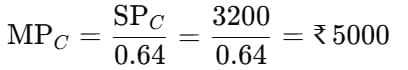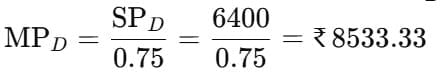Test: Quantitative Techniques- 1 - CLAT MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Quantitative Techniques- 1
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below. The table given below shows the discount offered on the marked price for two items - P and Q on four online websites - A, B, C and D.
The ratio of the cost price of item P is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively. The ratio of the selling price of item Q is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively.
If the marked price of Q on A is Rs.4,000 and the marked price of Q on B is 20% more than the marked price of Q on A, what is the total marked price of Q in all 4 given online websites?
The ratio of the cost price of item P is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively. The ratio of the selling price of item Q is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively.
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below. The table given below shows the discount offered on the marked price for two items - P and Q on four online websites - A, B, C and D.
The ratio of the cost price of item P is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively. The ratio of the selling price of item Q is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively.
If the discount on P on B is Rs. 300 and the profit is 10%, what is the cost price of P on B?
The ratio of the cost price of item P is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively. The ratio of the selling price of item Q is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively.
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below. The table given below shows the discount offered on the marked price for two items - P and Q on four online websites - A, B, C and D.
The ratio of the cost price of item P is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively. The ratio of the selling price of item Q is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively.
The ratio of the marked price of Q on A to the marked price of Q on B is 3 : 5. What is the rate of discount on Q on B?
The ratio of the cost price of item P is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively. The ratio of the selling price of item Q is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively.
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below. The table given below shows the discount offered on the marked price for two items - P and Q on four online websites - A, B, C and D.
The ratio of the cost price of item P is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively. The ratio of the selling price of item Q is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively.
The total cost price of P on A and on C is Rs.8,000 and the selling price of P on A is Rs. 80 more than that on C. If the profit on P on C is 10%, then what is the selling price of P on A?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below.
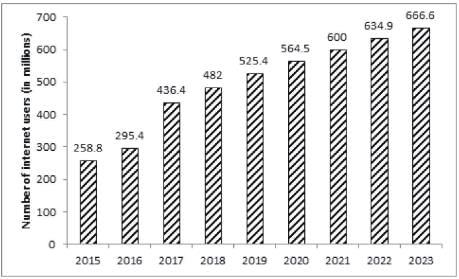
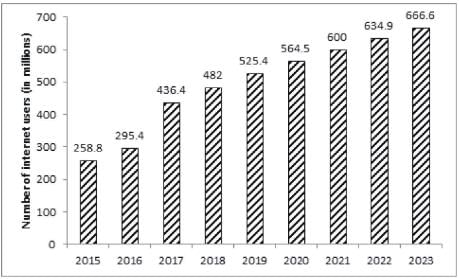
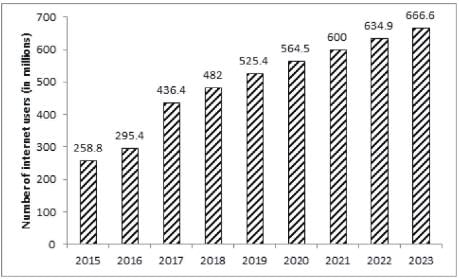
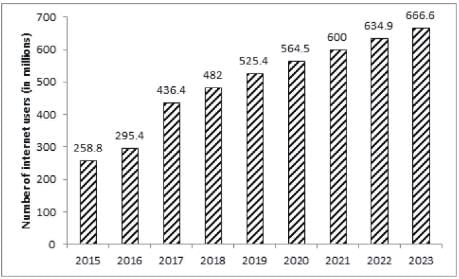
The bar graph given below shows the number of internet users in India from 2015 to 2019 as well as the projected number of internet users every year till 2023.
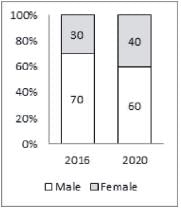
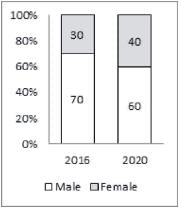
The second bar graph shows the percentage distribution of internet users in India in 2016 and estimated distribution for the year 2020 by gender
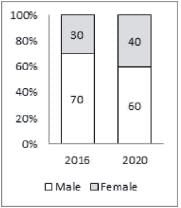
The number of years in which the number of internet users in India was more than the average number of internet users per year in India from 2015 to 2019 is:
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below.
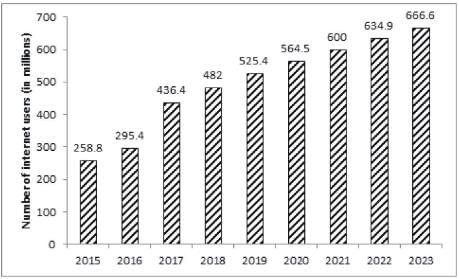
The bar graph given below shows the number of internet users in India from 2015 to 2019 as well as the projected number of internet users every year till 2023.
The second bar graph shows the percentage distribution of internet users in India in 2016 and estimated distribution for the year 2020 by gender
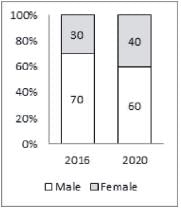
What is the estimated difference in the number of male and female internet users in the year 2020?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below.
The bar graph given below shows the number of internet users in India from 2015 to 2019 as well as the projected number of internet users every year till 2023.
The second bar graph shows the percentage distribution of internet users in India in 2016 and estimated distribution for the year 2020 by gender
In which of the following years did the number of internet users in India increase by less than 10% from 2015 to 2019?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below.
The bar graph given below shows the number of internet users in India from 2015 to 2019 as well as the projected number of internet users every year till 2023.
The second bar graph shows the percentage distribution of internet users in India in 2016 and estimated distribution for the year 2020 by gender
In percentage terms, approximately what will be the increase in number of male users in year 2020 as compared to year 2016?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below.
The bar graph given below shows the number of internet users in India from 2015 to 2019 as well as the projected number of internet users every year till 2023.
The second bar graph shows the percentage distribution of internet users in India in 2016 and estimated distribution for the year 2020 by gender
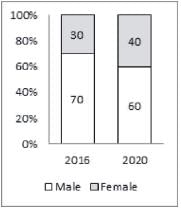
If male internet users increase by 10% and 20% in 2017 and 2018 respectively as compared to year 2016 and if female internet users are expected to increase by 20% and 40% in year 2021 and 2022 respectively as compared to year 2020, then, which of the following sequence is correct order of years in increasing order of female internet users?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below. The table given below shows the discount offered on the marked price for two items - P and Q on four online websites - A, B, C and D.
The ratio of the cost price of item P is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively. The ratio of the selling price of item Q is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively.
If the marked price of Q on D is Rs.6,000, then what is the marked price of Q on A?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below. The table given below shows the discount offered on the marked price for two items - P and Q on four online websites - A, B, C and D.
The ratio of the cost price of item P is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively. The ratio of the selling price of item Q is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively.
If the marked price of Q on A is Rs.4,000 and the marked price of Q on B is 20% more than the marked price of Q on A, what is the total marked price of Q in all 4 given online websites?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below. The table given below shows the discount offered on the marked price for two items - P and Q on four online websites - A, B, C and D.
The ratio of the cost price of item P is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively. The ratio of the selling price of item Q is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively.
If the discount on P on B is Rs. 300 and the profit is 10%, what is the cost price of P on B?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below. The table given below shows the discount offered on the marked price for two items - P and Q on four online websites - A, B, C and D.
The ratio of the cost price of item P is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively. The ratio of the selling price of item Q is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively.
The ratio of the marked price of Q on A to the marked price of Q on B is 3 : 5. What is the rate of discount on Q on B?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below. The table given below shows the discount offered on the marked price for two items - P and Q on four online websites - A, B, C and D.
The ratio of the cost price of item P is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively. The ratio of the selling price of item Q is 1 : 2 : 1 : 2 for websites A, B, C and D respectively.
The total cost price of P on A and on C is Rs.8,000 and the selling price of P on A is Rs. 80 more than that on C. If the profit on P on C is 10%, then what is the selling price of P on A?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below.
A rectangular park has length and breadth in the ratio 6 :
Ravi takes 2 minutes and 12 seconds to jog once around of the park at a speed of 5 feet/sec. At the centre of the park there is a circular water body, whereas the remaining area has a lawn. Ravi takes 1 minute and 28 seconds to jog once around the water body. There is a path of width 5 feet outside the perimeter and along the edges of the park.
Distance covered by Ravi in one round of the park = 5 x 132 = 660 feet
Let the length and breadth of the park be 6k and 5k respectively.
Perimeter = 2 x (6k + 5k) = 22k
⇒ 22k = 660 ⇒ k = 30
Length = 180 feet and breadth = 150 feet.
Total area of park = 180 x 150 = 27000 square feet. Circumference of water body = 5 x 88 = 440 feet 440
Radius = 70 feet
2n
The circular water body has a depth of five feet. What is the maximum volume water (in cubic feet) that can be contained in it?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below.
A rectangular park has length and breadth in the ratio 6 :
Ravi takes 2 minutes and 12 seconds to jog once around of the park at a speed of 5 feet/sec. At the centre of the park there is a circular water body, whereas the remaining area has a lawn. Ravi takes 1 minute and 28 seconds to jog once around the water body. There is a path of width 5 feet outside the perimeter and along the edges of the park.
Distance covered by Ravi in one round of the park = 5 x 132 = 660 feet
Let the length and breadth of the park be 6k and 5k respectively.
Perimeter = 2 x (6k + 5k) = 22k
⇒ 22k = 660 ⇒ k = 30
Length = 180 feet and breadth = 150 feet.
Total area of park = 180 x 150 = 27000 square feet. Circumference of water body = 5 x 88 = 440 feet 440
Radius = 70 feet
2n
What is the ratio of the area of the lawn to the area of the path surrounding the park?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below.
A rectangular park has length and breadth in the ratio 6 :
Ravi takes 2 minutes and 12 seconds to jog once around of the park at a speed of 5 feet/sec. At the centre of the park there is a circular water body, whereas the remaining area has a lawn. Ravi takes 1 minute and 28 seconds to jog once around the water body. There is a path of width 5 feet outside the perimeter and along the edges of the park.
Distance covered by Ravi in one round of the park = 5 x 132 = 660 feet
Let the length and breadth of the park be 6k and 5k respectively.
Perimeter = 2 x (6k + 5k) = 22k
⇒ 22k = 660 ⇒ k = 30
Length = 180 feet and breadth = 150 feet.
Total area of park = 180 x 150 = 27000 square feet. Circumference of water body = 5 x 88 = 440 feet 440
Radius = 70 feet
2n
What will be the total cost of paving the path surrounding the park at the rate of Rs.15 per square feet?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below.
The pie chart given below shows the number of Dengue patients in each of the states mentioned below during the year 2013.
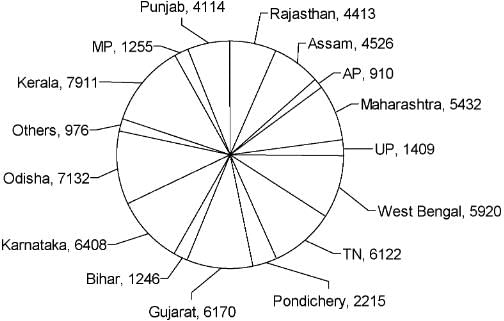
If the states are ranked according to the incidence of Dengue, then which three states have first, second and third ranks during the year 2013?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below.
The pie chart given below shows the number of Dengue patients in each of the states mentioned below during the year 2013.
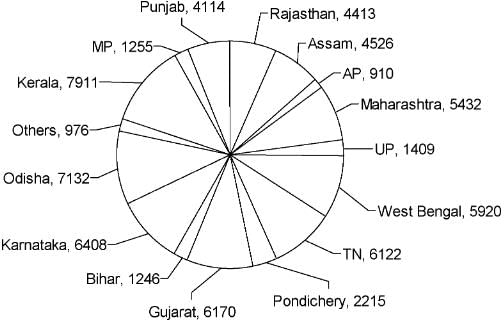
Select the option with the states in which approximately 25% of the total dengue cases occurred during 2013.
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below.
The pie chart given below shows the number of Dengue patients in each of the states mentioned below during the year 2013.
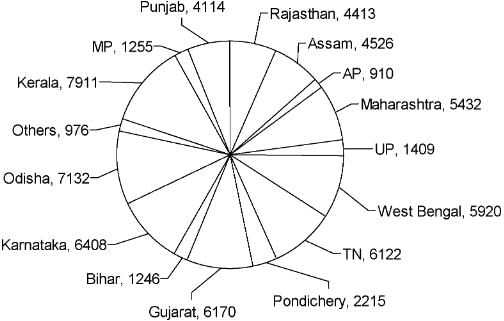
Approximately what percentage of the total Dengue cases in the country occurred in Assam and Bihar together?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below.
The pie chart given below shows the number of Dengue patients in each of the states mentioned below during the year 2013.
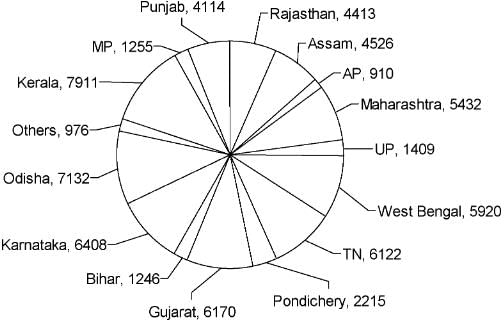
If the mortality rate among the Dengue victims of Gujarat in 2013 was 20%, then find the number of persons who survived the disease.
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below. Certain number of people order gifts for Christmas from three online shopping sites - X, Y and Z. Assume that they order from only three sites and each person orders from at least one of these three sites. 50% of people order from shopping site X and number of people ordering from only shopping site Z was 2/5 th of people ordering from X. Number of people ordering from both Z and Y but not from X are 50. People ordering from Y only are 50 more than the people ordering from Z only. Number of people ordering from X only is 20% more than number of people ordering from Y only. The number of people ordering from all three sites is one fifth of those who order from at least two sites. People who order from X and Y only is 100 more than the people who order from X and Z only.
Let total number of people be 100x.
People ordering from X = 50x People ordering from Z only = 20x People ordering from Y only = 20x + 50 People ordering from Y and Z but not X = 50 Also: (100x - 50x - 20x) - (20x + 50) = 50 => x = 10 Total number of people ordering from X = 50 * 10 = 500
People ordering from X only = 1°°0020 x 250 = 300 Poeple ordering from X and at least one more site = 200 People ordering from at least two or more sites = 200 + 50 = 250
1
People ordering from all three sites = 5 x 250 = 50
Since people who order from X and Y only is 100 more than the people who order from X and Z only.
. 2y + 100 + 50 = 200 => y = 25 People ordering from X and Y only = 125 Poeple ordering from X and Z only = 25
X Y
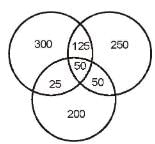
What is the total number of people who order from X, but not only from X?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below. Certain number of people order gifts for Christmas from three online shopping sites - X, Y and Z. Assume that they order from only three sites and each person orders from at least one of these three sites. 50% of people order from shopping site X and number of people ordering from only shopping site Z was 2/5 th of people ordering from X. Number of people ordering from both Z and Y but not from X are 50. People ordering from Y only are 50 more than the people ordering from Z only. Number of people ordering from X only is 20% more than number of people ordering from Y only. The number of people ordering from all three sites is one fifth of those who order from at least two sites. People who order from X and Y only is 100 more than the people who order from X and Z only.
Let total number of people be 100x.
People ordering from X = 50x People ordering from Z only = 20x People ordering from Y only = 20x + 50 People ordering from Y and Z but not X = 50 Also: (100x - 50x - 20x) - (20x + 50) = 50 => x = 10 Total number of people ordering from X = 50 * 10 = 500
People ordering from X only = 1°°0020 x 250 = 300 Poeple ordering from X and at least one more site = 200 People ordering from at least two or more sites = 200 + 50 = 250
1
People ordering from all three sites = 5 x 250 = 50
Since people who order from X and Y only is 100 more than the people who order from X and Z only.
. 2y + 100 + 50 = 200 => y = 25 People ordering from X and Y only = 125 Poeple ordering from X and Z only = 25
X Y
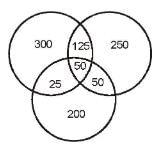
What is the total number of people ordering from at least two shopping sites?
Directions : Answer the questions on the basis of the information given below. Certain number of people order gifts for Christmas from three online shopping sites - X, Y and Z. Assume that they order from only three sites and each person orders from at least one of these three sites. 50% of people order from shopping site X and number of people ordering from only shopping site Z was 2/5 th of people ordering from X. Number of people ordering from both Z and Y but not from X are 50. People ordering from Y only are 50 more than the people ordering from Z only. Number of people ordering from X only is 20% more than number of people ordering from Y only. The number of people ordering from all three sites is one fifth of those who order from at least two sites. People who order from X and Y only is 100 more than the people who order from X and Z only.
Let total number of people be 100x.
People ordering from X = 50x People ordering from Z only = 20x People ordering from Y only = 20x + 50 People ordering from Y and Z but not X = 50 Also: (100x - 50x - 20x) - (20x + 50) = 50 => x = 10 Total number of people ordering from X = 50 * 10 = 500
People ordering from X only = 1°°0020 x 250 = 300 Poeple ordering from X and at least one more site = 200 People ordering from at least two or more sites = 200 + 50 = 250
1
People ordering from all three sites = 5 x 250 = 50
Since people who order from X and Y only is 100 more than the people who order from X and Z only.
. 2y + 100 + 50 = 200 => y = 25 People ordering from X and Y only = 125 Poeple ordering from X and Z only = 25
X Y
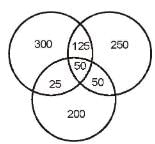
What is the number of people ordering only from a single shopping site?
At their wedding, Riz and Rekha received gifts amounting to a total of Rs. 1,00,000 – some of which was in cash and the rest was in the form of other articles. The cash received by them alone amounted to more than Rs. 35,000. All the cash received by them were by way of currency notes of the denominations of Rs. 2000, Rs. 500 and Rs. 200. When all the cash they received was pooled together, there were 10 notes of a certain denomination, 12 notes of a second denomination, and 16 notes of a third denomination. Riz and Rekha decided to spend an amount equal to the total value of the gifts received by them at their wedding (by way of cash and otherwise) in the ratio of 2:3 on buying a guitar and a sitar, respectively.
Which of the options below states the correct number of currency notes of each denomination received by Riz and Rekha?