All Exams >
Grade 9 >
AP Biology >
All Questions
All questions of Unit 5: Heredity for Grade 9 Exam
Homo sapiens arose in Africa and moved across continents and developed into distinct races during?- a)Ice age between 75000-10,000 years ago
- b)Ice age between 5000-6000 years ago
- c)Stone age between 10,000 years ago
- d)Stone age between 2000-4000 years ago
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Homo sapiens arose in Africa and moved across continents and developed into distinct races during?
a)
Ice age between 75000-10,000 years ago
b)
Ice age between 5000-6000 years ago
c)
Stone age between 10,000 years ago
d)
Stone age between 2000-4000 years ago
|
|
Kushagra Budhgaya answered |
Answer A is correct. why don't you go through the ncert once.
Which of the following bird will be called most successfully evolved?- a)Lays 5 eggs, 5 hatch and 5 reproduce
- b)Lays 9 eggs, 9 hatch and 3 reproduce
- c)Lays 2 eggs, 2 hatch and 2 reproduce
- d)Lays 10 eggs, 5 hatch and 4 reproduce
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following bird will be called most successfully evolved?
a)
Lays 5 eggs, 5 hatch and 5 reproduce
b)
Lays 9 eggs, 9 hatch and 3 reproduce
c)
Lays 2 eggs, 2 hatch and 2 reproduce
d)
Lays 10 eggs, 5 hatch and 4 reproduce

|
Rupesh Ganguli answered |
Correct answer is a because according to Darwin the who leaves more Number of reproducing individuals are more successful
Which of the following organs in man is vestigial : [CPMT 77]- a)Pinna
- b)Wisdom tooth
- c)Fossa ovalis
- d)Ileum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following organs in man is vestigial : [CPMT 77]
a)
Pinna
b)
Wisdom tooth
c)
Fossa ovalis
d)
Ileum

|
Surya answered |
Vestigial organs means evidence for the evolution.. so as per the given option...wisdom teeth is the vestigial organ...so the option B is correct...
Dinosaurs originated : [CPMT 86]- a)After evolution of mammals
- b)With mammals
- c)Much before mammals
- d)Before mammals and they formed them
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Dinosaurs originated : [CPMT 86]
a)
After evolution of mammals
b)
With mammals
c)
Much before mammals
d)
Before mammals and they formed them
|
|
Siddiq Zayeda answered |
Mammals appeared on the earth long before the extinction of the dinosaurs; in fact, dinosaurs and mammals originated within 10 million years of each other, in the late Triassic about 200 million years ago.........
Fossils are most commonly preserved in______.- a)Sedimentary rocks
- b)Igneous rocks
- c)Metamorphic rocks
- d)Any type of rock
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Fossils are most commonly preserved in______.
a)
Sedimentary rocks
b)
Igneous rocks
c)
Metamorphic rocks
d)
Any type of rock

|
Prerana M N answered |
Sedimentary rocks are mostly involved in forming fossils, owing to the way in which they are formed.
Homologous organs have :[MP PMT 01]- a)Similar origin and similar or dissimilar functions
- b)Dissimilar origin and structure
- c)Dissimilar origin and function
- d)Dissimilar origin and similar functions
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Homologous organs have :
[MP PMT 01]
a)
Similar origin and similar or dissimilar functions
b)
Dissimilar origin and structure
c)
Dissimilar origin and function
d)
Dissimilar origin and similar functions
|
|
Afifa Aaliya answered |
Organs such as bats of wings, wings of birds, seals of flippers, arms of humans have common underlying anatomy. That was present in last common Ancestors. forelimbs are homologous organs. homology refers to the traits inherited by two different organisms from common ancestry. so it has similar origin and different or similar functions.
So option " A " is correct answer.
So option " A " is correct answer.
Who called humans as Homo sapiens wiseman?- a)Carolus Linnaeus
- b)Hugo de Vries
- c)Joseph Walter
- d)Charles Darwin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who called humans as Homo sapiens wiseman?
a)
Carolus Linnaeus
b)
Hugo de Vries
c)
Joseph Walter
d)
Charles Darwin
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
The first scientific name of man was given by Carolus Linnaeus. He called them Homo sapiens wiseman. He added wiseman to the name as it was the only organism with high brain capacity.
Ancestor of man who first time showed bipedal movement [CPMT 80]- a)Cro-magnon
- b)Australopithecus
- c)Java apeman
- d)Peking man
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ancestor of man who first time showed bipedal movement
[CPMT 80]
a)
Cro-magnon
b)
Australopithecus
c)
Java apeman
d)
Peking man
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Bipedalism evolved well before the large human brain or the development of stone tools. Recent evidence regarding modern human sexual dimorphism (physical differences between male and female) in the lumbar spine has been seen in pre-modern primates such as Australopithecus africanus.
There are no life in which era :[CPMT 80]- a)Messozoic era
- b)Palaeozoic era
- c)Coenozoic era
- d)Azoic era
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
There are no life in which era :
[CPMT 80]
a)
Messozoic era
b)
Palaeozoic era
c)
Coenozoic era
d)
Azoic era
|
|
Ayeshashreya Mishra answered |
During Azoic era, the earth was with out plants and animals. The rock layers which were formed soon after azoic era contains the remains of limy sea plants.The word "Azoic" is derived from the Greek, a- meaning without and zoon meaning animal (or living being), it was first used to mean without life.....
An era ''age of birds and mammals'' is : [CPMT 93]- a)Mesozoic
- b)Palaecozoic
- c)Coenozoic
- d)Cretaceous
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An era ''age of birds and mammals'' is : [CPMT 93]
a)
Mesozoic
b)
Palaecozoic
c)
Coenozoic
d)
Cretaceous
|
|
Afifa Aaliya answered |
The Cenozoic era is the most recent of the three major sub division of the animal history. The other two are the Mesozoic and Peliozoic eras. The Cenozoic era only about 65 million years. From the end of the Cretaceous period and the extension of non avian dinosaurs to the present. The Cenozoic is sometimes called as age of mammals because the largest land animals have been mammals during that time.
So option " C " is correct answer.
So option " C " is correct answer.
Theory of spontaneous generation believed that : [NCERT 773]
- a)Life of originated from othe similar organisms or spontaneously
- b)life arises from the non-living matter
- c)Life originated from similar organisms
- d)Life originated from air
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Theory of spontaneous generation believed that : [NCERT 773]
a)
Life of originated from othe similar organisms or spontaneously
b)
life arises from the non-living matter
c)
Life originated from similar organisms
d)
Life originated from air
|
|
Mayank Chavan answered |
Believers of spontaneous generation believed that life originated only spontaneously. Let's understand this statement in detail.
Explanation:
Spontaneous generation is the theory that proposed that living organisms could arise from non-living matter under certain conditions. This theory was widely accepted for many centuries, until it was disproven by Louis Pasteur in the mid-19th century.
a) Life originated from other similar organisms or spontaneously:
According to the theory of spontaneous generation, life could arise either from other similar organisms or spontaneously from non-living matter. However, this is not the correct answer as the believers of spontaneous generation did not consider the possibility of life originating from other similar organisms.
b) Life originated only spontaneously:
This is the correct answer. The believers of spontaneous generation argued that life could only originate spontaneously from non-living matter. They believed that under certain conditions, such as the presence of air, moisture, and organic material, life could arise spontaneously.
c) Life originated from similar organisms:
This is not the correct answer. The believers of spontaneous generation did not consider the possibility of life originating from similar organisms. They believed that life could only arise from non-living matter.
d) Life originated from air:
While air was considered to be one of the necessary conditions for spontaneous generation, it was not believed to be the source of life. The believers of spontaneous generation thought that life could originate from the combination of non-living matter, air, and other environmental factors.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'B' - the believers of spontaneous generation believed that life originated only spontaneously from non-living matter under certain conditions. However, it's important to note that this theory has been disproven by scientific experiments and observations, and the modern understanding of life's origin is based on the principles of biogenesis, which states that life only arises from pre-existing life.
Explanation:
Spontaneous generation is the theory that proposed that living organisms could arise from non-living matter under certain conditions. This theory was widely accepted for many centuries, until it was disproven by Louis Pasteur in the mid-19th century.
a) Life originated from other similar organisms or spontaneously:
According to the theory of spontaneous generation, life could arise either from other similar organisms or spontaneously from non-living matter. However, this is not the correct answer as the believers of spontaneous generation did not consider the possibility of life originating from other similar organisms.
b) Life originated only spontaneously:
This is the correct answer. The believers of spontaneous generation argued that life could only originate spontaneously from non-living matter. They believed that under certain conditions, such as the presence of air, moisture, and organic material, life could arise spontaneously.
c) Life originated from similar organisms:
This is not the correct answer. The believers of spontaneous generation did not consider the possibility of life originating from similar organisms. They believed that life could only arise from non-living matter.
d) Life originated from air:
While air was considered to be one of the necessary conditions for spontaneous generation, it was not believed to be the source of life. The believers of spontaneous generation thought that life could originate from the combination of non-living matter, air, and other environmental factors.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'B' - the believers of spontaneous generation believed that life originated only spontaneously from non-living matter under certain conditions. However, it's important to note that this theory has been disproven by scientific experiments and observations, and the modern understanding of life's origin is based on the principles of biogenesis, which states that life only arises from pre-existing life.
By studying analogous structures we look for ______.- a)Similarities in appearance but differences in functions
- b)Similarities in appearance and function but different in structure
- c)Similarities in organ structure
- d)Similarities in cell make up
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
By studying analogous structures we look for ______.
a)
Similarities in appearance but differences in functions
b)
Similarities in appearance and function but different in structure
c)
Similarities in organ structure
d)
Similarities in cell make up
|
|
Jaideep Chakraborty answered |
Introduction:
Studying analogous structures helps us understand the similarities and differences between organisms that have evolved independently. These structures may have similar functions but different evolutionary origins. By studying these structures, we can gain insights into convergent evolution and the adaptations that organisms have developed to fulfill similar roles in their environments.
Explanation:
Similarities in appearance and function:
Analogous structures refer to structures in different organisms that have similar functions but different evolutionary origins. These structures have evolved independently in response to similar environmental pressures, resulting in similar functions. For example, the wings of birds and bats are analogous structures because they serve the same purpose of enabling flight, but they have evolved from different ancestral structures.
Differences in structure:
While analogous structures may have similar functions, they often have different underlying structures. This is because they have evolved through convergent evolution, where different species independently develop similar traits. For example, the wings of birds are composed of feathers, while the wings of bats are formed by a thin membrane of skin stretched between elongated fingers.
Importance of studying analogous structures:
1. Understanding convergent evolution: By studying analogous structures, we can gain insights into how different organisms have independently evolved similar traits. This helps us understand the process of convergent evolution and how organisms adapt to similar environmental challenges.
2. Determining evolutionary relationships: Analogous structures can sometimes be misleading when trying to determine evolutionary relationships between organisms. For example, dolphins and sharks have similar streamlined body shapes, but they are not closely related. By studying analogous structures in conjunction with other evidence such as genetics, scientists can more accurately determine evolutionary relationships.
3. Identifying adaptive traits: Analogous structures often represent adaptations to similar ecological niches. By studying these structures, we can identify the key traits that enable organisms to thrive in specific environments. This knowledge can be applied to various fields, such as biomimicry, where engineers and designers draw inspiration from nature to create innovative solutions.
Conclusion:
Studying analogous structures allows us to explore the fascinating world of convergent evolution. By comparing the similarities and differences in appearance, function, and structure of these structures, we can gain a deeper understanding of how organisms adapt to their environments and the complex processes of evolution.
Studying analogous structures helps us understand the similarities and differences between organisms that have evolved independently. These structures may have similar functions but different evolutionary origins. By studying these structures, we can gain insights into convergent evolution and the adaptations that organisms have developed to fulfill similar roles in their environments.
Explanation:
Similarities in appearance and function:
Analogous structures refer to structures in different organisms that have similar functions but different evolutionary origins. These structures have evolved independently in response to similar environmental pressures, resulting in similar functions. For example, the wings of birds and bats are analogous structures because they serve the same purpose of enabling flight, but they have evolved from different ancestral structures.
Differences in structure:
While analogous structures may have similar functions, they often have different underlying structures. This is because they have evolved through convergent evolution, where different species independently develop similar traits. For example, the wings of birds are composed of feathers, while the wings of bats are formed by a thin membrane of skin stretched between elongated fingers.
Importance of studying analogous structures:
1. Understanding convergent evolution: By studying analogous structures, we can gain insights into how different organisms have independently evolved similar traits. This helps us understand the process of convergent evolution and how organisms adapt to similar environmental challenges.
2. Determining evolutionary relationships: Analogous structures can sometimes be misleading when trying to determine evolutionary relationships between organisms. For example, dolphins and sharks have similar streamlined body shapes, but they are not closely related. By studying analogous structures in conjunction with other evidence such as genetics, scientists can more accurately determine evolutionary relationships.
3. Identifying adaptive traits: Analogous structures often represent adaptations to similar ecological niches. By studying these structures, we can identify the key traits that enable organisms to thrive in specific environments. This knowledge can be applied to various fields, such as biomimicry, where engineers and designers draw inspiration from nature to create innovative solutions.
Conclusion:
Studying analogous structures allows us to explore the fascinating world of convergent evolution. By comparing the similarities and differences in appearance, function, and structure of these structures, we can gain a deeper understanding of how organisms adapt to their environments and the complex processes of evolution.
Mortality in babies is an example of ______- a)Stabilizing selection
- b)Directional selection
- c)Disruptive selection
- d)Abortion selection
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mortality in babies is an example of ______
a)
Stabilizing selection
b)
Directional selection
c)
Disruptive selection
d)
Abortion selection
|
|
Dhruba Mukherjee answered |
Mortality in babies is an example of Stabilizing selection.
Stabilizing Selection:
Stabilizing selection, also known as normalizing selection or purifying selection, is a type of natural selection that favors the average individuals in a population while selecting against extreme phenotypes. This type of selection reduces genetic diversity and maintains the status quo, resulting in a stable population over time.
Explanation:
In the case of mortality in babies, stabilizing selection is at play. Stabilizing selection occurs when the average individuals in a population have a higher fitness compared to individuals with extreme phenotypes. In this context, babies with average characteristics have a higher chance of survival compared to those with extreme characteristics.
Factors that contribute to baby mortality can include genetic abnormalities, birth defects, premature birth, low birth weight, maternal health issues, and environmental factors. Babies with extreme phenotypes, such as severe genetic abnormalities or extremely low birth weight, may have a lower chance of survival due to the increased risks associated with these conditions.
By favoring babies with average characteristics, stabilizing selection helps to maintain a stable population over time. This is because extreme phenotypes are more likely to be less fit and less likely to survive to reproductive age, reducing their contribution to future generations.
Stabilizing selection in the context of baby mortality helps to ensure that the average characteristics of the population are maintained and that genetic diversity is not significantly reduced. It acts as a natural mechanism to maintain the health and stability of the population by selecting against extreme phenotypes that may have a higher risk of mortality.
In conclusion, mortality in babies is an example of stabilizing selection because it favors average individuals in a population while selecting against extreme phenotypes, helping to maintain a stable population over time.
Stabilizing Selection:
Stabilizing selection, also known as normalizing selection or purifying selection, is a type of natural selection that favors the average individuals in a population while selecting against extreme phenotypes. This type of selection reduces genetic diversity and maintains the status quo, resulting in a stable population over time.
Explanation:
In the case of mortality in babies, stabilizing selection is at play. Stabilizing selection occurs when the average individuals in a population have a higher fitness compared to individuals with extreme phenotypes. In this context, babies with average characteristics have a higher chance of survival compared to those with extreme characteristics.
Factors that contribute to baby mortality can include genetic abnormalities, birth defects, premature birth, low birth weight, maternal health issues, and environmental factors. Babies with extreme phenotypes, such as severe genetic abnormalities or extremely low birth weight, may have a lower chance of survival due to the increased risks associated with these conditions.
By favoring babies with average characteristics, stabilizing selection helps to maintain a stable population over time. This is because extreme phenotypes are more likely to be less fit and less likely to survive to reproductive age, reducing their contribution to future generations.
Stabilizing selection in the context of baby mortality helps to ensure that the average characteristics of the population are maintained and that genetic diversity is not significantly reduced. It acts as a natural mechanism to maintain the health and stability of the population by selecting against extreme phenotypes that may have a higher risk of mortality.
In conclusion, mortality in babies is an example of stabilizing selection because it favors average individuals in a population while selecting against extreme phenotypes, helping to maintain a stable population over time.
Links between organisms that show branching pattern of evolutionary relationships are shown by- a)Phylogenetic trees
- b)Living fossils
- c)Comparative embryology
- d)Two fossil layers
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Links between organisms that show branching pattern of evolutionary relationships are shown by
a)
Phylogenetic trees
b)
Living fossils
c)
Comparative embryology
d)
Two fossil layers
|
|
Krithika Kumar answered |
Phylogenetic trees are diagrams that show the evolutionary relationships between different organisms. They are used to display the branching pattern of evolutionary relationships between organisms. The diagram looks like a tree with branches that represent different groups of organisms. These branches are called clades, and they represent groups of organisms that have descended from a common ancestor.
Phylogenetic trees are constructed based on a variety of data, including:
1. Morphological characteristics: The physical features of organisms, such as their shape, size, and structure.
2. Molecular data: DNA and RNA sequences are used to compare the genetic makeup of different organisms.
3. Fossil records: The study of fossils provides evidence of the evolutionary history of organisms.
Phylogenetic trees are an important tool for understanding the relationships between organisms and how they have evolved over time. They can be used to answer questions about the origins of different species and how they are related to one another.
In conclusion, phylogenetic trees are diagrams that show the branching pattern of evolutionary relationships between organisms. They are constructed based on a variety of data, including morphological characteristics, molecular data, and fossil records. They are an important tool for understanding the evolutionary history of organisms.
Phylogenetic trees are constructed based on a variety of data, including:
1. Morphological characteristics: The physical features of organisms, such as their shape, size, and structure.
2. Molecular data: DNA and RNA sequences are used to compare the genetic makeup of different organisms.
3. Fossil records: The study of fossils provides evidence of the evolutionary history of organisms.
Phylogenetic trees are an important tool for understanding the relationships between organisms and how they have evolved over time. They can be used to answer questions about the origins of different species and how they are related to one another.
In conclusion, phylogenetic trees are diagrams that show the branching pattern of evolutionary relationships between organisms. They are constructed based on a variety of data, including morphological characteristics, molecular data, and fossil records. They are an important tool for understanding the evolutionary history of organisms.
Evolution of birds and mammals occurred in : [CPMT 83]- a)Eocene and oligocene periods
- b)Silurian and Devonian periods
- c)Carboniferous and Permain epochs
- d)Jurasic period
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Evolution of birds and mammals occurred in :
[CPMT 83]
a)
Eocene and oligocene periods
b)
Silurian and Devonian periods
c)
Carboniferous and Permain epochs
d)
Jurasic period
|
|
Baishali Joshi answered |
The evolution of birds and mammals occurred in Jurassic period. The earliest birds were derived from a clade of theropod dinosaurs named paraves. Mammals evolved 10 times faster in the middle of the Jurassic period.
If a starfish possess 6 arms instead of 5, it is an example of :[CPMT 84]- a)Variation
- b)Metamorphosis
- c)Biogenesis
- d)Evolution
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a starfish possess 6 arms instead of 5, it is an example of :
[CPMT 84]
a)
Variation
b)
Metamorphosis
c)
Biogenesis
d)
Evolution
|
|
Afifa Aaliya answered |
If a starfish possess 6 arms instead of 5 it's an example of variations. Because it is in difference between cells individual organisms of any species caused either genetic difference. Variations may show physical appearance, metabolism, fertility.., etc..,
So option " A " is correct answer.
So option " A " is correct answer.
The mesozoic era of earth is called the : [CPMT 84]- a)Age of amphibians
- b)Age of armoured fishes
- c)Age of primitive man
- d)Age of ruling reptiles
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The mesozoic era of earth is called the : [CPMT 84]
a)
Age of amphibians
b)
Age of armoured fishes
c)
Age of primitive man
d)
Age of ruling reptiles
|
|
Yamuna Mani answered |
Mesozoic era or middle life era is the life diversified rapidly and giant reptiles,dinosaurs and other monstrous beads roamed the earth. so it is called as age of reptiles era.
Most recent man found as fossil was :[CPMT 73]- a)Java man
- b)Peking man
- c)Cro-magnon man
- d)Hiedelberg man
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most recent man found as fossil was :
[CPMT 73]
a)
Java man
b)
Peking man
c)
Cro-magnon man
d)
Hiedelberg man

|
Shreya Saini answered |
Most recent man found fossil was Cromagnon man. It lived during the upper Paleolithic period (40,000 to 10,000 years ago) in Europe. The fossils were discovered in 1868 in a shallow cave at Cro-Magnon in southwestern France. The body was generally heavy and solid, apparently with strong musculature. The forehead was straight, with slight brow ridges, and the face short and wide. Cro-Magnons were the first humans to have a prominent chin. The brain capacity was about 1,600 cc. So, option c is correct.
Branch of biology which deals with fossils :[CPMT 75]- a)Ethology
- b)Ecology
- c)Palaeontology
- d)Ormitholgoy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Branch of biology which deals with fossils :
[CPMT 75]
a)
Ethology
b)
Ecology
c)
Palaeontology
d)
Ormitholgoy
|
|
Debolina Chopra answered |
Palaeontology is the branch of biology that deals with fossils. Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of ancient organisms that provide valuable information about the history of life on Earth. Palaeontologists study fossils to understand the evolution, diversity, and ecological interactions of organisms that lived in the past.
1. Definition of Palaeontology:
Palaeontology is the scientific study of fossils, including their formation, identification, classification, and interpretation. It combines elements of biology, geology, and paleoecology to reconstruct the ancient history of life on Earth.
2. Importance of Fossils:
Fossils are crucial evidence for understanding the evolutionary processes that have shaped life on our planet. They provide insights into the anatomy, behavior, and ecology of extinct organisms, as well as the past environments in which they lived. Fossils also help in dating rock layers, determining ancient climate conditions, and documenting the history of biodiversity.
3. Scope of Palaeontology:
Palaeontology covers a wide range of topics, including:
- Taxonomy: Classifying and identifying fossil organisms.
- Morphology: Studying the structure and form of fossil remains.
- Phylogeny: Reconstructing the evolutionary relationships between different species.
- Paleobiology: Understanding the biology and behavior of extinct organisms.
- Paleoecology: Investigating ancient ecosystems and their interactions.
- Biostratigraphy: Using fossils to date and correlate rock layers.
- Taphonomy: Examining the processes that lead to fossilization.
4. Methods and Techniques:
Palaeontologists use various methods and techniques to study fossils, including:
- Excavation: Careful removal of fossils from their geological context.
- Preparation: Cleaning and preserving fossil specimens for further analysis.
- Comparative Anatomy: Comparing fossil remains with living organisms to infer their characteristics.
- Microscopy: Examining fossil structures at a microscopic level.
- Radiometric Dating: Using radioactive isotopes to determine the age of rocks and fossils.
- CT Scanning: Non-destructive imaging of fossils to reveal internal structures.
In conclusion, palaeontology is a branch of biology that focuses on the study of fossils. It plays a crucial role in understanding the history of life on Earth, providing insights into evolution, biodiversity, and ancient ecosystems.
1. Definition of Palaeontology:
Palaeontology is the scientific study of fossils, including their formation, identification, classification, and interpretation. It combines elements of biology, geology, and paleoecology to reconstruct the ancient history of life on Earth.
2. Importance of Fossils:
Fossils are crucial evidence for understanding the evolutionary processes that have shaped life on our planet. They provide insights into the anatomy, behavior, and ecology of extinct organisms, as well as the past environments in which they lived. Fossils also help in dating rock layers, determining ancient climate conditions, and documenting the history of biodiversity.
3. Scope of Palaeontology:
Palaeontology covers a wide range of topics, including:
- Taxonomy: Classifying and identifying fossil organisms.
- Morphology: Studying the structure and form of fossil remains.
- Phylogeny: Reconstructing the evolutionary relationships between different species.
- Paleobiology: Understanding the biology and behavior of extinct organisms.
- Paleoecology: Investigating ancient ecosystems and their interactions.
- Biostratigraphy: Using fossils to date and correlate rock layers.
- Taphonomy: Examining the processes that lead to fossilization.
4. Methods and Techniques:
Palaeontologists use various methods and techniques to study fossils, including:
- Excavation: Careful removal of fossils from their geological context.
- Preparation: Cleaning and preserving fossil specimens for further analysis.
- Comparative Anatomy: Comparing fossil remains with living organisms to infer their characteristics.
- Microscopy: Examining fossil structures at a microscopic level.
- Radiometric Dating: Using radioactive isotopes to determine the age of rocks and fossils.
- CT Scanning: Non-destructive imaging of fossils to reveal internal structures.
In conclusion, palaeontology is a branch of biology that focuses on the study of fossils. It plays a crucial role in understanding the history of life on Earth, providing insights into evolution, biodiversity, and ancient ecosystems.
Praying mantis is a good example of- a)Warning colouration
- b)Social insects
- c)Mullerianmimcry
- d)Camouflage
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Praying mantis is a good example of
a)
Warning colouration
b)
Social insects
c)
Mullerianmimcry
d)
Camouflage
|
|
Lakshmi Khanna answered |
< b="" />Camouflage< />
The correct answer for the given question is option 'D' - Camouflage. A praying mantis is a perfect example of an organism that uses camouflage as a defense mechanism. Camouflage refers to the ability of an organism to blend in with its surroundings, making it difficult for predators to detect or capture it. Praying mantises have evolved unique adaptations that allow them to effectively camouflage in their environment, making them highly successful predators themselves.
Adaptations for Camouflage
Praying mantises have several physical adaptations that help them camouflage effectively:
1. Body Shape: Praying mantises have an elongated body shape that resembles sticks or plant stems, allowing them to blend in with the surrounding vegetation. Their thin bodies and elongated legs further aid in mimicking plant structures.
2. Coloration: Praying mantises come in a range of colors including green, brown, and even pink. These colors help them match the color of their surroundings, whether it be leaves, twigs, or flowers. Some species can even change their coloration to match their environment.
3. Texture: The texture of a praying mantis' exoskeleton also contributes to its camouflage. The rough and uneven surface helps break up its outline, making it harder for predators to spot them.
Benefits of Camouflage
Camouflage provides several benefits to praying mantises, including:
1. Predator Avoidance: By blending in with their surroundings, praying mantises can avoid being detected by predators such as birds, lizards, and even other insects. This allows them to hide in plain sight and increases their chances of survival.
2. Ambush Predation: Praying mantises are ambush predators, relying on their camouflage to remain undetected by their prey. They patiently wait for unsuspecting insects to come within striking distance, using their cryptic coloration and immobility to remain hidden until the opportune moment.
3. Reproductive Success: Camouflage also plays a role in the reproductive success of praying mantises. Females, in particular, benefit from their camouflage as it allows them to hide from males after mating, reducing the risk of cannibalism.
In conclusion, the praying mantis is an excellent example of an organism that utilizes camouflage as a defense mechanism. Its unique adaptations in body shape, coloration, and texture allow it to blend seamlessly with its surroundings, providing benefits such as predator avoidance and successful predation.
The correct answer for the given question is option 'D' - Camouflage. A praying mantis is a perfect example of an organism that uses camouflage as a defense mechanism. Camouflage refers to the ability of an organism to blend in with its surroundings, making it difficult for predators to detect or capture it. Praying mantises have evolved unique adaptations that allow them to effectively camouflage in their environment, making them highly successful predators themselves.
Adaptations for Camouflage
Praying mantises have several physical adaptations that help them camouflage effectively:
1. Body Shape: Praying mantises have an elongated body shape that resembles sticks or plant stems, allowing them to blend in with the surrounding vegetation. Their thin bodies and elongated legs further aid in mimicking plant structures.
2. Coloration: Praying mantises come in a range of colors including green, brown, and even pink. These colors help them match the color of their surroundings, whether it be leaves, twigs, or flowers. Some species can even change their coloration to match their environment.
3. Texture: The texture of a praying mantis' exoskeleton also contributes to its camouflage. The rough and uneven surface helps break up its outline, making it harder for predators to spot them.
Benefits of Camouflage
Camouflage provides several benefits to praying mantises, including:
1. Predator Avoidance: By blending in with their surroundings, praying mantises can avoid being detected by predators such as birds, lizards, and even other insects. This allows them to hide in plain sight and increases their chances of survival.
2. Ambush Predation: Praying mantises are ambush predators, relying on their camouflage to remain undetected by their prey. They patiently wait for unsuspecting insects to come within striking distance, using their cryptic coloration and immobility to remain hidden until the opportune moment.
3. Reproductive Success: Camouflage also plays a role in the reproductive success of praying mantises. Females, in particular, benefit from their camouflage as it allows them to hide from males after mating, reducing the risk of cannibalism.
In conclusion, the praying mantis is an excellent example of an organism that utilizes camouflage as a defense mechanism. Its unique adaptations in body shape, coloration, and texture allow it to blend seamlessly with its surroundings, providing benefits such as predator avoidance and successful predation.
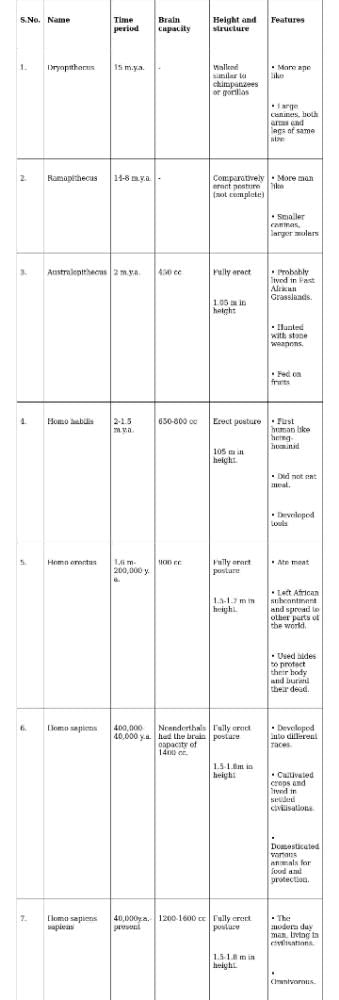
Cranial capacity of Cro-magnon man was :- a)900 cc
- b)1075 cc
- c)1450 cc
- d)1600 cc
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cranial capacity of Cro-magnon man was :
a)
900 cc
b)
1075 cc
c)
1450 cc
d)
1600 cc

|
User4284711 answered |
Cranial capacity of cro- magnan man is 1600-1650cc.. cranial capacity of neanderthal man is 1300-1450cc..
cranial capacity of Homo erectus is 600-700cc..
cranial capacity of modern man is 1200-1600cc..
cranial capacity of Homo habilis is 735cc...
cranial capacity of Homo erectus is 600-700cc..
cranial capacity of modern man is 1200-1600cc..
cranial capacity of Homo habilis is 735cc...
Characteristics of primitive monkey which was in the direction of evolution of man :- a)Thumb parallel to fingers
- b)32 teeth
- c)Prehensile tail
- d)Flat nose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Characteristics of primitive monkey which was in the direction of evolution of man :
a)
Thumb parallel to fingers
b)
32 teeth
c)
Prehensile tail
d)
Flat nose
|
|
Snehal Khanna answered |
Primates are heterodonts with four kinds of teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. The numbers of each kind of tooth vary by species. Humans, for example, have 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars, and 12 molars, for a total of 32 teeth.
Galapagos islands are connected with which scientist : [BHU 80]- a)Wallace
- b)Lamarck
- c)Malthus
- d)Darwin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Galapagos islands are connected with which scientist :
[BHU 80]
a)
Wallace
b)
Lamarck
c)
Malthus
d)
Darwin
|
|
Nayanika Patel answered |
The name of Charles Darwin and his famous book The Origin of Species will forever be linked with the Galapagos Islands. Although he was only in the Galapagos for five weeks in 1835, it was the wildlife that he saw there that inspired him to develop his Theory of Evolution.
Chapter doubts & questions for Unit 5: Heredity - AP Biology 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Unit 5: Heredity - AP Biology in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
AP Biology
130 videos|198 docs|114 tests
|