UPSC Paper 1 Mock Test - 21 - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UPSC Paper 1 Mock Test - 21
Which of the following functions is/are performed by the National Commission for Scheduled Castes?
1. To inquire into specific complaints with respect to the deprivation of rights and safeguards of the scheduled castes.
2. To determine an increase or decrease in quantum of reservation of scheduled castes in government jobs.
3. To prepare and update the list of schedule caste government employees and recommend their names for promotion through reserved quota.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
1. To inquire into specific complaints with respect to the deprivation of rights and safeguards of the scheduled castes.
2. To determine an increase or decrease in quantum of reservation of scheduled castes in government jobs.
3. To prepare and update the list of schedule caste government employees and recommend their names for promotion through reserved quota.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Indian Constitution is called a living document because
1. Indian Constitution is open to changes as per the changing needs of the society.
2. The constitution provides enough flexibility of interpretation for both political class and the Judiciary.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
1. Indian Constitution is open to changes as per the changing needs of the society.
2. The constitution provides enough flexibility of interpretation for both political class and the Judiciary.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
With reference to the contribution of Lord Dalhousie in India, consider the following statements:
1. Wood’s Educational Despatch was passed under his tenure.
2. First telegraphic line was started.
3. He used Doctrine of Lapse extensively.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
1. Wood’s Educational Despatch was passed under his tenure.
2. First telegraphic line was started.
3. He used Doctrine of Lapse extensively.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
The Directive Principles of State Policy under the Constitution of India prescribe:
1. Certain policies that the government should adopt.
2. The goals and objectives that we as a society should adopt.
3. Certain rights that individuals should enjoy apart from the Fundamental Rights.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
With reference to Pabna Agrarian movement, consider the following statements:
1. It was a movement of peasants and zamindars against British government.
2. The peasants took legal course of action for redressal of their grievances.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements with reference to High Courts:
1. It can withdraw a case pending in a subordinate court if it involves a substantial question of law that require the interpretation of the Constitution.
2. It has the power to review and correct its own judgement or order or decision .
3. It has the power to adjudicate inter-state dispute matters.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Article 20 of the Indian Constitution grants protection against self -incrimination. However, this protection does not extend to:
1. Oral evidence
2. Production of material objects
3. Blood specimens
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
With reference to revolutionary activities outside India, consider the following statements:
1. Raja Mahendra Pratap Singh set up a Provincial Government in Kabul.
2. Indian nationalist publication Bande Mataram was released from Paris.
3. Madan Lal Dhingra started an organisation named India House from London.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding Article 33 of the Indian Constitution:
1. The power to make laws under Article 33 is conferred only on Parliament and not on the state legislatures.
2. The laws made under Article 33 cannot be challenged in any court for violation of any of the fundamental rights.
3. Laws made under Article 33 cover only combatant employees and officers of armed forces.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
With reference to Rani Gaidinliu, consider the following statements:
1. She led the socio-political movement called as Heraka.
2. She was given the title Rani by Mahatma Gandhi.
3. She was released from imprisonment under the Gandhi-Irwin Pact.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
If a National Emergency is declared on the ground of armed rebellion:
1. Fundamental Rights under Article 19 are automatically suspended.
2. President can suspend the right to move the Court for the enforcement of fundamental rights.
3. The enforcement of the fundamental rights guaranteed by Articles 21 and 22 cannot be suspended.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following employees / Officers are covered under the jurisdiction of 'Central Administrative Tribunals'?
1. Officers and servants of the Supreme Court
2. The secretarial staff of the Parliament
3. Officers of All India Services
4. Civilian employees of defense services
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
With reference to the Royal Indian Navy (RIN) Mutiny of 1946, consider the following statements:
1. Second World War was instrumental in the formation of collective consciousness in the RIN.
2. The civilians of Madras were against the RIN demonstrations.
3. The Communist Party of India was directly involved in the strikes.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Right to contest elections to a Panchayat in India is a:
With reference to the Vernacular Press Act 1878, consider the following statements:
1. This act was designed for better control of the vernacular press and effectively punish and repress seditious writing.
2. The District Magistrate was empowered to call upon the printer of any vernacular newspaper to enter into a bond with Government Undertaking.
3. The Act was repealed under the regime of Lord Lytton.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding ' Election Commission':
1. The Constitution has prescribed qualifications and terms of the members of the Election Commission.
2. Retiring election commissioners are debarred from any further appointment by the government.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to Morley-Minto reforms, consider the following statements:
1. It increased the number of elected members in Imperial Legislative Council.
2. It provided separate electorate for Muslims.
3. Under the provisions of the reforms, Satyendranath Sinha became the first member to Governor General Executive Council.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
'Right to Freedom of Religion' under the Indian Constitution provides that:
1. A person cannot be forced to attend religious instruction in a state-recognized educational institution.
2. A fee or tax cannot be levied by governments on religious endowments and pilgrims.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
The expression 'Union of India' under Article 1 of the Indian Constitution includes which of the following?
1. Territories of the states
2. Union territories
3. Territories that may be acquired by the Government of India at any time.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
During the 2nd World War, British government came forward with the August Offer. Which of the following was/were the components of August Offer?
1. Self-government as the objective for India.
2. Setting up of a Constituent Assembly after the war.
3. No future constitution to be adopted without the consent of minorities.
4. Indians would decide the Constitution according to their social, economic and political conceptions.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
With reference to the relationship between Liberty and Equality, consider the following statements:
1. Without equality, liberty would produce the supremacy of the few over the many.
2. Equality, without liberty, would inhibit individual initiative.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Name of a state can be altered by Parliament through a bill passed by:
With reference to the Coriolis Force, consider the following statements:
1. It deflects the wind to their right direction in the northern hemisphere.
2. Higher the Pressure Gradient Force, lesser will be the effect of Coriolis Force.
3. Coriolis Force is inversely proportional to the angle of latitude.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to State Reorganisation Commission (SRC), consider the following statements:
1. It was set up in 1947 to decide on the question of reorganisation of States.
2. It was set up under the chairmanship of Fazl Ali.
3. It rejected the theory of 'one language one state'.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
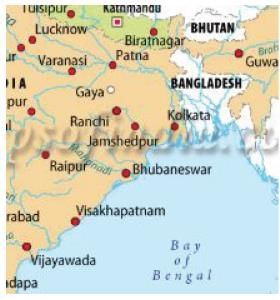
Arrange the following state capitals from South to North.
1. Raipur
2. Kolkata
3. Ranchi
4. Bhubaneshwar
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following pairs:

Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
The Siliguri Corridor, popularly known as ‘India’s Chicken Neck’ connects which of the following states of India?
Under the Constitution of India, “to protect monuments, places and objects of artistic or historic interest which are declared to be of national importance” is a
Which of the following can be considered as forms of precipitation?
1. Hail
2. Sleet
3. Dew
4. Mist
5. Frost
Select the correct answer using the code given below: