
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The important function of lymph is toA:Return RBCs to lymph nodesB:Return interstitial fluid to the bloodC:Transport oxygen to the brainD:Transport CO2 to the lungsThe answer is b.
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Lymph is the fluid present in lymphatic system. Its main function is to return interstitial fluid back to the blood. Interstitial fluid is also called extracellular fluid, which is formed from blood due to various factor such as hydrostatic pressure, osmotic gradients, etc.
Which of the following is a non-granulocyte?- a)Neutrophils
- b)Monocytes
- c)Basophils
- d)Eosinophils
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a non-granulocyte?
a)
Neutrophils
b)
Monocytes
c)
Basophils
d)
Eosinophils
|
|
Anjana Chakraborty answered |
Non-Granulocytes in Blood
Blood cells are divided into two groups: granulocytes and agranulocytes. Granulocytes have granules in their cytoplasm and include neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. Agranulocytes, on the other hand, lack granules and include lymphocytes and monocytes.
Non-Granulocyte
A non-granulocyte is simply an agranulocyte or a leukocyte that lacks granules in its cytoplasm. Monocytes are non-granulocytes and belong to the agranulocyte group of leukocytes.
Monocytes
Monocytes are the largest leukocytes in the blood, accounting for 2-8% of all leukocytes. They have a large kidney-shaped nucleus and are characterized by their ability to differentiate into macrophages, which are cells that engulf and digest foreign particles, dead cells, and cellular debris in the body.
Functions of Monocytes
Monocytes have several functions in the body, including:
1. Phagocytosis: Monocytes, when differentiated into macrophages, are capable of phagocytosis, which is the process of engulfing and digesting foreign particles, dead cells, and cellular debris in the body.
2. Antigen presentation: Monocytes play a crucial role in the immune response by presenting antigens to T cells, which are responsible for activating the immune response.
3. Cytokine production: Monocytes produce cytokines, which are signaling molecules that regulate the immune response.
Conclusion
In conclusion, monocytes are non-granulocytes and belong to the agranulocyte group of leukocytes. They are characterized by their ability to differentiate into macrophages, which are cells that engulf and digest foreign particles, dead cells, and cellular debris in the body. Monocytes also play a crucial role in the immune response by presenting antigens to T cells and producing cytokines.
Blood cells are divided into two groups: granulocytes and agranulocytes. Granulocytes have granules in their cytoplasm and include neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. Agranulocytes, on the other hand, lack granules and include lymphocytes and monocytes.
Non-Granulocyte
A non-granulocyte is simply an agranulocyte or a leukocyte that lacks granules in its cytoplasm. Monocytes are non-granulocytes and belong to the agranulocyte group of leukocytes.
Monocytes
Monocytes are the largest leukocytes in the blood, accounting for 2-8% of all leukocytes. They have a large kidney-shaped nucleus and are characterized by their ability to differentiate into macrophages, which are cells that engulf and digest foreign particles, dead cells, and cellular debris in the body.
Functions of Monocytes
Monocytes have several functions in the body, including:
1. Phagocytosis: Monocytes, when differentiated into macrophages, are capable of phagocytosis, which is the process of engulfing and digesting foreign particles, dead cells, and cellular debris in the body.
2. Antigen presentation: Monocytes play a crucial role in the immune response by presenting antigens to T cells, which are responsible for activating the immune response.
3. Cytokine production: Monocytes produce cytokines, which are signaling molecules that regulate the immune response.
Conclusion
In conclusion, monocytes are non-granulocytes and belong to the agranulocyte group of leukocytes. They are characterized by their ability to differentiate into macrophages, which are cells that engulf and digest foreign particles, dead cells, and cellular debris in the body. Monocytes also play a crucial role in the immune response by presenting antigens to T cells and producing cytokines.
Mark the odd one:- a)Neutrophil
- b)Erythrocyte
- c)Monocyte
- d)Lymphocyte
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mark the odd one:
a)
Neutrophil
b)
Erythrocyte
c)
Monocyte
d)
Lymphocyte
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Erythrocytes bcs its stands for rbc's whereas others are different types of wbc's
Can you explain the answer of this question below: Find out the wrong match:
- A:
Eosinophils – Allergic response
- B:
Basophils – Secrete histamine and serotonin
- C:
Monocytes – Secrete heparin
- D:
Neutrophils – Phagocytic and eat foreign organisms
The answer is c.
Find out the wrong match:
Eosinophils – Allergic response
Basophils – Secrete histamine and serotonin
Monocytes – Secrete heparin
Neutrophils – Phagocytic and eat foreign organisms
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Monocytes and macrophages synthesize and secrete thrombospondin.
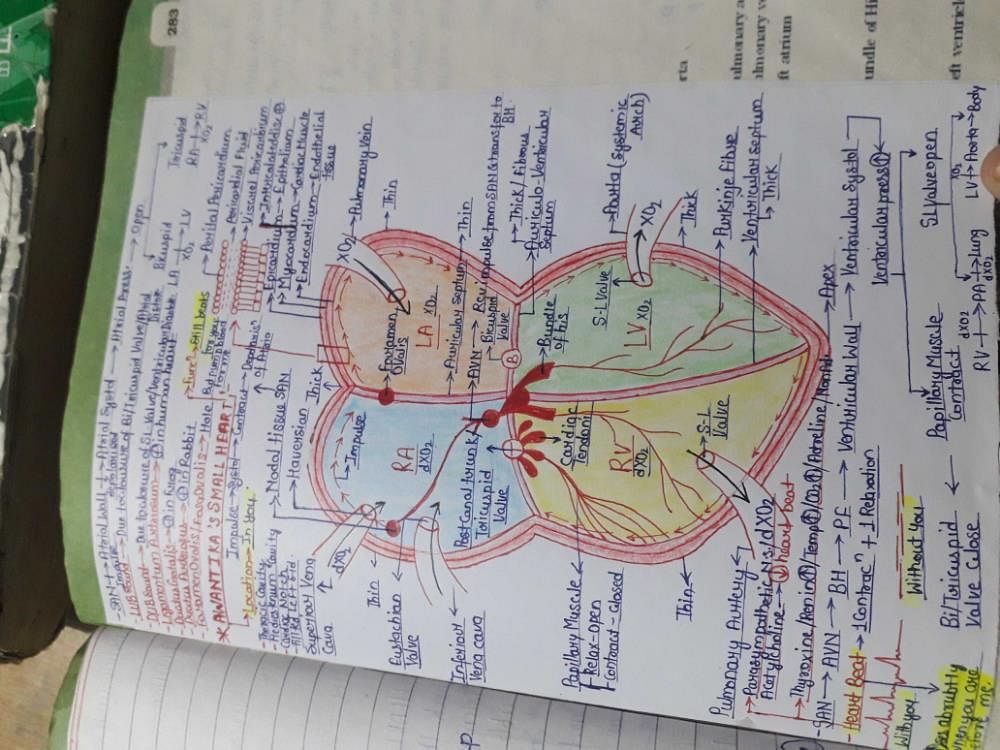
The valve situated between the left atrium and the left ventricle is called
(1) Bicuspid valve
(2) Tricuspid valve
(3) Mitral valve
(4) Eustachian tube- a)2 and 4 are correct.
- b)1 and 2 are correct.
- c)1 and 3 are correct.
- d)1, 2 and 3 are correct.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The valve situated between the left atrium and the left ventricle is called
(1) Bicuspid valve
(2) Tricuspid valve
(3) Mitral valve
(4) Eustachian tube
(1) Bicuspid valve
(2) Tricuspid valve
(3) Mitral valve
(4) Eustachian tube
a)
2 and 4 are correct.
b)
1 and 2 are correct.
c)
1 and 3 are correct.
d)
1, 2 and 3 are correct.
|
|
Bhaskar Ala answered |
The valve situated between left atria and the left ventricle is BICUSPID VALVE also known as MITRAL VALVE.. closure of this valve produce first heart sound "LUB"..
Which of these has a closed type of circulatory system :-- a)Cockroach
- b)Fish
- c)Mollusca
- d)Scorpion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these has a closed type of circulatory system :-
a)
Cockroach
b)
Fish
c)
Mollusca
d)
Scorpion
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Phylum Arthropoda and Mollusca include open circulatory system . Fish is member of phylum Chordata which contain close circulatory system.
Cockroach and scorpion are members of class inscecta phylum Arthropoda.
Cockroach and scorpion are members of class inscecta phylum Arthropoda.
Papillary muscles are found in :-- a)Haemocoel of cockroach
- b)Auricles of heart
- c)Ventricles of heart
- d)Arm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Papillary muscles are found in :-
a)
Haemocoel of cockroach
b)
Auricles of heart
c)
Ventricles of heart
d)
Arm

|
Syed Hussain answered |
The papillary muscles are muscles located in the ventricles of the heart. They attach to the cusps of the atrioventricular valves (also known as the mitral and tricuspid valves) via the chordae tendineae and contract to prevent inversion or prolapse of these valves on systole (or ventricular contraction)
The blood during diastole :-- a)Leaves the heart
- b)Enters the heart
- c)Enters lungs
- d)Leaves the ventricles
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The blood during diastole :-
a)
Leaves the heart
b)
Enters the heart
c)
Enters lungs
d)
Leaves the ventricles
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Diastole This should really be called “ventricular diastole”, but don't worry about this for GCSE. During diastole the thick muscular walls of the ventricles relax. Again, this happens to both sides of the heart. The pressure of the blood in the ventricles falls low enough for the bicuspid valve to open.
Blood circulation take following course in heart of man :-- a)Left auricle - left ventricle - body - right auricle -right ventricle
- b)Right auricle - left ventricle
- c)Left auricle - left ventricle - lungs-right auricle -right ventricle
- d)None of them
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Blood circulation take following course in heart of man :-
a)
Left auricle - left ventricle - body - right auricle -right ventricle
b)
Right auricle - left ventricle
c)
Left auricle - left ventricle - lungs-right auricle -right ventricle
d)
None of them
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The blood pumped by the right ventricle enters the pulmonary artery, whereas the left ventricle pumps blood into the aorta. The deoxygenated blood pumped into the pulmonary artery is passed onto the lungs from where the oxygenated blood is carried by the pulmonary veins into the left atrium. This pathway constitutes the pulmonary circulation. The oxygenated blood entering the aorta is carried by a network of arteries, arterioles, and capillaries to the tissues from where the deoxygenated blood is collected by a system of venules, veins and vena cava and emptied into the right atrium. This is the systemic circulation. The systemic circulation provides nutrients, O2 and other essential substances to the tissues and takes CO2 and other harmful substances away for elimination.
So, the correct answer is option A.
So, the correct answer is option A.
Pulse beat is measured from :- a)Vein
- b)Artery
- c)Nerve
- d)Capillary
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Pulse beat is measured from :
a)
Vein
b)
Artery
c)
Nerve
d)
Capillary
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Pulse (or the count of arterial pulse per minute) is equivalent to measuring the heart rate. The heart rate can also be measured by listening to the heart beat by auscultation, traditionally using a stethoscope and counting it for a minute. The radial pulse is commonly measured using three fingers.
Read the following :
i. Blood vessels include arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood from heart to body parts and veins bring back blood from body parts to heart.
ii. The blood vessel which carry blood from heart to lungs is pulmonary artery and it carries oxygenated blood.- a)Statement ii) is correct and i) is wrong.
- b)both are correct
- c)Statement ii) is wrong and i) is correct.
- d)both are wrong
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following :
i. Blood vessels include arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood from heart to body parts and veins bring back blood from body parts to heart.
ii. The blood vessel which carry blood from heart to lungs is pulmonary artery and it carries oxygenated blood.
i. Blood vessels include arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood from heart to body parts and veins bring back blood from body parts to heart.
ii. The blood vessel which carry blood from heart to lungs is pulmonary artery and it carries oxygenated blood.
a)
Statement ii) is correct and i) is wrong.
b)
both are correct
c)
Statement ii) is wrong and i) is correct.
d)
both are wrong
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
- The arteries carry blood from the heart to all over body parts. Hence, statement (i) is correct.
- The vessels which carry blood from the heart to the lungs is the pulmonary artery but it carries deoxygenated blood. Hence, statement (ii) is correct.
The specialised patch of modified heart muscles from where contraction initiates, is/are :- a)Pacesetter of heart
- b)both SAN and AVN together
- c)Pacemaker of heart
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The specialised patch of modified heart muscles from where contraction initiates, is/are :
a)
Pacesetter of heart
b)
both SAN and AVN together
c)
Pacemaker of heart
d)
none of these
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
- The nodal musculature has the ability to generate action potentials without any external stimuli.
- The number of action potentials that could be generated in a minute varies at different parts of the nodal system.
- The SAN can generate the maximum number of action potentials and is responsible for initiating and maintaining the rhythmic contractile activity of the heart.
- Therefore, it is called the pacemaker.
Lymph can be defined as :-- a)Blood minus corpuscles
- b)Blood minus Plasma
- c)Blood minus WBC
- d)Blood minus RBC & Platlates
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Lymph can be defined as :-
a)
Blood minus corpuscles
b)
Blood minus Plasma
c)
Blood minus WBC
d)
Blood minus RBC & Platlates
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Lymph is a colorless fluid, containing specialized lymphocytes, which are responsible for the immune responses of the body.
Lymph is also an important carrier for nutrients, hormones, etc. Fats are absorbed through lymph in the lacteals present in the intestinal villi.
Lymph lacks RBCs and platelets. Lymph contains white blood cells. So option D is correct.
Which one of the following is correct?- a)Plasma = Blood − Lymphocytes
- b)Neuron = Cyton + Dendron + Axon + Synapse
- c)Lymph = Plasma + WBCs + RBCs
- d)Blood = Plasma + RBCs + WBCs + Platelets
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is correct?
a)
Plasma = Blood − Lymphocytes
b)
Neuron = Cyton + Dendron + Axon + Synapse
c)
Lymph = Plasma + WBCs + RBCs
d)
Blood = Plasma + RBCs + WBCs + Platelets
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
It has four main components: plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Blood has many different functions, including: transporting oxygen and nutrients to the lungs and tissues. forming blood clots to prevent excess blood loss.
pH of blood in arteries and veins is :-- a)More in veins and less in arteries
- b)More in arteries and less in veins
- c)same
- d)Not definite
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
pH of blood in arteries and veins is :-
a)
More in veins and less in arteries
b)
More in arteries and less in veins
c)
same
d)
Not definite
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
pH is a measure of the amount of hydrogen ion present in a solution. Thus, a high level of H+ is a low pH (or an acid environment) while a low level of H+ is a high pH (or an alkali or basic environment).
Veins have a slightly lower pH than arteries. This is because the blood circulates through working tissues in our bodies, and drops off oxygen, and picks up carbon dioxide.
Carbon dioxide in water forms a weak acid. In arteries, they carry oxygenated blood, and less carbon dioxide, so the pH is more.
In veins, there is less oxygen and more carbon dioxide which is acidic so the blood in veins has less pH.
So, the correct answer is option B.
So, the correct answer is option B.
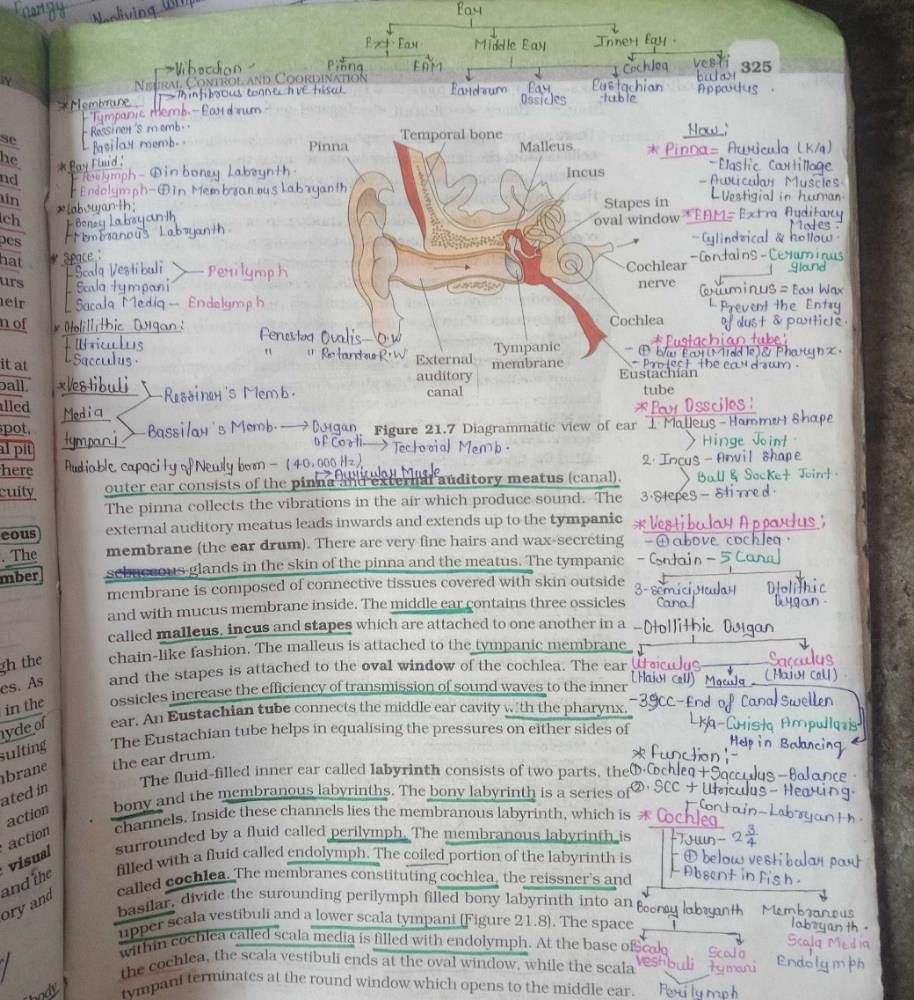
Read the following and choose the correct option:
(i) The instrument used for recording the heart’s electrical events is named electrocardiograph.
(ii) In any ECG the part of the baseline between any two deflections is called interval.
(iii) Abnormality in the working of heart changes wave pattern of ECG.
- a)Only (ii) and (iii) are correct.
- b)Only (iii) is correct.
- c)All statements are correct.
- d)Only (i) and (iii) are correct.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following and choose the correct option:
(i) The instrument used for recording the heart’s electrical events is named electrocardiograph.
(ii) In any ECG the part of the baseline between any two deflections is called interval.
(iii) Abnormality in the working of heart changes wave pattern of ECG.
(i) The instrument used for recording the heart’s electrical events is named electrocardiograph.
(ii) In any ECG the part of the baseline between any two deflections is called interval.
(iii) Abnormality in the working of heart changes wave pattern of ECG.
a)
Only (ii) and (iii) are correct.
b)
Only (iii) is correct.
c)
All statements are correct.
d)
Only (i) and (iii) are correct.
|
|
Sonal Khanna answered |
Rate is a(n) _______.
(a) thermometer
(b) stethoscope
(c) sphygmomanometer
(d) electrocardiogram machine
Answer:
(d) electrocardiogram machine
(a) thermometer
(b) stethoscope
(c) sphygmomanometer
(d) electrocardiogram machine
Answer:
(d) electrocardiogram machine
In human beings, the duration of the cardiac cycle is- a)8.0 second
- b)0.5 second
- c)0.8 second
- d)0.08 second
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In human beings, the duration of the cardiac cycle is
a)
8.0 second
b)
0.5 second
c)
0.8 second
d)
0.08 second
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Cardiac cycle a complex process which involves a sequence of activities and that too within 0.8 sec. The cardiac cycle consists of a systole and a diastole. The cardiac cycle begins with a joint diastole (relaxation of all four chambers of the heart).
Blood Capillaries are made of :-- a)Endothelium and thin coat of connective tissue
- b)Endothelium and thin coat of muscle fibres
- c)Endothelium and thin coat of connective tissue and muscle fibres.
- d)Only endothelium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Blood Capillaries are made of :-
a)
Endothelium and thin coat of connective tissue
b)
Endothelium and thin coat of muscle fibres
c)
Endothelium and thin coat of connective tissue and muscle fibres.
d)
Only endothelium
|
|
Siddiq Zayeda answered |
Capillaries are much thinner than arteries and veins, because their walls are made up of only a single layer of endothelial cells, the flat cells that line all blood vessels......
Role of spleen in mammals is :-- a)To control Blood pressure
- b)To assist liver
- c)To assist kidneys
- d)To act as haemopoitic tissue in embryo
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Role of spleen in mammals is :-
a)
To control Blood pressure
b)
To assist liver
c)
To assist kidneys
d)
To act as haemopoitic tissue in embryo

|
Prisha Singh answered |
Ans.
The spleen plays important roles in regard to red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the immune system. It removes old red blood cells and holds a reserve of blood, which can be valuable in case of hemorrhagic shock, and also recycles iron. As a part of the mononuclear phagocyte system, it metabolizes hemoglobin removed from senescent red blood cells (erythrocytes). The globin portion of hemoglobin is degraded to its constitutive amino acids, and the heme portion is metabolized to bilirubin, which is removed in the liver.
Ramesh has Rh antigen and Anti-A as well as Anti-B antibodies in his blood. During blood transfusion he can receive blood from :
- a)person with AB positive blood group
- b)person with O positive blood group
- c)person with AB negative blood group
- d)person with O negative blood group
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ramesh has Rh antigen and Anti-A as well as Anti-B antibodies in his blood. During blood transfusion he can receive blood from :
a)
person with AB positive blood group
b)
person with O positive blood group
c)
person with AB negative blood group
d)
person with O negative blood group

|
Jatin Chakraborty answered |
Since he has both antibodies A and Band has Rh antigen and hence has O + blood group. So, hecan receive blood from O-positive blood group.
The maximum surface area of the circulatory system is seen in- a)Heart
- b)Capillaries
- c)Arterioles
- d)Veins
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The maximum surface area of the circulatory system is seen in
a)
Heart
b)
Capillaries
c)
Arterioles
d)
Veins
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
An adult human has been estimated to have some 60,000 miles (96,560 km) of capillaries with a total surface area of some 8001000 m2. The total volume of this system is roughly 5 liters, the same as the total volume of blood.
Antigens are present- a)Inside the cytoplasm
- b)Inside the nucleus
- c)On the nuclear membrane
- d)On the cell surface
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Antigens are present
a)
Inside the cytoplasm
b)
Inside the nucleus
c)
On the nuclear membrane
d)
On the cell surface

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
Cell markers, also known as cell surface antigens, serve as monograms to help identify and classify cells. The majority of them are molecules or antigens within cell's plasma membrane. Unique to different cell types, there exist specific combinations of markers or antigens.
The SA node is located in- a)Upper lateral wall of the left atrium
- b)Lower lateral wall of the right atrium
- c)Lower lateral wall of the left atrium
- d)Upper lateral wall of the right atrium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The SA node is located in
a)
Upper lateral wall of the left atrium
b)
Lower lateral wall of the right atrium
c)
Lower lateral wall of the left atrium
d)
Upper lateral wall of the right atrium
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
SA node (sino-atrial node) is located in right upper corner of right atrium .of heart..option D is the answer
All arteries carry oxygenated blood except :-- a)Systemic
- b)Hepatic
- c)Pulmonary
- d)Cardiac
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
All arteries carry oxygenated blood except :-
a)
Systemic
b)
Hepatic
c)
Pulmonary
d)
Cardiac
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Systemic circulation is the flow of blood from left ventricle of heart to all body parts and return of blood from all body parts to the right auricle. The pathway of systemic circulation can be summarised as:
Pulmonary vein brings oxygenated blood from lungs to the left auricle.
From the left auricle blood passes to left ventricle through bicuspid valve.
From the left ventricle, blood is pumped into aorta.
Aorta divides into many arteries and supply blood to body tissues.
The oxygen in blood is utilised by tissues and deoxygenated blood is collected by veins.
The vena cava brings this deoxygenated blood into the right atrium from where it passes to right ventricle through tricuspid valve.
From the right ventricle, deoxygenated blood is carried to lungs by the pulmonary artery where it is gets oxygenated and returns to left auricle through pulmonary vein.
Hence, in this way, the cycle starts again.
Pulmonary vein brings oxygenated blood from lungs to the left auricle.
From the left auricle blood passes to left ventricle through bicuspid valve.
From the left ventricle, blood is pumped into aorta.
Aorta divides into many arteries and supply blood to body tissues.
The oxygen in blood is utilised by tissues and deoxygenated blood is collected by veins.
The vena cava brings this deoxygenated blood into the right atrium from where it passes to right ventricle through tricuspid valve.
From the right ventricle, deoxygenated blood is carried to lungs by the pulmonary artery where it is gets oxygenated and returns to left auricle through pulmonary vein.
Hence, in this way, the cycle starts again.
Heart of Man is :-- a)Myogenic
- b)Neurogenic
- c)Cardiogenic
- d)Digenic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Heart of Man is :-
a)
Myogenic
b)
Neurogenic
c)
Cardiogenic
d)
Digenic
|
|
Rocky Handsome answered |
The muscles of the human heart are stimulated to contract by nerve impulses generated by the Sino Atrial(SA) node. It is a cluster of cells which are part of the heart muscle.
•Hence the human heart is myogenic.
•Hence the human heart is myogenic.
Pace maker influences :-- a)Contraction of heart muscles
- b)Flow of blood in heat
- c)Rate of heart beat
- d)Formation of nerve impulse
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Pace maker influences :-
a)
Contraction of heart muscles
b)
Flow of blood in heat
c)
Rate of heart beat
d)
Formation of nerve impulse

|
Mamta Sharma answered |
Sa node represents the pacemaker of our heart which is specialised in generating impluses and initiation of heart beat. it maintains the rhythmic contractile activity of heart. so it can only determine rate of heart beat and not contraction of heart muscles. contraction of heart muscles depends on how intense the impulse is which mainly decided by the conducting fibres.
In the systemic circulation, blood vessel that carries blood from the intestine to liver is named :- a)Hepatic portal arch
- b)none of these
- c)Hepatic portal artery
- d)Hepatic portal vein
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the systemic circulation, blood vessel that carries blood from the intestine to liver is named :
a)
Hepatic portal arch
b)
none of these
c)
Hepatic portal artery
d)
Hepatic portal vein
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
Lienal vein is an old term for splenic vein. The portal vein or hepatic portal vein is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents.
In a normal man blood pressure is :-- a)120/80mm of Hg
- b)80/100 mm of Hg
- c)80/120 mm of Hg
- d)100/80 mm of Hg
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a normal man blood pressure is :-
a)
120/80mm of Hg
b)
80/100 mm of Hg
c)
80/120 mm of Hg
d)
100/80 mm of Hg
|
|
Harshitha Reddy answered |
Normal Blood Pressure
The normal blood pressure in a man is 120/80 mm of Hg.
Explanation
Blood pressure is the force exerted by blood against the walls of arteries. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). The two numbers in blood pressure readings represent systolic pressure (the top number) and diastolic pressure (the bottom number).
The normal blood pressure reading for an adult is 120/80 mm of Hg. The systolic pressure represents the pressure when the heart beats and pumps blood into the arteries. The diastolic pressure represents the pressure when the heart is at rest between beats.
If the blood pressure reading is consistently higher than normal, it may indicate hypertension or high blood pressure. Hypertension can lead to serious health problems like heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
On the other hand, if the blood pressure reading is consistently lower than normal, it may indicate hypotension or low blood pressure. Hypotension can cause dizziness, fainting, and other health problems.
It's important to monitor blood pressure regularly and take necessary steps to maintain normal blood pressure. A healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management can help maintain normal blood pressure levels.
The normal blood pressure in a man is 120/80 mm of Hg.
Explanation
Blood pressure is the force exerted by blood against the walls of arteries. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). The two numbers in blood pressure readings represent systolic pressure (the top number) and diastolic pressure (the bottom number).
The normal blood pressure reading for an adult is 120/80 mm of Hg. The systolic pressure represents the pressure when the heart beats and pumps blood into the arteries. The diastolic pressure represents the pressure when the heart is at rest between beats.
If the blood pressure reading is consistently higher than normal, it may indicate hypertension or high blood pressure. Hypertension can lead to serious health problems like heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
On the other hand, if the blood pressure reading is consistently lower than normal, it may indicate hypotension or low blood pressure. Hypotension can cause dizziness, fainting, and other health problems.
It's important to monitor blood pressure regularly and take necessary steps to maintain normal blood pressure. A healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management can help maintain normal blood pressure levels.
The course of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart is called- a)Systemic circulation
- b)Double circulation
- c)Pulmonary circulation
- d)Single circulation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The course of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart is called
a)
Systemic circulation
b)
Double circulation
c)
Pulmonary circulation
d)
Single circulation

|
Vipe Saga answered |
The blood circulation from heart to lungs and back to heart is pulmonary circulation and the circulation between heart to tissue and back to heart is systematic circulation and both are included in double circulation.
What would be the cardiac output of a person having 72 heart beats per minute and a stroke volume of 50 ml?- a)360 ml
- b)7200 ml
- c)5000 ml
- d)3600 ml
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What would be the cardiac output of a person having 72 heart beats per minute and a stroke volume of 50 ml?
a)
360 ml
b)
7200 ml
c)
5000 ml
d)
3600 ml
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
(d) Cardiac Output (i) The volume of blood pumped by each ventricle per minute is called the cardiac output. It is 500 mL or 5 liters in a healthy individual. It is determined by multiplying the heart rate with the volume of blood ejected by each ventricle during each beat, which is called as stroke volume. Cardiac output = Heart rate x Stroke volume = 72 beats/min x 0.08 litre/beat = 5.5 litre/min (iii) Cardiac index is the minute volume per sq. m. of body surface area. Its normal value is 3.3 lit/min/sq.m.
In which of the following charactor a vein differs from an artery :-- a)Having valves to control flow of blood
- b)Having narrow lumen
- c)Having muscular wall
- d)Having pigmented wall to give dark look
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following charactor a vein differs from an artery :-
a)
Having valves to control flow of blood
b)
Having narrow lumen
c)
Having muscular wall
d)
Having pigmented wall to give dark look
|
|
Nandita Rane answered |
Difference between Vein and Artery:
Vein and artery are two types of blood vessels that play an important role in the circulation of blood in the body. Although both of them have similar functions, there are some key differences between them. One of the main differences between veins and arteries is the presence of valves.
Presence of Valves in Veins:
Veins are blood vessels that carry blood from the body back to the heart. They have thin walls and are located closer to the surface of the skin. One of the main features of veins is the presence of valves. These valves are one-way flaps that prevent the backflow of blood. They work by opening and closing as the blood flows through them. This helps to maintain the flow of blood towards the heart and prevents the blood from flowing back into the veins.
Absence of Valves in Arteries:
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the rest of the body. They have thick walls and are located deeper in the body. Unlike veins, arteries do not have valves. This is because the flow of blood in the arteries is maintained by the pumping action of the heart. The blood flows in one direction only, from the heart to the rest of the body.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' which states that veins differ from arteries in having valves to control the flow of blood.
Vein and artery are two types of blood vessels that play an important role in the circulation of blood in the body. Although both of them have similar functions, there are some key differences between them. One of the main differences between veins and arteries is the presence of valves.
Presence of Valves in Veins:
Veins are blood vessels that carry blood from the body back to the heart. They have thin walls and are located closer to the surface of the skin. One of the main features of veins is the presence of valves. These valves are one-way flaps that prevent the backflow of blood. They work by opening and closing as the blood flows through them. This helps to maintain the flow of blood towards the heart and prevents the blood from flowing back into the veins.
Absence of Valves in Arteries:
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the rest of the body. They have thick walls and are located deeper in the body. Unlike veins, arteries do not have valves. This is because the flow of blood in the arteries is maintained by the pumping action of the heart. The blood flows in one direction only, from the heart to the rest of the body.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' which states that veins differ from arteries in having valves to control the flow of blood.
Which of the following statements doesn’t hold true for blood clotting cascade?
i. Ruptured platelets release thromboplastin.
ii. Prothrombinis converted into thrombin in the presence of vitamin K and Na+ions.
iii. Fibrinogen is converted into fibrin through enzymatic action of thrombin in the presence of Ca++ions
iv. Fibrin makes clot via process of polymerisation.- a)only statement i) and iv) are wrong
- b)only statement ii) and iii) are wrong
- c)all statements are wrong
- d)only statement iv) is wrong
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements doesn’t hold true for blood clotting cascade?
i. Ruptured platelets release thromboplastin.
ii. Prothrombinis converted into thrombin in the presence of vitamin K and Na+ions.
iii. Fibrinogen is converted into fibrin through enzymatic action of thrombin in the presence of Ca++ions
iv. Fibrin makes clot via process of polymerisation.
i. Ruptured platelets release thromboplastin.
ii. Prothrombinis converted into thrombin in the presence of vitamin K and Na+ions.
iii. Fibrinogen is converted into fibrin through enzymatic action of thrombin in the presence of Ca++ions
iv. Fibrin makes clot via process of polymerisation.
a)
only statement i) and iv) are wrong
b)
only statement ii) and iii) are wrong
c)
all statements are wrong
d)
only statement iv) is wrong

|
Prakash Gharte answered |
Second statement is wrong because prothrombin is converted into thrombin in the presence of enzyme thrombokinase and Ca++ ions and third statement is right
Coronary heart disease is due to- a)Insufficient blood supply to the heart muscles
- b)Weakening of the heart valves
- c)Inflammation of pericardium
- d)Streptococci bacteria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Coronary heart disease is due to
a)
Insufficient blood supply to the heart muscles
b)
Weakening of the heart valves
c)
Inflammation of pericardium
d)
Streptococci bacteria
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a disease in which a waxy substance called plaque builds up inside the coronary arteries. These arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to your heart muscle. When plaque builds up in the arteries, the condition is called atherosclerosis. The buildup of plaque occurs over many years.
Blood enters the heart because muscles of the- a)Ventricles contract
- b)Ventricles relax
- c)Atria contract
- d)Atria relax
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Blood enters the heart because muscles of the
a)
Ventricles contract
b)
Ventricles relax
c)
Atria contract
d)
Atria relax
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Atrial diastole is characterized by the relaxation of the atrial muscles. During this stage, the blood enters into the atria, as the volume of the blood in the atria increases the pressure within it decreases.
So, the correct answer is option D.
So, the correct answer is option D.
Rh incompatibility develops when :- a)foetus is Rh-ve and father is Rh+ve
- b)foetus is Rh+ve and mother is Rh-ve
- c)foetus is Rh-ve and mother is Rh+ve
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rh incompatibility develops when :
a)
foetus is Rh-ve and father is Rh+ve
b)
foetus is Rh+ve and mother is Rh-ve
c)
foetus is Rh-ve and mother is Rh+ve
d)
None of these

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
A special case of Rh incompatibility (mismatching) has been observed between the Rh-veblood of a pregnant mother with Rh+ve blood of the foetus.
Where is the pace maker situated :-- a)In left auricle near opening of pulmonary vein
- b)In right auricle near eustachian valve
- c)On inter - auricular septum
- d)On inter-ventricular septum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Where is the pace maker situated :-
a)
In left auricle near opening of pulmonary vein
b)
In right auricle near eustachian valve
c)
On inter - auricular septum
d)
On inter-ventricular septum
|
|
Janani Chopra answered |
Location of Pacemaker in Heart
The pacemaker is a small device that helps regulate the heartbeat. It is usually implanted in the chest or abdomen, and it sends electrical signals to the heart to help it beat at a regular pace. However, in the context of this question, the pacemaker being referred to is the natural pacemaker of the heart, also known as the sinoatrial (SA) node.
The Correct Answer is B - In the Right Auricle Near Eustachian Valve
The SA node is located in the right atrium of the heart, near the opening of the superior vena cava. It is a small group of cells that generate electrical impulses that spread throughout the heart, causing it to contract and pump blood. The impulses generated by the SA node travel through the atria and then to the atrioventricular (AV) node, which is located in the interatrial septum.
From the AV node, the impulses are conducted to the bundle of His, which is located in the interventricular septum. The bundle of His then divides into the left and right bundle branches, which spread the impulses throughout the ventricles and cause them to contract.
In summary, the location of the pacemaker in the heart is as follows:
- The natural pacemaker of the heart is the sinoatrial (SA) node.
- The SA node is located in the right atrium of the heart.
- The SA node is located near the opening of the superior vena cava.
- The SA node is located in the right auricle near the eustachian valve.
The pacemaker is a small device that helps regulate the heartbeat. It is usually implanted in the chest or abdomen, and it sends electrical signals to the heart to help it beat at a regular pace. However, in the context of this question, the pacemaker being referred to is the natural pacemaker of the heart, also known as the sinoatrial (SA) node.
The Correct Answer is B - In the Right Auricle Near Eustachian Valve
The SA node is located in the right atrium of the heart, near the opening of the superior vena cava. It is a small group of cells that generate electrical impulses that spread throughout the heart, causing it to contract and pump blood. The impulses generated by the SA node travel through the atria and then to the atrioventricular (AV) node, which is located in the interatrial septum.
From the AV node, the impulses are conducted to the bundle of His, which is located in the interventricular septum. The bundle of His then divides into the left and right bundle branches, which spread the impulses throughout the ventricles and cause them to contract.
In summary, the location of the pacemaker in the heart is as follows:
- The natural pacemaker of the heart is the sinoatrial (SA) node.
- The SA node is located in the right atrium of the heart.
- The SA node is located near the opening of the superior vena cava.
- The SA node is located in the right auricle near the eustachian valve.
Manoj has AB blood group, so he will have the following antibodies in his blood plasma :- a)a antibody
- b)both a and b antibodies
- c)b antibody
- d)No antibodies are present
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Manoj has AB blood group, so he will have the following antibodies in his blood plasma :
a)
a antibody
b)
both a and b antibodies
c)
b antibody
d)
No antibodies are present

|
Kunal Rane answered |
AB blood group does not have any antibodies in plasma.
Rh factor is present in- a)All reptiles
- b)All mammals
- c)Man and rhesus monkey only
- d)All vertebrates
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Rh factor is present in
a)
All reptiles
b)
All mammals
c)
Man and rhesus monkey only
d)
All vertebrates
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Rh factor was discovered by K Landsteiner and A S Wiener (1940) from rabbits immunized with the blood of monkey Macaco, rhesus. It is found is man and rhesus monkey only.
Red cell count is carried out by- a)Haemoglobinometer
- b)Haemocytometer
- c)Electrocardiogram
- d)Sphygmomanometer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Red cell count is carried out by
a)
Haemoglobinometer
b)
Haemocytometer
c)
Electrocardiogram
d)
Sphygmomanometer
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The haemocytometer is a device used to count red blood cells. It consists of a thick glass microscopic slide with a rectangular indentation which creates a chamber. This chamber is engraved with a laser-etched of perpendicular lines. It is therefore possible to count the number of cells or particles in a specific volume of fluid, and thereby calculate the concentration of cells in the fluid.
Which has no muscular walls :-- a)Capillary
- b)Arteriole
- c)Veins
- d)Artery
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which has no muscular walls :-
a)
Capillary
b)
Arteriole
c)
Veins
d)
Artery

|
sankalp raj answered |
Yes capillary has no muscular wall because it is smallest blood vessels and made up of single layer wall not that of muscular type...
Carotid artery carries the blood which is :-- a)Impure blood to kidneys
- b)Oxygenated blood to brain
- c)Oxygenated blood to heart
- d)Impure blood from brain
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Carotid artery carries the blood which is :-
a)
Impure blood to kidneys
b)
Oxygenated blood to brain
c)
Oxygenated blood to heart
d)
Impure blood from brain
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The most important artery running up the side of your neck is called the common carotid artery. It splits into two branches. One of the branches is called the external carotid artery, which supplies your neck and face with oxygenated blood. The other branch of the common carotid artery, which supplies the brain with oxygenated blood, is the internal carotid artery. The internal carotid artery, again, is a branch of the common carotid artery that supplies the brain with oxygenated blood. Each side of your body, more specifically, each side of your neck and head, has one internal carotid artery supplying blood to the brain.
Chapter doubts & questions for Transport in Mammals - Biology A-Level 2024 is part of A Level exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the A Level exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for A Level 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Transport in Mammals - Biology A-Level in English & Hindi are available as part of A Level exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for A Level Exam by signing up for free.
Biology A-Level
280 videos|166 docs|147 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup