Test: Medieval History - 1 - UPSC MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Medieval History - 1
Who among the following Mughal Emperors Shifted emphasis from illustrated manuscripts to album and individual portrait?
[2019]
With reference to the Mian Tansen, which one of the following statement is not correct
[2019]
Consider the following statements:
1. Saint Nimbarka was a contemporary of Akbar.
2. Saint Kabir was greatly influenced by Shaikh Ahmad Sirhindi.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
[2019]
1. Saint Nimbarka was a contemporary of Akbar.
2. Saint Kabir was greatly influenced by Shaikh Ahmad Sirhindi.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. In the revenue administration of Delhi Sultanate, the in-charge of revenue collection was known as 'Amil'.
2. The Iqta system of Sultans of Delhi was an ancient indigenous institution.
3. The office of' Mir Bakshi' came into existence during the reign of Khalji Sultans of Delhi.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
[2019]
With reference to Mughal India, what is/are the difference/differences between Jagirdar and Zamindar?
1. Jagirdars were holders of land assignments in lieu of judicial and police duties, whereas Zamindars were holders of revenue rights without obligation to perform any duty other than revenue collection.
2. Land assignments to Jagirdars were hereditary and revenue rights of Zamindars were not hereditary.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
[2019]
The well-known painting "Bani Thani" belongs to the
[2018]
With reference to the cultural history of India, consider the following statements :
1. White marble was used in making Buland Darwaza and Khankah at Fatehpur Sikri.
2. Red sandstone and marble were used in making Ilara Imambara and Rumi Darwaza at Lucknow.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
[2018]
Regarding the taxation system of Krishna Deva, the ruler of Vijayanagar, consider the following statements:
1. The tax rate on land was fixed depending on the quality of the land.
2. Private owners of workshops paid an industries tax.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
[2016]
With reference to the cultural history of medieval India, consider the following statements:
1. Siddhas (Sittars) of Tamil region were monotheistic and condemned idolatry.
2. Lingayats of Kannada region questioned the theory of rebirth and rejected the caste hierarchy.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
[2016]
Consider the following pairs:
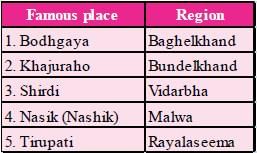
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
[2016]
With reference to the cultural history of India, the memorizing of chronicles, dynastic histories and Epic tales was the profession of who of the following?
[2016]
With reference to the economic history of medieval India, the term Araghatta’ refers to
[2016]
What is/are common to the two historical places known as Ajanta and Mahabalipuram?
1. Both were built in the same period.
2. Both belong to the same religious denomination.
3. Both have rock-cut monuments.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
[2016]
With reference to the religious history of India, consider the following statements:
1. The concept of Bodhisattva is central to Hinayana sect of Buddhism.
2. Bodhisattva is a compassionate one on his way to enlightenment.
3. Bodhisattva delays achieving his own salvation to help all sentient beings on their path to it.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
[2016]
Who of the following had first deciphered the edicts of Emperor Ashoka?
[2016]














