All Exams >
Chemistry >
Physical Chemistry >
All Questions
All questions of Ionic Equilibrium for Chemistry Exam
. What is the molar solubility (s) of Ba3(PO4)2 in terms of Ksp?- a)s = [Ksp/27]1/5
- b)s = Ksp1/5
- c)s = Ksp1/2
- d)s = [Ksp/108]1/5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
. What is the molar solubility (s) of Ba3(PO4)2 in terms of Ksp?
a)
s = [Ksp/27]1/5
b)
s = Ksp1/5
c)
s = Ksp1/2
d)
s = [Ksp/108]1/5

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Ba3(PO4)2 ⇌ 3Ba+2 (2PO4)-3
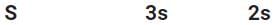
Ksp = [Ba+2>]3 [(PO4)-3]2
[3s]3[2s]2
Ksp = 108s5
Or s = (Ksp/108)⅕
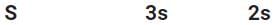
Ksp = [Ba+2>]3 [(PO4)-3]2
[3s]3[2s]2
Ksp = 108s5
Or s = (Ksp/108)⅕
The [Ag+(aq)] = 10-5 in a solution .The [Cl–(aq)] to precipitate AgCl having Ksp of 1.8×10-10 M2 is — M
- a)10-7
- b)10-8
- c)10-9
- d)10-5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The [Ag+(aq)] = 10-5 in a solution .The [Cl–(aq)] to precipitate AgCl having Ksp of 1.8×10-10 M2 is — M
a)
10-7
b)
10-8
c)
10-9
d)
10-5
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
For precipitation, Qrkn > Ksp, then tto establish equilibrium, ions will combine to give molecule as ppt.
So applying the above concept,
1.8×10-10 < [Ag+][Cl-]
1.8×10-10 < 10-5 × [Cl-]
Or [Cl-] > 1.8×10-5
By seeing the option, only option d satisfies this condtion.
So applying the above concept,
1.8×10-10 < [Ag+][Cl-]
1.8×10-10 < 10-5 × [Cl-]
Or [Cl-] > 1.8×10-5
By seeing the option, only option d satisfies this condtion.
Solubility of BaCl2 if Ksp is 10-6 at 25°C is- a)Cannot be predicted
- b)6.3 10-3 M
- c)10-6 M
- d)10-3 M
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Solubility of BaCl2 if Ksp is 10-6 at 25°C is
a)
Cannot be predicted
b)
6.3 10-3 M
c)
10-6 M
d)
10-3 M
|
|
Ram Mohith answered |
BaCl₂ ⇔ Ba²⁺ + 2Cl⁻
Ksp = (s)(2s)² = 4s³
Given, 4s³ = 10⁻⁶
⇒s³ = 0.25 ⨯ 10⁻⁶
⇒s = (0.25)³ ⨯ 10⁻²
⇒s = 0.629 ⨯ 10⁻²
⇒s = 6.3 ⨯ 10⁻³
Consider the following solubility data for various chromates at 25°C.
Salt Ksp
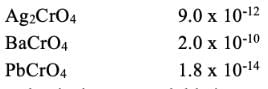 the chromate that is most suitable is?
the chromate that is most suitable is?
- a)Ag2CrO4
- b)BaCrO4
- c)PbCrO4
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following solubility data for various chromates at 25°C.
Salt Ksp
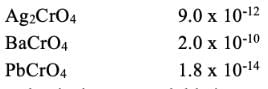
the chromate that is most suitable is?
a)
Ag2CrO4
b)
BaCrO4
c)
PbCrO4
d)
none of these
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
The salt with more Ksp is more soluble in water. Hence BaCrO4 is more soluble.
The solubility product expression for silver(I) sulphide, using x to represent the molar concentration of silver(I) and y to represent the molar concentration of sulphide, is formulated as:- a)x2y2
- b)xy3
- c)x2y
- d)xy2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The solubility product expression for silver(I) sulphide, using x to represent the molar concentration of silver(I) and y to represent the molar concentration of sulphide, is formulated as:
a)
x2y2
b)
xy3
c)
x2y
d)
xy2
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The correct answer is Option C.
The ionization equilibrium of silver (I) sulfide is
Ag2S⇌2Ag+ +S2−
The solubility product expression for silver (I) sulfide is KSP[Ag+]2 [S2−].
But [Ag+]2 = x and [S2−] = y.
Hence the expression for the solubility product becomes KSP[Ag+]2 [S2−] = x2y.
The ionization equilibrium of silver (I) sulfide is
Ag2S⇌2Ag+ +S2−
The solubility product expression for silver (I) sulfide is KSP[Ag+]2 [S2−].
But [Ag+]2 = x and [S2−] = y.
Hence the expression for the solubility product becomes KSP[Ag+]2 [S2−] = x2y.
Precipitation requires- a)Ionic product to be less than solubility product
- b)Ionic product to be equal to solubility product
- c)Ionic product to be more than pH
- d)Ionic product to be more than solubility product
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Precipitation requires
a)
Ionic product to be less than solubility product
b)
Ionic product to be equal to solubility product
c)
Ionic product to be more than pH
d)
Ionic product to be more than solubility product
|
|
Ananya Datta answered |
The correct answer is option 'D': Ionic product to be more than solubility product.
Explanation:
1. Understanding Solubility and Ionic Product:
Solubility refers to the maximum amount of a solute that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a specific temperature. It is usually expressed in terms of grams of solute per 100 grams of solvent.
Ionic product (Q) is the product of the concentrations (or activities) of ions in a solution, raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced chemical equation.
2. Relationship between Ionic Product and Solubility Product:
The solubility product (Ksp) is a constant value that represents the equilibrium between a solid solute and its ions in a solution. It is the product of the concentrations (or activities) of the ions, each raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients.
Ionic product (Q) is a measure of the actual concentrations (or activities) of ions in a solution, regardless of whether the solution is at equilibrium or not. If Q is less than Ksp, the solution is unsaturated and more solute can dissolve. If Q is equal to Ksp, the solution is at equilibrium and the solution is saturated. If Q is greater than Ksp, the solution is supersaturated and precipitation will occur.
3. Precipitation and the Ionic Product:
When the ionic product (Q) exceeds the solubility product (Ksp), the solution becomes supersaturated with respect to the solute. This means that there are more ions in the solution than can be maintained in equilibrium with the solid solute.
As a result, the excess ions will start to come together and form a solid precipitate. This precipitation process is driven by the need to reduce the concentration of ions in the solution and restore equilibrium according to Le Chatelier's principle. The precipitate will continue to form until the ionic product (Q) equals the solubility product (Ksp) and the solution becomes saturated again.
Therefore, precipitation occurs when the ionic product (Q) is greater than the solubility product (Ksp). This is why the correct answer is option 'D': Ionic product to be more than solubility product.
Summary:
- Precipitation occurs when the ionic product (Q) exceeds the solubility product (Ksp).
- The ionic product is a measure of the actual concentrations (or activities) of ions in a solution.
- The solubility product is a constant value representing the equilibrium between a solid solute and its ions in a solution.
- When the solution becomes supersaturated, precipitation will occur to restore equilibrium.
Explanation:
1. Understanding Solubility and Ionic Product:
Solubility refers to the maximum amount of a solute that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a specific temperature. It is usually expressed in terms of grams of solute per 100 grams of solvent.
Ionic product (Q) is the product of the concentrations (or activities) of ions in a solution, raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced chemical equation.
2. Relationship between Ionic Product and Solubility Product:
The solubility product (Ksp) is a constant value that represents the equilibrium between a solid solute and its ions in a solution. It is the product of the concentrations (or activities) of the ions, each raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients.
Ionic product (Q) is a measure of the actual concentrations (or activities) of ions in a solution, regardless of whether the solution is at equilibrium or not. If Q is less than Ksp, the solution is unsaturated and more solute can dissolve. If Q is equal to Ksp, the solution is at equilibrium and the solution is saturated. If Q is greater than Ksp, the solution is supersaturated and precipitation will occur.
3. Precipitation and the Ionic Product:
When the ionic product (Q) exceeds the solubility product (Ksp), the solution becomes supersaturated with respect to the solute. This means that there are more ions in the solution than can be maintained in equilibrium with the solid solute.
As a result, the excess ions will start to come together and form a solid precipitate. This precipitation process is driven by the need to reduce the concentration of ions in the solution and restore equilibrium according to Le Chatelier's principle. The precipitate will continue to form until the ionic product (Q) equals the solubility product (Ksp) and the solution becomes saturated again.
Therefore, precipitation occurs when the ionic product (Q) is greater than the solubility product (Ksp). This is why the correct answer is option 'D': Ionic product to be more than solubility product.
Summary:
- Precipitation occurs when the ionic product (Q) exceeds the solubility product (Ksp).
- The ionic product is a measure of the actual concentrations (or activities) of ions in a solution.
- The solubility product is a constant value representing the equilibrium between a solid solute and its ions in a solution.
- When the solution becomes supersaturated, precipitation will occur to restore equilibrium.
The molar solubility of PbBr2 is 2.17 x 10-3 M at a certain temperature. Calculate Kspfor PbBr2- a)4.1 x 10-8
- b)6.2 x 10-6
- c)6.4 x 10-7
- d)3.4 x 106
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The molar solubility of PbBr2 is 2.17 x 10-3 M at a certain temperature. Calculate Kspfor PbBr2
a)
4.1 x 10-8
b)
6.2 x 10-6
c)
6.4 x 10-7
d)
3.4 x 106
|
|
Upasana Bose answered |
Molar solubility(s) for PbBr2 = 2.17×10-3 M
PbBr2 ⇌ Pb+2 + 2Br-
s s 2s
Ksp = [Pb+2][Br-]2
= [s][s]2
= 4s3 = 4(2.17×10-3)3
= 4.1×10-8
PbBr2 ⇌ Pb+2 + 2Br-
s s 2s
Ksp = [Pb+2][Br-]2
= [s][s]2
= 4s3 = 4(2.17×10-3)3
= 4.1×10-8
Solubility of a soluble salt is- a)more than 0.1M
- b)less than 0.01M
- c)more than 0.001M
- d)more than 0.01M
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Solubility of a soluble salt is
a)
more than 0.1M
b)
less than 0.01M
c)
more than 0.001M
d)
more than 0.01M
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
A salt is soluble if it dissolves in water to give a solution with a concentration of at least 0.1 moles per liter at room temperature.
What is the Ksp expression for the salt PbI2?
- a)[Pb2+][2I–]2
- b)[Pb2+][I2]2
- c)[Pb2+][2I–]
- d)[Pb2+][I–]2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the Ksp expression for the salt PbI2?
a)
[Pb2+][2I–]2
b)
[Pb2+][I2]2
c)
[Pb2+][2I–]
d)
[Pb2+][I–]2
|
|
Jyoti Dey answered |
A general equation of equilibrium constant for a reaction of dissociation of PbI2 as PbI2⇌Pb2++2I-can be written as,
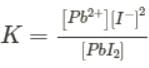
But we know that Ksp is the equilibrium constant at the saturated level. At saturation, no more PbI2 will dissolve. Thus the concentration of PbI2 will be constant and can be taken as 1.
Therefore the above equation can be written as,
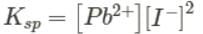
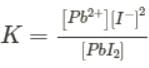
But we know that Ksp is the equilibrium constant at the saturated level. At saturation, no more PbI2 will dissolve. Thus the concentration of PbI2 will be constant and can be taken as 1.
Therefore the above equation can be written as,
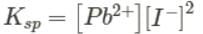
When in a saturated solution of NaCl, HCl is passed, pure precipitate of NaCl is formed. This is due to the fact:- a)That solubility of NaCl decreases
- b)That HCl is strong acid
- c)That the ionic product of NaCl exceeds the solubility product of NaCl.
- d)That HCl is highly soluble in water
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When in a saturated solution of NaCl, HCl is passed, pure precipitate of NaCl is formed. This is due to the fact:
a)
That solubility of NaCl decreases
b)
That HCl is strong acid
c)
That the ionic product of NaCl exceeds the solubility product of NaCl.
d)
That HCl is highly soluble in water
|
|
Simran Chauhan answered |
Explanation:
When HCl is passed through a saturated solution of NaCl, a pure precipitate of NaCl is formed. This phenomenon can be explained by the following reasons:
1. Solubility of NaCl decreases:
When HCl is added to a saturated solution of NaCl, the chloride ions (Cl-) from HCl combine with the sodium ions (Na+) present in the solution to form NaCl. This reaction reduces the concentration of Na+ ions in the solution, which in turn decreases the solubility of NaCl. As a result, NaCl precipitates out of the solution.
2. Ionic product exceeds solubility product:
The solubility product (Ksp) of NaCl represents the maximum amount of NaCl that can be dissolved in a given solvent. When HCl is added to the saturated solution, the concentration of Na+ ions decreases, while the concentration of Cl- ions increases. This increase in the concentration of Cl- ions exceeds the solubility product of NaCl, leading to the precipitation of pure NaCl.
3. HCl is a strong acid:
HCl is a strong acid, meaning it ionizes completely in water to release H+ ions. The presence of H+ ions in the solution can react with the Na+ ions to form NaCl. This reaction further reduces the concentration of Na+ ions, promoting the precipitation of NaCl.
4. HCl solubility in water:
HCl is highly soluble in water, which means it readily dissolves and dissociates into H+ and Cl- ions. The high solubility of HCl allows for a high concentration of Cl- ions to be present in the solution, facilitating the formation of NaCl precipitate.
In conclusion, the formation of a pure precipitate of NaCl when HCl is passed through a saturated solution of NaCl is due to the decrease in solubility of NaCl, the excess of the ionic product over the solubility product, the strong acid nature of HCl, and the high solubility of HCl in water.
When HCl is passed through a saturated solution of NaCl, a pure precipitate of NaCl is formed. This phenomenon can be explained by the following reasons:
1. Solubility of NaCl decreases:
When HCl is added to a saturated solution of NaCl, the chloride ions (Cl-) from HCl combine with the sodium ions (Na+) present in the solution to form NaCl. This reaction reduces the concentration of Na+ ions in the solution, which in turn decreases the solubility of NaCl. As a result, NaCl precipitates out of the solution.
2. Ionic product exceeds solubility product:
The solubility product (Ksp) of NaCl represents the maximum amount of NaCl that can be dissolved in a given solvent. When HCl is added to the saturated solution, the concentration of Na+ ions decreases, while the concentration of Cl- ions increases. This increase in the concentration of Cl- ions exceeds the solubility product of NaCl, leading to the precipitation of pure NaCl.
3. HCl is a strong acid:
HCl is a strong acid, meaning it ionizes completely in water to release H+ ions. The presence of H+ ions in the solution can react with the Na+ ions to form NaCl. This reaction further reduces the concentration of Na+ ions, promoting the precipitation of NaCl.
4. HCl solubility in water:
HCl is highly soluble in water, which means it readily dissolves and dissociates into H+ and Cl- ions. The high solubility of HCl allows for a high concentration of Cl- ions to be present in the solution, facilitating the formation of NaCl precipitate.
In conclusion, the formation of a pure precipitate of NaCl when HCl is passed through a saturated solution of NaCl is due to the decrease in solubility of NaCl, the excess of the ionic product over the solubility product, the strong acid nature of HCl, and the high solubility of HCl in water.
What is the Ksp expression for lead (II) chloride?- a)[Pb2+][Cl–]2
- b)[Pb2+]2[Cl–]
- c)[Pb+][Cl-]2/[PbCl2]
- d)[Pb22+][Cl–]2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the Ksp expression for lead (II) chloride?
a)
[Pb2+][Cl–]2
b)
[Pb2+]2[Cl–]
c)
[Pb+][Cl-]2/[PbCl2]
d)
[Pb22+][Cl–]2
|
|
Samridhi Pillai answered |
PbCl2 ⇌ Pb2+ + 2Cl– or, Ksp = [Pb2+][Cl–]2
Solubility product is defined as- a)product of molar concentration of ions of a salt as per stoichiometry in a supersaturated solution
- b)product of molar concentration of ions of a salt as per stoichiometry in a saturated solution at STP
- c)product of molar concentration of ions of a salt as per stoichiometry in a saturated solution
- d)product of molar concentration of ions of a salt as per stoichiometry in an unsaturated solution
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Solubility product is defined as
a)
product of molar concentration of ions of a salt as per stoichiometry in a supersaturated solution
b)
product of molar concentration of ions of a salt as per stoichiometry in a saturated solution at STP
c)
product of molar concentration of ions of a salt as per stoichiometry in a saturated solution
d)
product of molar concentration of ions of a salt as per stoichiometry in an unsaturated solution
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
Definition of Solubility Product, K.A substance's solubility product, Ksp, is the mathematical product of its dissolved ion concentrations raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients. Solubility products are relevant when a sparingly soluble ionic compound releases ions into solution.
What is the correct equilibrium expression (Ksp) for the reaction below:
Ca3(PO4)2(s)  3Ca2+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq)
3Ca2+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq)- a)Ksp = [Ca2+]3[PO43-]2
- b)Ksp = [3Ca2+] + [2PO43-]
- c)Ksp = [3Ca2+][2PO43-]
- d)Ksp = [3Ca2+]3 + [2PO43-]2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the correct equilibrium expression (Ksp) for the reaction below:
Ca3(PO4)2(s) 3Ca2+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq)
3Ca2+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq)
Ca3(PO4)2(s)
 3Ca2+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq)
3Ca2+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq)a)
Ksp = [Ca2+]3[PO43-]2
b)
Ksp = [3Ca2+] + [2PO43-]
c)
Ksp = [3Ca2+][2PO43-]
d)
Ksp = [3Ca2+]3 + [2PO43-]2

|
Edurev.iitjam answered |
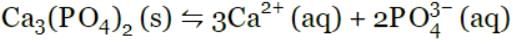
The expression for the solubility product is Ksp =
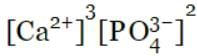
The solubility product is the product of ionic concentrations raised to appropriate stoichiometric coefficients.
Chapter doubts & questions for Ionic Equilibrium - Physical Chemistry 2025 is part of Chemistry exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Chemistry 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Ionic Equilibrium - Physical Chemistry in English & Hindi are available as part of Chemistry exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free.
Physical Chemistry
90 videos|144 docs|67 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup