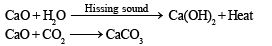All Exams >
JEE >
35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE >
All Questions
All questions of The s-Block Elements for JEE Exam
Which one of the following statements about water is FALSE?- a)There is extensive intr amolecular hydrogen bonding in the condensed phase.
- b)Ice formed by heavy water sinks in normal water.
- c)Water is oxidized to oxygen during photosynthesis.
- d)Water can act both as an acid and as a base.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements about water is FALSE?
a)
There is extensive intr amolecular hydrogen bonding in the condensed phase.
b)
Ice formed by heavy water sinks in normal water.
c)
Water is oxidized to oxygen during photosynthesis.
d)
Water can act both as an acid and as a base.
|
|
Devika Iyer answered |
False Statement: There is extensive intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the condensed phase.
Explanation:
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding occurs when hydrogen atoms in a molecule are bonded to highly electronegative atoms like oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. These electronegative atoms have lone pairs of electrons that can form a hydrogen bond with a neighboring hydrogen atom.
Water (H2O) is a polar molecule due to the electronegativity difference between hydrogen and oxygen atoms. The oxygen atom is more electronegative and attracts the shared electrons more strongly, creating a partial negative charge (δ-) on the oxygen atom and a partial positive charge (δ+) on the hydrogen atoms.
Condensed Phase:
The condensed phase refers to the state in which water exists as a liquid or solid. In the condensed phase, water molecules are close together and experience intermolecular interactions.
Intramolecular vs. Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding:
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding occurs within a single molecule, while intermolecular hydrogen bonding occurs between different molecules.
Explanation of the False Statement:
The false statement in this case is that there is extensive intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the condensed phase of water. In reality, water molecules form intermolecular hydrogen bonds with each other in the condensed phase.
Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding in Water:
In the condensed phase, water molecules form hydrogen bonds with neighboring water molecules. The oxygen atom of one water molecule can form a hydrogen bond with a hydrogen atom of another water molecule.
These intermolecular hydrogen bonds are responsible for many of the unique properties of water, such as its high boiling point, high specific heat capacity, and surface tension.
Conclusion:
In summary, the false statement is that there is extensive intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the condensed phase of water. In reality, water molecules form intermolecular hydrogen bonds with each other in the condensed phase.
Explanation:
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding occurs when hydrogen atoms in a molecule are bonded to highly electronegative atoms like oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. These electronegative atoms have lone pairs of electrons that can form a hydrogen bond with a neighboring hydrogen atom.
Water (H2O) is a polar molecule due to the electronegativity difference between hydrogen and oxygen atoms. The oxygen atom is more electronegative and attracts the shared electrons more strongly, creating a partial negative charge (δ-) on the oxygen atom and a partial positive charge (δ+) on the hydrogen atoms.
Condensed Phase:
The condensed phase refers to the state in which water exists as a liquid or solid. In the condensed phase, water molecules are close together and experience intermolecular interactions.
Intramolecular vs. Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding:
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding occurs within a single molecule, while intermolecular hydrogen bonding occurs between different molecules.
Explanation of the False Statement:
The false statement in this case is that there is extensive intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the condensed phase of water. In reality, water molecules form intermolecular hydrogen bonds with each other in the condensed phase.
Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding in Water:
In the condensed phase, water molecules form hydrogen bonds with neighboring water molecules. The oxygen atom of one water molecule can form a hydrogen bond with a hydrogen atom of another water molecule.
These intermolecular hydrogen bonds are responsible for many of the unique properties of water, such as its high boiling point, high specific heat capacity, and surface tension.
Conclusion:
In summary, the false statement is that there is extensive intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the condensed phase of water. In reality, water molecules form intermolecular hydrogen bonds with each other in the condensed phase.
The compound(s) formed upon combustion of sodium metal in excess air is (are)- a)Na2O2
- b)Na2O
- c)NaO2
- d)NaOH
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound(s) formed upon combustion of sodium metal in excess air is (are)
a)
Na2O2
b)
Na2O
c)
NaO2
d)
NaOH

|
Sahil Yadav answered |
Sodium when heated in dry air, first forms sodium oxide, then sodium peroxide.
2
N
a
+
1
2
O
2
→
Δ
N
a
2
O
+
1
2
O
2
→
Δ
N
a
2
O
2
Which one of the following alkaline earth metal sulphates has its hydration enthalpy greater than its lattice enthalpy ?- a)BaSO4
- b)SrSO4
- c)CaSO4
- d)BeSO4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following alkaline earth metal sulphates has its hydration enthalpy greater than its lattice enthalpy ?
a)
BaSO4
b)
SrSO4
c)
CaSO4
d)
BeSO4
|
|
Utkarsh Pandey answered |
Because of smallest size of Be2+, its hydration energy is maximum and is greater than the lattice energy of BeSO4.
The ionic mobility of alkali metal ions in aqueous solution is maximum for- a)Li+
- b)Na+
- c)K+
- d)Rb+
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The ionic mobility of alkali metal ions in aqueous solution is maximum for
a)
Li+
b)
Na+
c)
K+
d)
Rb+
|
|
Tejas Verma answered |
Smaller the size of cation higher is its hydration energy and greater is its ionic mobility hence the correct order is Li+ < Na+ < K+ < Rb+
Highly pure dilute solution of sodium in liquid ammonia- a)shows blue colour
- b)exhibits electrical conductivity
- c)produces sodium amide
- d)produces hydrogen gas.
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Highly pure dilute solution of sodium in liquid ammonia
a)
shows blue colour
b)
exhibits electrical conductivity
c)
produces sodium amide
d)
produces hydrogen gas.
|
|
Ruchi Shah answered |
A small piece of sodium is cut to expose a fresh surface. The sodium is dropped into liquid ammonia at a temperature of approximately -33 degrees Celsius. Some of the sodium dissolves, forming sodium cations surrounded by ammonia molecules and electrons surrounded by ammonia molecules. The solvated electrons give the blue color to the solution.
Because of the mobility of the electrons, the solution is a good electrical conductor. Bubbles of hydrogen gas are formed by a second reaction that also produces sodium amide. More concentrated solutions appear bronze-colored and have a conductivity similar to metals.
2Na+2NH3 → 2NaNH2+H2.
Hence options A,B,C & D are correct
Because of the mobility of the electrons, the solution is a good electrical conductor. Bubbles of hydrogen gas are formed by a second reaction that also produces sodium amide. More concentrated solutions appear bronze-colored and have a conductivity similar to metals.
2Na+2NH3 → 2NaNH2+H2.
Hence options A,B,C & D are correct
The oxide that gives hydrogen peroxide on treatment with a dilute acid is :- a)PbO2
- b)Na2O2
- c)MnO2
- d)TiO2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxide that gives hydrogen peroxide on treatment with a dilute acid is :
a)
PbO2
b)
Na2O2
c)
MnO2
d)
TiO2

|
Anjali Deshpande answered |
The correct option (b) Na2O2
Explanation:
Na2O2 + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O2
Other oxides (PbO2, MnO2 and TiO2) do not contain peroxide ( - O - O -) linkage.
Explanation:
Na2O2 + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O2
Other oxides (PbO2, MnO2 and TiO2) do not contain peroxide ( - O - O -) linkage.
The volume strength of 1.5 N H2O2 solution is- a)4.8
- b)8.4
- c)3.0
- d)8.0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The volume strength of 1.5 N H2O2 solution is
a)
4.8
b)
8.4
c)
3.0
d)
8.0

|
Prisha Yadav answered |
The correct option is: (b) 8.4
Explanation:
Normality (N) = 1.5
We know that equivalent weight of H2O2 is 17 and strength of H2O2 = Normality x Equivalent weight
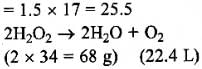
Since 68 grams of H2O2 produces 22.4 litres oxygen at NTP, therefore 25.5 grams of H2O2 will produce
= 22.4/68 x 25.5 = 8.4 litre of oxygen
Thus, volume strength of given H2O2 solution is 8.4.
Explanation:
Normality (N) = 1.5
We know that equivalent weight of H2O2 is 17 and strength of H2O2 = Normality x Equivalent weight
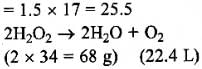
Since 68 grams of H2O2 produces 22.4 litres oxygen at NTP, therefore 25.5 grams of H2O2 will produce
= 22.4/68 x 25.5 = 8.4 litre of oxygen
Thus, volume strength of given H2O2 solution is 8.4.
Hydrogen peroxide in its reaction with KIO4 and NH2OH respectively, is acting as a- a)Reducing agent, oxidising agent
- b)Reducing agent, reducing agent
- c)Oxidising agent, oxidising agent
- d)Oxidising agent, reducing agent
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen peroxide in its reaction with KIO4 and NH2OH respectively, is acting as a
a)
Reducing agent, oxidising agent
b)
Reducing agent, reducing agent
c)
Oxidising agent, oxidising agent
d)
Oxidising agent, reducing agent

|
Akash Shah answered |
Explanation:
Oxidizing Agent is defined as the agent which helps the other substance to get oxidized and itself gets reduced. The oxidation state of the oxidizing agent gets reduced.
Reducing Agent is defined as the agent which helps the other substance to get reduced and itself gets oxidized. The oxidation state of the reducing agent is increased.
1. Reaction of Hydrogen Peroxide with KIO4 follows the equation:
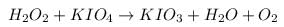
Oxidation state of Iodine on reactant side = +7
Oxidation state of Iodine on product side = +5
As, the oxidation state of iodine is getting reduced, hence it is getting reduced. So, it will act as oxidizing agent and h2O2 will act as reducing agent.
2. Reaction of Hydrogen Peroxide with NH2O4 follows the equation:
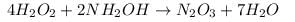
Oxidation state of Nitrogen on reactant side = -1
Oxidation state of Nitrogen on product side = +3
As, the oxidation state of nitrogen is increasing, hence it is getting oxidized. So, it will act as reducing agent and will act as oxidizing agent.
So, the correct option is option a.
Oxidizing Agent is defined as the agent which helps the other substance to get oxidized and itself gets reduced. The oxidation state of the oxidizing agent gets reduced.
Reducing Agent is defined as the agent which helps the other substance to get reduced and itself gets oxidized. The oxidation state of the reducing agent is increased.
1. Reaction of Hydrogen Peroxide with KIO4 follows the equation:
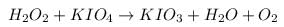
Oxidation state of Iodine on reactant side = +7
Oxidation state of Iodine on product side = +5
As, the oxidation state of iodine is getting reduced, hence it is getting reduced. So, it will act as oxidizing agent and h2O2 will act as reducing agent.
2. Reaction of Hydrogen Peroxide with NH2O4 follows the equation:
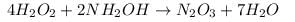
Oxidation state of Nitrogen on reactant side = -1
Oxidation state of Nitrogen on product side = +3
As, the oxidation state of nitrogen is increasing, hence it is getting oxidized. So, it will act as reducing agent and will act as oxidizing agent.
So, the correct option is option a.
Which of the following species is diamagnetic in nature?- a)
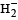
- b)
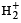
- c)H2
- d)
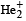
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following species is diamagnetic in nature?
a)
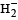
b)
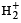
c)
H2
d)
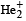
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
TIPS/Formulae :
A diamagnetic substance contains no unpaired electron.
H2 is diamagnetic as it contains all paired electrons
A diamagnetic substance contains no unpaired electron.
H2 is diamagnetic as it contains all paired electrons
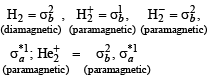
In which of the following reactions H2O2 acts as a reducing agent?- a)H2O2 + 2H+ + 2e-→ 2H2O
- b)H2O2 + 2e- → O2+ 2H+
- c)H2O2 + 2e- → 2OH-
- d)H2O2 + 2OH- - 2e- → O2+ 2H2O
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following reactions H2O2 acts as a reducing agent?
a)
H2O2 + 2H+ + 2e-→ 2H2O
b)
H2O2 + 2e- → O2+ 2H+
c)
H2O2 + 2e- → 2OH-
d)
H2O2 + 2OH- - 2e- → O2+ 2H2O
|
|
Aditya Kaul answered |
As we know that a reducing agent leads to oxidation of the reaction and an oxidising agent resultantly leads to reduction of the reaction.
Here if you see carefully -
. Addition of oxygen
. Removal of electrons
And
. Removal of hydrogen (which defines an oxidation reaction) is taking place for H2O2
Resulting in the formation of water.
Here if you see carefully -
. Addition of oxygen
. Removal of electrons
And
. Removal of hydrogen (which defines an oxidation reaction) is taking place for H2O2
Resulting in the formation of water.
The main oxides formed on combustion of Li, Na and K in excess of air are, respectively:- a)Li2O2, Na2O2 and KO2
- b)Li2O, Na2O2 and KO2
- c)Li2O, Na2O and KO2
- d)LiO2, Na2O2 and K2O
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The main oxides formed on combustion of Li, Na and K in excess of air are, respectively:
a)
Li2O2, Na2O2 and KO2
b)
Li2O, Na2O2 and KO2
c)
Li2O, Na2O and KO2
d)
LiO2, Na2O2 and K2O
|
|
Mr.perfect answered |
In excess of air ...can we say that they are burned during roasting??
Which of the following atoms has the highest first ionization energy?- a)K
- b)Sc
- c)Rb
- d)Na
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following atoms has the highest first ionization energy?
a)
K
b)
Sc
c)
Rb
d)
Na

|
Roshni Chavan answered |
Alkali metals have the lowest ionization energy in each period on the other hand Sc is a d - block element.
Transition metals have smaller atomic radii and higher nuclear charge leading to high ionisation energy.
Transition metals have smaller atomic radii and higher nuclear charge leading to high ionisation energy.
From the following statements regarding H2O2, choose the incorrect statement :- a)It has to be stored in plastic or wax lined glass bottles in dark
- b)It has to be kept away from dust
- c)It can act only as an oxidizing agent
- d)It decomposes on exposure to light
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
From the following statements regarding H2O2, choose the incorrect statement :
a)
It has to be stored in plastic or wax lined glass bottles in dark
b)
It has to be kept away from dust
c)
It can act only as an oxidizing agent
d)
It decomposes on exposure to light
|
|
Yash Modi answered |
All are correct except C. H2O2 can act as both oxidizing as well as reducing agent depending upon the nature of medium (acidic/basic).
KO2 (potassium super oxide) is used in oxygen cylinders in space and submarines because it- a)absorbs CO2 and increases O2 content
- b)eliminates moisture
- c)absorbs CO2
- d)produces ozone.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
KO2 (potassium super oxide) is used in oxygen cylinders in space and submarines because it
a)
absorbs CO2 and increases O2 content
b)
eliminates moisture
c)
absorbs CO2
d)
produces ozone.
|
|
Disha Mishra answered |
2KO2 + 2H2O → 2 KOH + H2O2 + O2.
KO2 is used as an oxidising agent. It is used as air purifier in space capsules. Submarines and breathing masks as it produces oxygen and remove carbon dioxide.
KO2 is used as an oxidising agent. It is used as air purifier in space capsules. Submarines and breathing masks as it produces oxygen and remove carbon dioxide.
The reagent(s) used for softening the temporary hardness of water is (are)- a)Ca3 (PO4)2
- b)Ca(OH)2
- c)Na2CO3
- d)NaOCl
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The reagent(s) used for softening the temporary hardness of water is (are)
a)
Ca3 (PO4)2
b)
Ca(OH)2
c)
Na2CO3
d)
NaOCl
|
|
Ishani Menon answered |
Reagents for Softening Temporary Hardness of Water
Temporary hardness of water is caused by the presence of bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium. It can be removed by adding certain reagents that react with the bicarbonates to form insoluble precipitates that can be removed by filtration or settling. The reagents used for softening the temporary hardness of water are:
1. Calcium Hydroxide (Ca(OH)2)
Calcium hydroxide, also known as slaked lime, is a white crystalline solid that is sparingly soluble in water. When added to hard water, it reacts with the bicarbonates to form insoluble calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) precipitates:
Ca(OH)2 + 2HCO3- → CaCO3↓ + CO2↑ + 2H2O
Mg(HCO3)2 + Ca(OH)2 → Mg(OH)2↓ + CaCO3↓ + 2CO2↑
The precipitates can be removed by filtration or settling, leaving the water soft.
2. Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3)
Sodium carbonate, also known as washing soda, is a white crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. When added to hard water, it reacts with the bicarbonates to form insoluble calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) precipitates:
Na2CO3 + Ca(HCO3)2 → CaCO3↓ + 2NaHCO3
Na2CO3 + Mg(HCO3)2 → MgCO3↓ + 2NaHCO3
The precipitates can be removed by filtration or settling, leaving the water soft.
3. Sodium Hypochlorite (NaOCl)
Sodium hypochlorite, also known as bleach, is a pale yellowish liquid that is highly soluble in water. When added to hard water, it oxidizes the bicarbonates to carbonates, which then react with the calcium and magnesium ions to form the corresponding insoluble precipitates:
2NaOCl + 2HCO3- → 2NaCl + CO2↑ + H2O + O2↑
Ca2+ + CO32- → CaCO3↓
Mg2+ + CO32- → MgCO3↓
The precipitates can be removed by filtration or settling, leaving the water soft.
Conclusion
In summary, the reagents used for softening the temporary hardness of water are calcium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, and sodium hypochlorite. These reagents react with the bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium to form insoluble precipitates that can be removed by filtration or settling, leaving the water soft.
Temporary hardness of water is caused by the presence of bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium. It can be removed by adding certain reagents that react with the bicarbonates to form insoluble precipitates that can be removed by filtration or settling. The reagents used for softening the temporary hardness of water are:
1. Calcium Hydroxide (Ca(OH)2)
Calcium hydroxide, also known as slaked lime, is a white crystalline solid that is sparingly soluble in water. When added to hard water, it reacts with the bicarbonates to form insoluble calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) precipitates:
Ca(OH)2 + 2HCO3- → CaCO3↓ + CO2↑ + 2H2O
Mg(HCO3)2 + Ca(OH)2 → Mg(OH)2↓ + CaCO3↓ + 2CO2↑
The precipitates can be removed by filtration or settling, leaving the water soft.
2. Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3)
Sodium carbonate, also known as washing soda, is a white crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. When added to hard water, it reacts with the bicarbonates to form insoluble calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) precipitates:
Na2CO3 + Ca(HCO3)2 → CaCO3↓ + 2NaHCO3
Na2CO3 + Mg(HCO3)2 → MgCO3↓ + 2NaHCO3
The precipitates can be removed by filtration or settling, leaving the water soft.
3. Sodium Hypochlorite (NaOCl)
Sodium hypochlorite, also known as bleach, is a pale yellowish liquid that is highly soluble in water. When added to hard water, it oxidizes the bicarbonates to carbonates, which then react with the calcium and magnesium ions to form the corresponding insoluble precipitates:
2NaOCl + 2HCO3- → 2NaCl + CO2↑ + H2O + O2↑
Ca2+ + CO32- → CaCO3↓
Mg2+ + CO32- → MgCO3↓
The precipitates can be removed by filtration or settling, leaving the water soft.
Conclusion
In summary, the reagents used for softening the temporary hardness of water are calcium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, and sodium hypochlorite. These reagents react with the bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium to form insoluble precipitates that can be removed by filtration or settling, leaving the water soft.
This question contains STATEMENT-1 (Assertion) and STATEMENT-2 (Reason) and has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.STATEMENT-1 : Alkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia to give blue solutions. becauseSTATEMENT-2 : Alkali metals is liquid ammonia give solvated species of the type [M(NH3)n]+ (M = alkali metals).- a)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1
- b)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is not correct explanation for Statement-1
- c)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False
- d)Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
This question contains STATEMENT-1 (Assertion) and STATEMENT-2 (Reason) and has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
STATEMENT-1 : Alkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia to give blue solutions. because
STATEMENT-2 : Alkali metals is liquid ammonia give solvated species of the type [M(NH3)n]+ (M = alkali metals).
a)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1
b)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is not correct explanation for Statement-1
c)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False
d)
Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True.

|
Ashwini Khanna answered |
Statement-1 is correct. Statement-2 is also correct but not the correct explanation becuase blue colour of the solution is due to the solvated electrons.
The substance not likely to contain CaCO3 is- a)calcined gypsum
- b)sea shells
- c)dolomite
- d)a marble statue
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The substance not likely to contain CaCO3 is
a)
calcined gypsum
b)
sea shells
c)
dolomite
d)
a marble statue

|
Jaideep Sengupta answered |
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula CaSO4.2H2O
calcined gypsum is correct answer.
Hence (a) is the correct answer.
Which of the following on thermal decomposition yields a basic as well as acidic oxide ?- a)NaNO3
- b)KClO3
- c)CaCO3
- d)NH4NO3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following on thermal decomposition yields a basic as well as acidic oxide ?
a)
NaNO3
b)
KClO3
c)
CaCO3
d)
NH4NO3

|
Sahana Ahuja answered |
Answer:
(c) CaCO3 is the correct answer.
Explanation:
Thermal decomposition is the process in which heat is required.
It is also known as thermolysis.
It is process in which a compund breaks into two or more products when heat is supplied.
This reaction is used for production of oxygen.
This reaction is also used for production of acidic as well as basic oxides.
(c) CaCO3 is the correct answer.
Explanation:
Thermal decomposition is the process in which heat is required.
It is also known as thermolysis.
It is process in which a compund breaks into two or more products when heat is supplied.
This reaction is used for production of oxygen.
This reaction is also used for production of acidic as well as basic oxides.
Oxide is a compund which primarily consists one oxygen and any other element.
Oxide are of two types
1) acidic oxide
2) basic oxide
Acidic oxide are oxides which react with water to form acids or they react with base to form salts.
Basic oxides are oxides which are formed when oxygen reacts with metals which maybe alkaline or alkaline earth like metals.
CaCO3 is the only compund which on thermal decomposition gives both acidic as well as basic compunds.
The reaction is given as follows
CaCO3 ===> CaO+ CO2
Here CaO is basic oxide.
And CO2 is acidic oxide.
Hence
c) CaCO3 is the correct answer.
Oxide are of two types
1) acidic oxide
2) basic oxide
Acidic oxide are oxides which react with water to form acids or they react with base to form salts.
Basic oxides are oxides which are formed when oxygen reacts with metals which maybe alkaline or alkaline earth like metals.
CaCO3 is the only compund which on thermal decomposition gives both acidic as well as basic compunds.
The reaction is given as follows
CaCO3 ===> CaO+ CO2
Here CaO is basic oxide.
And CO2 is acidic oxide.
Hence
c) CaCO3 is the correct answer.
The species present in solution when CO2 is dissolved in water are- a)CO2, H2CO3, HCO3–, CO32–
- b)H2CO3, CO32–
- c)CO32–, HCO3–
- d)CO2, H2CO3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The species present in solution when CO2 is dissolved in water are
a)
CO2, H2CO3, HCO3–, CO32–
b)
H2CO3, CO32–
c)
CO32–, HCO3–
d)
CO2, H2CO3
|
|
Madhurima Rane answered |
-, and CO32-.
When CO2 dissolves in water, it reacts with water to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), which then dissociates into hydrogen ions (H+) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-). A small fraction of the bicarbonate ions can further dissociate into carbonate ions (CO32-). Therefore, the species present in solution when CO2 is dissolved in water are CO2, H2CO3, HCO3-, and CO32-.
When CO2 dissolves in water, it reacts with water to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), which then dissociates into hydrogen ions (H+) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-). A small fraction of the bicarbonate ions can further dissociate into carbonate ions (CO32-). Therefore, the species present in solution when CO2 is dissolved in water are CO2, H2CO3, HCO3-, and CO32-.
HCl is added to following oxides. Which one would give H2O2?- a)MnO2
- b)PbO2
- c)BaO2.8H2O
- d)NO2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
HCl is added to following oxides. Which one would give H2O2?
a)
MnO2
b)
PbO2
c)
BaO2.8H2O
d)
NO2
|
|
Shalini Bose answered |
BaO2.8H2O + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + H2O2 + 8H2O
The following compounds have been arranged in order of their increasing thermal stabilities. Identify the correct order.K2CO3 (I) MgCO3 (II) CaCO3 (III) BeCO3 (IV)- a)I < II < III < IV
- b)IV < II< III < I
- c)IV < II < I < III
- d)II < IV < III < I
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The following compounds have been arranged in order of their increasing thermal stabilities. Identify the correct order.
K2CO3 (I) MgCO3 (II) CaCO3 (III) BeCO3 (IV)
a)
I < II < III < IV
b)
IV < II< III < I
c)
IV < II < I < III
d)
II < IV < III < I

|
Raksha Nambiar answered |
The increasing thermal stability is
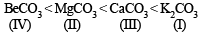
NOTE : Increasing size of cation decreases its polarization ability towards carbonate, making the compound more stable.
Read the following statement and explanation and answer as per the options given below :Statement : The alkali metals can form ionic hydrides which contain the hydride ion H–.Explanation : The alkali metals have low electronegativity; their hydrides conduct electricity when fused and liberate hydrogen at the anode.- a)Both S and E are true and E is the correct explanation of S.
- b)Both S and E are true but E is not the correct explanation of S.
- c)S is true but E is false.
- d)S is false but E is true
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statement and explanation and answer as per the options given below :
Statement : The alkali metals can form ionic hydrides which contain the hydride ion H–.
Explanation : The alkali metals have low electronegativity; their hydrides conduct electricity when fused and liberate hydrogen at the anode.
a)
Both S and E are true and E is the correct explanation of S.
b)
Both S and E are true but E is not the correct explanation of S.
c)
S is true but E is false.
d)
S is false but E is true

|
Aryan Dasgupta answered |
The correct option (a) Statement I is true; Statement II is true; Statement II is a correct explanation of Statement I.
Explanation:
Both are correct and statement II is the correct explanation of statement I.
Explanation:
Both are correct and statement II is the correct explanation of statement I.
Which of the following statements in relation to the hydrogen atom is correct ?- a)3s, 3p and 3d orbitals all have the same energy
- b)3s and 3p orbitals are of lower energy than 3d orbital
- c)3p orbital is lower in energy than 3d orbital
- d)3s orbital is lower in energy than 3p orbital
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements in relation to the hydrogen atom is correct ?
a)
3s, 3p and 3d orbitals all have the same energy
b)
3s and 3p orbitals are of lower energy than 3d orbital
c)
3p orbital is lower in energy than 3d orbital
d)
3s orbital is lower in energy than 3p orbital

|
Mehul Chavan answered |
Correct option: (a) 3s, 3p, and 3d orbitals all have the same energy
Explanation:
A hydrogen atom has 1s^1 configuration and these Its, 3p and 3d orbitals will have same energy wrt 1s orbital.
Explanation:
A hydrogen atom has 1s^1 configuration and these Its, 3p and 3d orbitals will have same energy wrt 1s orbital.
Molecular formula of Glauber ’s salt is :- a)MgSO4.7H2O
- b)CuSO4.5H2O
- c)FeSO4.7H2O
- d)Na2SO4.10H2O
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Molecular formula of Glauber ’s salt is :
a)
MgSO4.7H2O
b)
CuSO4.5H2O
c)
FeSO4.7H2O
d)
Na2SO4.10H2O

|
Raj Raunak answered |
Glauber's salt, common name for sodium sulfate decahydrate, Na2SO4·10H2O; it occurs as white or colorless monoclinic crystals. Upon exposure to fairly dry air it effloresces, forming powdery anhydrous sodium sulfate.
The molecular formula of a commercial resin used for exchanging ions in water softening is C8H7SO3– Na+ (Mol. wt. 206. What would be the maximum uptake of Ca2+ ions by the resin when expressed in mole per gram resin ?- a)2/309
- b)1/412
- c)1/103
- d)1/206
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The molecular formula of a commercial resin used for exchanging ions in water softening is C8H7SO3– Na+ (Mol. wt. 206. What would be the maximum uptake of Ca2+ ions by the resin when expressed in mole per gram resin ?
a)
2/309
b)
1/412
c)
1/103
d)
1/206

|
Ritika Kulkarni answered |
Correct option (d) 1/412
Explanation:
Explanation:
We know the molecular weight of C8H7SO3Na
=12 x8 + 1 x7 + 32 + 16 x 3+ 23=206
We have to find. moie per gram of resin.
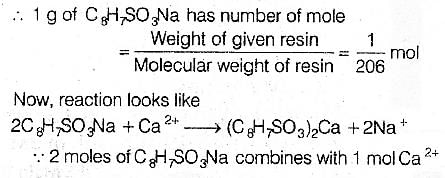
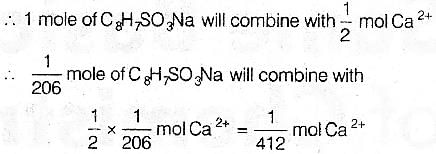
=12 x8 + 1 x7 + 32 + 16 x 3+ 23=206
We have to find. moie per gram of resin.
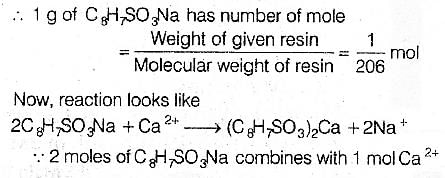
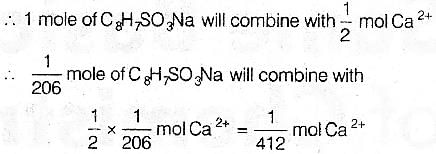
Based on lattice energy and other considerations which one of the following alkali metal chlorides is expected to have the highest melting point ? - a)RbCl
- b)KCl
- c)NaCl
- d)LiCl
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Based on lattice energy and other considerations which one of the following alkali metal chlorides is expected to have the highest melting point ?
a)
RbCl
b)
KCl
c)
NaCl
d)
LiCl

|
Sahana Joshi answered |
LiCl has partly covalent character. Other halides are ionic in nature. Lattice energy decreases with increase of ionic radius of cation, anion being the same. Larger is the lattice energy, the higher will be m. pt. hence NaCl will have highest lattice energy.
In context with the industrial preparation of hydrogen from water gas (CO + H2), which of the following is the correct statement?- a)CO and H2, are fractionally separated using differences in their densities
- b)CO is removed by absor ption in aqueous Cu2Cl2 solution
- c)H2 is removed through occlusion with pd
- d)CO is oxidised to CO2 with steam in the presence of a catalyst followed by absorption of of CO2 in alkali
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In context with the industrial preparation of hydrogen from water gas (CO + H2), which of the following is the correct statement?
a)
CO and H2, are fractionally separated using differences in their densities
b)
CO is removed by absor ption in aqueous Cu2Cl2 solution
c)
H2 is removed through occlusion with pd
d)
CO is oxidised to CO2 with steam in the presence of a catalyst followed by absorption of of CO2 in alkali

|
Anjali Deshpande answered |
Correct option(D) CO is oxidised to CO2 with steam in the presence of a catalyst followed by absorption of CO2 in alkali
Explanation:
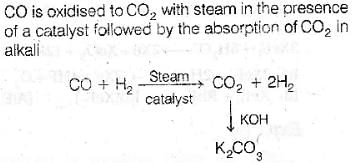
Explanation:

Which one of the following processes will produce hard water ?- a)Saturation of water with MgCO3
- b)Saturation of water with CaSO4
- c)Addition of Na2SO4 to water
- d)Saturation of water with CaCO3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following processes will produce hard water ?
a)
Saturation of water with MgCO3
b)
Saturation of water with CaSO4
c)
Addition of Na2SO4 to water
d)
Saturation of water with CaCO3

|
Gauri Chauhan answered |
Correct option(b) Saturation of water with CaSO4
Explanation:

Explanation:

The set representing the correct order of first ionization potential is- a)K > Na > Li
- b)Be > Mg > Ca
- c)B > C > N
- d)Ge > Si > C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The set representing the correct order of first ionization potential is
a)
K > Na > Li
b)
Be > Mg > Ca
c)
B > C > N
d)
Ge > Si > C

|
Akshita Nair answered |
Correct option (b) Be>Mg>Ca
Explanation:
Ionisation potential decreases on moving from top to bottom in a group of periodic table.
Explanation:
Ionisation potential decreases on moving from top to bottom in a group of periodic table.
Heavy water is- a)H218O
- b)water obtained by repeated distillation
- c)D2O
- d)water at 4ºC
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Heavy water is
a)
H218O
b)
water obtained by repeated distillation
c)
D2O
d)
water at 4ºC
|
|
Reena Dhanesh Kumar answered |
Heavy water (deuterium oxide-D2O)is a form of water that contains a larger than normal amount of the hydrogen isotope deuterium
MgSO4 on reaction with NH4OH and Na2HPO4 forms a white crystalline precipitate. What is its formula?- a)Mg (NH4)PO4
- b)Mg3 (PO4)2
- c)MgCl2.MgSO4
- d)MgSO4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
MgSO4 on reaction with NH4OH and Na2HPO4 forms a white crystalline precipitate. What is its formula?
a)
Mg (NH4)PO4
b)
Mg3 (PO4)2
c)
MgCl2.MgSO4
d)
MgSO4

|
Mohit Patel answered |
The correct option (a) Mg(NH4)PO4
Explanation:
MgSO4 on reaction with Na2HPO4 (disodium hydrogen phosphate) in presence of NH4OH give white precipitate of magnesium ammonium phosphate [Mg(NH4)PO4]
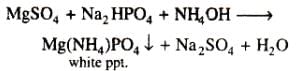
The metallic sodium disolves in liquid ammonia to form a deep blue coloured solution. The deep blue colour is due to formation of:- a)solvated electron,
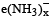
- b)solvated atomic sodium, Na(NH3)y
- c)(Na+ + Na–)
- d)NaNH2 + H2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The metallic sodium disolves in liquid ammonia to form a deep blue coloured solution. The deep blue colour is due to formation of:
a)
solvated electron, 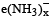
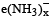
b)
solvated atomic sodium, Na(NH3)y
c)
(Na+ + Na–)
d)
NaNH2 + H2

|
Om Rana answered |
When sodium dissolves in ammonia, it make a solvated COMPLEX. In this complex, the solvated electron CAN makes transition between orbital of different energy level. So when the solution is illuminated, the electron makes a transition to HIGHER orbital by absorbing the photons. Being UNSTABLE it returns to its ground state in nanosecond interval. WHILE COMING BACK TO THE GROUND STATE IT RELEASE THE PHOTONS WHICH IMPARTS THE DEEP BLUE COLOUR TO THE SOLUTION.
The hydration energy of Mg++ is larger than that of :- a)Al3+
- b)Na+
- c)Be++
- d)Mg3+
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The hydration energy of Mg++ is larger than that of :
a)
Al3+
b)
Na+
c)
Be++
d)
Mg3+

|
Rounak Desai answered |
Adsorption of ions at the solid - aqueous interface is the primary mechanism in fast biological processes to very slow geological transformations. Despite, little is known about role of ion charge, hydration energy and hydration structure on competitive adsorption of ions, their structure and coverage at the interface. In this report, we investigate the structure and adsorption behavior of monovalent (Rb+ and Na+) and divalent (Sr2+ and Mg2+) cations ranging from 0-4.5 M of bulk concentrations on the muscovite mica surface. Divalent ions have stronger adsorption strength compared to monovalent ions due higher charge. However, we observed counter-intuitive behavior of lesser adsorption of divalent cations compared to monovalent cations. Our detailed analysis reveals that hydration structure of divalent cations hinders their adsorption. Both, Na+ and Rb+ ions exhibits similar adsorption behavior, however, the adsorption mechanism of Na+ ions is different from Rb+ ions in terms of redistribution of the water molecules in their hydration shell. In addition, we observed surface mediated RbCl salting out behavior, which is absent in Na+ and divalent ions. We observed direct correlation in hydration energy of cations and their adsorption behavior. The obtained understanding will have tremendous impact in super-capacitors, nanotribology, colloidal chemistry and water purifications.
The species that do not contain peroxide ions are- a)PbO2
- b)H2O2
- c)SrO2
- d)BaO2
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The species that do not contain peroxide ions are
a)
PbO2
b)
H2O2
c)
SrO2
d)
BaO2

|
Anuj Saini answered |
The correct option (a) PbO2
Explanation:
PbO2 does not have peroxide ion [in peroxide ion bar O - bar O bond is present].
Explanation:
PbO2 does not have peroxide ion [in peroxide ion bar O - bar O bond is present].
Calcium is obtained by - a)electrolysis of molten CaCl2.
- b)electrolysis of solution of CaCl2 in water.
- c)Reduction of CaCl2 with carbon.
- d)roasting of limestone.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Calcium is obtained by
a)
electrolysis of molten CaCl2.
b)
electrolysis of solution of CaCl2 in water.
c)
Reduction of CaCl2 with carbon.
d)
roasting of limestone.

|
Preethi Kaur answered |
Ca is obtained by electrolysis of molten mixture of CaCl2 mixed with CaF2.
A sodium salt on treatment with MgCl2 gives white precipitate only on heating. The anion of the sodium salt is- a)
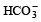
- b)
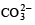
- c)
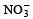
- d)
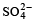
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A sodium salt on treatment with MgCl2 gives white precipitate only on heating. The anion of the sodium salt is
a)
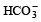
b)
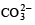
c)
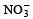
d)
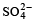

|
Sanchita Patel answered |
The correct option (a) HCO-3
Explanation:
A sodium salt of an unknown anion when treated with MgCl2 gives white precipitate (MgCO3) only on boiling. The anion is HCO-3 ion.
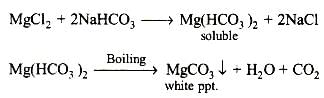
Explanation:
A sodium salt of an unknown anion when treated with MgCl2 gives white precipitate (MgCO3) only on boiling. The anion is HCO-3 ion.
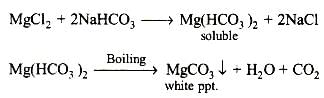
Very pure hydrogen (99.9) can be made by which of the following processes ?- a)Reaction of methane with steam
- b)Mixing natural hydrocarbons of high molecular weight
- c)Electrolysis of water
- d)Reaction of salts like hydrides with water
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Very pure hydrogen (99.9) can be made by which of the following processes ?
a)
Reaction of methane with steam
b)
Mixing natural hydrocarbons of high molecular weight
c)
Electrolysis of water
d)
Reaction of salts like hydrides with water

|
Rounak Desai answered |
Correct option(d) Reaction of salts like hydrides with water
Explanation:
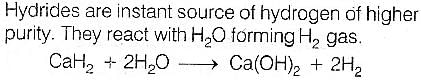
Explanation:
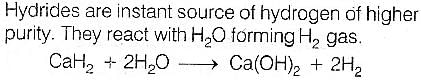
The solubilities of carbonates decrease down the magnesium group due to a decrease in- a)hydration energies of cations
- b)inter-ionic attraction
- c)entropy of solution formation
- d)lattice energies of solids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The solubilities of carbonates decrease down the magnesium group due to a decrease in
a)
hydration energies of cations
b)
inter-ionic attraction
c)
entropy of solution formation
d)
lattice energies of solids

|
Krish Ghoshal answered |
The stability of the carbonates of the alkaline earth metals increases on moving down the group. The solubility of carbonate of metals in water is generally low. However, they dissolve in water containing CO2 yielding bicarbonates, and this solubility decreases on going down in a group with the increase in stability of carbonates of metals, and decrease in hydration energy of the cations.
The correct option is A.
The correct option is A.
In curing cement plasters water is sprinkled from time to time. This helps in- a)developing interlocking needle-like crystals of hydrated silicates
- b)hydrating sand and gravel mixed with cement
- c)converting sand into silicic acid
- d)keeping it cool
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In curing cement plasters water is sprinkled from time to time. This helps in
a)
developing interlocking needle-like crystals of hydrated silicates
b)
hydrating sand and gravel mixed with cement
c)
converting sand into silicic acid
d)
keeping it cool

|
Anuj Saini answered |
Correct option(A) developing interlocking needle like crystals of hydrated silicates
Explanation:

Explanation:

A solution of sodium metal in liquid ammonia is strongly reducing due to the presence of- a)sodium atoms
- b)sodium hydride
- c)sodium amide
- d)solvated electrons
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A solution of sodium metal in liquid ammonia is strongly reducing due to the presence of
a)
sodium atoms
b)
sodium hydride
c)
sodium amide
d)
solvated electrons

|
Subhankar Mukherjee answered |
The free ammoniated electrons make the solution of Na in liquid NH3 a very powerful reducing agent.
NOTE : The ammonical solution of an alkali metal is rather favoured as a reducing agent than its aqueous solution because in aqueous solution the alkali metal being highly electropositive evolves hydrogen from water (thus H2O acts as an oxidisng agent) while its solution in ammonia is quite stable, provided no catalyst (transition metal) is present.
NOTE : The ammonical solution of an alkali metal is rather favoured as a reducing agent than its aqueous solution because in aqueous solution the alkali metal being highly electropositive evolves hydrogen from water (thus H2O acts as an oxidisng agent) while its solution in ammonia is quite stable, provided no catalyst (transition metal) is present.
Hydrogen gas will not reduce : - a)heated cupric oxide
- b)heated ferric oxide
- c)heated stannic oxide
- d)heated aluminium oxide
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen gas will not reduce :
a)
heated cupric oxide
b)
heated ferric oxide
c)
heated stannic oxide
d)
heated aluminium oxide

|
Athira Datta answered |
NOTE : The more electropositive metal will not be reduced by hydrogen.
Among given choices only Al is more electropositive than hydrogen.
∴ It will not be reduced by hydrogen.
Among given choices only Al is more electropositive than hydrogen.
∴ It will not be reduced by hydrogen.
The metallic lustre exhibited by sodium is explained by- a)diffusion of sodium ions
- b)oscillation of loose electrons
- c)excitation of free protons
- d)existence of body centered cubic lattice
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The metallic lustre exhibited by sodium is explained by
a)
diffusion of sodium ions
b)
oscillation of loose electrons
c)
excitation of free protons
d)
existence of body centered cubic lattice

|
Aryan Dasgupta answered |
The metallic luster exhibited by sodium is explained by: (B) oscillation of loose electrons
When light falls on metals such as sodium, the free electrons start oscillating at their mean positions and get excited to higher levels. On returning back to lower levels, they emit light which spreads in all directions. Due to this metals have a characteristic metallic lustre.
The pair of compounds which can not exist together in solution is : - a)NaHCO3 and NaOH
- b)Na2CO3 and NaHCO3
- c)Na2CO3 and NaOH
- d)NaHCO3 and NaCl
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The pair of compounds which can not exist together in solution is :
a)
NaHCO3 and NaOH
b)
Na2CO3 and NaHCO3
c)
Na2CO3 and NaOH
d)
NaHCO3 and NaCl

|
Sanaya Menon answered |
The correct option (a) NaHCO3 and NaOH
Explanation:
Acidic salt (NaHCO3) and base (NaOH) cannot exist together in solution.
NaHCO3 + NaOH → Na2CO3 + H2O
Explanation:
Acidic salt (NaHCO3) and base (NaOH) cannot exist together in solution.
NaHCO3 + NaOH → Na2CO3 + H2O
A metal M readily forms its sulphate MSO4 which is watersoluble. It forms its oxide MO which becomes inert on heating. It forms an insoluble hyroxide M(OH)2 which is soluble in NaOH solution. Then M is- a)Mg
- b)Ba
- c)Ca
- d)Be.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A metal M readily forms its sulphate MSO4 which is watersoluble. It forms its oxide MO which becomes inert on heating. It forms an insoluble hyroxide M(OH)2 which is soluble in NaOH solution. Then M is
a)
Mg
b)
Ba
c)
Ca
d)
Be.

|
Amrutha Chaudhary answered |
On moving down, water solubility of alkaline earth metals decreases.
Oxides and hydroxides of alkaline earth metal are basic except Be which is amphoteric.
Hence, the metal is Be.
Oxides and hydroxides of alkaline earth metal are basic except Be which is amphoteric.
Hence, the metal is Be.
One mole of magnesium nitride on the reaction with an excess of water gives :- a)two moles of ammonia
- b)one mole of nitric acid
- c)one mole of ammonia
- d)two moles of nitric acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One mole of magnesium nitride on the reaction with an excess of water gives :
a)
two moles of ammonia
b)
one mole of nitric acid
c)
one mole of ammonia
d)
two moles of nitric acid

|
Bhavana Dey answered |
Correct option: (A) two moles of ammonia
Explanation:

Explanation:

Chapter doubts & questions for The s-Block Elements - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of The s-Block Elements - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily