KVS PGT Biology Mock Test - 2 - KVS PGT/TGT/PRT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test KVS PGT Exam Mock Test Series 2025 - KVS PGT Biology Mock Test - 2
Which one of the following statements is implied in the passage?
According to the writer, which one of the following is not the responsibility of the police?
Select the most appropriate SYNONYM of the given word.
Export
'सभ्यता का विकास ________ से ही संभव है।‘ रिक्त स्थान के लिये उपयुक्त शब्द चुनिये।
Select the most appropriate ANTONYM of the given word.
Clumsy
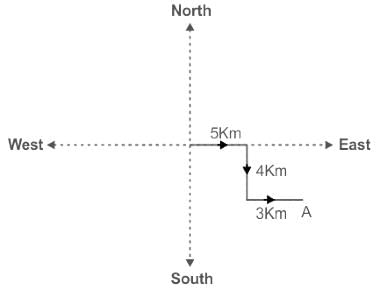
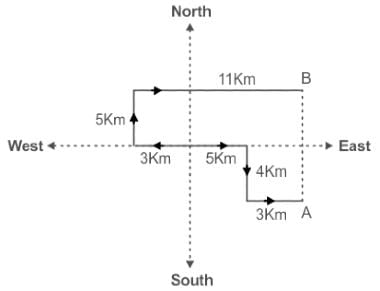
Two persons A and B, stand at the same point. A walks 5 km East, takes a right turn and walks 4 km and turns left and walks 3 km. B walks 3 km towards West, turns right and walks 5 km; turns right again and walks 11 km. How far is A from B?
Directions : In the following questions, few statements are given and these statements are followed by two conclusions numbered i and ii. You have to t statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusion follows from the given statements, disregarding commonly known facts.
Choose,
(A) Only (i) conclusion follows
(B) Only (ii) conclusion follows
(C) Neither (i) nor (ii) follows
(D) Both (i) and (ii) follow
(E) Either (i) or (ii) follows
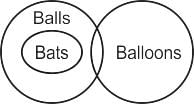
Statements :
All Bats are balls.
Some balls are Balloons.
Conclusions :
i) Some Bats are Balloons.
ii) Some balls are Bats.
Which of the following is NOT a primary area of focus for the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA)?
What is the highest level in the multi-level planning framework for community development in India?
which of the following techniques used for identification of hearing impairement of children?
(a). neuro psychological test
(b). development scale
(c). case study of the child
(d). electro encephalogram
‘‘Development is a never-ending process. ’’ This idea is associated with
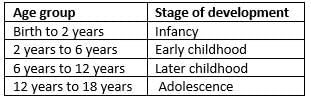
In which of the following stage the rate of physical development is slowest?
Jatin usually participates in team sports and always gains a sense of team success as well as personal success. Jatin shows the developmental task of which stage of development?
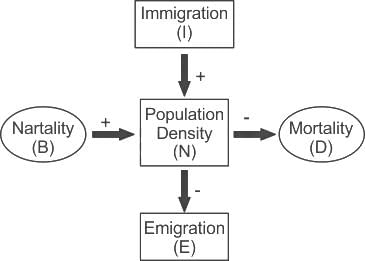
_________ is the number of individuals of a population who have left the habitat and gone elsewhere during the time period under consideration.
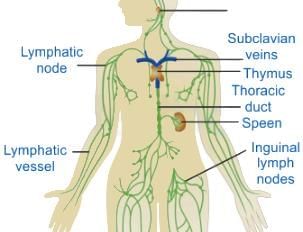
MALT constitutes about ___________ percent of the lymphoid tissue in human body
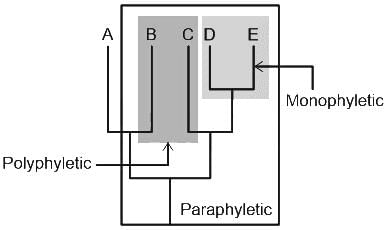
Three living species X, Y and Z share a common ancestor T, as do extinct species U and V. A grouping that consists of species T, X, Y, and Z (but not U or V) makes up:
From the following identify the factor that has not led to population explosion in India.