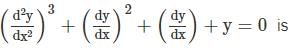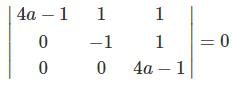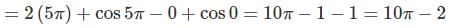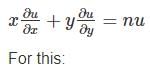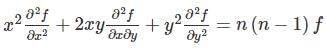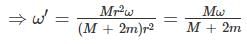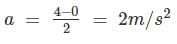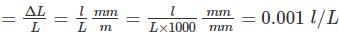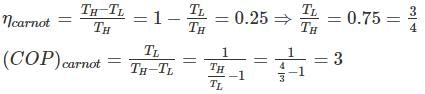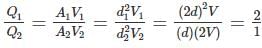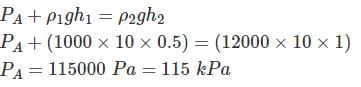Full Test 2 - EKT Mechanical - AFCAT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Full Test 2 - EKT Mechanical
The system of linear equations
(4a – 1)x + y + z = 0
-y + z = 0
(4a – 1) z = 0
has a non-trivial solution, if a equals
(4a – 1)x + y + z = 0
-y + z = 0
(4a – 1) z = 0
has a non-trivial solution, if a equals
If f(x, y)is a function satisfying Euler’ s theorem then
If the centre of a circle is (-6, 8) and it passes through the origin, then equation to its tangent at the origin is
A streamlined body is defined as a body about which ________.
A thin circular ring of mass M and radius r is rotating about its axis with a constant angular velocity ω. Two objects each of mass ‘m’ are attached gently to the opposite ends of a diameter of the ring. The ring will now rotate with an angular velocity –
One Coulomb passing a point in one second is one ______.
All the magnetic materials lose their magnetic properties when they are
When setting up a mechanical drawing in AutoCAD the drafter should set the units to _________
In the assembly design of shaft, pulley and key the weakest member is
The most suitable bearing for carrying very heavy loads with slow speed is _____.
In the multiple disc clutch, if there are 6 discs on the driving shaft and 5 discs on the driven shaft, then the number of pairs of contact surfaces will be equal to
If a light and a heavy body have equal kinetic energy of translation, then ________.
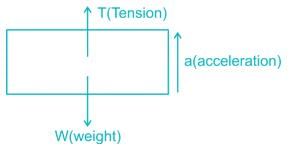
An elevator weighing 1000 kg attains an upward velocity of 4 m/sec in two seconds with uniform acceleration. The tension in the supporting cables will be:-
A bar of length ‘L' meters extends by ‘l' mm under a tensile force of ‘P’. The strain produced in the bar is
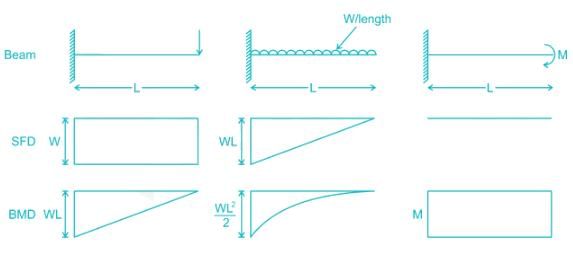
When a point load on the free end of a cantilever beam is increased, failure will occur
The shear force and bending moment are zero at the free end of a cantilever beam, if it carries a
After reaching the yielding stage while testing a mild steel specimen strain
How much heat energy is gained when 5 kg of water at 20°C is brought to its boiling point (Specific heat of water = 4.2 kJ/kg oC)
A Carnot engine receiving heat at 400 K has an efficiency of 25%. The COP of Carnot refrigerator , working between same temperature limits is
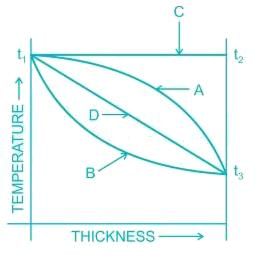
The figure given below shows the variation of temperature across the thickness of materials with different thermal conductivities under steady states. Curve C will be applicable when thermal conductivity of the material______
The liquid is flowing separately through each of two pipes whose diameters are in the ratio of 2 : 1, if the ratio of the velocities of flow in the two pipes by 1 : 2, then the ratio of the amounts of the liquid flowing per sec through the pipe will be
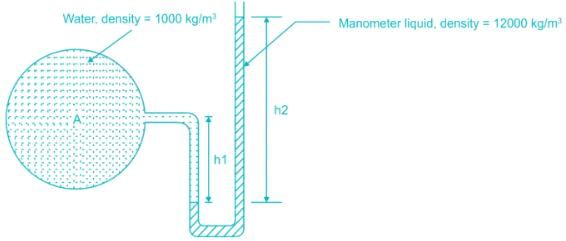
A U tube manometer shown in figure is used to measure the gauge pressure of water of density ρ1 = 1000 kg/m3. If the density of manometer liquid ρ2 is 12000 kg/m3, h1 = 0.5 m & h2 = 1.0 m, gauge pressure at ‘A’, the centre of tube is (take g = 10 m/s2)
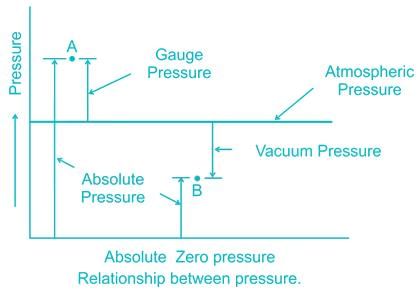
The reading of the pressure gauge fitted on a vessel is 25 bar. The atmospheric Pressure 1.03 bar and the value of g is 9.81 m/s2. The absolute pressure in the Vessel is