Shankar IAS Test: Terrestrial Ecosystems- 2 - UPSC MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) - Shankar IAS Test: Terrestrial Ecosystems- 2
Statement 1: Shifting cultivation involves clearing land, burning vegetation, and mixing ash with the soil.
Statement 2: The primary purpose of shifting cultivation is to enhance soil fertility for long-term agricultural use.
Statement 2: The primary purpose of shifting cultivation is to enhance soil fertility for long-term agricultural use.
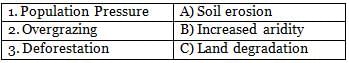
Match the following causes of desertification with their effects:

Assertion (A): Afforestation in desert regions is necessary to prevent desertification.
Reason (R): Trees help in changing the climate and meeting the local needs for firewood, timber, and fodder.
Reason (R): Trees help in changing the climate and meeting the local needs for firewood, timber, and fodder.
Sequence the following steps in the water cycle disruption caused by deforestation:
A) Reduced rainfall
B) Increased runoff
C) Trees absorb less water
D) Decline in groundwater levels
Statement 1: The "Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas of India" reports that 29.07% of India's land is undergoing land degradation.
Statement 2: The main contributor to land degradation in India is the expansion of urban areas.
Which of the following is NOT a direct impact of deforestation?
Assertion (A): The State of the World's Forests 2022 report highlights a decline in the rate of deforestation.
Reason (R): This is primarily due to increased global awareness and sustainable forestry practices.
In the context of desertification, what role does increased agriculture play?
What percentage of India’s total land area is undergoing land degradation, according to the Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas of India?
Which program is NOT part of India's efforts to combat desertification?
Which of the following best describes the concept of 'shifting cultivation'?
What is the main environmental impact of development projects like large dams and reservoirs?
Which industry is NOT typically associated with high demand for wood as a raw material?
Forests influence the water cycle primarily through which process?
What is the primary consequence of mining operations in forested regions?
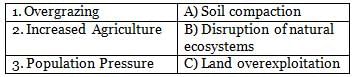
Match the following desertification causes with their impacts:
What is the target set by India to restore degraded land by the year 2030?
Which of the following is NOT a direct benefit of afforestation?
According to the State of the World's Forests 2022, what percentage of total forest area was lost between 1990 and 2020?
Assertion (A): The State of the World's Forests 2022 report links 15% of emerging infectious diseases to forests.
Reason (R): Forest degradation and deforestation increase human exposure to zoonotic pathogens.
|
782 videos|1239 docs|633 tests
|
|
782 videos|1239 docs|633 tests
|




















