All Exams >
Class 10 >
Olympiad Preparation for Class 10 >
All Questions
All questions of Reproduction in Organism for Class 10 Exam
Which one of the following, best describes the function of the umbilical cord?- a)Supplies oxygenated blood from the mother to the embryo
- b)Feeds of the embryo with digested substances
- c)Coveys nutrients and wastes to and from the embryo respectively
- d)Removes waste from the embryo to the mother’s blood
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following, best describes the function of the umbilical cord?
a)
Supplies oxygenated blood from the mother to the embryo
b)
Feeds of the embryo with digested substances
c)
Coveys nutrients and wastes to and from the embryo respectively
d)
Removes waste from the embryo to the mother’s blood
|
|
Aashi iyer answered |
C) Conveys nutrients and wastes to and from the embryo respectively
Which among the following statements are true for unisexual flowers?
(i) They possess both stamen and pistil
(ii) They possess either stamen or pistil
(iii) They exhibit cross pollination
(iv) Unisexual flower possessing only stamens cannot produce fruits- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(ii), (iii) and (iv)
- d)(i), (ii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following statements are true for unisexual flowers?
(i) They possess both stamen and pistil
(ii) They possess either stamen or pistil
(iii) They exhibit cross pollination
(iv) Unisexual flower possessing only stamens cannot produce fruits
(i) They possess both stamen and pistil
(ii) They possess either stamen or pistil
(iii) They exhibit cross pollination
(iv) Unisexual flower possessing only stamens cannot produce fruits
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(ii), (iii) and (iv)
d)
(i), (ii) and (iv)
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
- Unisexual flowers are those, which bear only male or female flowers, but never both together. They can either possess stamen or pistil.
- As only one sex is present, it undergoes cross-fertilization, where gametes are produced by two different plants.
- Fruit develops from the female flower and hence, fruit cannot be produced by the unisexual plants which possess male flowers (stamen).
Thus, the correct answer is option (c), '(ii), (iii) and (iv)'.
The correct sequence of organs in the male reproductive system for the transport of sperm is- a)Testis → vas deferens → ureter
- b)Testis → vas deferens → urethra
- c)Testis → ureter → urethra
- d)Testis → urethra → ureter
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct sequence of organs in the male reproductive system for the transport of sperm is
a)
Testis → vas deferens → ureter
b)
Testis → vas deferens → urethra
c)
Testis → ureter → urethra
d)
Testis → urethra → ureter
|
|
Pragya garg answered |
B)Epididymis
c)Vas deferens
d)Ejaculatory duct
e)Urethra
c)Vas deferens
d)Ejaculatory duct
e)Urethra
Which of the following flower is bisexual- a)Jasmine
- b)Hibiscus
- c)Lotus
- d)Rose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following flower is bisexual
a)
Jasmine
b)
Hibiscus
c)
Lotus
d)
Rose
|
|
Sonam malhotra answered |
Bisexual Flower - Hibiscus
The correct answer is option 'B', Hibiscus.
Explanation:
Bisexual flowers, also known as perfect flowers, are flowers that have both male and female reproductive organs. These organs include the stamen (male organ) and the pistil (female organ). The stamen produces pollen, while the pistil contains the ovary where the ovules are located.
Now let's discuss why the Hibiscus flower is bisexual.
1. Hibiscus flower structure:
The Hibiscus flower has a typical bisexual flower structure, containing both male and female reproductive organs. It consists of a central, tubular structure known as the pistil, which is the female reproductive part, and a ring of stamens surrounding the pistil, which are the male reproductive parts.
2. Pistil:
The pistil of the Hibiscus flower is located in the center of the flower. It consists of three parts: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the sticky surface at the top of the pistil that receives pollen. The style is the elongated tube that connects the stigma to the ovary. The ovary is the swollen base of the pistil where the ovules are contained.
3. Stamens:
The stamens of the Hibiscus flower are arranged in a ring around the pistil. Each stamen consists of a filament and an anther. The anther is the part of the stamen that produces pollen, which is necessary for fertilization.
4. Pollination:
In bisexual flowers like the Hibiscus, pollination can occur in two ways: self-pollination and cross-pollination. Self-pollination happens when the pollen from the anther of a flower lands on the stigma of the same flower or a flower on the same plant. Cross-pollination occurs when the pollen is transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on a different plant.
Conclusion:
The Hibiscus flower is bisexual because it contains both male (stamens) and female (pistil) reproductive organs. This allows for self-pollination or cross-pollination, ensuring the fertilization and production of seeds.
The correct answer is option 'B', Hibiscus.
Explanation:
Bisexual flowers, also known as perfect flowers, are flowers that have both male and female reproductive organs. These organs include the stamen (male organ) and the pistil (female organ). The stamen produces pollen, while the pistil contains the ovary where the ovules are located.
Now let's discuss why the Hibiscus flower is bisexual.
1. Hibiscus flower structure:
The Hibiscus flower has a typical bisexual flower structure, containing both male and female reproductive organs. It consists of a central, tubular structure known as the pistil, which is the female reproductive part, and a ring of stamens surrounding the pistil, which are the male reproductive parts.
2. Pistil:
The pistil of the Hibiscus flower is located in the center of the flower. It consists of three parts: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the sticky surface at the top of the pistil that receives pollen. The style is the elongated tube that connects the stigma to the ovary. The ovary is the swollen base of the pistil where the ovules are contained.
3. Stamens:
The stamens of the Hibiscus flower are arranged in a ring around the pistil. Each stamen consists of a filament and an anther. The anther is the part of the stamen that produces pollen, which is necessary for fertilization.
4. Pollination:
In bisexual flowers like the Hibiscus, pollination can occur in two ways: self-pollination and cross-pollination. Self-pollination happens when the pollen from the anther of a flower lands on the stigma of the same flower or a flower on the same plant. Cross-pollination occurs when the pollen is transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on a different plant.
Conclusion:
The Hibiscus flower is bisexual because it contains both male (stamens) and female (pistil) reproductive organs. This allows for self-pollination or cross-pollination, ensuring the fertilization and production of seeds.
A planaria worm is cut horizontally into two halves P and Q such that the part P contains the whole head of the worm. Another Planaria worm is cut vertically into two halves R and S in such a way that both the cut pieces R and S contain half head each. Which of the two planaria worms could regenerate to form the complete respective worms?- a)Only R and S
- b)Only P
- c)P, R and S
- d)P, Q, R and S
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A planaria worm is cut horizontally into two halves P and Q such that the part P contains the whole head of the worm. Another Planaria worm is cut vertically into two halves R and S in such a way that both the cut pieces R and S contain half head each. Which of the two planaria worms could regenerate to form the complete respective worms?
a)
Only R and S
b)
Only P
c)
P, R and S
d)
P, Q, R and S
|
|
Sarita iyer answered |
The correct answer is option 'D' - P, Q, R, and S.
Regeneration is the ability of an organism to replace damaged or lost body parts. Planaria worms are known for their remarkable regenerative abilities. They have the ability to regenerate their entire body from just a small fragment. Let's analyze the given information to understand which worms can regenerate fully.
1. Worm cut horizontally into two halves P and Q:
The part P contains the whole head of the worm. The head region of a planaria worm contains the majority of its vital organs, including the brain and sensory organs. Therefore, if part P contains the entire head, it has the potential to regenerate the entire organism.
2. Worm cut vertically into two halves R and S:
Both cut pieces R and S contain half of the head each. Since the head region is split between the two pieces, neither R nor S alone can regenerate the complete worm. However, if both pieces R and S are combined, they can regenerate the complete head region. This is because planaria worms have the ability to fuse together and regenerate missing body parts.
Therefore, the worms that can regenerate to form the complete respective worms are P, Q, R, and S. Part P can regenerate the entire worm as it contains the whole head. Parts R and S, although individually incomplete, can fuse together to regenerate the complete head region. And part Q, although not mentioned specifically, would likely be able to regenerate the tail region or other body parts.
In conclusion, planaria worms have a remarkable ability to regenerate, and in this case, the worms that can regenerate to form complete organisms are P, Q, R, and S.
Regeneration is the ability of an organism to replace damaged or lost body parts. Planaria worms are known for their remarkable regenerative abilities. They have the ability to regenerate their entire body from just a small fragment. Let's analyze the given information to understand which worms can regenerate fully.
1. Worm cut horizontally into two halves P and Q:
The part P contains the whole head of the worm. The head region of a planaria worm contains the majority of its vital organs, including the brain and sensory organs. Therefore, if part P contains the entire head, it has the potential to regenerate the entire organism.
2. Worm cut vertically into two halves R and S:
Both cut pieces R and S contain half of the head each. Since the head region is split between the two pieces, neither R nor S alone can regenerate the complete worm. However, if both pieces R and S are combined, they can regenerate the complete head region. This is because planaria worms have the ability to fuse together and regenerate missing body parts.
Therefore, the worms that can regenerate to form the complete respective worms are P, Q, R, and S. Part P can regenerate the entire worm as it contains the whole head. Parts R and S, although individually incomplete, can fuse together to regenerate the complete head region. And part Q, although not mentioned specifically, would likely be able to regenerate the tail region or other body parts.
In conclusion, planaria worms have a remarkable ability to regenerate, and in this case, the worms that can regenerate to form complete organisms are P, Q, R, and S.
The factors responsible for the rapid spreading of bread mould on slices of bread are:
(i) Presence of large number of spores in air
(ii) Presence of large number of thread-like branches hyphae
(iii) Presence of moisture and nutrients
(iv) Formation of round shaped sporangia- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(i) and (iii)
- c)(ii) and (iv)
- d)(iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The factors responsible for the rapid spreading of bread mould on slices of bread are:
(i) Presence of large number of spores in air
(ii) Presence of large number of thread-like branches hyphae
(iii) Presence of moisture and nutrients
(iv) Formation of round shaped sporangia
(i) Presence of large number of spores in air
(ii) Presence of large number of thread-like branches hyphae
(iii) Presence of moisture and nutrients
(iv) Formation of round shaped sporangia
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(i) and (iii)
c)
(ii) and (iv)
d)
(iii) and (iv)
|
|
Shambavi joshi answered |
Factors responsible for the rapid spreading of bread mould on slices of bread are:
(i) Presence of large number of spores in air:
- Bread mould, also known as Rhizopus, produces a large number of spores that are microscopic and lightweight.
- These spores are easily dispersed in the air and can travel over long distances.
- When they land on a suitable surface, such as a slice of bread, they can germinate and grow into new mould colonies.
(ii) Presence of large number of thread-like branches hyphae:
- The bread mould consists of thread-like branches called hyphae.
- These hyphae grow rapidly and spread across the surface of the bread.
- They secrete enzymes that break down the bread's complex carbohydrates into simpler forms that can be absorbed as nutrients by the mould.
(iii) Presence of moisture and nutrients:
- Bread provides an ideal environment for mould growth, as it contains moisture and nutrients.
- Moisture can come from various sources such as water droplets, high humidity, or even the bread itself if it is not stored properly.
- Nutrients in bread include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, which can be utilized by the mould for its growth and reproduction.
(iv) Formation of round-shaped sporangia:
- As the bread mould grows and spreads, it forms round-shaped structures called sporangia.
- These sporangia contain numerous spores that can be released into the air, further contributing to the spread of the mould.
- The sporangia can burst open, releasing the spores, which can then be carried by air currents to new locations, including other slices of bread.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' (i) and (iii) because the presence of a large number of spores in the air and the presence of moisture and nutrients are the key factors responsible for the rapid spreading of bread mould on slices of bread.
(i) Presence of large number of spores in air:
- Bread mould, also known as Rhizopus, produces a large number of spores that are microscopic and lightweight.
- These spores are easily dispersed in the air and can travel over long distances.
- When they land on a suitable surface, such as a slice of bread, they can germinate and grow into new mould colonies.
(ii) Presence of large number of thread-like branches hyphae:
- The bread mould consists of thread-like branches called hyphae.
- These hyphae grow rapidly and spread across the surface of the bread.
- They secrete enzymes that break down the bread's complex carbohydrates into simpler forms that can be absorbed as nutrients by the mould.
(iii) Presence of moisture and nutrients:
- Bread provides an ideal environment for mould growth, as it contains moisture and nutrients.
- Moisture can come from various sources such as water droplets, high humidity, or even the bread itself if it is not stored properly.
- Nutrients in bread include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, which can be utilized by the mould for its growth and reproduction.
(iv) Formation of round-shaped sporangia:
- As the bread mould grows and spreads, it forms round-shaped structures called sporangia.
- These sporangia contain numerous spores that can be released into the air, further contributing to the spread of the mould.
- The sporangia can burst open, releasing the spores, which can then be carried by air currents to new locations, including other slices of bread.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' (i) and (iii) because the presence of a large number of spores in the air and the presence of moisture and nutrients are the key factors responsible for the rapid spreading of bread mould on slices of bread.
Vegetative propagation refers to the formation of new plants from the following existing organs of the old plants- a)Stems, roots and flowers
- b)Stems, leaves and flowers
- c)Stems, roots and leaves
- d)Stem, flowers and fruits
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Vegetative propagation refers to the formation of new plants from the following existing organs of the old plants
a)
Stems, roots and flowers
b)
Stems, leaves and flowers
c)
Stems, roots and leaves
d)
Stem, flowers and fruits
|
|
Kalyan rane answered |
Vegetative Propagation
Vegetative propagation is the process of forming new plants from the existing organs of old plants. This method is used to produce clones of the parent plant. There are different methods of vegetative propagation such as cutting, layering, grafting, and budding.
Organs involved in Vegetative Propagation
The following organs of the old plants are involved in vegetative propagation:
1. Stems: Stems are one of the most common organs used in vegetative propagation. The stem cuttings of plants such as roses, bougainvillea, and chrysanthemums are used to produce new plants.
2. Roots: Roots can also be used in vegetative propagation. Adventitious roots that grow from the stem of a plant can be used to produce new plants. Examples of such plants are sweet potato and cassava.
3. Leaves: In some plants, leaves can be used for vegetative propagation. The leaves of plants such as African violet and jade plants can be used to produce new plants.
4. Bulbs: Bulbs are underground storage organs that can be used in vegetative propagation. Examples of such plants are onion and garlic.
5. Tubers: Tubers are underground storage organs that can also be used in vegetative propagation. Examples of such plants are potato and yam.
Advantages of Vegetative Propagation
1. The plants produced by vegetative propagation are genetically identical to the parent plant.
2. It is a quick and easy method of producing new plants.
3. The plants produced by vegetative propagation are disease-free.
4. It is a reliable method of producing plants that are true to type.
Conclusion
In conclusion, vegetative propagation is a method of producing new plants from the existing organs of old plants. The organs involved in vegetative propagation are stems, roots, leaves, bulbs, and tubers. It is a reliable and quick method of producing plants that are genetically identical to the parent plant.
Vegetative propagation is the process of forming new plants from the existing organs of old plants. This method is used to produce clones of the parent plant. There are different methods of vegetative propagation such as cutting, layering, grafting, and budding.
Organs involved in Vegetative Propagation
The following organs of the old plants are involved in vegetative propagation:
1. Stems: Stems are one of the most common organs used in vegetative propagation. The stem cuttings of plants such as roses, bougainvillea, and chrysanthemums are used to produce new plants.
2. Roots: Roots can also be used in vegetative propagation. Adventitious roots that grow from the stem of a plant can be used to produce new plants. Examples of such plants are sweet potato and cassava.
3. Leaves: In some plants, leaves can be used for vegetative propagation. The leaves of plants such as African violet and jade plants can be used to produce new plants.
4. Bulbs: Bulbs are underground storage organs that can be used in vegetative propagation. Examples of such plants are onion and garlic.
5. Tubers: Tubers are underground storage organs that can also be used in vegetative propagation. Examples of such plants are potato and yam.
Advantages of Vegetative Propagation
1. The plants produced by vegetative propagation are genetically identical to the parent plant.
2. It is a quick and easy method of producing new plants.
3. The plants produced by vegetative propagation are disease-free.
4. It is a reliable method of producing plants that are true to type.
Conclusion
In conclusion, vegetative propagation is a method of producing new plants from the existing organs of old plants. The organs involved in vegetative propagation are stems, roots, leaves, bulbs, and tubers. It is a reliable and quick method of producing plants that are genetically identical to the parent plant.
The protozoan having a flagellum at its one end is- a)Hydra
- b)Leishmania
- c)Paramecium
- d)Amoeba
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The protozoan having a flagellum at its one end is
a)
Hydra
b)
Leishmania
c)
Paramecium
d)
Amoeba

|
Meera Mehta answered |
Protozoan with a flagellum at one end
The correct answer to the given question is option 'B', Leishmania.
Protozoans are single-celled microscopic organisms that belong to the Kingdom Protista. They are eukaryotes, meaning they have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Protozoans exhibit a wide range of characteristics, including locomotion, reproduction, and feeding mechanisms.
Flagellum is a whip-like structure that protrudes from the cell surface and aids in locomotion. It is composed of microtubules and acts as a propeller, allowing the organism to move through liquid environments.
Leishmania is a genus of protozoans that causes the disease known as leishmaniasis. It is characterized by the presence of a single flagellum at one end of the cell. Leishmania is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected sandflies and can cause various clinical manifestations, including cutaneous, mucocutaneous, and visceral forms of the disease.
Other options:
- Option 'A', Hydra, is a multicellular organism belonging to the phylum Cnidaria. It does not possess a flagellum.
- Option 'C', Paramecium, is a ciliate protozoan that moves using hair-like structures called cilia, not a flagellum.
- Option 'D', Amoeba, is a unicellular protozoan that moves using temporary extensions of its cell membrane called pseudopodia. It also lacks a flagellum.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B', Leishmania, as it is a protozoan that possesses a flagellum at one end of its cell.
The correct answer to the given question is option 'B', Leishmania.
Protozoans are single-celled microscopic organisms that belong to the Kingdom Protista. They are eukaryotes, meaning they have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Protozoans exhibit a wide range of characteristics, including locomotion, reproduction, and feeding mechanisms.
Flagellum is a whip-like structure that protrudes from the cell surface and aids in locomotion. It is composed of microtubules and acts as a propeller, allowing the organism to move through liquid environments.
Leishmania is a genus of protozoans that causes the disease known as leishmaniasis. It is characterized by the presence of a single flagellum at one end of the cell. Leishmania is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected sandflies and can cause various clinical manifestations, including cutaneous, mucocutaneous, and visceral forms of the disease.
Other options:
- Option 'A', Hydra, is a multicellular organism belonging to the phylum Cnidaria. It does not possess a flagellum.
- Option 'C', Paramecium, is a ciliate protozoan that moves using hair-like structures called cilia, not a flagellum.
- Option 'D', Amoeba, is a unicellular protozoan that moves using temporary extensions of its cell membrane called pseudopodia. It also lacks a flagellum.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B', Leishmania, as it is a protozoan that possesses a flagellum at one end of its cell.
The ratio of number of chromosomes in a human zygote and a human sperm is- a)2 : 1
- b)3 : 1
- c)1 : 2
- d)1 : 3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of number of chromosomes in a human zygote and a human sperm is
a)
2 : 1
b)
3 : 1
c)
1 : 2
d)
1 : 3
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
The reproductive cells contain only half the number of chromosomes as compared to the normal body cells of an organism. The human sperm and egg have 23 chromosomes each. So when they fuse together, the zygote formed has 23 + 23 = 46 chromosomes. So the required ratio is 46 : 23, i.e., 2 : 1.
The offsprings formed as a result of sexual reproduction exhibit more variations because - a)Sexual reproduction is lengthy process
- b)Genetic material comes from two parents of some species
- c)Genetic material comes from two parents of different species
- d)Genetic material comes from many parents
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The offsprings formed as a result of sexual reproduction exhibit more variations because
a)
Sexual reproduction is lengthy process
b)
Genetic material comes from two parents of some species
c)
Genetic material comes from two parents of different species
d)
Genetic material comes from many parents
|
|
Samta patel answered |
Explanation:
Sexual reproduction is a process in which genetic material from two parents combines to form offspring. This process leads to more variations in the offspring compared to asexual reproduction, where offspring are genetically identical to the parent. The correct answer to this question is option 'B', which states that the genetic material comes from two parents of some species. This is the main reason why sexual reproduction results in more variations in the offspring.
Genetic Material from Two Parents:
In sexual reproduction, the offspring inherit genetic material from both the male and female parent. Each parent contributes half of their genetic material, which contains genes responsible for various traits. This combination of genetic material from two parents results in new combinations of genes in the offspring, leading to variations.
Recombination of Genes:
During sexual reproduction, the genetic material from both parents undergoes a process called recombination. This is when the chromosomes from each parent pair up and exchange segments of DNA. This exchange of genetic material leads to the shuffling and mixing of genes, creating new combinations that were not present in either parent. As a result, the offspring inherit a unique set of genes, contributing to their individual characteristics and variations.
Independent Assortment:
Another factor that contributes to variations in sexual reproduction is independent assortment. During the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells), the chromosomes segregate randomly. This means that each gamete receives a random assortment of chromosomes from the parent. As a result, the offspring inherit a unique combination of chromosomes, further increasing the genetic variations.
Mutation:
Although not directly related to sexual reproduction, mutations also play a role in generating genetic variations. Mutations are spontaneous changes in the DNA sequence and can occur in any organism. These mutations can be inherited by the offspring through sexual reproduction, contributing to additional variations.
Overall, sexual reproduction leads to more variations in offspring because it involves the combination and recombination of genetic material from two parents. This process introduces new gene combinations and increases genetic diversity, ultimately resulting in a wide range of phenotypic variations among the offspring.
Sexual reproduction is a process in which genetic material from two parents combines to form offspring. This process leads to more variations in the offspring compared to asexual reproduction, where offspring are genetically identical to the parent. The correct answer to this question is option 'B', which states that the genetic material comes from two parents of some species. This is the main reason why sexual reproduction results in more variations in the offspring.
Genetic Material from Two Parents:
In sexual reproduction, the offspring inherit genetic material from both the male and female parent. Each parent contributes half of their genetic material, which contains genes responsible for various traits. This combination of genetic material from two parents results in new combinations of genes in the offspring, leading to variations.
Recombination of Genes:
During sexual reproduction, the genetic material from both parents undergoes a process called recombination. This is when the chromosomes from each parent pair up and exchange segments of DNA. This exchange of genetic material leads to the shuffling and mixing of genes, creating new combinations that were not present in either parent. As a result, the offspring inherit a unique set of genes, contributing to their individual characteristics and variations.
Independent Assortment:
Another factor that contributes to variations in sexual reproduction is independent assortment. During the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells), the chromosomes segregate randomly. This means that each gamete receives a random assortment of chromosomes from the parent. As a result, the offspring inherit a unique combination of chromosomes, further increasing the genetic variations.
Mutation:
Although not directly related to sexual reproduction, mutations also play a role in generating genetic variations. Mutations are spontaneous changes in the DNA sequence and can occur in any organism. These mutations can be inherited by the offspring through sexual reproduction, contributing to additional variations.
Overall, sexual reproduction leads to more variations in offspring because it involves the combination and recombination of genetic material from two parents. This process introduces new gene combinations and increases genetic diversity, ultimately resulting in a wide range of phenotypic variations among the offspring.
In which one of the following birth control methods, a small portion of oviducts of a woman is removed by surgical operation and the cut ends are ligated?- a)Copper-T
- b)Vasectomy
- c)Tubectomy
- d)Diaphragm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which one of the following birth control methods, a small portion of oviducts of a woman is removed by surgical operation and the cut ends are ligated?
a)
Copper-T
b)
Vasectomy
c)
Tubectomy
d)
Diaphragm
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
The surgical method of birth control in females is termed as tubectomy.
In asexual reproduction, two offsprings having the same genetic material and the same body features are called- a)Twins
- b)Clones
- c)Chromosomes
- d)Callus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In asexual reproduction, two offsprings having the same genetic material and the same body features are called
a)
Twins
b)
Clones
c)
Chromosomes
d)
Callus
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
The genetically identical offsprings formed by asexual reproduction are called clones.
Reproduction is essential for living organism in order to- a)Keep the individual organ alive
- b)Maintain growth
- c)Continue the species for ever
- d)Fulfill their energy requirements
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Reproduction is essential for living organism in order to
a)
Keep the individual organ alive
b)
Maintain growth
c)
Continue the species for ever
d)
Fulfill their energy requirements
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
Reproduction is essential for all organisms for continuation of the species generation after generation and to maintain a steady species population, so that, it does not become extinct.
One of the following process does not lead to the formation of clones. This is- a)Fragmentation
- b)Fission
- c)Fertilisation
- d)Tissue culture
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the following process does not lead to the formation of clones. This is
a)
Fragmentation
b)
Fission
c)
Fertilisation
d)
Tissue culture
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
Fertilisation is the fusion of two gametes in a sexual reproduction. It produces genetically different offsprings and does not lead to the formation of clones.
Binary fission describes the type of reproduction where the organism divides to form- a)Many buds
- b)Two daughters
- c)Two hyphal
- d)Many spores
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Binary fission describes the type of reproduction where the organism divides to form
a)
Many buds
b)
Two daughters
c)
Two hyphal
d)
Many spores
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
In binary fission, a single-celled organism divides into two daughter cells that are identical to their parent.
In a flower, the parts that produce male and female gametes are respectively:- a)Filament and stigma
- b)Anther and ovary
- c)Stamen and style
- d)Sepal and anther
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a flower, the parts that produce male and female gametes are respectively:
a)
Filament and stigma
b)
Anther and ovary
c)
Stamen and style
d)
Sepal and anther
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Anther is part of stamen (male sex organ) that produce pollen (male gamete). Ovary is inferior part of pistil (female sex organ) which contains ovule. Female gametophyte develops in ovule.
The figure given alongside show the human male reproductive organs, which structures make sperms and seminal fluid?
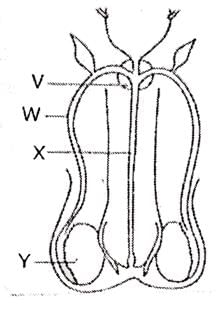
- a)X makes sperms and W makes seminal fluid
- b)Y makes sperms and V makes seminal fluid
- c)V makes sperms and X makes seminal fluid
- d)W makes sperms and Y makes seminal fluid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The figure given alongside show the human male reproductive organs, which structures make sperms and seminal fluid?


a)
X makes sperms and W makes seminal fluid
b)
Y makes sperms and V makes seminal fluid
c)
V makes sperms and X makes seminal fluid
d)
W makes sperms and Y makes seminal fluid
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
Y represents the testes that produce sperms and V represents the prostrate gland that produces seminal fluid.
In human males, the testes lie in the scrotum outside the body because it helps in the- a)Process of mating
- b)Easy transfer of sperms
- c)Formation of sperms
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In human males, the testes lie in the scrotum outside the body because it helps in the
a)
Process of mating
b)
Easy transfer of sperms
c)
Formation of sperms
d)
All the above
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
In human males, testes descend into a muscular bag called as the scrotum, which lies outside the body cavity, before birth and remains there for rest of life because sperm production occurs at a temperature lower than the body temperature.
In spirogyra asexual reproduction takes place by - a)Division of a cell into two cells
- b)Division of a cell into many cells
- c)Breaking up of filaments into smaller bits
- d)Formation of a large number of buds
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In spirogyra asexual reproduction takes place by
a)
Division of a cell into two cells
b)
Division of a cell into many cells
c)
Breaking up of filaments into smaller bits
d)
Formation of a large number of buds
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Spirogyra reproduces asexually by fragmentation and sexually by conjugation. In the fragmentation method, Spirogyra breaks into two or more segments and each segment forms a new organism.
The sexually transmitted disease which is caused by bacteria is- a)Malaria
- b)Gonorrhoea
- c)AIDS
- d)Diarrhoea
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The sexually transmitted disease which is caused by bacteria is
a)
Malaria
b)
Gonorrhoea
c)
AIDS
d)
Diarrhoea
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Gonorrhea, syphilis and chlamydia are examples of STIs that are caused by bacteria.
Which of the following is not a part of human male reproductive system. This is- a)Tesrtis
- b)Seminal vesicle
- c)Prostrate gland
- d)Oviduct
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a part of human male reproductive system. This is
a)
Tesrtis
b)
Seminal vesicle
c)
Prostrate gland
d)
Oviduct
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
Oviducts is the tube through which an ovum or egg passes through the ovary.
The disease kala-azar is caused by a microorganism is known as- a)Leech
- b)Leishmania
- c)Planaria
- d)Plasmodium
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The disease kala-azar is caused by a microorganism is known as
a)
Leech
b)
Leishmania
c)
Planaria
d)
Plasmodium
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
Visceral leishmaniasis (VL), also known as kala-azar, black fever, and Dumdum fever, is the most severe form of leishmaniasis and, without proper diagnosis and treatment, is associated with high fatality. Leishmaniasis is a disease caused by protozoan parasites of the genus Leishmania.
The number of chromosomes in parents and offsprings of a particular species remains constant due to - a)Doubling of chromosomes after gamete formation
- b)Halving of chromosomes after gamete formation
- c)Doubling of chromosomes after zygote formation
- d)Halving of chromosomes during gamete formation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of chromosomes in parents and offsprings of a particular species remains constant due to
a)
Doubling of chromosomes after gamete formation
b)
Halving of chromosomes after gamete formation
c)
Doubling of chromosomes after zygote formation
d)
Halving of chromosomes during gamete formation
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
The gametes have half the number of chromosomes. After their fusion, the zygote thus formed has a full set of chromosomes. Therefore, the numbers of chromosomes in parents and offsprings of a particular species remain constant.
The length of pollen tube depends on the distance between- a)Upper surface of stigma and lower part of style
- b)Pollen grain and upper surface of stigma
- c)Pollen grain on upper surface of stigma and ovule
- d)Pollen grain in anther and upper surface of stigma
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The length of pollen tube depends on the distance between
a)
Upper surface of stigma and lower part of style
b)
Pollen grain and upper surface of stigma
c)
Pollen grain on upper surface of stigma and ovule
d)
Pollen grain in anther and upper surface of stigma
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Length of pollen tube depends upon distance of pollen on stigma and ovule because after pollination pollen germinates and form pollen tube that reaches upto ovule in ovary and release male gamete to fuse with female gamete.
Chapter doubts & questions for Reproduction in Organism - Olympiad Preparation for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Reproduction in Organism - Olympiad Preparation for Class 10 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









