All Exams >
Civil Engineering (CE) >
Environmental Engineering >
All Questions
All questions of Air Pollution for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam
Which one of the following procedures is used for sampling of the flue gas in a chimney for SPM?- a)Isothermal sampling
- b)Isokinetic sampling
- c)Adiabatic condition
- d)Variable rate of sampling
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following procedures is used for sampling of the flue gas in a chimney for SPM?
a)
Isothermal sampling
b)
Isokinetic sampling
c)
Adiabatic condition
d)
Variable rate of sampling

|
Partho Singh answered |
Isokinetic Sampling for SPM Sampling in Chimney Flue Gas
Isokinetic sampling is used for sampling of the flue gas in a chimney for SPM (Suspended Particulate Matter) measurement. It is a widely used method for the measurement of particulate matter emissions from stationary sources.
Working Principle:
The principle of isokinetic sampling is based on the concept of maintaining the velocity of the sampled gas constant. This is done to ensure that the particles in the sampled gas are captured accurately and representatively. The sampling rate is adjusted to match the velocity of the gas in the chimney, which is determined by measuring the gas velocity using a pitot tube or other velocity measurement device.
Procedure:
The isokinetic sampling procedure involves the following steps:
1. Determination of the gas velocity in the chimney using a pitot tube or other velocity measurement device.
2. Selection of the sampling location in the chimney based on the gas velocity.
3. Adjustment of the sampling rate to match the gas velocity.
4. Collection of the sample in a filter holder.
5. Weighing the filter before and after sampling to determine the concentration of SPM in the flue gas.
Advantages:
Isokinetic sampling has several advantages, including:
1. It ensures accurate and representative sampling of flue gas.
2. It is widely accepted and recognized as a standard method for particulate matter sampling.
3. It can be used for a wide range of particulate matter concentrations.
4. It is a cost-effective method for particulate matter measurement.
Conclusion:
Isokinetic sampling is a reliable and accurate method for sampling of the flue gas in a chimney for SPM measurement. It is widely used in the industry and is recognized as a standard method for particulate matter sampling.
Isokinetic sampling is used for sampling of the flue gas in a chimney for SPM (Suspended Particulate Matter) measurement. It is a widely used method for the measurement of particulate matter emissions from stationary sources.
Working Principle:
The principle of isokinetic sampling is based on the concept of maintaining the velocity of the sampled gas constant. This is done to ensure that the particles in the sampled gas are captured accurately and representatively. The sampling rate is adjusted to match the velocity of the gas in the chimney, which is determined by measuring the gas velocity using a pitot tube or other velocity measurement device.
Procedure:
The isokinetic sampling procedure involves the following steps:
1. Determination of the gas velocity in the chimney using a pitot tube or other velocity measurement device.
2. Selection of the sampling location in the chimney based on the gas velocity.
3. Adjustment of the sampling rate to match the gas velocity.
4. Collection of the sample in a filter holder.
5. Weighing the filter before and after sampling to determine the concentration of SPM in the flue gas.
Advantages:
Isokinetic sampling has several advantages, including:
1. It ensures accurate and representative sampling of flue gas.
2. It is widely accepted and recognized as a standard method for particulate matter sampling.
3. It can be used for a wide range of particulate matter concentrations.
4. It is a cost-effective method for particulate matter measurement.
Conclusion:
Isokinetic sampling is a reliable and accurate method for sampling of the flue gas in a chimney for SPM measurement. It is widely used in the industry and is recognized as a standard method for particulate matter sampling.
When Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR) is greater than Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR), then which of the following occurs?- a)Sub adiabatic lapse rate
- b)Super adiabatic lapse rate
- c)Neutral lapse rate
- d)Adiabatic lapse rate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When Environmental Lapse Rate (ELR) is greater than Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR), then which of the following occurs?
a)
Sub adiabatic lapse rate
b)
Super adiabatic lapse rate
c)
Neutral lapse rate
d)
Adiabatic lapse rate
|
|
Baishali Roy answered |
Explanation: In Super adiabatic lapse rate, the environment is unstable due to quick dispersion of pollutants.
Which of the following plume is worst for the dispersion of pollutants?- a)Trapping
- b)Fanning
- c)Neutral
- d)Fumigating
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following plume is worst for the dispersion of pollutants?
a)
Trapping
b)
Fanning
c)
Neutral
d)
Fumigating
|
|
Nikhil Kumar answered |
Explanation: In Fumigating plume, the pollutants come down near the ground due to turbulence instead of escaping above the stack. This makes it the most dangerous plume.
In which of the following plumes, unstable condition prevails?- a)Trapping
- b)Fanning
- c)Looping
- d)Neutral
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following plumes, unstable condition prevails?
a)
Trapping
b)
Fanning
c)
Looping
d)
Neutral
|
|
Shivani Basu answered |
Explanation: Rapid dispersion of pollutants takes place under Looping plume. It occurs under super adiabatic conditions.
The minimum size of the smoke particle is ______- a)0.2 μm
- b)1 μm
- c)0.8 μm
- d)0.5 μm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The minimum size of the smoke particle is ______
a)
0.2 μm
b)
1 μm
c)
0.8 μm
d)
0.5 μm
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
Smoke is produced due to incomplete combustion of coal. Its size lies between 0.5 μm to 1 μm.
Match List-l with List-lI and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:

- a)A
- b)B
- c)C
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Match List-l with List-lI and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:




a)
A
b)
B
c)
C
d)
D

|
Sarthak Kulkarni answered |
Carbon monoxide affect human aerobic metabolism by forming carboxy-haemogiobin (CoHb).
Oxides of nitrogen (NOx) includes - nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), nitrous Oxide (N2O), nitrogen sesquioxide (N2O3), Nitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) and nitrogen pentoxide (N2O5). NO and NO2 are of primary concern as air pollutants. NO2 plays major role in the production of secondary air pollutant ozone (O3).
SO2 is responsible for acid rains as it combines with water vapour to form secondary pollutants like H2SO4 which cause acidity.
Oxides of nitrogen (NOx) includes - nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), nitrous Oxide (N2O), nitrogen sesquioxide (N2O3), Nitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) and nitrogen pentoxide (N2O5). NO and NO2 are of primary concern as air pollutants. NO2 plays major role in the production of secondary air pollutant ozone (O3).
SO2 is responsible for acid rains as it combines with water vapour to form secondary pollutants like H2SO4 which cause acidity.
The chimney is emitting particulate matter. Which of the following is the correct expression of the height of the chimney? Here ‘Kp’ represents the emission of particulate matter. - a)HC = 74 Kp0.27
- b)HC = 14 Kp0.27
- c)HC = 14 Kp0.47
- d)HC = 74 Kp0.33
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The chimney is emitting particulate matter. Which of the following is the correct expression of the height of the chimney? Here ‘Kp’ represents the emission of particulate matter.
a)
HC = 74 Kp0.27
b)
HC = 14 Kp0.27
c)
HC = 14 Kp0.47
d)
HC = 74 Kp0.33
|
|
Mihir Kumar answered |
Explanation: Height of the chimney HC = 74 Kp0.27 where HC is in metre and ‘Kp’ is in tonnes per hours.
The upward vertical rise prevails in which of the following plume?- a)Trapping
- b)Fanning
- c)Looping
- d)Neutral
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The upward vertical rise prevails in which of the following plume?
a)
Trapping
b)
Fanning
c)
Looping
d)
Neutral
|
|
Preethi Das answered |
Explanation: In Neutral plume, the Environmental lapse rate is equal to the Adiabatic lapse rate.
Which type of light energy is effectively absorbed by CO2 in the lower boundary of the troposphere?- a)X-rays
- b)UV-rays
- c)Visible light
- d)Infrared rays
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of light energy is effectively absorbed by CO2 in the lower boundary of the troposphere?
a)
X-rays
b)
UV-rays
c)
Visible light
d)
Infrared rays

|
Swati Gupta answered |
CO2 is major green house gas and absorbs long wave radiations like infrared radiation.
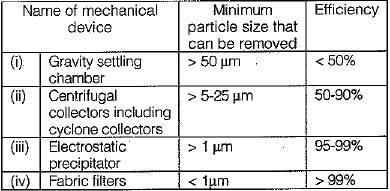
Which of the following is incorrect regarding fabric filter?- a)They can remove very small particle
- b)They are liable to chemical attack
- c)They have low efficiency in comparison to venturi scrubber
- d)They can handle large volume of gas at relatively high speed
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is incorrect regarding fabric filter?
a)
They can remove very small particle
b)
They are liable to chemical attack
c)
They have low efficiency in comparison to venturi scrubber
d)
They can handle large volume of gas at relatively high speed
|
|
Amrutha Chatterjee answered |
Explanation: The efficiency of Electrostatic precipitator is <99%, whereas the efficiency of Fabric filter is >99%.
What is the minimum height of the chimney in a thermal power plant of capacity 350MW?- a)100m
- b)220m
- c)380m
- d)60m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the minimum height of the chimney in a thermal power plant of capacity 350MW?
a)
100m
b)
220m
c)
380m
d)
60m
|
|
Ipsita Basu answered |
Explanation: As the capacity of thermal plant lies between 200MW and 500MW, the minimum height height of the chimney is 220m.
Which of the following is not a part of photochemical smog?- a)NO2
- b)O3
- c)PAN
- d)SPM
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a part of photochemical smog?
a)
NO2
b)
O3
c)
PAN
d)
SPM
|
|
Gargi Desai answered |
Explanation: Photochemical smog includes NO2 , O3 and PAN. The damage to vegetation is caused by NO2, O3 and PAN.
Which one of the following plume behaviours occurs when atmospheric inversion begins from the ground level and continues?- a)Looping
- b)Fumigation
- c)Coning
- d)Fanning
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following plume behaviours occurs when atmospheric inversion begins from the ground level and continues?
a)
Looping
b)
Fumigation
c)
Coning
d)
Fanning

|
Devika Tiwari answered |
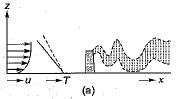
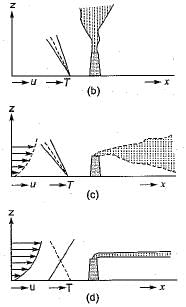
1. When the ambient lapse rate is super - adiabatic (greater than the adiabatic), the turbulence of the air itself causes the atmosphere to serve as an effective vehicle of dispersion. As indicated in fig-a, the resultant plume is designated as a looping plume.
2. When the ambient lapse rate is equal to or very near the dry adiabatic lapse rate, the plume issuing from a single chimney or smokestack tends to rise directly into the atmosphere until it reaches air of density similar to that of the plume itself. This type emission, called a neutral plume, is seen in fig-b.
3. When the ambient lapse rate is sub-adiabatic (less than the dry adiabatic), the atmosphere is slightly stable. Under such conditions, there is limited vertical mixing, and the probability of air pollution problems in the area is increased. The typical plume in such a situation is said to be coning.
4. When the lapse rate is negative, as in the ' presence of an inversion, the dispersion of stack gas is minimal, because of lack of. turbulence. In the extremely stable air, a plume spreads horizontally, with little vertical mixing, and is said to be fanning (fig-d).
5. When the lapse rate is super-adiabatic above the emission source and inversion conditions, exist below the source, the plume is said to be lofting. As shown in fig-e, a lofting plume' has minimal downward mixing, and the pollutants are dispersed downwind without any significant ground-level concentrations.
6. When an inversion layer occurs at a short distance above the top of the stack and super adiabatic conditions prevail below the stack, then plume is said to be fumigating (fig-d).
7. When inversion layer exists above the emission source, as well as below the source, then naturally, the emitted plume will neither go up, nor will it go down and would remain confined between the two inversion (fig-g). Such a plume is called a trapping.
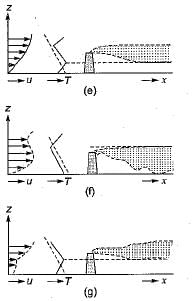

2. When the ambient lapse rate is equal to or very near the dry adiabatic lapse rate, the plume issuing from a single chimney or smokestack tends to rise directly into the atmosphere until it reaches air of density similar to that of the plume itself. This type emission, called a neutral plume, is seen in fig-b.
3. When the ambient lapse rate is sub-adiabatic (less than the dry adiabatic), the atmosphere is slightly stable. Under such conditions, there is limited vertical mixing, and the probability of air pollution problems in the area is increased. The typical plume in such a situation is said to be coning.
4. When the lapse rate is negative, as in the ' presence of an inversion, the dispersion of stack gas is minimal, because of lack of. turbulence. In the extremely stable air, a plume spreads horizontally, with little vertical mixing, and is said to be fanning (fig-d).
5. When the lapse rate is super-adiabatic above the emission source and inversion conditions, exist below the source, the plume is said to be lofting. As shown in fig-e, a lofting plume' has minimal downward mixing, and the pollutants are dispersed downwind without any significant ground-level concentrations.
6. When an inversion layer occurs at a short distance above the top of the stack and super adiabatic conditions prevail below the stack, then plume is said to be fumigating (fig-d).
7. When inversion layer exists above the emission source, as well as below the source, then naturally, the emitted plume will neither go up, nor will it go down and would remain confined between the two inversion (fig-g). Such a plume is called a trapping.




Acoustics of an auditorium is considered to be excellent when its reverberation time is between- a)0.50 and 1.50 s
- b)1,50 and 2.00 s
- c)2.00 and 3.00 s
- d)3.00 and 5.00 s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Acoustics of an auditorium is considered to be excellent when its reverberation time is between
a)
0.50 and 1.50 s
b)
1,50 and 2.00 s
c)
2.00 and 3.00 s
d)
3.00 and 5.00 s
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
For excellent acoustic conditions, reverberation time should be between 0.5 to 1.5 seconds.
Which of the following air pollution control device has maximum efficiency?- a)Electrostatic precipitator
- b)Dynamic precipitator
- c)Spray tower
- d)Wet cyclonic scrubber
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following air pollution control device has maximum efficiency?
a)
Electrostatic precipitator
b)
Dynamic precipitator
c)
Spray tower
d)
Wet cyclonic scrubber
|
|
Niharika Kaur answered |
Explanation: Electrostatic precipitator has the maximum efficiency among the rest with a value of 99%.
Concentration of fluorine that cause a phototoxicological effect on the plant is- a)0.1μg/m3
- b)0.3μg/m3
- c)0.5μg/m3
- d)1μg/m3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Concentration of fluorine that cause a phototoxicological effect on the plant is
a)
0.1μg/m3
b)
0.3μg/m3
c)
0.5μg/m3
d)
1μg/m3
|
|
Ipsita Basu answered |
Explanation: Fluorine is produced through aluminium or glass industries and it causes a phototoxicological effect on the plant at a concentration of 0.3μg/m3.
A rainfall is generally classified as acidic, if its pH is less than or equal to.- a)5
- b)6.5
- c)7
- d)7.5
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A rainfall is generally classified as acidic, if its pH is less than or equal to.
a)
5
b)
6.5
c)
7
d)
7.5

|
Sahana Dey answered |
The acidity in rain water is caused due to the formation of secondary pollutants, like H2S04, HNO3, HCI, etc., due to the reaction of water vapour with SO2, NOx, and HCI gas. It has been certified that when the pH of the rain water falls to 5.6 or below, the rain is specifically termed as acidic.
_______ occurs when atmospheric temperature increases with height.- a)Negative lapse rate
- b)Positive lapse rate
- c)Neutral lapse rate
- d)Sub adiabatic lapse rate
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
_______ occurs when atmospheric temperature increases with height.
a)
Negative lapse rate
b)
Positive lapse rate
c)
Neutral lapse rate
d)
Sub adiabatic lapse rate
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
Explanation: When the temperature increases with an increase in altitude, Sub adiabatic lapse rate occur and there will be stable environment. ... Explanation: Under negative lapse rate, the colder air is below the warmer air. It can be occurred near the earth's surface.
Wet scrubbers are classified into ____ types.- a)2
- b)3
- c)5
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Wet scrubbers are classified into ____ types.
a)
2
b)
3
c)
5
d)
6
|
|
Deepak Mehta answered |
Explanation: Web scrubbers are used to remove air pollutants and are classified into Spray towers, Wet cyclonic scrubber and Venturi scrubber.
Which of the following is not an adsorbent?- a)Molecular sieves
- b)Activated carbon
- c)Activated alumina
- d)Water
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an adsorbent?
a)
Molecular sieves
b)
Activated carbon
c)
Activated alumina
d)
Water
|
|
Avi Banerjee answered |
Explanation: Water is an absorbent whereas molecular sieves, activated carbon and activated alumina are adsorbents.
Coning plume occurs under which conditions?- a)Super adiabatic
- b)Sub adiabatic
- c)Neutral
- d)Inversion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Coning plume occurs under which conditions?
a)
Super adiabatic
b)
Sub adiabatic
c)
Neutral
d)
Inversion
|
|
Prasad Menon answered |
Coning plume occurs under which conditions?
Coning plume occurs under sub adiabatic conditions.
Explanation:
A coning plume refers to the shape the plume takes as it rises from a source, such as a chimney or a stack. The shape is conical, with a wider base and narrower top. Coning plumes are commonly observed in industrial processes and can have significant environmental impacts.
Sub adiabatic conditions:
Under sub adiabatic conditions, the temperature of the surrounding air is lower than the temperature of the plume. This temperature difference causes the plume to rise and expand, resulting in a conical shape. The sub adiabatic condition occurs when there is heat loss from the plume to the surrounding air.
Other conditions:
Let's briefly discuss the other conditions mentioned in the question and why they are not correct:
- Super adiabatic conditions: Under super adiabatic conditions, the temperature of the surrounding air is higher than the temperature of the plume. In this case, the plume will not rise and expand, and therefore, a coning plume will not occur.
- Neutral conditions: Under neutral conditions, the temperature of the surrounding air is equal to the temperature of the plume. In this case, the plume will rise vertically without significant expansion, resulting in a columnar shape rather than a coning shape.
- Inversion conditions: Inversion refers to a situation where the temperature of the surrounding air increases with height. Under inversion conditions, the plume will be trapped beneath the inversion layer and will not rise vertically or expand, leading to a different plume shape rather than a coning shape.
Therefore, the correct condition for a coning plume to occur is sub adiabatic conditions, where the temperature of the surrounding air is lower than the temperature of the plume, causing the plume to rise and expand in a conical shape.
Coning plume occurs under sub adiabatic conditions.
Explanation:
A coning plume refers to the shape the plume takes as it rises from a source, such as a chimney or a stack. The shape is conical, with a wider base and narrower top. Coning plumes are commonly observed in industrial processes and can have significant environmental impacts.
Sub adiabatic conditions:
Under sub adiabatic conditions, the temperature of the surrounding air is lower than the temperature of the plume. This temperature difference causes the plume to rise and expand, resulting in a conical shape. The sub adiabatic condition occurs when there is heat loss from the plume to the surrounding air.
Other conditions:
Let's briefly discuss the other conditions mentioned in the question and why they are not correct:
- Super adiabatic conditions: Under super adiabatic conditions, the temperature of the surrounding air is higher than the temperature of the plume. In this case, the plume will not rise and expand, and therefore, a coning plume will not occur.
- Neutral conditions: Under neutral conditions, the temperature of the surrounding air is equal to the temperature of the plume. In this case, the plume will rise vertically without significant expansion, resulting in a columnar shape rather than a coning shape.
- Inversion conditions: Inversion refers to a situation where the temperature of the surrounding air increases with height. Under inversion conditions, the plume will be trapped beneath the inversion layer and will not rise vertically or expand, leading to a different plume shape rather than a coning shape.
Therefore, the correct condition for a coning plume to occur is sub adiabatic conditions, where the temperature of the surrounding air is lower than the temperature of the plume, causing the plume to rise and expand in a conical shape.
X ray films are a source of which of the following gas?- a)SO2
- b)CO2
- c)NO2
- d)SO3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
X ray films are a source of which of the following gas?
a)
SO2
b)
CO2
c)
NO2
d)
SO3
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
NO2 is produced from X ray film. It causes irritation to eyes and cause respiratory disease.
In which of the following plumes, stable condition prevails?- a)Lofting
- b)Fanning
- c)Neutral
- d)Fumigating
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following plumes, stable condition prevails?
a)
Lofting
b)
Fanning
c)
Neutral
d)
Fumigating
|
|
Preethi Das answered |
Explanation: The stability prevails in Fanning plume. It occurs during inversion conditions.
Which of the following catalyst is used for removing hydrocarbon from gaseous pollutant in combustion unit?- a)Platinum
- b)Activated alumina
- c)Vanadium
- d)Potassium permanganate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following catalyst is used for removing hydrocarbon from gaseous pollutant in combustion unit?
a)
Platinum
b)
Activated alumina
c)
Vanadium
d)
Potassium permanganate
|
|
Hiral Khanna answered |
Activated alumina is used as a catalyst for removing hydrocarbons from gaseous pollutants in a combustion unit.
Activated Alumina as a Catalyst:
Activated alumina is a highly porous form of aluminum oxide that has a large surface area, high adsorption capacity, and excellent thermal stability. It is commonly used as a catalyst in various chemical processes, including the removal of hydrocarbons from gaseous pollutants.
Mechanism of Hydrocarbon Removal:
When hydrocarbons are present in gaseous pollutants, they can contribute to air pollution and pose a threat to human health and the environment. Therefore, it is essential to remove these hydrocarbons before releasing the gases into the atmosphere. Activated alumina acts as a catalyst to facilitate the conversion of hydrocarbons into carbon dioxide and water through the process of catalytic oxidation.
Adsorption:
Activated alumina has a high affinity for hydrocarbons and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The porous structure of activated alumina provides a large surface area, allowing for efficient adsorption of hydrocarbon molecules onto its surface.
Oxidation:
Once the hydrocarbon molecules are adsorbed onto the surface of activated alumina, oxidation reactions take place. The catalyst provides active sites where oxygen molecules can react with the adsorbed hydrocarbons, leading to their conversion into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). This process is known as catalytic oxidation.
Regeneration:
Over time, the adsorption capacity of activated alumina may decrease as it becomes saturated with hydrocarbons. Therefore, periodic regeneration is required to restore its adsorption capacity. This can be achieved by heating the activated alumina at high temperatures, which removes the adsorbed hydrocarbons and allows the catalyst to be reused.
Advantages of Activated Alumina Catalyst:
- High adsorption capacity: Activated alumina has a large surface area, allowing for efficient adsorption of hydrocarbons.
- Thermal stability: The catalyst can withstand high temperatures without losing its effectiveness.
- Regenerability: Activated alumina can be regenerated, making it suitable for long-term use.
- Versatility: Activated alumina can be used for the removal of various pollutants, including hydrocarbons and VOCs.
In conclusion, activated alumina is an effective catalyst for removing hydrocarbons from gaseous pollutants in a combustion unit. Its high adsorption capacity, thermal stability, and regenerability make it a suitable choice for this application.
Activated Alumina as a Catalyst:
Activated alumina is a highly porous form of aluminum oxide that has a large surface area, high adsorption capacity, and excellent thermal stability. It is commonly used as a catalyst in various chemical processes, including the removal of hydrocarbons from gaseous pollutants.
Mechanism of Hydrocarbon Removal:
When hydrocarbons are present in gaseous pollutants, they can contribute to air pollution and pose a threat to human health and the environment. Therefore, it is essential to remove these hydrocarbons before releasing the gases into the atmosphere. Activated alumina acts as a catalyst to facilitate the conversion of hydrocarbons into carbon dioxide and water through the process of catalytic oxidation.
Adsorption:
Activated alumina has a high affinity for hydrocarbons and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The porous structure of activated alumina provides a large surface area, allowing for efficient adsorption of hydrocarbon molecules onto its surface.
Oxidation:
Once the hydrocarbon molecules are adsorbed onto the surface of activated alumina, oxidation reactions take place. The catalyst provides active sites where oxygen molecules can react with the adsorbed hydrocarbons, leading to their conversion into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). This process is known as catalytic oxidation.
Regeneration:
Over time, the adsorption capacity of activated alumina may decrease as it becomes saturated with hydrocarbons. Therefore, periodic regeneration is required to restore its adsorption capacity. This can be achieved by heating the activated alumina at high temperatures, which removes the adsorbed hydrocarbons and allows the catalyst to be reused.
Advantages of Activated Alumina Catalyst:
- High adsorption capacity: Activated alumina has a large surface area, allowing for efficient adsorption of hydrocarbons.
- Thermal stability: The catalyst can withstand high temperatures without losing its effectiveness.
- Regenerability: Activated alumina can be regenerated, making it suitable for long-term use.
- Versatility: Activated alumina can be used for the removal of various pollutants, including hydrocarbons and VOCs.
In conclusion, activated alumina is an effective catalyst for removing hydrocarbons from gaseous pollutants in a combustion unit. Its high adsorption capacity, thermal stability, and regenerability make it a suitable choice for this application.
What type of noise can be abated by providing lining on walls and ceiling with sound absorbing materials?- a)Source noise
- b)Reflection noise
- c)Structural noise
- d)Direct airborne noise
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What type of noise can be abated by providing lining on walls and ceiling with sound absorbing materials?
a)
Source noise
b)
Reflection noise
c)
Structural noise
d)
Direct airborne noise

|
Pallabi Kulkarni answered |
Reflection noise is the correct answer.
Explanation:
When sound waves hit a surface, they can be reflected, transmitted, or absorbed. Reflection noise occurs when sound waves bounce off surfaces and create echoes or reverberations in a space. This can result in an increase in overall noise levels and decrease speech intelligibility. Reflection noise can be particularly problematic in spaces with hard, smooth surfaces such as walls and ceilings.
How sound absorbing materials work:
Sound absorbing materials are designed to reduce reflection noise by absorbing sound waves rather than allowing them to bounce off surfaces. These materials are typically soft, porous, and lightweight, and they have the ability to convert sound energy into heat energy. When sound waves pass through these materials, they cause the fibers or particles in the material to vibrate, which in turn converts the sound energy into heat. This reduces the amount of sound that is reflected back into the space.
Benefits of lining walls and ceiling with sound absorbing materials:
By providing lining on walls and ceiling with sound absorbing materials, the following benefits can be achieved:
1. Reduced reflection noise: The primary benefit of using sound absorbing materials is the reduction of reflection noise. These materials help to absorb sound waves, preventing them from bouncing off surfaces and creating echoes or reverberations in the space. This can result in a quieter and more acoustically comfortable environment.
2. Improved speech intelligibility: Reflection noise can make it difficult to understand speech, especially in larger spaces such as conference rooms or auditoriums. By reducing reflection noise, sound absorbing materials can improve speech intelligibility and enhance communication.
3. Enhanced sound quality: Reflection noise can distort or muffle sound, affecting the overall quality of audio playback. By minimizing reflection noise, sound absorbing materials can improve the clarity and fidelity of sound reproduction.
4. Increased privacy: Reflection noise can also result in a lack of privacy, as sound can easily travel through walls and ceilings. By reducing reflection noise, sound absorbing materials can help create more private and confidential spaces.
5. Aesthetic appeal: In addition to their functional benefits, sound absorbing materials can also be visually appealing. They are available in a variety of colors, textures, and designs, allowing them to be integrated seamlessly into the overall design of a space.
Conclusion:
By providing lining on walls and ceiling with sound absorbing materials, reflection noise can be effectively abated. These materials absorb sound waves, reducing the amount of noise that is reflected back into the space. This can result in a quieter and more acoustically comfortable environment, with improved speech intelligibility, enhanced sound quality, increased privacy, and aesthetic appeal.
Explanation:
When sound waves hit a surface, they can be reflected, transmitted, or absorbed. Reflection noise occurs when sound waves bounce off surfaces and create echoes or reverberations in a space. This can result in an increase in overall noise levels and decrease speech intelligibility. Reflection noise can be particularly problematic in spaces with hard, smooth surfaces such as walls and ceilings.
How sound absorbing materials work:
Sound absorbing materials are designed to reduce reflection noise by absorbing sound waves rather than allowing them to bounce off surfaces. These materials are typically soft, porous, and lightweight, and they have the ability to convert sound energy into heat energy. When sound waves pass through these materials, they cause the fibers or particles in the material to vibrate, which in turn converts the sound energy into heat. This reduces the amount of sound that is reflected back into the space.
Benefits of lining walls and ceiling with sound absorbing materials:
By providing lining on walls and ceiling with sound absorbing materials, the following benefits can be achieved:
1. Reduced reflection noise: The primary benefit of using sound absorbing materials is the reduction of reflection noise. These materials help to absorb sound waves, preventing them from bouncing off surfaces and creating echoes or reverberations in the space. This can result in a quieter and more acoustically comfortable environment.
2. Improved speech intelligibility: Reflection noise can make it difficult to understand speech, especially in larger spaces such as conference rooms or auditoriums. By reducing reflection noise, sound absorbing materials can improve speech intelligibility and enhance communication.
3. Enhanced sound quality: Reflection noise can distort or muffle sound, affecting the overall quality of audio playback. By minimizing reflection noise, sound absorbing materials can improve the clarity and fidelity of sound reproduction.
4. Increased privacy: Reflection noise can also result in a lack of privacy, as sound can easily travel through walls and ceilings. By reducing reflection noise, sound absorbing materials can help create more private and confidential spaces.
5. Aesthetic appeal: In addition to their functional benefits, sound absorbing materials can also be visually appealing. They are available in a variety of colors, textures, and designs, allowing them to be integrated seamlessly into the overall design of a space.
Conclusion:
By providing lining on walls and ceiling with sound absorbing materials, reflection noise can be effectively abated. These materials absorb sound waves, reducing the amount of noise that is reflected back into the space. This can result in a quieter and more acoustically comfortable environment, with improved speech intelligibility, enhanced sound quality, increased privacy, and aesthetic appeal.
Which of the following gas is not colorless?- a)NO
- b)O3
- c)Pb
- d)SO3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following gas is not colorless?
a)
NO
b)
O3
c)
Pb
d)
SO3
|
|
Janani Chakraborty answered |
Explanation: NO is a highly reactive gas which is reddish brown in color, whereas O3, Pb and SO3 are colorless gas.
Which of the following is the absorption unit?- a)Cyclone collector
- b)Plate tower
- c)Gravitation settling chamber
- d)Dynamic precipitator
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the absorption unit?
a)
Cyclone collector
b)
Plate tower
c)
Gravitation settling chamber
d)
Dynamic precipitator
|
|
Arjun Chawla answered |
Explanation: Cyclone collector, Gravitation settling chamber and Dynamic precipitator are used to remove particulate matter, whereas Plate tower is used to remove gaseous matter and is an absorption unit.
When environmental Lapse Rate (ELR) is less is than Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR), then which of the following occurs?- a)Sub adiabatic lapse rate
- b)Super adiabatic lapse rate
- c)Neutral lapse rate
- d)Adiabatic lapse rate
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When environmental Lapse Rate (ELR) is less is than Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR), then which of the following occurs?
a)
Sub adiabatic lapse rate
b)
Super adiabatic lapse rate
c)
Neutral lapse rate
d)
Adiabatic lapse rate
|
|
Arjun Chawla answered |
Sub Adiabatic Lapse Rate
When the environmental lapse rate (ELR) is less than the adiabatic lapse rate (ALR), a sub-adiabatic lapse rate occurs. This means that the temperature of the air decreases at a slower rate than the dry adiabatic lapse rate as it rises in the atmosphere.
Reason behind Sub Adiabatic Lapse Rate
This occurs because the air is not rising high enough or fast enough to cool at the dry adiabatic lapse rate through adiabatic cooling. Instead, the air is being cooled by other processes such as radiation or mixing with cooler air.
Effect of Sub Adiabatic Lapse Rate
A sub-adiabatic lapse rate can have a significant effect on weather patterns and atmospheric stability. It can lead to the formation of temperature inversions, where a layer of warm air is trapped below a layer of cooler air. This can lead to poor air quality and the accumulation of pollutants in the lower atmosphere.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when the environmental lapse rate (ELR) is less than the adiabatic lapse rate (ALR), a sub-adiabatic lapse rate occurs. This can have important implications for weather patterns and atmospheric stability.
When the environmental lapse rate (ELR) is less than the adiabatic lapse rate (ALR), a sub-adiabatic lapse rate occurs. This means that the temperature of the air decreases at a slower rate than the dry adiabatic lapse rate as it rises in the atmosphere.
Reason behind Sub Adiabatic Lapse Rate
This occurs because the air is not rising high enough or fast enough to cool at the dry adiabatic lapse rate through adiabatic cooling. Instead, the air is being cooled by other processes such as radiation or mixing with cooler air.
Effect of Sub Adiabatic Lapse Rate
A sub-adiabatic lapse rate can have a significant effect on weather patterns and atmospheric stability. It can lead to the formation of temperature inversions, where a layer of warm air is trapped below a layer of cooler air. This can lead to poor air quality and the accumulation of pollutants in the lower atmosphere.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when the environmental lapse rate (ELR) is less than the adiabatic lapse rate (ALR), a sub-adiabatic lapse rate occurs. This can have important implications for weather patterns and atmospheric stability.
The centrifugal collectors are classified into how many types?- a)3
- b)4
- c)5
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The centrifugal collectors are classified into how many types?
a)
3
b)
4
c)
5
d)
2
|
|
Nishtha Tiwari answered |
Explanation: The Centrifugal collectors are classified into the Cyclone collector and Dynamic precipitator.
Which is the major pollutant present in photochemical smog?- a)PAN
- b)SO2
- c)HC
- d)NO2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the major pollutant present in photochemical smog?
a)
PAN
b)
SO2
c)
HC
d)
NO2

|
Sreemoyee Deshpande answered |
Photochemically, the NOx and hydrocarbons are two groups of chemical compounds which are the necessary ingredients for the production of photochemical smog.

The end product of photochemical reactions is photo chemical smog consisting of air contaminants such as O3, PAN, aldehydes, ketones, alkyl nitrates and carbon monoxide.

The end product of photochemical reactions is photo chemical smog consisting of air contaminants such as O3, PAN, aldehydes, ketones, alkyl nitrates and carbon monoxide.
Which of the following is used in ceramic industries?- a)Electrostatic precipitator
- b)Dynamic precipitator
- c)Spray tower
- d)Wet cyclonic scrubber
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is used in ceramic industries?
a)
Electrostatic precipitator
b)
Dynamic precipitator
c)
Spray tower
d)
Wet cyclonic scrubber
|
|
Shivani Basu answered |
Dynamic precipitator is used in ceramic industries.
Explanation:
Ceramic industries involve the production of ceramics, which are non-metallic solid materials that are typically made from clay and other raw materials. These industries often generate dust and other particulate matter during various processes such as grinding, crushing, milling, and drying. To control the emission of these particulates and ensure the production area remains clean, various air pollution control devices are employed.
One such device used in ceramic industries is the dynamic precipitator. Here is a detailed explanation of its working principle and advantages:
Working principle:
1. The dynamic precipitator is an electrostatic air cleaner that removes particles from the gas stream using the principle of electrostatic precipitation.
2. The gas stream containing particulates is passed through an ionization section, where corona discharge electrodes emit electrons that ionize the gas molecules.
3. The ionized gas molecules create a cloud of charged ions and electrons, which then interact with the particles in the gas stream.
4. The charged particles are attracted to oppositely charged collection electrodes, while the clean gas passes through.
5. The collected particles form a layer on the collection electrodes, and periodic rapping or shaking removes them, allowing continuous operation.
Advantages of dynamic precipitator:
1. High collection efficiency: Dynamic precipitators are highly efficient in removing particulates, even those with very small particle sizes.
2. Low pressure drop: These devices have a relatively low pressure drop, resulting in minimal energy consumption.
3. Continuous operation: The periodic rapping or shaking of collection electrodes allows continuous operation without frequent shutdowns for cleaning.
4. Versatile applications: Dynamic precipitators can handle a wide range of gas volumes and particulate concentrations, making them suitable for various ceramic industry processes.
5. Cost-effective: These devices offer long service life and require minimal maintenance, making them cost-effective solutions for air pollution control in ceramic industries.
In conclusion, the dynamic precipitator is used in ceramic industries to control particulate emissions and maintain a clean working environment. Its efficient particle collection, low pressure drop, continuous operation, and versatility make it a preferred choice for air pollution control in this industry.
Explanation:
Ceramic industries involve the production of ceramics, which are non-metallic solid materials that are typically made from clay and other raw materials. These industries often generate dust and other particulate matter during various processes such as grinding, crushing, milling, and drying. To control the emission of these particulates and ensure the production area remains clean, various air pollution control devices are employed.
One such device used in ceramic industries is the dynamic precipitator. Here is a detailed explanation of its working principle and advantages:
Working principle:
1. The dynamic precipitator is an electrostatic air cleaner that removes particles from the gas stream using the principle of electrostatic precipitation.
2. The gas stream containing particulates is passed through an ionization section, where corona discharge electrodes emit electrons that ionize the gas molecules.
3. The ionized gas molecules create a cloud of charged ions and electrons, which then interact with the particles in the gas stream.
4. The charged particles are attracted to oppositely charged collection electrodes, while the clean gas passes through.
5. The collected particles form a layer on the collection electrodes, and periodic rapping or shaking removes them, allowing continuous operation.
Advantages of dynamic precipitator:
1. High collection efficiency: Dynamic precipitators are highly efficient in removing particulates, even those with very small particle sizes.
2. Low pressure drop: These devices have a relatively low pressure drop, resulting in minimal energy consumption.
3. Continuous operation: The periodic rapping or shaking of collection electrodes allows continuous operation without frequent shutdowns for cleaning.
4. Versatile applications: Dynamic precipitators can handle a wide range of gas volumes and particulate concentrations, making them suitable for various ceramic industry processes.
5. Cost-effective: These devices offer long service life and require minimal maintenance, making them cost-effective solutions for air pollution control in ceramic industries.
In conclusion, the dynamic precipitator is used in ceramic industries to control particulate emissions and maintain a clean working environment. Its efficient particle collection, low pressure drop, continuous operation, and versatility make it a preferred choice for air pollution control in this industry.
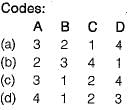
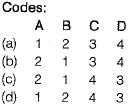
Match List-I (Equipment) with List-lI (Pollutants removed) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:

- a)A
- b)B
- c)C
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match List-I (Equipment) with List-lI (Pollutants removed) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:




a)
A
b)
B
c)
C
d)
D

|
Sai Sarkar answered |
(i) Electrostatic precipitator (High voltage) is used for > 1 mm but can collect submicron particles also.
(ii) Cyclone collector (based on centrifugal force) is used for 5 to 25 μm size particle
(iii) Wet scrubber are used for gaseous pollutants
(ii) Cyclone collector (based on centrifugal force) is used for 5 to 25 μm size particle
(iii) Wet scrubber are used for gaseous pollutants
(iv) Adsorbers are specific to gases. A reactive liquid adsorbent (water or limestone) may be used to remove SO2 from flue gases.
Which of the following is a liquid form of aerosol?- a)Fume
- b)Dust
- c)Mist
- d)Smoke
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a liquid form of aerosol?
a)
Fume
b)
Dust
c)
Mist
d)
Smoke

|
Moumita Dasgupta answered |
Understanding Aerosols
Aerosols are tiny particles or droplets suspended in the air. They can be in different physical states, including solid and liquid. The distinction is important when classifying aerosols, as they have varying impacts on health, environment, and engineering applications.
Different Forms of Aerosols
- Fume: This is typically a solid aerosol, formed from the condensation of vaporized metals or other materials. Fumes are generally composed of very fine particles and are not considered liquid.
- Dust: Dust consists of solid particles that are often larger than those in fumes. It is primarily composed of soil, pollen, or other solid materials and does not fall under the liquid category.
- Mist: Mist is a liquid aerosol formed from tiny droplets of water suspended in the air. This is the correct answer as it represents a liquid form of aerosol. Mist can occur naturally (like fog) or be artificially generated (like in humidifiers).
- Smoke: Smoke is a complex mixture of gases and solid particles produced by the incomplete combustion of organic matter. While it contains liquid droplets, it is primarily classified as a solid aerosol due to its particulate nature.
Conclusion
In summary, among the options provided, mist is the only liquid form of aerosol. Understanding these classifications is crucial in various fields, including civil engineering, where aerosol behavior can affect air quality and material performance.
Aerosols are tiny particles or droplets suspended in the air. They can be in different physical states, including solid and liquid. The distinction is important when classifying aerosols, as they have varying impacts on health, environment, and engineering applications.
Different Forms of Aerosols
- Fume: This is typically a solid aerosol, formed from the condensation of vaporized metals or other materials. Fumes are generally composed of very fine particles and are not considered liquid.
- Dust: Dust consists of solid particles that are often larger than those in fumes. It is primarily composed of soil, pollen, or other solid materials and does not fall under the liquid category.
- Mist: Mist is a liquid aerosol formed from tiny droplets of water suspended in the air. This is the correct answer as it represents a liquid form of aerosol. Mist can occur naturally (like fog) or be artificially generated (like in humidifiers).
- Smoke: Smoke is a complex mixture of gases and solid particles produced by the incomplete combustion of organic matter. While it contains liquid droplets, it is primarily classified as a solid aerosol due to its particulate nature.
Conclusion
In summary, among the options provided, mist is the only liquid form of aerosol. Understanding these classifications is crucial in various fields, including civil engineering, where aerosol behavior can affect air quality and material performance.
Which gas is mainly produced due to incomplete burning of wood?- a)CO
- b)SO2
- c)NO2
- d)NO3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which gas is mainly produced due to incomplete burning of wood?
a)
CO
b)
SO2
c)
NO2
d)
NO3

|
Mira Sharma answered |
Incomplete burning of wood leads to the production of mainly carbon monoxide (CO) gas.
Explanation:
Incomplete combustion occurs when there is not enough oxygen present during the burning process. In the case of burning wood, incomplete combustion can occur if the fire is not hot enough, if there is not enough air flow, or if there is too much fuel and not enough oxygen. Incomplete combustion of wood releases a number of gases, including carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O), and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a toxic gas that is produced when there is not enough oxygen present during combustion. Carbon monoxide is odorless, colorless, and tasteless, making it difficult to detect. In high concentrations, carbon monoxide can be deadly. Carbon monoxide is produced when wood is burned incompletely because the carbon in the wood does not fully combine with oxygen to form carbon dioxide.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, incomplete burning of wood leads to the production of mainly carbon monoxide (CO) gas, which is a toxic gas that can be deadly in high concentrations. Therefore, it is important to ensure complete combustion of wood by providing enough air flow and maintaining a hot fire.
Explanation:
Incomplete combustion occurs when there is not enough oxygen present during the burning process. In the case of burning wood, incomplete combustion can occur if the fire is not hot enough, if there is not enough air flow, or if there is too much fuel and not enough oxygen. Incomplete combustion of wood releases a number of gases, including carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O), and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a toxic gas that is produced when there is not enough oxygen present during combustion. Carbon monoxide is odorless, colorless, and tasteless, making it difficult to detect. In high concentrations, carbon monoxide can be deadly. Carbon monoxide is produced when wood is burned incompletely because the carbon in the wood does not fully combine with oxygen to form carbon dioxide.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, incomplete burning of wood leads to the production of mainly carbon monoxide (CO) gas, which is a toxic gas that can be deadly in high concentrations. Therefore, it is important to ensure complete combustion of wood by providing enough air flow and maintaining a hot fire.
Which of the following is not a part of adsorption unit?- a)Packed towers
- b)Multiple fixed bed
- c)Fluidized bed
- d)Moving bed
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a part of adsorption unit?
a)
Packed towers
b)
Multiple fixed bed
c)
Fluidized bed
d)
Moving bed
|
|
Puja Bose answered |
Explanation: Packed tower is a part of the absorption unit, whereas multiple fixed bed, fluidized bed and moving bed are the examples of absorbers.
Pollution by depletion of ozone layer, in the environment, is caused due to the reaction of ozone with- a)carbon monoxide
- b)chlorine
- c)sulphur dioxide
- d)nitrous oxide
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Pollution by depletion of ozone layer, in the environment, is caused due to the reaction of ozone with
a)
carbon monoxide
b)
chlorine
c)
sulphur dioxide
d)
nitrous oxide

|
Anirudh Kulkarni answered |
Ozone reacts with chlorine atom and gets breakdown into chlorine monoxide (CIO) and oxygen molecule
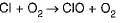
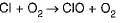
Which of the following leads to a disease called broncho spasm?- a)SO2
- b)SO3
- c)SO4
- d)CO2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following leads to a disease called broncho spasm?
a)
SO2
b)
SO3
c)
SO4
d)
CO2
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
SO3 reacts with body fluids forming H2SO4 leading to Broncho spasm.
Which of the following is the correct expression of the height of chimney emitting sulfur dioxide? - a)HC = 74 Kp0.27
- b)HC = 14 Kp0.33
- c)HC = 14 Kp0.47
- d)HC = 74 Kp0.33
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct expression of the height of chimney emitting sulfur dioxide?
a)
HC = 74 Kp0.27
b)
HC = 14 Kp0.33
c)
HC = 14 Kp0.47
d)
HC = 74 Kp0.33
|
|
Nitya Bajaj answered |
Explanation: Height of the chimney, HC = 14 Kp0.33 when the chimney is emitting sulfur dioxide. Here, the unit of ‘Kp’ is in kg/hour and HC is in metre.
Which of the following air pollutant effects plants the most?- a)Fluorine
- b)SO2
- c)PAN
- d)HCl
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following air pollutant effects plants the most?
a)
Fluorine
b)
SO2
c)
PAN
d)
HCl
|
|
Surbhi Kulkarni answered |
Explanation: Fluorine is the most dangerous air pollutant that affects plant, whereas SO2, PAN and HCl effects the leaf of the plant.
The effective height of stack is given by- a)Plume height / Actual height of the stack
- b)Plume height * Actual height of the stack
- c)Plume height – Actual height of the stack
- d)Plume height + Actual height of the stack
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The effective height of stack is given by
a)
Plume height / Actual height of the stack
b)
Plume height * Actual height of the stack
c)
Plume height – Actual height of the stack
d)
Plume height + Actual height of the stack
|
|
Janani Chakraborty answered |
Explanation: Effective height of the stack, H = h1 + h2 where, h1 is the plume height and h2is the actual height of stack.
When environmental Lapse Rate (ELR) is equal to the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR), then which of the following occurs?- a)Sub adiabatic lapse rate
- b)Super adiabatic lapse rate
- c)Neutral lapse rate
- d)Adiabatic lapse rate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When environmental Lapse Rate (ELR) is equal to the Adiabatic Lapse Rate (ALR), then which of the following occurs?
a)
Sub adiabatic lapse rate
b)
Super adiabatic lapse rate
c)
Neutral lapse rate
d)
Adiabatic lapse rate
|
|
Avi Banerjee answered |
Explanation: When the temperature is constant with height, then neutral lapse rate occurs.
The size of cigarette particles is- a)1μm
- b)10μm
- c)<1μm
- d)>10μm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The size of cigarette particles is
a)
1μm
b)
10μm
c)
<1μm
d)
>10μm
|
|
Krish Shah answered |
Explanation: Cigarette particles are <1μm and >25% particles are deposited in the lungs.
State whether the following statement is true or false.
The wet adiabatic rate is greater than the dry adiabatic rate. - a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
State whether the following statement is true or false.
The wet adiabatic rate is greater than the dry adiabatic rate.
The wet adiabatic rate is greater than the dry adiabatic rate.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Nayanika Gupta answered |
Explanation: The value of wet adiabatic rate is 60C per 1000m whereas of dry adiabatic rate is 9.80C per 1000m.
The following is a well known formula for estimating the plume rise: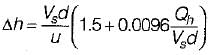
where the letters have their usual meaning.
The estimated plume rise (by the above formula) with a stack gas having heat emission rate 2000 kJ/s, the wind speed 4 m/s, stack gas speed 8 m/s inside a stack diameter of 1 m at the top is - a)7.8 m
- b)8.7 m
- c)3.15 m
- d)
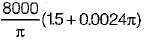
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The following is a well known formula for estimating the plume rise:
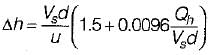
where the letters have their usual meaning.
The estimated plume rise (by the above formula) with a stack gas having heat emission rate 2000 kJ/s, the wind speed 4 m/s, stack gas speed 8 m/s inside a stack diameter of 1 m at the top is
a)
7.8 m
b)
8.7 m
c)
3.15 m
d)
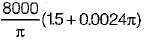

|
Simran Mukherjee answered |
Wind Speed u = 4 m/s
Stack gas speed Vs = 8 m/s
Diameter d = 1 m
Heat rise Qh = 2000 kJ/s
We know that effective height of stack,
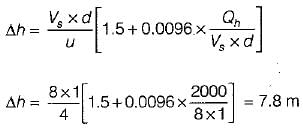
Stack gas speed Vs = 8 m/s
Diameter d = 1 m
Heat rise Qh = 2000 kJ/s
We know that effective height of stack,
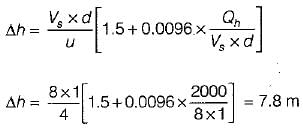
The primary air pollutant, which is formed due to incomplete combustion of organic matter, is- a)methane
- b)sulphur dioxide
- c)both (a) and (b)
- d)carbon monoxide
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The primary air pollutant, which is formed due to incomplete combustion of organic matter, is
a)
methane
b)
sulphur dioxide
c)
both (a) and (b)
d)
carbon monoxide

|
Pallabi Kulkarni answered |
The primary air pollutant that is formed due to incomplete combustion of organic matter is carbon monoxide (CO). When organic matter such as fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) or biomass (wood, crops, and agricultural waste) is burned in an environment with insufficient oxygen supply, incomplete combustion occurs, leading to the formation of carbon monoxide.
Incomplete combustion happens when there is not enough oxygen available to fully react with the carbon in the fuel. Instead of producing carbon dioxide (CO2), which is the desired end product of complete combustion, carbon monoxide is formed. Carbon monoxide is a colorless and odorless gas that is highly toxic to humans and animals.
**Formation of Carbon Monoxide:**
During the process of incomplete combustion, the carbon in the organic matter combines with only one oxygen atom instead of two, forming carbon monoxide. The chemical equation for this reaction can be represented as:
C + O2 -> CO
In this equation, C represents carbon, O2 represents oxygen, and CO represents carbon monoxide.
**Sources of Incomplete Combustion:**
Incomplete combustion can occur in various sources, including:
1. Vehicles: Inadequate air supply in the engine can lead to incomplete combustion in vehicles, especially those with older or poorly maintained engines.
2. Industrial Processes: Certain industrial processes that involve the burning of fossil fuels or biomass may produce carbon monoxide if there is insufficient oxygen supply.
3. Residential Heating: Incomplete combustion can occur in households that use wood-burning stoves, fireplaces, or other heating appliances that do not provide enough oxygen for complete combustion.
4. Wildfires: During wildfires, the burning of vegetation can result in incomplete combustion and the release of carbon monoxide into the atmosphere.
**Health and Environmental Impacts:**
Carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas that can have severe health effects on humans and animals. When inhaled, it binds to hemoglobin in the blood, reducing its ability to transport oxygen throughout the body. This can lead to symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, nausea, confusion, and in severe cases, it can be fatal.
In addition to its health impacts, carbon monoxide is also an air pollutant that contributes to the formation of smog and can contribute to the greenhouse effect and climate change. It reacts with other pollutants in the atmosphere to form ground-level ozone, which is harmful to human health and the environment.
**Conclusion:**
The primary air pollutant formed due to incomplete combustion of organic matter is carbon monoxide. It is important to ensure proper combustion conditions and adequate oxygen supply to minimize the production of carbon monoxide and reduce its harmful impacts on human health and the environment.
Incomplete combustion happens when there is not enough oxygen available to fully react with the carbon in the fuel. Instead of producing carbon dioxide (CO2), which is the desired end product of complete combustion, carbon monoxide is formed. Carbon monoxide is a colorless and odorless gas that is highly toxic to humans and animals.
**Formation of Carbon Monoxide:**
During the process of incomplete combustion, the carbon in the organic matter combines with only one oxygen atom instead of two, forming carbon monoxide. The chemical equation for this reaction can be represented as:
C + O2 -> CO
In this equation, C represents carbon, O2 represents oxygen, and CO represents carbon monoxide.
**Sources of Incomplete Combustion:**
Incomplete combustion can occur in various sources, including:
1. Vehicles: Inadequate air supply in the engine can lead to incomplete combustion in vehicles, especially those with older or poorly maintained engines.
2. Industrial Processes: Certain industrial processes that involve the burning of fossil fuels or biomass may produce carbon monoxide if there is insufficient oxygen supply.
3. Residential Heating: Incomplete combustion can occur in households that use wood-burning stoves, fireplaces, or other heating appliances that do not provide enough oxygen for complete combustion.
4. Wildfires: During wildfires, the burning of vegetation can result in incomplete combustion and the release of carbon monoxide into the atmosphere.
**Health and Environmental Impacts:**
Carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas that can have severe health effects on humans and animals. When inhaled, it binds to hemoglobin in the blood, reducing its ability to transport oxygen throughout the body. This can lead to symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, nausea, confusion, and in severe cases, it can be fatal.
In addition to its health impacts, carbon monoxide is also an air pollutant that contributes to the formation of smog and can contribute to the greenhouse effect and climate change. It reacts with other pollutants in the atmosphere to form ground-level ozone, which is harmful to human health and the environment.
**Conclusion:**
The primary air pollutant formed due to incomplete combustion of organic matter is carbon monoxide. It is important to ensure proper combustion conditions and adequate oxygen supply to minimize the production of carbon monoxide and reduce its harmful impacts on human health and the environment.
Photochemical smog is formed from automobile exhaust- a)By reaction of hydrocarbon & nitric oxide in presence of sunlight
- b)Appears only on sunny days
- c)Is harmful for crops and trees also besides causing eye irritation & asthma
- d)All (a), (b) & (c)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Photochemical smog is formed from automobile exhaust
a)
By reaction of hydrocarbon & nitric oxide in presence of sunlight
b)
Appears only on sunny days
c)
Is harmful for crops and trees also besides causing eye irritation & asthma
d)
All (a), (b) & (c)

|
Pallabi Chavan answered |
And nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight. The hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides (NOx) are emitted from vehicle exhaust and other sources. When they react in the presence of sunlight, a complex chain of chemical reactions occurs, leading to the formation of photochemical smog. This type of smog is characterized by a brownish haze, and can cause respiratory problems, eye irritation, and other health issues. To reduce photochemical smog, it is important to reduce emissions of hydrocarbons and NOx from vehicles and other sources, as well as to minimize exposure to sunlight during peak hours.
Which one of the following pollutants or pairs of pollutants is formed due to photochemical reactions?- a)CO alone
- b)O3 and PAN
- c)PAN and NH3
- d)NH3 and CO
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pollutants or pairs of pollutants is formed due to photochemical reactions?
a)
CO alone
b)
O3 and PAN
c)
PAN and NH3
d)
NH3 and CO

|
Priyanka Shah answered |
Photochemical reactions form O3, PAN, formaldehyde, etc.
Chapter doubts & questions for Air Pollution - Environmental Engineering 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Air Pollution - Environmental Engineering in English & Hindi are available as part of Civil Engineering (CE) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Environmental Engineering
14 videos|142 docs|98 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily