All Exams >
Computer Science Engineering (CSE) >
Computer Networks >
All Questions
All questions of Network Layer and Internetworking for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam
Which of the following assertions is FALSE about the Internet Protocol (IP)?- a)It is possible for a computer to have multiple IP addresses
- b)IP packets from the same source to the same destination can take different routes in the network
- c)IP ensures that a packet is discarded if it is unable to reach its destination within a given number of hops
- d)The packet source cannot set the route of an outgoing packets; the route is determined only by the routing tables in therouters on the way
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following assertions is FALSE about the Internet Protocol (IP)?
a)
It is possible for a computer to have multiple IP addresses
b)
IP packets from the same source to the same destination can take different routes in the network
c)
IP ensures that a packet is discarded if it is unable to reach its destination within a given number of hops
d)
The packet source cannot set the route of an outgoing packets; the route is determined only by the routing tables in therouters on the way
|
|
Anand Unni answered |
In computer networking, source routing, also called path addressing, allows a sender of a packet to partially or completely specify the route of the packet takes
through the network. In contrast, in non-source routing protocols, routers in the network determine the path based on the packet's destination.
through the network. In contrast, in non-source routing protocols, routers in the network determine the path based on the packet's destination.
Answer-D
Which one of the following is not a function of network layer?- a)routing
- b)inter-networking
- c)congestion control
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is not a function of network layer?
a)
routing
b)
inter-networking
c)
congestion control
d)
none of the mentioned
|
|
Avinash Mehta answered |
Network Layer :-
The network layer is responsible for the source-to-destination delivery of a packet, possibly across multiple networks (links).
Other functions of the network layer include the following :-
Logical addressing :- In order to identify each device on internetwork uniquely, network layer defines an addressing scheme.
Routing :- The network layer protocols determine which route is suitable from source to destination.
In OSPF, which protocol is used to discover neighbour routers automatically?- a)Link state protocol
- b)Error-correction protocol
- c)Routing information protocol
- d)Hello protocol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In OSPF, which protocol is used to discover neighbour routers automatically?
a)
Link state protocol
b)
Error-correction protocol
c)
Routing information protocol
d)
Hello protocol
|
|
Sanya Agarwal answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: Hello protocol is used to discover neighbour routers automatically.
Explanation: Hello protocol is used to discover neighbour routers automatically.
The network layer concerns with- a)bits
- b)frames
- c)packets
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The network layer concerns with
a)
bits
b)
frames
c)
packets
d)
none of the mentioned

|
Bijoy Kapoor answered |
The network layer is responsible for routing packets from the source to destination. The routing algorithm is the piece of software that decides where a packet goes next (e.g., which output line, or which node on a broadcast channel).
For connectionless networks, the routing decision is made for each datagram. For connection-oriented networks, the decision is made once, at circuit setup time.
RIP is- a)Protocol used for transmission of IP datagrams across a serial line
- b)Resource information protocol
- c)Protocol used to exchange information between the routers
- d)Protocol used to exchanger information between the layers
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
RIP is
a)
Protocol used for transmission of IP datagrams across a serial line
b)
Resource information protocol
c)
Protocol used to exchange information between the routers
d)
Protocol used to exchanger information between the layers
|
|
Prisha Sharma answered |
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a routing protocol based on the distance vector algorithm, In this each router periodically shares its knowledge about the entire network with its neighbours.
Which of the following fields of an IP header is NOT modified by a typical IP router?- a)Check sum
- b)Source address
- c)Time to Live (TTL)
- d)Length
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following fields of an IP header is NOT modified by a typical IP router?
a)
Check sum
b)
Source address
c)
Time to Live (TTL)
d)
Length
|
|
Nilesh Jain answered |
Header Fields of an IP Packet
An IP (Internet Protocol) packet consists of a header followed by the data payload. The header contains various fields that provide information about the packet and help in routing it across the network. These fields are typically modified by IP routers as the packet is forwarded from the source to the destination.
Fields Modified by a Typical IP Router
1. Checksum: The IP header includes a checksum field which is used to detect errors in the packet during transmission. The checksum is calculated by the sender and verified by each router along the path. If errors are detected, the packet is discarded. Routers may update the checksum field if modifications are made to the IP header.
2. Source Address: The source address field in the IP header specifies the IP address of the sender. As the packet is forwarded through different routers, the source address remains unchanged. It is an essential field as it helps in identifying the origin of the packet.
3. Time to Live (TTL): The TTL field in the IP header indicates the maximum number of hops or routers the packet can traverse before being discarded. Each router that processes the packet decrements the TTL value by 1. If the TTL reaches 0, the packet is dropped. Routers must update the TTL field as they forward the packet to ensure its proper handling.
Field NOT Modified by a Typical IP Router
- Length: The length field in the IP header specifies the total length of the IP packet, including both the header and the data payload. This field is set by the sender and remains unchanged throughout the routing process. Routers do not modify the length field as they forward the packet.
Conclusion
In summary, among the given options, the field that is NOT modified by a typical IP router is the source address. The checksum, TTL, and length fields may be updated or modified by routers as they process and forward the IP packet.
An IP (Internet Protocol) packet consists of a header followed by the data payload. The header contains various fields that provide information about the packet and help in routing it across the network. These fields are typically modified by IP routers as the packet is forwarded from the source to the destination.
Fields Modified by a Typical IP Router
1. Checksum: The IP header includes a checksum field which is used to detect errors in the packet during transmission. The checksum is calculated by the sender and verified by each router along the path. If errors are detected, the packet is discarded. Routers may update the checksum field if modifications are made to the IP header.
2. Source Address: The source address field in the IP header specifies the IP address of the sender. As the packet is forwarded through different routers, the source address remains unchanged. It is an essential field as it helps in identifying the origin of the packet.
3. Time to Live (TTL): The TTL field in the IP header indicates the maximum number of hops or routers the packet can traverse before being discarded. Each router that processes the packet decrements the TTL value by 1. If the TTL reaches 0, the packet is dropped. Routers must update the TTL field as they forward the packet to ensure its proper handling.
Field NOT Modified by a Typical IP Router
- Length: The length field in the IP header specifies the total length of the IP packet, including both the header and the data payload. This field is set by the sender and remains unchanged throughout the routing process. Routers do not modify the length field as they forward the packet.
Conclusion
In summary, among the given options, the field that is NOT modified by a typical IP router is the source address. The checksum, TTL, and length fields may be updated or modified by routers as they process and forward the IP packet.
Which packet is NOT an OSPF packet type?- a)LSU
- b)LSR
- c)DBD
- d)Query
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which packet is NOT an OSPF packet type?
a)
LSU
b)
LSR
c)
DBD
d)
Query
|
|
Shubham Ghoshal answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: Query packet is NOT an OSPF packet type.
Explanation: Query packet is NOT an OSPF packet type.
Which of the following is related to ipconfig in Microsoft Windows ?- a)Display all current TCP/IP network configuration values
- b)Modify DHCP settings
- c)Modify DNS settings
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is related to ipconfig in Microsoft Windows ?
a)
Display all current TCP/IP network configuration values
b)
Modify DHCP settings
c)
Modify DNS settings
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Harshad Mukherjee answered |
Answer: d
Explanation: None.
Explanation: None.
Who can send ICMP error-reporting messages?
- a)Routers
- b)Destination hosts
- c)Source host
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Who can send ICMP error-reporting messages?
a)
Routers
b)
Destination hosts
c)
Source host
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Krithika Kaur answered |
Both router and destination host can send ICMP error-reporting message to inform the source host about any failure or error occurred in packet.
Distance vector protocols use the concept of split horizon, but link-state routing protocols, such as OSPF, do not. - a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Distance vector protocols use the concept of split horizon, but link-state routing protocols, such as OSPF, do not.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Shubham Ghoshal answered |
Answer: b
Explanation: Distance vector protocols use the concept of split horizon, but link-state routing protocols, such as OSPF, do not use this.
Explanation: Distance vector protocols use the concept of split horizon, but link-state routing protocols, such as OSPF, do not use this.
__________ command is used to manipulate TCP/IP routing table.- a)route
- b)Ipconfig
- c)Ifconfig
- d)Traceroute
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
__________ command is used to manipulate TCP/IP routing table.
a)
route
b)
Ipconfig
c)
Ifconfig
d)
Traceroute
|
|
Tanvi Datta answered |
The "route" command is used to manipulate the TCP/IP routing table.
The TCP/IP routing table is a critical component of networking that helps determine the path that network traffic takes from one network to another. It contains a list of routes, each specifying a destination network and the next-hop IP address or interface through which the traffic should be forwarded.
The "route" command is a command-line utility that allows users to view and manipulate the routing table on a computer. It is available on most operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Usage of the "route" command:
The "route" command can be used with various options and parameters to perform different tasks. Some of the commonly used options include:
1. View the routing table: The command "route print" displays the current routing table on the system. It provides information such as the destination network, subnet mask, gateway, interface, and metric.
2. Add a new route: The command "route add" is used to add a new route to the routing table. It requires specifying the destination network, subnet mask, gateway, and interface. For example, "route add 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.1" adds a route for the network 192.168.1.0/24 using the gateway 192.168.0.1.
3. Delete an existing route: The command "route delete" is used to remove a route from the routing table. It requires specifying the destination network and subnet mask. For example, "route delete 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0" deletes the route for the network 192.168.1.0/24.
4. Modify an existing route: The command "route change" is used to modify the properties of an existing route. It requires specifying the destination network, subnet mask, gateway, and interface. For example, "route change 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.2" changes the gateway for the route to 192.168.0.2.
Summary:
In summary, the "route" command is a powerful tool used to manipulate the TCP/IP routing table. It allows users to view, add, delete, and modify routes in the routing table, which determines how network traffic is routed.
The TCP/IP routing table is a critical component of networking that helps determine the path that network traffic takes from one network to another. It contains a list of routes, each specifying a destination network and the next-hop IP address or interface through which the traffic should be forwarded.
The "route" command is a command-line utility that allows users to view and manipulate the routing table on a computer. It is available on most operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Usage of the "route" command:
The "route" command can be used with various options and parameters to perform different tasks. Some of the commonly used options include:
1. View the routing table: The command "route print" displays the current routing table on the system. It provides information such as the destination network, subnet mask, gateway, interface, and metric.
2. Add a new route: The command "route add" is used to add a new route to the routing table. It requires specifying the destination network, subnet mask, gateway, and interface. For example, "route add 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.1" adds a route for the network 192.168.1.0/24 using the gateway 192.168.0.1.
3. Delete an existing route: The command "route delete" is used to remove a route from the routing table. It requires specifying the destination network and subnet mask. For example, "route delete 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0" deletes the route for the network 192.168.1.0/24.
4. Modify an existing route: The command "route change" is used to modify the properties of an existing route. It requires specifying the destination network, subnet mask, gateway, and interface. For example, "route change 192.168.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.2" changes the gateway for the route to 192.168.0.2.
Summary:
In summary, the "route" command is a powerful tool used to manipulate the TCP/IP routing table. It allows users to view, add, delete, and modify routes in the routing table, which determines how network traffic is routed.
In an IPv4 datagram, the M bit is 0, the value of HLEN is 10, the value of total length is 400 and the fragment offset value is300. The position of the datagram, the sequence numbers of the first and the last bytes of the payload, respectively are- a)Last fragment, 2400 and 2789
- b)First fragment, 2400 and 2759
- c)Last fragment, 2400 and 2759
- d)Middle fragment, 300 and 689
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an IPv4 datagram, the M bit is 0, the value of HLEN is 10, the value of total length is 400 and the fragment offset value is300. The position of the datagram, the sequence numbers of the first and the last bytes of the payload, respectively are
a)
Last fragment, 2400 and 2789
b)
First fragment, 2400 and 2759
c)
Last fragment, 2400 and 2759
d)
Middle fragment, 300 and 689
|
|
Arnab Desai answered |
M = 0 meaning no more fragments after this. Hence, its the last fragment.
IHL = internet header length = 10 x 8 = 2400 B coz 4 is the scaling factor for this field.
Total Length = 2400 B
Payload size = Total length - Header length = 400-40 = 360B
fragment offset = = represents how many Bytes are before this. 8 is the scaling factor here.
the first byte # = 2400
Last byte # = 300 x 8 = 2400 B first byte # + total bytes in payload - 1 = 2400+360-1=2759
option C is correct
IHL = internet header length = 10 x 8 = 2400 B coz 4 is the scaling factor for this field.
Total Length = 2400 B
Payload size = Total length - Header length = 400-40 = 360B
fragment offset = = represents how many Bytes are before this. 8 is the scaling factor here.
the first byte # = 2400
Last byte # = 300 x 8 = 2400 B first byte # + total bytes in payload - 1 = 2400+360-1=2759
option C is correct
In virtual circuit network each packet contains- a)full source and destination address
- b)a short VC number
- c)both (a) and (b)
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In virtual circuit network each packet contains
a)
full source and destination address
b)
a short VC number
c)
both (a) and (b)
d)
none of the mentioned
|
|
Raghav Joshi answered |
Explanation:
Virtual Circuit Network is a type of network in which a dedicated path is established between the source and destination before transmitting the data. In this network, each packet contains a short VC (Virtual Circuit) number instead of a full source and destination address.
Advantages of using VC number:
- It reduces the overhead of routing and forwarding packets by eliminating the need for address lookup in each router along the path.
- It provides faster and more efficient packet switching as the network can quickly route the packets based on the VC number.
Disadvantages of using VC number:
- It requires a lot of resources to establish and maintain the virtual circuit path, which can result in higher latency and delay in transmission.
- It can also lead to network congestion as multiple virtual circuits may share the same physical link.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'B', which states that each packet in a virtual circuit network contains a short VC number instead of a full source and destination address.
Virtual Circuit Network is a type of network in which a dedicated path is established between the source and destination before transmitting the data. In this network, each packet contains a short VC (Virtual Circuit) number instead of a full source and destination address.
Advantages of using VC number:
- It reduces the overhead of routing and forwarding packets by eliminating the need for address lookup in each router along the path.
- It provides faster and more efficient packet switching as the network can quickly route the packets based on the VC number.
Disadvantages of using VC number:
- It requires a lot of resources to establish and maintain the virtual circuit path, which can result in higher latency and delay in transmission.
- It can also lead to network congestion as multiple virtual circuits may share the same physical link.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'B', which states that each packet in a virtual circuit network contains a short VC number instead of a full source and destination address.
Internet access by transmitting digital data over the wires of a local telephone network is provided by- a)leased line
- b)digital subscriber line
- c)digital signal line
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Internet access by transmitting digital data over the wires of a local telephone network is provided by
a)
leased line
b)
digital subscriber line
c)
digital signal line
d)
none of the mentioned
|
|
Vaibhav Choudhary answered |
Answer: b
Explanation:
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) is the correct answer. It enables internet access by transmitting digital data over the wires of a local telephone network. DSL uses existing copper telephone lines and separates voice and data signals through different frequency bands. It provides high-speed internet and offers advantages such as wide availability, cost-effectiveness, and an always-on connection. Leased lines (option 'A') are dedicated point-to-point connections, while digital signal line (option 'C') is not a standard term in internet access technology.
Explanation:
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) is the correct answer. It enables internet access by transmitting digital data over the wires of a local telephone network. DSL uses existing copper telephone lines and separates voice and data signals through different frequency bands. It provides high-speed internet and offers advantages such as wide availability, cost-effectiveness, and an always-on connection. Leased lines (option 'A') are dedicated point-to-point connections, while digital signal line (option 'C') is not a standard term in internet access technology.
During normal IP packet forwarding by routers which of the following packet fields are updated?- a)IP header source address
- b)IP header destination address
- c)IP header TTL
- d)IP header check sum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During normal IP packet forwarding by routers which of the following packet fields are updated?
a)
IP header source address
b)
IP header destination address
c)
IP header TTL
d)
IP header check sum
|
|
Nilesh Mukherjee answered |
During forwarding of an IP packet by routers, the packet fields namely IP header source address and IP header destination address remains same whereas check own and TTL are updated.
How many bits internet address is assigned to each host on a TCP/IP internet which is used in all communication with the host?- a)16 bits
- b)32 bits
- c)48 bits
- d)64 bits
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many bits internet address is assigned to each host on a TCP/IP internet which is used in all communication with the host?
a)
16 bits
b)
32 bits
c)
48 bits
d)
64 bits
|
|
Krish Datta answered |
Internet address has 32 bits, which is assigned to each host for communication on network.
The frame relay committed information rate represents- a)Maximum data rate on the network
- b)Steady state data rate on the network
- c)Minimum data rate on the network
- d)Interface data rate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The frame relay committed information rate represents
a)
Maximum data rate on the network
b)
Steady state data rate on the network
c)
Minimum data rate on the network
d)
Interface data rate
|
|
Mainak Kulkarni answered |
Frame relay committed information rate represents minimum data rate on the network.
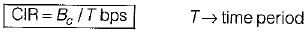
Here cumulative number of bits sent during the predefined period should not exceed Bc.
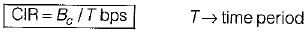
Here cumulative number of bits sent during the predefined period should not exceed Bc.
An example of a network layer is- a)Internet Protocol (IP)-ARPANET
- b)X.25 Packet Level Protocol (PLP)-ISO
- c)Source routing and domain naming-USENET
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of a network layer is
a)
Internet Protocol (IP)-ARPANET
b)
X.25 Packet Level Protocol (PLP)-ISO
c)
Source routing and domain naming-USENET
d)
All of these
|
|
Mira Rane answered |
Internet protocol (IP-ARPA NET, X.25 packet level protocoi-ISO and source routing and domain naming-USENET are example of network layer.
Multidestination routing- a)is same as broadcast routing
- b)contains the list of all destinations
- c)data is not sent by packets
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Multidestination routing
a)
is same as broadcast routing
b)
contains the list of all destinations
c)
data is not sent by packets
d)
none of the mentioned

|
Anirban Khanna answered |
Algorithms for effectively routing messages from a source to multiple destination nodes in a store-and-forward computer network are studied. The focus is on minimizing the network cost (NC), which is the sum of weights of the links in the routing path.
In the TCP/IP protocol suite, which one of the following is NOT part of the IP header?- a)Fragment Offset
- b)Source IP address
- c)Destination IP address
- d)Destination port number
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the TCP/IP protocol suite, which one of the following is NOT part of the IP header?
a)
Fragment Offset
b)
Source IP address
c)
Destination IP address
d)
Destination port number
|
|
Rounak Chavan answered |
D.) Destination Port number.
Why? Because the IP header has nothing to do with the port number.
Port numbers are used by the transport layer to ensure process to process delivery.
Why? Because the IP header has nothing to do with the port number.
Port numbers are used by the transport layer to ensure process to process delivery.
There is an Ethernet port on a router were assigned an IP address of 172.16.112.1/25. Which of the following would be the valid subnet address of this host?- a)172.16.112.0
- b)172.16.0.0
- c)172.16.96.0
- d)72.16.255.0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
There is an Ethernet port on a router were assigned an IP address of 172.16.112.1/25. Which of the following would be the valid subnet address of this host?
a)
172.16.112.0
b)
172.16.0.0
c)
172.16.96.0
d)
72.16.255.0
|
|
Rohan Patel answered |
Explanation:
To determine the valid subnet address of the given IP address, we need to determine the network portion of the IP address. The subnet mask for the given IP address is /25, which means the first 25 bits of the IP address are used for the network portion, and the remaining 7 bits are used for the host portion.
The valid subnet address is obtained by setting all the host bits to zero. Therefore, we need to determine the network address that corresponds to the given IP address.
The given IP address is 172.16.112.1/25. To determine the network address, we need to perform a logical AND operation between the IP address and the subnet mask:
IP address: 172.16.112.1
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.128 (/25)
Performing a logical AND operation between the IP address and the subnet mask gives us:
Network address: 172.16.112.0
Therefore, the valid subnet address for the given IP address is 172.16.112.0.
HTML-formatted answer:
To determine the valid subnet address of the given IP address, we need to determine the network portion of the IP address. The subnet mask for the given IP address is /25, which means the first 25 bits of the IP address are used for the network portion, and the remaining 7 bits are used for the host portion.
The valid subnet address is obtained by setting all the host bits to zero. Therefore, we need to determine the network address that corresponds to the given IP address.
The given IP address is 172.16.112.1/25. To determine the network address, we need to perform a logical AND operation between the IP address and the subnet mask:
IP address: 172.16.112.1
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.128 (/25)
Performing a logical AND operation between the IP address and the subnet mask gives us:
Network address: 172.16.112.0
Therefore, the valid subnet address for the given IP address is 172.16.112.0.
HTML-formatted answer:
Explanation:
To determine the valid subnet address of the given IP address, we need to determine the network portion of the IP address. The subnet mask for the given IP address is /25, which means the first 25 bits of the IP address are used for the network portion, and the remaining 7 bits are used for the host portion.
The valid subnet address is obtained by setting all the host bits to zero. Therefore, we need to determine the network address that corresponds to the given IP address.
The given IP address is 172.16.112.1/25. To determine the network address, we need to perform a logical AND operation between the IP address and the subnet mask:
- IP address: 172.16.112.1
- Subnet mask: 255.255.255.128 (/25)
Performing a logical AND operation between the IP address and the subnet mask gives us:
- Network address: 172.16.112.0
Therefore, the valid subnet address for the given IP address is 172.16.112.0.
A classless address is given as 167.199.170.82/27. Find the number of addresses.- a)128
- b)64
- c)32
- d)16
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A classless address is given as 167.199.170.82/27. Find the number of addresses.
a)
128
b)
64
c)
32
d)
16
|
|
Sudhir Patel answered |
n =27
Therefore number of addresses is 2(32-n) = 32.
Therefore number of addresses is 2(32-n) = 32.
MIB is a collection of groups of objects that can be managed by- a)SMTP
- b)UDP
- c)SNMP
- d)TCP/IP
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
MIB is a collection of groups of objects that can be managed by
a)
SMTP
b)
UDP
c)
SNMP
d)
TCP/IP
|
|
Surbhi Kaur answered |
MIB (Management Information Base)
The Management Information Base (MIB) is a collection of groups of objects that can be managed using the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). It is a key component in network management systems, allowing administrators to monitor and control network devices.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
SNMP is an application layer protocol that is used to manage and monitor network devices. It provides a way for network administrators to manage network devices, such as routers, switches, and servers, by retrieving and setting information about these devices. SNMP operates over the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) or Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) network protocols.
How MIB and SNMP work together
MIB is a hierarchical database that organizes information about managed objects in a tree-like structure. Each node in the tree represents an object, and the branches represent relationships between objects. The MIB defines the structure and attributes of each object, allowing SNMP to retrieve or set values for these objects.
SNMP uses a manager-agent model, where the SNMP manager is responsible for collecting and monitoring information, and the SNMP agent is responsible for providing the information to the manager. The SNMP manager communicates with the SNMP agent using SNMP messages. These messages are used to retrieve information from the MIB, set values for objects, and receive traps or notifications from the agent.
Advantages of using SNMP and MIB
- Standardized protocol: SNMP is an industry-standard protocol that is supported by a wide range of network devices and management systems. This allows for interoperability between different vendors' devices and management systems.
- Scalability: SNMP and MIB provide a scalable solution for network management. The hierarchical structure of the MIB allows for easy organization and management of large networks with thousands of devices.
- Flexibility: SNMP allows for the monitoring and control of a wide range of network devices and parameters. The MIB can be extended or customized to include additional objects specific to a particular network or device.
- Real-time monitoring: SNMP provides real-time monitoring of network devices, allowing administrators to proactively identify and resolve issues before they impact network performance.
- Troubleshooting and diagnostics: SNMP and MIB provide valuable information for troubleshooting and diagnostics. By retrieving information from the MIB, administrators can analyze network performance, identify bottlenecks, and diagnose problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'C' SNMP. MIB is a collection of groups of objects that can be managed using SNMP. SNMP allows for the monitoring and control of network devices by retrieving and setting information from the MIB. This combination provides a powerful and flexible solution for network management.
The Management Information Base (MIB) is a collection of groups of objects that can be managed using the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). It is a key component in network management systems, allowing administrators to monitor and control network devices.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
SNMP is an application layer protocol that is used to manage and monitor network devices. It provides a way for network administrators to manage network devices, such as routers, switches, and servers, by retrieving and setting information about these devices. SNMP operates over the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) or Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) network protocols.
How MIB and SNMP work together
MIB is a hierarchical database that organizes information about managed objects in a tree-like structure. Each node in the tree represents an object, and the branches represent relationships between objects. The MIB defines the structure and attributes of each object, allowing SNMP to retrieve or set values for these objects.
SNMP uses a manager-agent model, where the SNMP manager is responsible for collecting and monitoring information, and the SNMP agent is responsible for providing the information to the manager. The SNMP manager communicates with the SNMP agent using SNMP messages. These messages are used to retrieve information from the MIB, set values for objects, and receive traps or notifications from the agent.
Advantages of using SNMP and MIB
- Standardized protocol: SNMP is an industry-standard protocol that is supported by a wide range of network devices and management systems. This allows for interoperability between different vendors' devices and management systems.
- Scalability: SNMP and MIB provide a scalable solution for network management. The hierarchical structure of the MIB allows for easy organization and management of large networks with thousands of devices.
- Flexibility: SNMP allows for the monitoring and control of a wide range of network devices and parameters. The MIB can be extended or customized to include additional objects specific to a particular network or device.
- Real-time monitoring: SNMP provides real-time monitoring of network devices, allowing administrators to proactively identify and resolve issues before they impact network performance.
- Troubleshooting and diagnostics: SNMP and MIB provide valuable information for troubleshooting and diagnostics. By retrieving information from the MIB, administrators can analyze network performance, identify bottlenecks, and diagnose problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'C' SNMP. MIB is a collection of groups of objects that can be managed using SNMP. SNMP allows for the monitoring and control of network devices by retrieving and setting information from the MIB. This combination provides a powerful and flexible solution for network management.
Network layer firewall works as a- a)Frame filter
- b)Packet filter
- c)Both (a) and (b)
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Network layer firewall works as a
a)
Frame filter
b)
Packet filter
c)
Both (a) and (b)
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Swara Sen answered |
The correct answer is option 'B', a network layer firewall works as a packet filter. Let's understand why:
Packet Filter:
A packet filter is a type of firewall that operates at the network layer (layer 3) of the OSI model. It examines the source and destination IP addresses, source and destination ports, and other parameters of each packet passing through it. Based on a set of predefined rules, the packet filter determines whether to allow or block the packet from passing through.
Working of a Network Layer Firewall:
A network layer firewall examines each packet that passes through it and applies a set of rules to determine whether to allow or block it. It does this by analyzing the packet header information, including source and destination IP addresses, source and destination port numbers, and other protocol-specific parameters.
Advantages of a Network Layer Firewall:
1. Granular Control: A network layer firewall provides granular control over network traffic by allowing administrators to define specific rules for packet filtering. This allows organizations to enforce their security policies and restrict access to specific resources or services.
2. Improved Performance: Since a network layer firewall operates at the network layer, it can process packets more efficiently compared to higher-layer firewalls. It filters packets based on their header information, making it faster and more scalable for handling large amounts of network traffic.
3. Protocol Independence: A network layer firewall is protocol-independent, meaning it can filter packets for various protocols such as TCP, UDP, ICMP, etc. This allows organizations to protect their networks from different types of attacks and vulnerabilities.
4. Flexibility: Network layer firewalls can be implemented using dedicated hardware appliances or software-based solutions. This provides flexibility in choosing the right firewall solution based on the organization's requirements and budget.
Conclusion:
In summary, a network layer firewall works as a packet filter by examining the header information of each packet and applying a set of rules to determine whether to allow or block it. It provides granular control, improved performance, protocol independence, and flexibility in protecting the network from unauthorized access and potential threats.
Packet Filter:
A packet filter is a type of firewall that operates at the network layer (layer 3) of the OSI model. It examines the source and destination IP addresses, source and destination ports, and other parameters of each packet passing through it. Based on a set of predefined rules, the packet filter determines whether to allow or block the packet from passing through.
Working of a Network Layer Firewall:
A network layer firewall examines each packet that passes through it and applies a set of rules to determine whether to allow or block it. It does this by analyzing the packet header information, including source and destination IP addresses, source and destination port numbers, and other protocol-specific parameters.
Advantages of a Network Layer Firewall:
1. Granular Control: A network layer firewall provides granular control over network traffic by allowing administrators to define specific rules for packet filtering. This allows organizations to enforce their security policies and restrict access to specific resources or services.
2. Improved Performance: Since a network layer firewall operates at the network layer, it can process packets more efficiently compared to higher-layer firewalls. It filters packets based on their header information, making it faster and more scalable for handling large amounts of network traffic.
3. Protocol Independence: A network layer firewall is protocol-independent, meaning it can filter packets for various protocols such as TCP, UDP, ICMP, etc. This allows organizations to protect their networks from different types of attacks and vulnerabilities.
4. Flexibility: Network layer firewalls can be implemented using dedicated hardware appliances or software-based solutions. This provides flexibility in choosing the right firewall solution based on the organization's requirements and budget.
Conclusion:
In summary, a network layer firewall works as a packet filter by examining the header information of each packet and applying a set of rules to determine whether to allow or block it. It provides granular control, improved performance, protocol independence, and flexibility in protecting the network from unauthorized access and potential threats.
Which of the following architecture uses CSMA/CD access method?- a)ARC net
- b)Ethernet
- c)Router
- d)STP server
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following architecture uses CSMA/CD access method?
a)
ARC net
b)
Ethernet
c)
Router
d)
STP server
|
|
Milan Mukherjee answered |
Explanation:
CSMA/CD Access Method:
CSMA/CD stands for Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection. It is a network protocol that allows multiple devices to share the same communication channel efficiently by listening to the channel, checking for traffic, and transmitting data when the channel is clear. In case of a collision, the devices involved detect the collision and follow a backoff algorithm to retransmit their data.
Which Architecture uses CSMA/CD Access Method?
The architecture that uses CSMA/CD access method is Ethernet.
Ethernet:
Ethernet is a widely used LAN technology that employs CSMA/CD as its access method. In Ethernet networks, devices listen to the communication channel before transmitting data. If the channel is clear, they go ahead and transmit their data. However, if a collision is detected, they use CSMA/CD to handle the collision and retransmit the data after a random backoff period.
Other Options:
- ARCnet: ARCnet uses a token-passing protocol instead of CSMA/CD.
- Router: A router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. It does not use CSMA/CD.
- STP Server: STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) is used to prevent loops in network topologies and does not use CSMA/CD for access control.
Therefore, the correct option is Ethernet when it comes to architectures that use CSMA/CD access method.
CSMA/CD Access Method:
CSMA/CD stands for Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection. It is a network protocol that allows multiple devices to share the same communication channel efficiently by listening to the channel, checking for traffic, and transmitting data when the channel is clear. In case of a collision, the devices involved detect the collision and follow a backoff algorithm to retransmit their data.
Which Architecture uses CSMA/CD Access Method?
The architecture that uses CSMA/CD access method is Ethernet.
Ethernet:
Ethernet is a widely used LAN technology that employs CSMA/CD as its access method. In Ethernet networks, devices listen to the communication channel before transmitting data. If the channel is clear, they go ahead and transmit their data. However, if a collision is detected, they use CSMA/CD to handle the collision and retransmit the data after a random backoff period.
Other Options:
- ARCnet: ARCnet uses a token-passing protocol instead of CSMA/CD.
- Router: A router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. It does not use CSMA/CD.
- STP Server: STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) is used to prevent loops in network topologies and does not use CSMA/CD for access control.
Therefore, the correct option is Ethernet when it comes to architectures that use CSMA/CD access method.
Which multicast address does the OSPF Hello protocol use?- a)224.0.0.5
- b)224.0.0.6
- c)224.0.0.7
- d)224.0.0.8
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which multicast address does the OSPF Hello protocol use?
a)
224.0.0.5
b)
224.0.0.6
c)
224.0.0.7
d)
224.0.0.8
|
|
Vaibhav Patel answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: 224.0.0.5 is the multicast address does the OSPF Hello protocol use.
Explanation: 224.0.0.5 is the multicast address does the OSPF Hello protocol use.
_____________ allows LAN users to share computer programs and data.- a)Communication server
- b)Print server
- c)File server
- d)Network
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
_____________ allows LAN users to share computer programs and data.
a)
Communication server
b)
Print server
c)
File server
d)
Network
|
|
Alok Desai answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: File server allows LAN users to share computer programs and data.
Explanation: File server allows LAN users to share computer programs and data.
What tells a firewall how to reassemble a data stream that has been divided into packets?- a)The source routing future
- b)The number in the header’s identification field
- c)The destination IP address
- d)The header checksum field in the packet header
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What tells a firewall how to reassemble a data stream that has been divided into packets?
a)
The source routing future
b)
The number in the header’s identification field
c)
The destination IP address
d)
The header checksum field in the packet header
|
|
Ishaan Saini answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: source routing future.
Explanation: source routing future.
An ISP has requested a block of 1000 addresses. How many blocks are granted to it?- a)512
- b)1000
- c)1024
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An ISP has requested a block of 1000 addresses. How many blocks are granted to it?
a)
512
b)
1000
c)
1024
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Shalini Chopra answered |
Explanation:
- An IP address is a 32-bit number that uniquely identifies a device on the internet.
- The IP address is divided into two parts: network address and host address.
- The network address is used to identify the network, while the host address is used to identify the device on that network.
- The IP address is divided into classes, and each class has a different number of network and host bits.
- The most commonly used classes are A, B, and C.
- Class A has 8 bits for network and 24 bits for host.
- Class B has 16 bits for network and 16 bits for host.
- Class C has 24 bits for network and 8 bits for host.
- An ISP that requests a block of 1000 addresses would require a Class C network, which has 256 possible network addresses and 256 possible host addresses.
- Therefore, the ISP would be granted 4 blocks of Class C networks, which is equal to 1024 addresses (4 x 256).
- Hence, the correct answer is option 'C' (1024).
- An IP address is a 32-bit number that uniquely identifies a device on the internet.
- The IP address is divided into two parts: network address and host address.
- The network address is used to identify the network, while the host address is used to identify the device on that network.
- The IP address is divided into classes, and each class has a different number of network and host bits.
- The most commonly used classes are A, B, and C.
- Class A has 8 bits for network and 24 bits for host.
- Class B has 16 bits for network and 16 bits for host.
- Class C has 24 bits for network and 8 bits for host.
- An ISP that requests a block of 1000 addresses would require a Class C network, which has 256 possible network addresses and 256 possible host addresses.
- Therefore, the ISP would be granted 4 blocks of Class C networks, which is equal to 1024 addresses (4 x 256).
- Hence, the correct answer is option 'C' (1024).
A wireless network interface controller can work in- a)infrastructure mode
- b)ad-hoc mode
- c)both (a) and (b)
- d)none of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A wireless network interface controller can work in
a)
infrastructure mode
b)
ad-hoc mode
c)
both (a) and (b)
d)
none of the mentioned
|
|
Soumya Dey answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: In infrastructure mode WNIC needs access point but in ad-hoc mode access point is not required.
Explanation: In infrastructure mode WNIC needs access point but in ad-hoc mode access point is not required.
What is max data capacity for optical fiber cable?- a)10 mbps
- b)100 mbps
- c)1000 mbps
- d)10000 mbps
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is max data capacity for optical fiber cable?
a)
10 mbps
b)
100 mbps
c)
1000 mbps
d)
10000 mbps
|
|
Milan Mukherjee answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: 1000 mbps is max data capacity for optical fiber cable.
Explanation: 1000 mbps is max data capacity for optical fiber cable.
A Link Control Protocol (LCP) is used for- a)Establishing ,configuring and testing the data-link connection
- b)Establishing and configuring different network-layer protocols
- c)Both a & b
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A Link Control Protocol (LCP) is used for
a)
Establishing ,configuring and testing the data-link connection
b)
Establishing and configuring different network-layer protocols
c)
Both a & b
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Bibek Choudhary answered |
Answer: a
Explanation: A Link Control Protocol (LCP) is used for establishing, configuring and testing the data-link connection.
Explanation: A Link Control Protocol (LCP) is used for establishing, configuring and testing the data-link connection.
The computation of the shortest path in OSPF is usually done by- a)Bellman-ford algorithm
- b)Routing information protocol
- c)Dijkstra’s algorithm
- d)Distance vector routing
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The computation of the shortest path in OSPF is usually done by
a)
Bellman-ford algorithm
b)
Routing information protocol
c)
Dijkstra’s algorithm
d)
Distance vector routing
|
|
Jay Basu answered |
Explanation:
Dijkstra's Algorithm:
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) uses Dijkstra's algorithm to compute the shortest path.
- Dijkstra's algorithm is a graph search algorithm that solves the single-source shortest path problem for a graph with non-negative edge weights.
- It starts at the source node and explores the neighboring nodes to find the shortest path to all other nodes in the graph.
Bellman-Ford Algorithm:
- The Bellman-Ford algorithm is another algorithm used for finding the shortest path in a network.
- It can handle graphs with negative edge weights but is not typically used in OSPF.
Routing Information Protocol (RIP):
- RIP is another routing protocol that uses distance vector routing, which is different from OSPF.
- It does not use Dijkstra's algorithm for computing the shortest path.
Distance Vector Routing:
- Distance vector routing, used by protocols like RIP, determines the best path based on the number of hops to a destination.
- OSPF, on the other hand, uses Dijkstra's algorithm which considers the actual cost or weight of the paths.
In conclusion, OSPF uses Dijkstra's algorithm for computing the shortest path because it is efficient and suitable for networks with non-negative edge weights.
Dijkstra's Algorithm:
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) uses Dijkstra's algorithm to compute the shortest path.
- Dijkstra's algorithm is a graph search algorithm that solves the single-source shortest path problem for a graph with non-negative edge weights.
- It starts at the source node and explores the neighboring nodes to find the shortest path to all other nodes in the graph.
Bellman-Ford Algorithm:
- The Bellman-Ford algorithm is another algorithm used for finding the shortest path in a network.
- It can handle graphs with negative edge weights but is not typically used in OSPF.
Routing Information Protocol (RIP):
- RIP is another routing protocol that uses distance vector routing, which is different from OSPF.
- It does not use Dijkstra's algorithm for computing the shortest path.
Distance Vector Routing:
- Distance vector routing, used by protocols like RIP, determines the best path based on the number of hops to a destination.
- OSPF, on the other hand, uses Dijkstra's algorithm which considers the actual cost or weight of the paths.
In conclusion, OSPF uses Dijkstra's algorithm for computing the shortest path because it is efficient and suitable for networks with non-negative edge weights.
Which of the following networks supports pipelining effect?- a)Circuit-switched networks
- b)Message-switched networks
- c)Packet-switched networks
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following networks supports pipelining effect?
a)
Circuit-switched networks
b)
Message-switched networks
c)
Packet-switched networks
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Tanishq Malik answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: Packet switched network is most preferred for pipelining process.
Explanation: Packet switched network is most preferred for pipelining process.
An ISP has requested a block of 1000 addresses. Can 18.14.12.0 be its first address?- a)Yes
- b)No
- c)Can’t Say
- d)Insufficient Data
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An ISP has requested a block of 1000 addresses. Can 18.14.12.0 be its first address?
a)
Yes
b)
No
c)
Can’t Say
d)
Insufficient Data
|
|
Niharika Ahuja answered |
B) No.
18.14.12.0 is not a valid host address as the last octet (0) represents the network address. The first usable host address for a block of 1000 addresses in the 18.14.12.0 network would be 18.14.12.1, and the last usable host address would be 18.14.15.254.
18.14.12.0 is not a valid host address as the last octet (0) represents the network address. The first usable host address for a block of 1000 addresses in the 18.14.12.0 network would be 18.14.12.1, and the last usable host address would be 18.14.15.254.
WiMAX uses the- a)orthogonal frequency division multiplexing
- b)time division multiplexing
- c)space division multiplexing
- d)all of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
WiMAX uses the
a)
orthogonal frequency division multiplexing
b)
time division multiplexing
c)
space division multiplexing
d)
all of the mentioned
|
|
Neha Mishra answered |
WiMAX, which stands for Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access, is a wireless communication technology that provides high-speed internet access over long distances. It is based on the IEEE 802.16 standard and operates in the microwave frequency range.
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) is the modulation scheme employed by WiMAX, making option A the correct answer. OFDM is a digital modulation technique that divides the available bandwidth into multiple subcarriers, each of which carries a portion of the data. These subcarriers are orthogonal to each other, meaning they do not interfere with one another, allowing for efficient use of the available spectrum.
Below, we will explain in detail why WiMAX uses OFDM and why the other options are not correct:
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
- OFDM is a widely used modulation scheme in wireless communication systems, including WiMAX.
- It divides the available bandwidth into multiple subcarriers, each carrying a portion of the data.
- The subcarriers are orthogonal to each other, meaning they can be transmitted simultaneously without interfering with one another.
- This allows for efficient use of the available spectrum, increasing the overall data throughput.
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)
- TDM is a different modulation scheme that divides the available bandwidth into time slots.
- Each user or device is assigned a specific time slot to transmit their data.
- While TDM is used in some communication systems, WiMAX does not use it as its primary modulation scheme.
Space Division Multiplexing (SDM)
- SDM is a technique that uses multiple antennas to transmit and receive data simultaneously.
- It takes advantage of the spatial dimension to increase the overall data throughput.
- While SDM is used in some wireless communication systems, WiMAX does not rely on it as its primary modulation scheme.
Conclusion
In summary, WiMAX uses Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) as its primary modulation scheme. OFDM allows for efficient use of the available spectrum by dividing it into multiple subcarriers that can be transmitted simultaneously without interference. This increases the overall data throughput and enables high-speed internet access over long distances.
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) is the modulation scheme employed by WiMAX, making option A the correct answer. OFDM is a digital modulation technique that divides the available bandwidth into multiple subcarriers, each of which carries a portion of the data. These subcarriers are orthogonal to each other, meaning they do not interfere with one another, allowing for efficient use of the available spectrum.
Below, we will explain in detail why WiMAX uses OFDM and why the other options are not correct:
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
- OFDM is a widely used modulation scheme in wireless communication systems, including WiMAX.
- It divides the available bandwidth into multiple subcarriers, each carrying a portion of the data.
- The subcarriers are orthogonal to each other, meaning they can be transmitted simultaneously without interfering with one another.
- This allows for efficient use of the available spectrum, increasing the overall data throughput.
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)
- TDM is a different modulation scheme that divides the available bandwidth into time slots.
- Each user or device is assigned a specific time slot to transmit their data.
- While TDM is used in some communication systems, WiMAX does not use it as its primary modulation scheme.
Space Division Multiplexing (SDM)
- SDM is a technique that uses multiple antennas to transmit and receive data simultaneously.
- It takes advantage of the spatial dimension to increase the overall data throughput.
- While SDM is used in some wireless communication systems, WiMAX does not rely on it as its primary modulation scheme.
Conclusion
In summary, WiMAX uses Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) as its primary modulation scheme. OFDM allows for efficient use of the available spectrum by dividing it into multiple subcarriers that can be transmitted simultaneously without interference. This increases the overall data throughput and enables high-speed internet access over long distances.
An IP packet has arrived with the first 8 bits as 0100 0010. Which of the following is correct ?- a)The number of hops this packet can travel is 2
- b)The total number of bytes in header is 16 bytes.
- c)The upper layer protocol is ICMP
- d)The receiver rejects the packet
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An IP packet has arrived with the first 8 bits as 0100 0010. Which of the following is correct ?
a)
The number of hops this packet can travel is 2
b)
The total number of bytes in header is 16 bytes.
c)
The upper layer protocol is ICMP
d)
The receiver rejects the packet
|
|
Megha Dasgupta answered |
Explanation:
To determine the correct option, let's analyze the given information about the IP packet:
The first 8 bits of the IP packet are 0100 0010.
IP Version:
The first 4 bits of an IP packet represent the IP version. In this case, the first 4 bits are '0100', which corresponds to IP version 4. Therefore, the IP packet is using IPv4.
Header Length:
The next 4 bits of an IP packet represent the header length. In this case, the next 4 bits are '0010', which corresponds to a header length of 2 words. Each word is 4 bytes. So, the total header length is 2 * 4 bytes = 8 bytes.
Hops:
The number of hops a packet can travel is determined by the Time to Live (TTL) field in the IP header. However, in this case, the first 8 bits do not provide any information about the TTL. Therefore, we cannot determine the number of hops from the given information.
Upper Layer Protocol:
The upper layer protocol is determined by the Protocol field in the IP header. However, the first 8 bits do not provide any information about the upper layer protocol. Therefore, we cannot determine the upper layer protocol from the given information.
Receiver's Action:
The receiver's action cannot be determined from the first 8 bits of the IP packet. The receiver may reject the packet for various reasons such as invalid checksum, incorrect IP version, or other errors. However, we cannot determine the receiver's action solely based on the given information.
Therefore, the correct option is 'D) The receiver rejects the packet' since it is the only option that cannot be determined from the given information.
To determine the correct option, let's analyze the given information about the IP packet:
The first 8 bits of the IP packet are 0100 0010.
IP Version:
The first 4 bits of an IP packet represent the IP version. In this case, the first 4 bits are '0100', which corresponds to IP version 4. Therefore, the IP packet is using IPv4.
Header Length:
The next 4 bits of an IP packet represent the header length. In this case, the next 4 bits are '0010', which corresponds to a header length of 2 words. Each word is 4 bytes. So, the total header length is 2 * 4 bytes = 8 bytes.
Hops:
The number of hops a packet can travel is determined by the Time to Live (TTL) field in the IP header. However, in this case, the first 8 bits do not provide any information about the TTL. Therefore, we cannot determine the number of hops from the given information.
Upper Layer Protocol:
The upper layer protocol is determined by the Protocol field in the IP header. However, the first 8 bits do not provide any information about the upper layer protocol. Therefore, we cannot determine the upper layer protocol from the given information.
Receiver's Action:
The receiver's action cannot be determined from the first 8 bits of the IP packet. The receiver may reject the packet for various reasons such as invalid checksum, incorrect IP version, or other errors. However, we cannot determine the receiver's action solely based on the given information.
Therefore, the correct option is 'D) The receiver rejects the packet' since it is the only option that cannot be determined from the given information.
In Network Management System, maps track each piece of hardware and its connection to the- a)IP Server
- b)Domain
- c)Network
- d)Data
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In Network Management System, maps track each piece of hardware and its connection to the
a)
IP Server
b)
Domain
c)
Network
d)
Data
|
|
Ameya Goyal answered |
Answer: c
Explanation: Network is main thing in connecting different entities in a place.
Explanation: Network is main thing in connecting different entities in a place.
Chapter doubts & questions for Network Layer and Internetworking - Computer Networks 2025 is part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Network Layer and Internetworking - Computer Networks in English & Hindi are available as part of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam by signing up for free.
Computer Networks
21 videos|145 docs|66 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup












