Test: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - 1 - Class 10 MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - 1
An electric fuse prevents damage to the appliances and circuits due to ____.
What defines a solenoid in the context of magnetic fields?
Assertion (A): Magnetic field lines around a current-carrying straight conductor form closed loops.
Reason (R): Magnetic monopoles do not exist in nature.
What did Hans Christian Oersted discover accidentally?
What is the purpose of the earth wire in a domestic electric circuit?
Assertion (A): A metallic wire carrying an electric current has associated with it a magnetic field.
Reason (R): The field lines about the wire consist of a series of concentric circles whose direction is given by the right-hand rule.
Assertion (A): The magnetic field lines around a bar magnet are closed curves.
Reason (R): Inside the magnet, the direction of field lines is from its south pole to its north pole.
Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a _____?
The magnetic field is stronger where the field lines are ______.
In Fleming’s left-hand rule the thumb indicates the direction of
Which property of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field?
Assertion (A): The deflection of a compass needle decreases as the distance from a current-carrying conductor increases.
Reason (R): The magnetic field produced by a given current in the conductor decreases as the distance from it increases.
A metallic wire carrying an electric current has associated with it a _______.
What is the name of the rule that determines the direction of magnetic field lines around a current-carrying straight conductor?
Assertion (A): When a circular loop of wire lies in the plane of the table with current passing through it clockwise, the magnetic field direction inside and outside the loop can be determined using the right-hand rule.
Reason (R): The magnetic field in a given region is uniform.
What is the purpose of a fuse in an electrical circuit?
What determines the pattern of the magnetic field generated by a current through a conductor?
What do concentric circles around a straight conducting wire represent?
What is the primary function of an electric fuse in a circuit?
An electron enters a magnetic field at right angles to it. The direction of force acting on the electron will be _____.
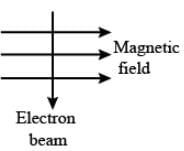
What is the relationship between the direction of the magnetic field and the direction of the current according to Fleming's left-hand rule?
The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid-carrying current _____.
Which of the following statements about the magnetic effect and the magnetic field are correct?
(i) An electric current through a copper wire produces a magnetic effect.
(ii) Iron filings align themselves along the magnetic field lines of a bar magnet.
(iii) A compass needle always points towards the magnetic north pole.
(iv) The magnetic field is the region surrounding a magnet where the force of the magnet can be detected.
What do the concentric circles around a straight conducting wire represent?
The wire with red insulation cover in the electric supply is called the _____ wire.
Choose the correctly matched pair.



















