All Exams >
Humanities/Arts >
Geography Class 11 >
All Questions
All questions of Minerals and Rocks (Old Syllabus) for Humanities/Arts Exam
Igneous rocks are- a)primary rocks.
- b)secondary rocks.
- c)tertiary rocks.
- d)soft rocks.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Igneous rocks are
a)
primary rocks.
b)
secondary rocks.
c)
tertiary rocks.
d)
soft rocks.
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
The igneous rocks (Ignis – in Latin means ‘Fire’) are formed when magma cools and solidifies. As igneous rocks form out of magma and lava from the interior of the earth, they are known as primary rocks.
A non-metallic mineral in the following minerals is- a)silver.
- b)copper.
- c)zinc.
- d)coal.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A non-metallic mineral in the following minerals is
a)
silver.
b)
copper.
c)
zinc.
d)
coal.
|
|
Anmol Banerjee answered |
Coal is used as a fossil fuel and is a non-metallic mineral with dull and non-reflective properties and it cannot be moulded in any form.
Rocks that were originally either sedimentary, igneous or metamorphic and have been changed further by heat and pressure are called:- a)Volcanic
- b)Sedimented
- c)Metamorphic
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Rocks that were originally either sedimentary, igneous or metamorphic and have been changed further by heat and pressure are called:
a)
Volcanic
b)
Sedimented
c)
Metamorphic
d)
None of these
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
Metamorphic rocks started out as some other type of rock, but have been substantially changed from their original igneous, sedimentary, or earlier metamorphic form. Metamorphic rocks form when rocks are subjected to high heat, high pressure, hot mineral-rich fluids or, more commonly, some combination of these factors.
Petrology is the scientific study of- a)minerals.
- b)rocks.
- c)soil.
- d)petroleum.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Petrology is the scientific study of
a)
minerals.
b)
rocks.
c)
soil.
d)
petroleum.
|
|
Devanshi Choudhury answered |
Petrology is the scientific study of rocks. It involves the examination and classification of rocks to understand their composition, origin, and formation processes. Petrologists analyze the mineralogy, texture, and structure of rocks to gain insights into Earth's geological history.
Explanation:
1. Definition of Petrology:
- Petrology is a branch of geology that focuses on the study of rocks.
- It involves the investigation of various aspects of rocks, including their composition, texture, structure, and origin.
2. Study of Rocks:
- Petrologists study different types of rocks, including igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks.
- Igneous rocks form from the solidification of molten material, such as lava or magma.
- Sedimentary rocks are formed through the accumulation and lithification of sediments.
- Metamorphic rocks are rocks that have undergone changes in mineralogy, texture, or structure due to high temperatures and pressures.
3. Composition of Rocks:
- Petrologists analyze the mineral composition of rocks.
- Minerals are naturally occurring inorganic substances with a specific chemical composition and crystal structure.
- By studying the minerals present in rocks, petrologists can identify the rock type and infer the conditions under which it formed.
4. Texture and Structure:
- Petrologists also examine the texture and structure of rocks.
- Texture refers to the size, shape, and arrangement of mineral grains within a rock.
- Structure refers to the overall spatial arrangement of rocks and their components.
- These characteristics provide valuable information about the processes that influenced the rock's formation.
5. Origin and Formation Processes:
- Petrologists aim to understand the origin and formation processes of rocks.
- This involves studying the geological history of an area and identifying the tectonic processes, geological events, and environmental conditions that influenced rock formation.
- Petrologists may also investigate the relationship between rocks and minerals, as well as the presence of fossils or other geological features.
Conclusion:
Petrology is a multidisciplinary field that combines aspects of geology, mineralogy, chemistry, and physics to study rocks. By analyzing the composition, texture, and structure of rocks, petrologists can gain insights into Earth's geological history and the processes that shape the planet's surface.
Explanation:
1. Definition of Petrology:
- Petrology is a branch of geology that focuses on the study of rocks.
- It involves the investigation of various aspects of rocks, including their composition, texture, structure, and origin.
2. Study of Rocks:
- Petrologists study different types of rocks, including igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks.
- Igneous rocks form from the solidification of molten material, such as lava or magma.
- Sedimentary rocks are formed through the accumulation and lithification of sediments.
- Metamorphic rocks are rocks that have undergone changes in mineralogy, texture, or structure due to high temperatures and pressures.
3. Composition of Rocks:
- Petrologists analyze the mineral composition of rocks.
- Minerals are naturally occurring inorganic substances with a specific chemical composition and crystal structure.
- By studying the minerals present in rocks, petrologists can identify the rock type and infer the conditions under which it formed.
4. Texture and Structure:
- Petrologists also examine the texture and structure of rocks.
- Texture refers to the size, shape, and arrangement of mineral grains within a rock.
- Structure refers to the overall spatial arrangement of rocks and their components.
- These characteristics provide valuable information about the processes that influenced the rock's formation.
5. Origin and Formation Processes:
- Petrologists aim to understand the origin and formation processes of rocks.
- This involves studying the geological history of an area and identifying the tectonic processes, geological events, and environmental conditions that influenced rock formation.
- Petrologists may also investigate the relationship between rocks and minerals, as well as the presence of fossils or other geological features.
Conclusion:
Petrology is a multidisciplinary field that combines aspects of geology, mineralogy, chemistry, and physics to study rocks. By analyzing the composition, texture, and structure of rocks, petrologists can gain insights into Earth's geological history and the processes that shape the planet's surface.
Which mineral group is abundantly found in the earth’s crust?
- a)Mica group
- b)Silicate group
- c)Carbonates group
- d)Phosphorus group
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which mineral group is abundantly found in the earth’s crust?
a)
Mica group
b)
Silicate group
c)
Carbonates group
d)
Phosphorus group
|
|
Harshad Sengupta answered |
The most abundant mineral group found in the Earth's crust is the group of silicate minerals. Silicate minerals are composed primarily of silicon and oxygen, and they make up approximately 90% of the Earth's crust. Some examples of common silicate minerals include quartz, feldspar, mica, and amphibole.
The most abundant rocks found on earth's crust are- a)igneous rocks.
- b)sedimentary rocks.
- c)metamorphic rocks.
- d)granite rock.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The most abundant rocks found on earth's crust are
a)
igneous rocks.
b)
sedimentary rocks.
c)
metamorphic rocks.
d)
granite rock.
|
|
Ishani Singh answered |
Igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 deg.C - 1300 deg.C, or 1100 deg. - 2400 deg. F) molten or partially molten rock material. The Earth is composed predominantly of a large mass of igneous rock with a very thin covering of sedimentary rock.
The minerals that do not contain metal contend are known as- a)precious minerals.
- b)ferrous minerals.
- c)non-metallic minerals.
- d)non-ferrous minerals.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The minerals that do not contain metal contend are known as
a)
precious minerals.
b)
ferrous minerals.
c)
non-metallic minerals.
d)
non-ferrous minerals.
|
|
Krish Chaudhary answered |
The minerals that do not contain metal contend are known as non-metallic minerals. Sulphur, phosphates and nitrates are examples of non-metallic minerals.
The diamond mine present in the given map is
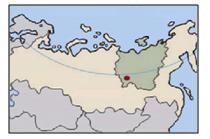
- a)Yakutia.
- b)Taymyria.
- c)Evenkia.
- d)Chukotia.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The diamond mine present in the given map is


a)
Yakutia.
b)
Taymyria.
c)
Evenkia.
d)
Chukotia.
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
Russia accounts for approx. 21% of global diamond production, most of which is mined in the largest diamond mine Sakha Respublikata in Yakut (Yakutia) of Siberia.
Which process involves the transformation of sediment deposits into sedimentary rocks characterized by distinct layers?- a)Denudation
- b)Erosion
- c)Lithification
- d)Weathering
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which process involves the transformation of sediment deposits into sedimentary rocks characterized by distinct layers?
a)
Denudation
b)
Erosion
c)
Lithification
d)
Weathering

|
Learning Educators answered |
Lithification: This is the process where sediments are compacted and cemented together to form solid rock. It includes the processes of compaction (due to pressure from overlying sediments) and cementation (where minerals precipitate from pore fluids and bind the sediment grains together).
Chapter doubts & questions for Minerals and Rocks (Old Syllabus) - Geography Class 11 2025 is part of Humanities/Arts exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Humanities/Arts exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Humanities/Arts 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Minerals and Rocks (Old Syllabus) - Geography Class 11 in English & Hindi are available as part of Humanities/Arts exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Humanities/Arts Exam by signing up for free.
Geography Class 11
70 videos|289 docs|44 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










