All Exams >
Grade 9 >
Biology for Grade 9 >
All Questions
All questions of Tissues for Grade 9 Exam
Branched involuntary muscle fibres are found in- a)limbs
- b)ureters
- c)heart
- d)tongue
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Branched involuntary muscle fibres are found in
a)
limbs
b)
ureters
c)
heart
d)
tongue
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Skeletal muscle fibers are cylindrical, multinucleated, striated, and under voluntary control. Smooth muscle cells are spindle shaped, have a single, centrally located nucleus, and lack striations. They are called involuntary muscles. Cardiac muscle has branching fibers, one nucleus per cell, striations, and intercalated disks. Its contraction is not under voluntary control.
Voluntary muscles are found in - a)Alimentary canal
- b)Limbs
- c)Iris of the eye
- d)Bronchi of lungs
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Voluntary muscles are found in
a)
Alimentary canal
b)
Limbs
c)
Iris of the eye
d)
Bronchi of lungs
|
|
Aradhiya Gupta answered |
Voluntary muscles are found in limbs arms feet hand etc
Cork cells are made impervious to water and gases by the presence of- a)cellulose
- b)lipids
- c)suberin
- d)lignin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cork cells are made impervious to water and gases by the presence of
a)
cellulose
b)
lipids
c)
suberin
d)
lignin

|
Vivek Shreyu answered |
Impervious to water and gases due to the presence of suberin
Name the non-nucleated blood cell.- a)Neutrophils
- b)Basophils
- c)Lymphocytes
- d)Erythrocytes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Name the non-nucleated blood cell.
a)
Neutrophils
b)
Basophils
c)
Lymphocytes
d)
Erythrocytes
|
|
Ananya Sharma answered |
There are important cells in your body that travel in the blood. They are involved in a gas exchange that is essential to human life. Red blood cells (RBCs) are their most common name, but they are also called erythrocytes. In medical terminology, erythro- means red, while -cyte means cell.
Erythrocytes have specific characteristics that all begin with the letter R:
Erythrocytes are red and consist of a protein called hemoglobin, which contains red iron. This is why our blood is red in color.
Erythrocytes are round. When these cells are normal, they can look like doughnuts with the holes in the center. Hemoglobin is responsible for the erythrocytes' round shape; it increases their surface area, allowing them to carry more oxygen molecules.
Finally, erythrocytes are like rubber, in that they're smooth and can easily bend. This gives them the ability to travel quickly in the blood and squeeze through small vessels to get to various locations in the body.
Chloroplasts occur in which of the following cells?a)collenchyma and sclerenchymab)parenchyma and collenchymac)chlorenchyma and sieve tubesd)xylem parenchyma and sclerenchymaCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Specialized parenchyma cells known as chlorenchyma found in plant leaves contain chloroplasts. This allows them to perform a photosynthetic function and responsible for the storage of starch.
So, the correct answer is 'Chlorenchyma and parenchyma.'
During a performance, if a dancer wants to stop her dancing, which muscles will execute this decision?- a)Striated
- b)Smooth
- c)Cardiac
- d)Involuntary
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During a performance, if a dancer wants to stop her dancing, which muscles will execute this decision?
a)
Striated
b)
Smooth
c)
Cardiac
d)
Involuntary
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Striated muscles can be controlled by one's own conscious will. Muscles present in our legs are striated muscles hence the following action will be executed by striated muscles present in the legs.
Blood is- a)Acidic
- b)Alkaline
- c)Variable
- d)Neutral
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Blood is
a)
Acidic
b)
Alkaline
c)
Variable
d)
Neutral

|
Rohini Seth answered |
Fats are stored in the human body as adipose tissue. Adipose tissue serves as a storage site for fat.
Lignified or thickened cell wall is a characteristic feature of______.
- a)collenchyma
- b)sclerenchyma
- c)parenchyma
- d)phloem
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Lignified or thickened cell wall is a characteristic feature of______.
a)
collenchyma
b)
sclerenchyma
c)
parenchyma
d)
phloem
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Sclerenchyma cells have thickened lignified walls, which make them strong and waterproof. They are commonly classified into support types and conducting forms. Support sclerenchyma is comprised of sclereids and fibers.
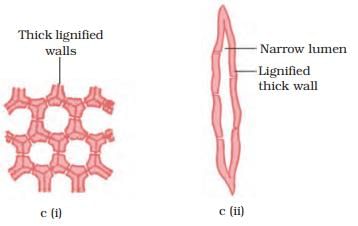
Sclerenchyma (i) transverse section, (ii) longitudinal section.

Sclerenchyma (i) transverse section, (ii) longitudinal section.
The husk of coconut is a ________ tissue.- a)Meristematic
- b)Sclerenchymatous
- c)Epithelial
- d)Vascular
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The husk of coconut is a ________ tissue.
a)
Meristematic
b)
Sclerenchymatous
c)
Epithelial
d)
Vascular
|
|
Arvind Singh answered |
Husk of coconut is made up of sclerenchymatous tissue.
It is present in mesocarp of fruit of coconut and a yield a coir a well known fibre used for making mats, ropes, cords, brushes e.t.c.
Sclerenchymatous tissue are found in stems( around the vascular bundle) , roots, vein of leaves, hard coverings of seeds and nuts.
The function of sclerenchymatous tissue is mainly mechanical & protective. It gives strength , rigidity ,flexibility and elasticity to the plant body.
Cells of tissue A have small intercellular spaces and walls thickened at the corners. Cells of tissue B do not have intercellular spaces and thickened cell walls. Identify tissue A and B.- a)A: Collenchyma, B: Sclerenchyma
- b)A: Sclerenchyma, B: Collenchyma
- c)A: Chlorenchyma, B: Sclerenchyma
- d)Collenchyma, B- Chlorenchyma
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cells of tissue A have small intercellular spaces and walls thickened at the corners. Cells of tissue B do not have intercellular spaces and thickened cell walls. Identify tissue A and B.
a)
A: Collenchyma, B: Sclerenchyma
b)
A: Sclerenchyma, B: Collenchyma
c)
A: Chlorenchyma, B: Sclerenchyma
d)
Collenchyma, B- Chlorenchyma
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Collenchyma: The cells have cell walls thickened at the corners due to pectin deposition.
Sclerenchyma: Their walls are thickened due to lignin deposition.
In an emergency, which tissue helps in making quick decisions after analyzing the situation?- a)Epithelial tissue
- b)Nervous tissue
- c)Muscular tissue
- d)Connective tissue
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In an emergency, which tissue helps in making quick decisions after analyzing the situation?
a)
Epithelial tissue
b)
Nervous tissue
c)
Muscular tissue
d)
Connective tissue
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Nervous tissue is found in the brain, spinal cord and nerves. It is responsible for coordinating and controlling many body activities. It stimulates muscle contraction, creates an awareness of the environment, and plays a major role in emotions, memory and reasoning. So, nervous tissue helps in making quick decisions after analyzing.
The function of secretion is shown by both, ________ and _________ epithelium.- a)Columnar, glandular
- b)Cuboidal, squamous
- c)Cuboidal, glandular
- d)Ciliated, squamous
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The function of secretion is shown by both, ________ and _________ epithelium.
a)
Columnar, glandular
b)
Cuboidal, squamous
c)
Cuboidal, glandular
d)
Ciliated, squamous

|
Nishita answered |
Columnar epithelium is located in thyroid vesicles... more , gonads eg. ovaries and testes and sweat and salivary gland thus secreting thyroxine , estrogen , sweat and saliva so performing secretion and glandular epithelium is located in intestine secreting mucous it is the modified form of columnar epithelium thus secreting some of its products also so both perform secretion.
Which of the following is not a feature of skeletal muscle?- a)Cylindrical
- b)Striated
- c)Multinucleate
- d)Branched
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a feature of skeletal muscle?
a)
Cylindrical
b)
Striated
c)
Multinucleate
d)
Branched
|
|
Aditya Shah answered |
Muscles are cylindrical, straighted and multinucleate but they would not be branched because there are no multiple bone makes one bone though there are such bones that are multiple but are fragments. There are branched cells like neuron.
Which body part is not composed of nervous tissue?- a)Muscles
- b)Nerves
- c)Brain
- d)Spinal cord
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which body part is not composed of nervous tissue?
a)
Muscles
b)
Nerves
c)
Brain
d)
Spinal cord
|
|
Aditya Chatterjee answered |
Body Part Composed of Nervous Tissue
The nervous tissue is a specialized tissue that forms the nervous system. It is responsible for transmitting signals between different parts of the body and the brain, which allows us to perceive and respond to the environment. The nervous tissue is composed of two main types of cells – neurons and glial cells. Neurons are the primary cells that transmit signals, while glial cells provide support and protection to neurons.
Body Part Not Composed of Nervous Tissue
Muscles are not composed of nervous tissue. Muscles are specialized tissues that are responsible for movement and contraction. They are composed of muscle fibers that are arranged in bundles. These muscle fibers are made up of specialized cells called myocytes, which are not composed of nervous tissue.
Conclusion
In conclusion, muscles are not composed of nervous tissue. While the nervous tissue is responsible for transmitting signals between different parts of the body and the brain, muscles are specialized tissues that are responsible for movement and contraction.
The nervous tissue is a specialized tissue that forms the nervous system. It is responsible for transmitting signals between different parts of the body and the brain, which allows us to perceive and respond to the environment. The nervous tissue is composed of two main types of cells – neurons and glial cells. Neurons are the primary cells that transmit signals, while glial cells provide support and protection to neurons.
Body Part Not Composed of Nervous Tissue
Muscles are not composed of nervous tissue. Muscles are specialized tissues that are responsible for movement and contraction. They are composed of muscle fibers that are arranged in bundles. These muscle fibers are made up of specialized cells called myocytes, which are not composed of nervous tissue.
Conclusion
In conclusion, muscles are not composed of nervous tissue. While the nervous tissue is responsible for transmitting signals between different parts of the body and the brain, muscles are specialized tissues that are responsible for movement and contraction.
The epidermis of desert plants has a thick waxy coating of:- a)Cork
- b)Suberin
- c)Cutin
- d)Epithelial tissue
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The epidermis of desert plants has a thick waxy coating of:
a)
Cork
b)
Suberin
c)
Cutin
d)
Epithelial tissue

|
Molik answered |
Answer is cutin because it prevents leaves from transpiration as water is crucial for desert vegetation.
Which tissue is responsible for bending of a stem, without breaking it?- a)Aerenchyma
- b)Chlorenchyma
- c)Collenchyma
- d)Sclerenchyma
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which tissue is responsible for bending of a stem, without breaking it?
a)
Aerenchyma
b)
Chlorenchyma
c)
Collenchyma
d)
Sclerenchyma
|
|
Arjun Sharma answered |
Collenchyma provides elasticity and flexibility to the plant organs and thereby, prevents its breaking when it is bent.
Which of the following protective tissue is absent in young stem of a plant?- a)Epidermis
- b)Parenchyma
- c)Cork
- d)Cuticle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following protective tissue is absent in young stem of a plant?
a)
Epidermis
b)
Parenchyma
c)
Cork
d)
Cuticle
|
|
Ravi Verma answered |
The outer protective layer or bark of a tree is known as the cork. It is made up of dead cells. Therefore, it protects the plant against mechanical injury, temperature extremes, etc. It also prevents the loss of water by evaporation.
Which of the following does not signify striated muscle?- a)Visceral muscle
- b)Voluntary muscle
- c)Striped muscle
- d)Skeletal muscle
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following does not signify striated muscle?
a)
Visceral muscle
b)
Voluntary muscle
c)
Striped muscle
d)
Skeletal muscle
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Visceral muscle is also called the smooth muscle.
Smooth muscle, neither striated in structure nor under voluntary control, is found within the walls of organs and structures such as the esophagus, stomach, intestine, bronchi, uterus, urethra, bladder, blood vessels and the arrector pili in the skin ( in which it controls erection of body hairs).
Smooth muscle, neither striated in structure nor under voluntary control, is found within the walls of organs and structures such as the esophagus, stomach, intestine, bronchi, uterus, urethra, bladder, blood vessels and the arrector pili in the skin ( in which it controls erection of body hairs).
Fat is abundant in- a)Liver cells
- b)Alveolar tissue
- c)Lymph glands
- d)Adipose tissue
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Fat is abundant in
a)
Liver cells
b)
Alveolar tissue
c)
Lymph glands
d)
Adipose tissue
|
|
Vikram Verma answered |
D is the correct option.The fat stored in adipose tissue comes from dietary fats or is produced in the body. hormone signaling; adipose tissueWhen hormones signal the need for energy, fatty acids and glycerol are released from triglycerides stored in fat cells (adipocytes) and are delivered to organs and tissues in the body.
Which hard and stiff tissue is present around vascular bundles, veins of leaves and hard covering of seeds?- a)Collenchyma
- b)Sclerenchyma
- c)Chlorenchyma
- d)Xylem
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which hard and stiff tissue is present around vascular bundles, veins of leaves and hard covering of seeds?
a)
Collenchyma
b)
Sclerenchyma
c)
Chlorenchyma
d)
Xylem
|
|
Vikram Khanna answered |
Sclerenchyma, in plants, support tissue composed of any of various kinds of hard woody cells. Mature sclerenchyma cells are usually dead cells that have heavily thickened secondary walls containing lignin. The cells are rigid and nonstretchable and are usually found in nongrowing regions of plant bodies, such as the bark or mature stems. Sclerenchyma is one of the three types of ground, or fundamental, tissue in plants; the other two types are parenchyma (living thin-walled tissue) and collenchyma (living support tissue with irregular walls). Sclerenchyma cells occur in many different shapes and sizes, but two main types occur: fibres and sclereids. Scelerenchyma permanent tissue and its wall is made up of lignin.
___________ smoothens the bone surfaces at the joints.- a)Cartilage
- b)Adipose tissue
- c)Ligament
- d)Areolar tissue
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
___________ smoothens the bone surfaces at the joints.
a)
Cartilage
b)
Adipose tissue
c)
Ligament
d)
Areolar tissue
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Cartilage is the tissue that smoothes bone surfaces at joints. It is a type of connective tissue. It is an elastic tissue.It protects the joints . It is present at the joints. Nose and
Ear also has cartilage tissues.
Ear also has cartilage tissues.
Striated muscles are found in- a)Gall bladder
- b)Wall of bronchi
- c)Skeletal muscles
- d)Lungs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Striated muscles are found in
a)
Gall bladder
b)
Wall of bronchi
c)
Skeletal muscles
d)
Lungs
|
|
Ananya Sharma answered |
Skeletal muscle is one of three major muscle types, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. It is a form of striated muscle tissue which is under the voluntary control of the somatic nervous system. Most skeletal muscles are attached to bones by bundles of collagen fibers known as tendons.
What does vascular bundle consist of?- a)Xylem and Parenchyma
- b)Epidermis and Meristem
- c)Epidermis and Cork
- d)Xylem and Phloem
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What does vascular bundle consist of?
a)
Xylem and Parenchyma
b)
Epidermis and Meristem
c)
Epidermis and Cork
d)
Xylem and Phloem
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
A vascular bundle is a part of the transport system in vascular plants. The transport itself happens in vascular tissue, which exists in two forms: xylem and phloem. Both these tissues are present in a vascular bundle, which in addition will include supporting and protective tissues.
In goitre, the thyroid gland enlarges and results in swelling in the throat region. Which epithelial tissue is involved in this condition?- a)Cuboidal epithelium
- b)Glandular epithelium
- c)Squamous epithelium
- d)Columnar epithelium
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In goitre, the thyroid gland enlarges and results in swelling in the throat region. Which epithelial tissue is involved in this condition?
a)
Cuboidal epithelium
b)
Glandular epithelium
c)
Squamous epithelium
d)
Columnar epithelium
|
|
Vikram Khanna answered |
A goitre (pronounced goy-ter, sometimes spelt as 'goiter') is an enlarged thyroid gland. This gives you a lump at the front of your neck. Some people with a goitre have an underactive or overactive thyroid gland. This means that they make too much or too little thyroid hormone. There are various causes of goitre and treatment depends on the cause.
Glandular Epithelium - A gland is one or more cells that produce and secrete a specific product. The product is always a water-based fluid (aqueous) and usually contains proteins (the product is referred to as a secretion).
Cells of tissue A have small intercellular spaces and walls thickened at the corners. Cells of tissue B do not have intercellular spaces and thickened cell walls. Identify tissue A and B.- a)A: Collenchyma, B: Sclerenchyma
- b)A: Sclerenchyma, B: Collenchyma
- c)A: Chlorenchyma, B: Sclerenchyma
- d)Collenchyma, B- Chlorenchyma
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cells of tissue A have small intercellular spaces and walls thickened at the corners. Cells of tissue B do not have intercellular spaces and thickened cell walls. Identify tissue A and B.
a)
A: Collenchyma, B: Sclerenchyma
b)
A: Sclerenchyma, B: Collenchyma
c)
A: Chlorenchyma, B: Sclerenchyma
d)
Collenchyma, B- Chlorenchyma
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Collenchyma: The cells have cell walls thickened at the corners due to pectin deposition.
Sclerenchyma: Their walls are thickened due to lignin deposition.
Practice Test/Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with Solutions of Chapter "Animal Tissues (Tissue)" are available for CBSE Class 9 Science and have been compiled as per the syllabus of CBSE Class 9 Science Q. A tissue is a :- a)Group of separate organs that are coordinated in their activities
- b)Group of similar cells that function together in a specialised activity
- c)Layer of cells surrounding an organ
- d)Sheet of cells, one layer thick
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Practice Test/Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with Solutions of Chapter "Animal Tissues (Tissue)" are available for CBSE Class 9 Science and have been compiled as per the syllabus of CBSE Class 9 Science
Q. A tissue is a :
a)
Group of separate organs that are coordinated in their activities
b)
Group of similar cells that function together in a specialised activity
c)
Layer of cells surrounding an organ
d)
Sheet of cells, one layer thick
|
|
Arjun Sharma answered |
Tissue is a cellular organizational level between cells and a complete organ. A tissue is an ensemble of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues.
Cells of squamous epithelium are- a)Columnar
- b)Tall with elongated nuclei
- c)Flat plate-like
- d)Cube like
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cells of squamous epithelium are
a)
Columnar
b)
Tall with elongated nuclei
c)
Flat plate-like
d)
Cube like
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
The three principal shapes associated with epithelial cells are—squamous, cuboidal and columnar. Squamous epithelium has cells that are wider than their height (flat and scale-like). This is found as the lining of the mouth, oesophagus, the blood vessels and in the alveoli of the lungs.
Which connective tissue is stored in specialized banks so that it can be obtained when needed during operations and accidents?- a)Bone
- b)Tendon
- c)Blood
- d)Cartilage
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which connective tissue is stored in specialized banks so that it can be obtained when needed during operations and accidents?
a)
Bone
b)
Tendon
c)
Blood
d)
Cartilage
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Blood is a major connective tissue which is stored in specialized banks so that it can be obtained in case of accident and requirement of blood.
Bone is important to the body since it:- a)Transports gases and nutrients within the body.
- b)Acts as a fat reservoir.
- c)Fills up the space inside organs.
- d)Gives well-defined shape to the body.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Bone is important to the body since it:
a)
Transports gases and nutrients within the body.
b)
Acts as a fat reservoir.
c)
Fills up the space inside organs.
d)
Gives well-defined shape to the body.
|
|
Vikram Khanna answered |
Bones play an important part in the overall function of your body. They provide a shape for your body, they protect vital organs such as your heart, and they even produce blood that is used by your body. When you walk or run, it is because your bones and muscles are working together.
The kidney shaped cells surrounding stomata are called:- a)Chlorenchyma cells
- b)Kidney cells
- c)Arc cells
- d)Guard cells
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The kidney shaped cells surrounding stomata are called:
a)
Chlorenchyma cells
b)
Kidney cells
c)
Arc cells
d)
Guard cells
|
|
Ananya Sharma answered |
They are called guard cells. It helps in regulating the opening and closing of stomata. When water enters the guard cells it swells up resulting in opening of stomata. When water exits the guard cells it shrinks and the stomata is closed.
Find out incorrect sentence.- a)Parenchymatous tissues have intercellular spaces
- b)Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at corners
- c)Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues
- d)Meristematic tissues, in its early stage, lack vacuoles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find out incorrect sentence.
a)
Parenchymatous tissues have intercellular spaces
b)
Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at corners
c)
Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues
d)
Meristematic tissues, in its early stage, lack vacuoles
|
|
Sarika Singh answered |
Incorrect Sentence: Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues.
Explanation:
Meristematic tissues are undifferentiated tissues that have the ability to divide and differentiate into various types of cells, tissues, and organs. They are responsible for the growth of the plant body.
There are two types of meristematic tissues:
1. Apical Meristem: It is present at the growing tips of roots and shoots of the plant. It helps in the elongation of the plant body.
2. Intercalary Meristem: It is present at the base of the leaves and internodes of the plant. It helps in the elongation of the plant body.
Both types of meristematic tissues are temporary tissues and are not permanent.
Permanent tissues are those tissues that have lost the ability to divide and differentiate further. They are derived from meristematic tissues and are responsible for the functioning of the plant body.
Types of permanent tissues in plants are:
1. Simple Permanent Tissues: These tissues are composed of a single type of cell.
Examples: Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and Sclerenchyma.
2. Complex Permanent Tissues: These tissues are composed of more than one type of cell.
Examples: Xylem and Phloem.
Therefore, option C is the incorrect sentence as Apical and Intercalary Meristems are temporary tissues and not permanent tissues.
Explanation:
Meristematic tissues are undifferentiated tissues that have the ability to divide and differentiate into various types of cells, tissues, and organs. They are responsible for the growth of the plant body.
There are two types of meristematic tissues:
1. Apical Meristem: It is present at the growing tips of roots and shoots of the plant. It helps in the elongation of the plant body.
2. Intercalary Meristem: It is present at the base of the leaves and internodes of the plant. It helps in the elongation of the plant body.
Both types of meristematic tissues are temporary tissues and are not permanent.
Permanent tissues are those tissues that have lost the ability to divide and differentiate further. They are derived from meristematic tissues and are responsible for the functioning of the plant body.
Types of permanent tissues in plants are:
1. Simple Permanent Tissues: These tissues are composed of a single type of cell.
Examples: Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and Sclerenchyma.
2. Complex Permanent Tissues: These tissues are composed of more than one type of cell.
Examples: Xylem and Phloem.
Therefore, option C is the incorrect sentence as Apical and Intercalary Meristems are temporary tissues and not permanent tissues.
Identify the voluntary muscle:- a)Finger muscles
- b)Heart muscle
- c)Muscles in bronchi of lungs
- d)Muscles of intestine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the voluntary muscle:
a)
Finger muscles
b)
Heart muscle
c)
Muscles in bronchi of lungs
d)
Muscles of intestine
|
|
Arjun Sharma answered |
Voluntary muscles are those which are under conscious control, which means under the control of the somatosensory nervous system.
This includes the skeletal muscles that attach to the bones and skin. The skeletal muscles allow the body to move by contracting and relaxing against bones and skin. They also maintain posture in the body. They attach to bones by connective tissue called tendons.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Parenchymatous cells performing photosynthesis are called:
- A:
Sclerenchyma
- B:
Aerenchyma
- C:
Collenchyma
- D:
Chlorenchyma
The answer is d.
Parenchymatous cells performing photosynthesis are called:
Sclerenchyma
Aerenchyma
Collenchyma
Chlorenchyma
|
|
Anjali Singh answered |
Chlorenchyma cells are parenchymatous cells that perform photosynthesis in plants. These cells are specifically adapted for this function and contain chloroplasts, which are responsible for capturing light energy and converting it into chemical energy through the process of photosynthesis.
Chlorenchyma cells are found in the mesophyll of leaves, where they are closely packed together to form a continuous layer. They are also present in other green parts of the plant, such as the stems and fruits.
Here are some key characteristics of chlorenchyma cells:
1. Chloroplasts: Chlorenchyma cells contain a high concentration of chloroplasts, which are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis. The chloroplasts contain the pigment chlorophyll, which gives plants their green color and enables them to absorb light energy.
2. Large central vacuole: Chlorenchyma cells typically have a large central vacuole, which helps maintain the turgidity of the cell. This allows the chloroplasts to be positioned close to the cell surface, maximizing their exposure to light.
3. Thin cell walls: The cell walls of chlorenchyma cells are thin and flexible, allowing for efficient gas exchange and the movement of nutrients between cells.
4. Interconnected cytoplasm: Chlorenchyma cells are interconnected through plasmodesmata, which are small channels in the cell walls that allow for the exchange of materials and communication between cells.
5. Photosynthetic function: Chlorenchyma cells are responsible for producing glucose, the primary source of energy for plants. Through photosynthesis, they convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, using light energy absorbed by the chlorophyll.
Overall, chlorenchyma cells are highly specialized for photosynthesis and play a crucial role in the production of food and oxygen in plants. Their unique structural and functional adaptations enable them to efficiently capture and utilize light energy for the synthesis of glucose, supporting the growth and survival of the plant.
Chlorenchyma cells are found in the mesophyll of leaves, where they are closely packed together to form a continuous layer. They are also present in other green parts of the plant, such as the stems and fruits.
Here are some key characteristics of chlorenchyma cells:
1. Chloroplasts: Chlorenchyma cells contain a high concentration of chloroplasts, which are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis. The chloroplasts contain the pigment chlorophyll, which gives plants their green color and enables them to absorb light energy.
2. Large central vacuole: Chlorenchyma cells typically have a large central vacuole, which helps maintain the turgidity of the cell. This allows the chloroplasts to be positioned close to the cell surface, maximizing their exposure to light.
3. Thin cell walls: The cell walls of chlorenchyma cells are thin and flexible, allowing for efficient gas exchange and the movement of nutrients between cells.
4. Interconnected cytoplasm: Chlorenchyma cells are interconnected through plasmodesmata, which are small channels in the cell walls that allow for the exchange of materials and communication between cells.
5. Photosynthetic function: Chlorenchyma cells are responsible for producing glucose, the primary source of energy for plants. Through photosynthesis, they convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, using light energy absorbed by the chlorophyll.
Overall, chlorenchyma cells are highly specialized for photosynthesis and play a crucial role in the production of food and oxygen in plants. Their unique structural and functional adaptations enable them to efficiently capture and utilize light energy for the synthesis of glucose, supporting the growth and survival of the plant.
Bone forming cells are- a)Osteoblasts
- b)Osteoclasts
- c)Chondroblasts
- d)Chondroclasts
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bone forming cells are
a)
Osteoblasts
b)
Osteoclasts
c)
Chondroblasts
d)
Chondroclasts

|
Khushneet Kaur answered |
OSTEOBLASTS are the cells that form new bone. They also come from the bone marrow and are related to structural cells. They have only one nucleus.Osteoblasts work in teams to build bone. They produce new bone called "osteoid" which is made of bone collagen and other protein.
Cartilage is produced by- a)Osteoblasts
- b)Epithelium
- c)Fibroblasts
- d)Chondroblasts
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cartilage is produced by
a)
Osteoblasts
b)
Epithelium
c)
Fibroblasts
d)
Chondroblasts

|
Shruti answered |
Cartilage is produced by chondroblasts. explanation :-chondroblasts connective tissue is comprised of living cells within an extracellular matrix. the extracellular matrix in cartilage is produced by specialized cells called chondroblasts.
Glisson's capsule is a delicate connective tissue capsule covering the- a)Spleen
- b)Liver
- c)Kidney
- d)Gall bladder
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Glisson's capsule is a delicate connective tissue capsule covering the
a)
Spleen
b)
Liver
c)
Kidney
d)
Gall bladder
|
|
Bibek Sengupta answered |
Glisson's capsule is a delicate connective tissue capsule covering the liver.
The liver is an essential organ in the human body that performs various functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion. It is located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, just below the diaphragm.
What is Glisson's capsule?
Glisson's capsule, also known as the Glissonian sheath, is a delicate connective tissue capsule that surrounds and protects the liver. It is named after Francis Glisson, an English anatomist who first described it in the 17th century. The capsule is fibrous and tough, providing structural support and maintaining the shape of the liver.
Composition and structure:
Glisson's capsule is composed of collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and smooth muscle cells. It is relatively thin and transparent and adheres tightly to the surface of the liver. The capsule also extends into the liver, forming a network of connective tissue that surrounds the liver lobules, blood vessels, and bile ducts.
Functions:
1. Protection: Glisson's capsule acts as a protective barrier for the liver, shielding it from external physical trauma and preventing infection or injury.
2. Structural support: The capsule provides structural support to the liver, maintaining its shape and preventing collapse or distortion.
3. Compartmentalization: Glisson's capsule helps in compartmentalizing the liver by separating it from neighboring organs and tissues.
4. Anchorage: The capsule anchors the liver to the surrounding structures, such as the diaphragm and abdominal wall, ensuring its stability and proper positioning within the abdominal cavity.
Role in liver diseases:
Glisson's capsule can be involved in certain liver diseases. In conditions like cirrhosis, inflammation, or fibrosis, the capsule may become thickened and less elastic, leading to increased pressure within the liver. This can impair liver function and contribute to complications such as portal hypertension.
In conclusion, Glisson's capsule is a delicate connective tissue capsule covering the liver. It provides protection, structural support, compartmentalization, and anchorage to the liver. Understanding its role and structure is essential in the study of liver anatomy and the diagnosis and management of liver diseases.
The liver is an essential organ in the human body that performs various functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion. It is located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, just below the diaphragm.
What is Glisson's capsule?
Glisson's capsule, also known as the Glissonian sheath, is a delicate connective tissue capsule that surrounds and protects the liver. It is named after Francis Glisson, an English anatomist who first described it in the 17th century. The capsule is fibrous and tough, providing structural support and maintaining the shape of the liver.
Composition and structure:
Glisson's capsule is composed of collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and smooth muscle cells. It is relatively thin and transparent and adheres tightly to the surface of the liver. The capsule also extends into the liver, forming a network of connective tissue that surrounds the liver lobules, blood vessels, and bile ducts.
Functions:
1. Protection: Glisson's capsule acts as a protective barrier for the liver, shielding it from external physical trauma and preventing infection or injury.
2. Structural support: The capsule provides structural support to the liver, maintaining its shape and preventing collapse or distortion.
3. Compartmentalization: Glisson's capsule helps in compartmentalizing the liver by separating it from neighboring organs and tissues.
4. Anchorage: The capsule anchors the liver to the surrounding structures, such as the diaphragm and abdominal wall, ensuring its stability and proper positioning within the abdominal cavity.
Role in liver diseases:
Glisson's capsule can be involved in certain liver diseases. In conditions like cirrhosis, inflammation, or fibrosis, the capsule may become thickened and less elastic, leading to increased pressure within the liver. This can impair liver function and contribute to complications such as portal hypertension.
In conclusion, Glisson's capsule is a delicate connective tissue capsule covering the liver. It provides protection, structural support, compartmentalization, and anchorage to the liver. Understanding its role and structure is essential in the study of liver anatomy and the diagnosis and management of liver diseases.
Glands in our body are formed by- a)connective tissue
- b)smooth muscles
- c)epithelial tissue
- d)adipose tissue
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Glands in our body are formed by
a)
connective tissue
b)
smooth muscles
c)
epithelial tissue
d)
adipose tissue
|
|
Aravind Patel answered |
**Glands in our body are formed by Epithelial Tissue**
**Introduction:**
Glands are specialized organs or tissues in the body that produce and secrete substances for various functions. These substances can include hormones, enzymes, oils, sweat, and saliva. Glands are formed by epithelial tissue, which is a type of tissue found throughout the body that lines the external and internal surfaces of organs and structures.
**Explanation:**
Epithelial tissue is composed of closely packed cells with very little extracellular matrix between them. It is responsible for forming the linings and coverings of organs, as well as the glands that produce and secrete substances. Epithelial tissue can be classified into two main types: glandular epithelium and surface epithelium.
1. **Glandular Epithelium:**
Glandular epithelium is specialized for secretion and is responsible for forming glands in the body. It is made up of cells that are capable of producing and releasing substances. Glandular epithelium can be further classified into two types: exocrine glands and endocrine glands.
- **Exocrine Glands:** Exocrine glands secrete their substances onto the surface of an organ or tissue, either directly or through ducts. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat glands, salivary glands, and sebaceous glands. These glands are composed of epithelial cells that secrete substances into ducts, which then transport the substances to the surface of the organ or tissue.
- **Endocrine Glands:** Endocrine glands secrete their substances directly into the bloodstream. These substances, called hormones, are then transported to target organs or tissues where they exert their effects. Examples of endocrine glands include the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and pituitary gland. Endocrine glands are also composed of epithelial cells that secrete substances, but unlike exocrine glands, they lack ducts.
2. **Surface Epithelium:**
Surface epithelium forms the linings and coverings of organs and structures. It is responsible for protecting underlying tissues, regulating the exchange of substances, and providing sensory information. Surface epithelium can be further classified based on the number of cell layers (simple or stratified) and the shape of the cells (squamous, cuboidal, or columnar). Examples of surface epithelium include the lining of the respiratory tract, digestive tract, and blood vessels.
**Conclusion:**
In conclusion, glands in our body are formed by epithelial tissue, which is responsible for producing and secreting substances. Glandular epithelium specifically forms exocrine and endocrine glands, while surface epithelium forms the linings and coverings of organs and structures.
**Introduction:**
Glands are specialized organs or tissues in the body that produce and secrete substances for various functions. These substances can include hormones, enzymes, oils, sweat, and saliva. Glands are formed by epithelial tissue, which is a type of tissue found throughout the body that lines the external and internal surfaces of organs and structures.
**Explanation:**
Epithelial tissue is composed of closely packed cells with very little extracellular matrix between them. It is responsible for forming the linings and coverings of organs, as well as the glands that produce and secrete substances. Epithelial tissue can be classified into two main types: glandular epithelium and surface epithelium.
1. **Glandular Epithelium:**
Glandular epithelium is specialized for secretion and is responsible for forming glands in the body. It is made up of cells that are capable of producing and releasing substances. Glandular epithelium can be further classified into two types: exocrine glands and endocrine glands.
- **Exocrine Glands:** Exocrine glands secrete their substances onto the surface of an organ or tissue, either directly or through ducts. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat glands, salivary glands, and sebaceous glands. These glands are composed of epithelial cells that secrete substances into ducts, which then transport the substances to the surface of the organ or tissue.
- **Endocrine Glands:** Endocrine glands secrete their substances directly into the bloodstream. These substances, called hormones, are then transported to target organs or tissues where they exert their effects. Examples of endocrine glands include the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and pituitary gland. Endocrine glands are also composed of epithelial cells that secrete substances, but unlike exocrine glands, they lack ducts.
2. **Surface Epithelium:**
Surface epithelium forms the linings and coverings of organs and structures. It is responsible for protecting underlying tissues, regulating the exchange of substances, and providing sensory information. Surface epithelium can be further classified based on the number of cell layers (simple or stratified) and the shape of the cells (squamous, cuboidal, or columnar). Examples of surface epithelium include the lining of the respiratory tract, digestive tract, and blood vessels.
**Conclusion:**
In conclusion, glands in our body are formed by epithelial tissue, which is responsible for producing and secreting substances. Glandular epithelium specifically forms exocrine and endocrine glands, while surface epithelium forms the linings and coverings of organs and structures.
The contraction of muscle tissue is carried out by the action of- a)Actin and myosin
- b)Actin and relaxin
- c)Fibrin and relaxin
- d)Secretin and myosin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The contraction of muscle tissue is carried out by the action of
a)
Actin and myosin
b)
Actin and relaxin
c)
Fibrin and relaxin
d)
Secretin and myosin
|
|
Vikram Khanna answered |
Muscles are composed of two major protein filaments: a thick filament composed of the protein myosin and a thin filament composed of the protein actin. Muscle contraction occurs when these filaments slide over one another in a series of repetitive events.
Which of the following is not a characteristic of epithelial tissue?- a)Epithelial tissue cells have only a small amount of cementing material between them.
- b)Basement membrane is absent in epithelial tissue cells.
- c)Epithelial tissue cells have almost no intercellular spaces.
- d)Epithelial tissue cells are tightly packed and form a continuous sheet.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a characteristic of epithelial tissue?
a)
Epithelial tissue cells have only a small amount of cementing material between them.
b)
Basement membrane is absent in epithelial tissue cells.
c)
Epithelial tissue cells have almost no intercellular spaces.
d)
Epithelial tissue cells are tightly packed and form a continuous sheet.

|
Gajendra Kumawat answered |
It is so because it is present in epithelial tissue just under the epithelium and if it would not be present then there would be no one to anchor down the epithelium and also there would be absence of mechanical barrier.
Which of the following tissues has dead cells?- a)Parenchyma
- b)Sclerenchyma
- c)Collenchyma
- d)Epithelial tissue
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following tissues has dead cells?
a)
Parenchyma
b)
Sclerenchyma
c)
Collenchyma
d)
Epithelial tissue
|
|
Krishna Singi answered |
Option b is the correct answer reason pls search on Google
Mammary glands are modified- a)Sebaceous gland
- b)Sweat gland
- c)Oil gland
- d)Lymph gland
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mammary glands are modified
a)
Sebaceous gland
b)
Sweat gland
c)
Oil gland
d)
Lymph gland
|
|
Sarita Reddy answered |
These exocrine glands are enlarged and modified sweat glands and are the characteristic of mammals which gave the class its name. The basic components of the mammary gland are the alveoli (hollow cavities, a few millimetres large) lined with milk-secreting cuboidal cells and surrounded by myoepithelial cells.
Name the long part of neuron.- a)Axon
- b)Dendrites
- c)Terminal branches
- d)Cyton
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Name the long part of neuron.
a)
Axon
b)
Dendrites
c)
Terminal branches
d)
Cyton
|
|
Amrutha Anoop answered |
The axon brings the message to the target of the nerve cell. Most of the cell bodies of the human nerves are located in the brain and in the spinal cord. Axons have to be long in order to reach every part of our body from the central regulating places in the brain and the spine.
The protein deposited in the dead superficial cells that make the skin epithelium impervious to water is- a)Keratin
- b)Elastin
- c)Collagen
- d)Mucus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The protein deposited in the dead superficial cells that make the skin epithelium impervious to water is
a)
Keratin
b)
Elastin
c)
Collagen
d)
Mucus
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
A is the correct option.The protein deposited in the dead superficial cells that make the skin epithelium impervious to water is Keratin which makes this epithelium impervious to water.
Dermis of mammalian skin is mainly composed of- a)Muscular tissue
- b)Epithelial tissue
- c)Connective tissue
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Dermis of mammalian skin is mainly composed of
a)
Muscular tissue
b)
Epithelial tissue
c)
Connective tissue
d)
All of the above
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The dermis forms the bulk of the mammalian skin. It is composed of an association of connective tissue fibres, mainly collagen, with a ground substance of mucopolysaccharide materials (glycosaminoglycans), which can hold a quantity of water in its domain.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Suberin is impervious to:
- A:
Neither water nor gases
- B:
Only gases
- C:
Only water
- D:
Both water and gases
The answer is d.
Suberin is impervious to:
Neither water nor gases
Only gases
Only water
Both water and gases
|
|
Sarita Reddy answered |
Cellulose is the basic of the cell wall present in plants. The cell wall of almost all the organism are made up of cellulose whereas lipids along with some proteins forms the basic building blocks of plasma membrane. Plasma membrane is semipermeable and it is not impervious to water. Lignin is a complex polymer which acts as a cement and hardens the cell wall. It provides flexibility, great tensile and compressional strength to the cell wall and makes the cell wall impermeable. It is present in sclerenchyma cells and not in cork cells. The walls of cork cells are heavily thickened with an organic substance, suberin. Suberin makes these cells impervious to water and gases.
Intestine absorbs the digested food materials. What type of epithelial cells are responsible for that?- a)Stratified squamous epithelium
- b)Columnar epithelium
- c)Spindle fibres
- d)Cuboidal epithelium
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Intestine absorbs the digested food materials. What type of epithelial cells are responsible for that?
a)
Stratified squamous epithelium
b)
Columnar epithelium
c)
Spindle fibres
d)
Cuboidal epithelium

|
Cheshta Sidana answered |
Columnar epithelium contains large columns of cells which provide more surface area for absorption . More surface area allows the cels to easily absorb substances . That's why wherever absorption occurs , Columnar epithelium is present.
Which of the following statements about meristematic tissue are correct?
(i) Consists of cells that are very active, with dense cytoplasm, thin cellulose walls, and prominent nuclei.
(ii) Lacks vacuoles because they are involved in rapid cell division.
(iii) Is classified into apical, lateral, and intercalary based on their location.
(iv) Is responsible for the permanent shape, size, and function of cells.- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(iii) and (iv)
- c)(i), (ii) and (iii)
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about meristematic tissue are correct?
(i) Consists of cells that are very active, with dense cytoplasm, thin cellulose walls, and prominent nuclei.
(ii) Lacks vacuoles because they are involved in rapid cell division.
(iii) Is classified into apical, lateral, and intercalary based on their location.
(iv) Is responsible for the permanent shape, size, and function of cells.
(i) Consists of cells that are very active, with dense cytoplasm, thin cellulose walls, and prominent nuclei.
(ii) Lacks vacuoles because they are involved in rapid cell division.
(iii) Is classified into apical, lateral, and intercalary based on their location.
(iv) Is responsible for the permanent shape, size, and function of cells.
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(iii) and (iv)
c)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
d)
(i) and (iv)

|
Prepworks Coaching answered |
- Meristematic tissue is characterized by cells that are very active, with dense cytoplasm, thin cellulose walls, and prominent nuclei.
- These cells lack vacuoles because they are involved in rapid cell division and do not require storage.
- Meristematic tissue is indeed classified into apical, lateral, and intercalary based on their location.
- However, it is not directly responsible for the permanent shape, size, and function of cells; that role is taken up by permanent tissue formed after differentiation.
- Therefore, statements (i), (ii), and (iii) are correct.
Chapter doubts & questions for Tissues - Biology for Grade 9 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Tissues - Biology for Grade 9 in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for Grade 9
28 videos|68 docs|33 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










