Test: Class 9 Polity NCERT Based-2 - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Indian Polity for UPSC CSE - Test: Class 9 Polity NCERT Based-2
Regarding the system of Apartheid, consider the following statements:
1. Apartheid was the name of a system of racial discrimination unique to South Africa.
2. Nelson Mandela, was tried for treason by the white South African government for daring to oppose the apartheid regime in his country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following are the features of the constitution?
1. It generates a degree of trust and coordination that is necessary for different kinds of people to live together.
2. It does not specify how the government will be constituted.
3. It is the supreme law that determines the relationship among people living in a territory (called citizens).
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Consider the following statements:
1. In 1928, Motilal Nehru and other Congress leaders drafted a constitution for India.
2. In 1941, the resolution at the Karachi session of the Indian National Congress dwelt on how independent India’s constitution should look like.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to making of the constitution, consider the following statements:
1. The drafting of the document called the constitution was done by an assembly of elected representatives called the Constituent Assembly.
2. The Assembly adopted the Constitution on 26 November 1947 but it came into effect on 26 January 1950.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Regarding the constituent assembly, consider the following statements:
1. The Constituent Assembly represented the people of India.
2. The Constituent Assembly was chosen directly by all the people of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. Mahatma Gandhi was a member of the Constituent Assembly.
2. He wrote a magazine called 'Young India'.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
See the Image.
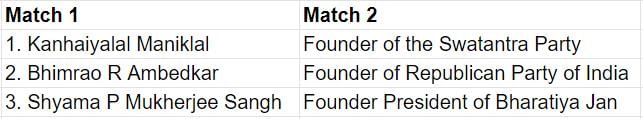
Regarding the Preamble Of the constitution, consider the following statements:
1. The Constitution begins with a short statement of its basic values called the Preamble to the constitution.
2. Preamble contains the philosophy on which the entire Constitution has been built.
3. Preamble provides a standard to examine and evaluate any law and action of government, to find out whether it is good or bad.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the following with reference to the meaning of various terms which feature in Preamble to the Indian constitution.
1. Term Socialist means wealth is generated socially and should be shared equally by society.
2. Term Secular means all of us should behave as if we are members of the same family.
3. Term Liberty means there are no unreasonable restrictions on the citizens in what they think, how they wish to express their thoughts.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
See the Image.
Consider the following Pairs:
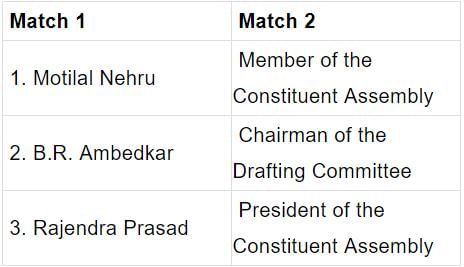
Regarding the Election Commission, consider the following statements:
1. It enjoys the same kind of independence that the judiciary enjoys.
2. The Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) is appointed by the Cabinet Committee on Appointments.
3. The Chief Election Commissioner is not answerable to the President or the government.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Regarding the powers of Election Commission, consider the following statements:
1. EC takes decisions on every aspect of conduct and control of elections.
2. When on election duty, government officers work under the control of the EC and not the government.
3. It implements the Code of Conduct and punishes any candidate or party that violates it.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following are illegal as per election laws of India?
1. Bribing or threatening voters.
2. Appealing to voters in the name of caste or religion.
3. Use government resources for election campaigns by party or candidate.
4. A candidate can spend more than Rs. 25 lakh in a constituency for an Lok Sabha election.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Regarding the model code of conduct, consider the following statements:
1. No party or candidate can use any place of worship for election propaganda.
2. Once elections dates are announced, Ministers shall not lay foundation stones of any projects.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following legal declarations a candidate has to make while filing his nomination for election?
1. Serious criminal cases pending against the candidate.
2. Details of the assets and liabilities of the candidate and his or her family
3. Education qualifications of the candidate
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following are the minimum conditions of a democratic election?
1. Everyone should have one vote and every vote should have equal value.
2. Parties and candidates should be free to contest elections.
3. Elections may or may not be held regularly.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. In our country we follow an area based system of representation for elections.
2. For Lok Sabha elections, the country is divided into 545 constituencies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following is not a feature of the Election system in India?
Which of the following is not the work of the Election Commission?
Which among the following statements is/are incorrect?
Consider the following statements:
1. The Government of India had appointed the First Backward Classes Commission in 1979.
2. It was headed by B.P. Mandal and was popularly called the Mandal Commission.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Regarding Parliament, consider the following statements:
1. Parliament is the final authority for making laws in any country.
2. Parliaments control all the money that governments have.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. In our country, the Parliament consists of two Houses.
2. The President of India is not a part of the Parliament.
3. All laws made in the Houses come into force only after they receive the assent of the President.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Regarding the powers of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha , consider the following statements:
1. Any ordinary law needs to be passed by both the Houses.
2. Lok Sabha exercises more powers in money matters.
3. The Rajya Sabha can only delay the budget passed Lok sabha by 28 days or suggest changes in it.
4. If the majority of the Rajya Sabha members say they have ‘no confidence’ in the Council of Ministers, all ministers including the Prime Minister, have to quit.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to Prime Minister and his ministers, consider the following statements:
1. The President appoints the Prime Minister.
2. The Prime Minister does not have a fixed tenure.
3. After his appointment, the Prime Minister appoints other ministers.
4. A person who is not a member of Parliament can also become a minister but such a person has to get elected to one of the Houses of the Parliament within six months of appointment as minister.
Consider the following regarding Council of ministers:
1. Council of Ministers is the official name for the body that includes all the Ministers.
2. Cabinet is the inner ring of the Council of Ministers.
3. Ministers of State are attached to and required to assist Cabinet Ministers.
4. Parliamentary democracy in most countries is often known as the Cabinet form of government.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. The Constitution contains in detail about the powers of the Prime Minister and his ministers. 2. When the Prime Minister quits, the entire ministry quits.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to President, consider the following statements:
1. The President is the head of the government.
2. The President of India is like the Queen of Britain whose functions are to a large extent ceremonial.
3. The President supervises the overall functioning of all the political institutions in the country so that they operate in harmony to achieve the objectives of the State.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following powers are enjoyed by the President?
1. All governmental activities take place in the name of the President.
2. All laws and major policy decisions of the government are issued in President’s name
3. All international treaties and agreements are made in the name of the President.
4. The President is the supreme commander of the defence forces of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding the Presidential System of the USA.
1. In this system the President is both the head of the state and the head of the government.
2. The President of the United States of America is the most well-known example of this kind of President.
3. The US President is indirectly elected.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
|
145 videos|633 docs|203 tests
|




















