Full Test 3 - EKT Mechanical - AFCAT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Full Test 3 - EKT Mechanical
The smallest and largest Eigen values of the following matrix are:
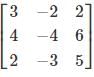
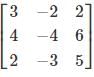
If the area of the square is increased by 69% the side of the square increase by
Euler number is defined as the ratio of inertia forces to
Permeance of a magnetic circuit corresponds to the following quantity in electrical circuit
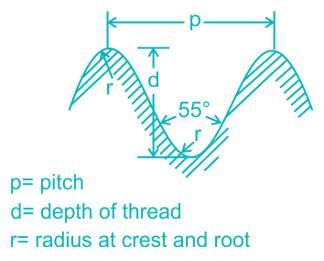
A double start thread has a pitch of 4 mm. The lead of the thread is
One quick way to view the entire drawing area is to use the Zoom command by typing ________.
For maximum power transmitted by belt, the maximum permissible tension T in the belt is
In a flange coupling, the flanges are coupled together by means of
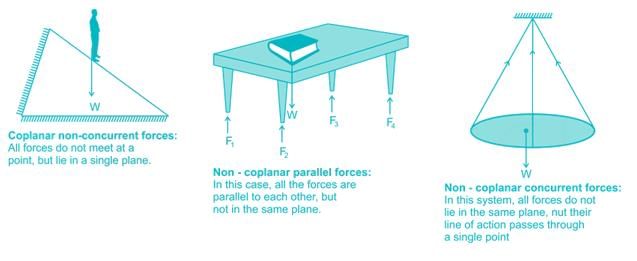
The forces which meet at one point and have their lines of action in different planes are called _____.
A ball of mass 1 kg moving with the velocity of 2 m/s collide directly with another stationary ball of mass 2 kg and comes to rest after impact. The velocity of second baII after impact is:
Two forces of 30 N and 40 N are acting at 90° to each other, the resultant force is
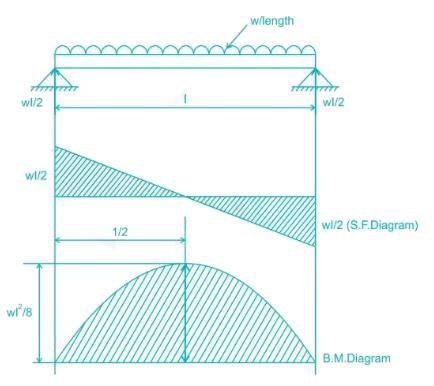
In a simply supported beam carrying a uniformly distributed load ‘w’ per unit length, the point of contraflexure
The load at which the column just buckles, is known as
Kinetic energy of the molecules in terms of absolute temperature (T) is proportional to
In solving a lumped parameter problem, which one of the following pair of non-dimensional numbers is used?
The boundary layer is formed as the flowing fluid comes in contact with the solid surface, because of the action of:
The divergent portion of a venturimeter is made longer than the convergent portion in order to
As a ship enters into a river from sea, one can expect that


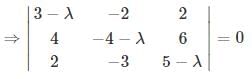
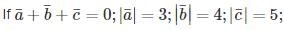 then angle between
then angle between 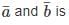
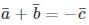
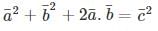
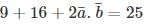
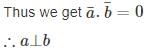
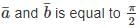

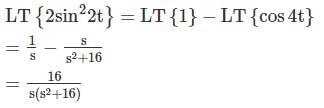
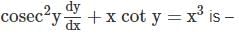
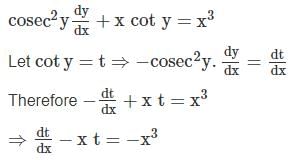
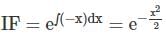
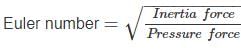
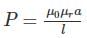
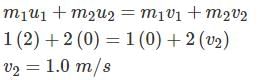
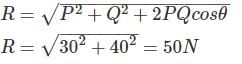
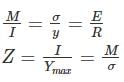
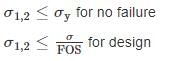

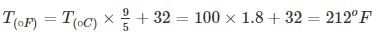
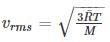
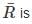 the universal gas constant. R has the same value for all gases: 8.3145 kJ/kmol K
the universal gas constant. R has the same value for all gases: 8.3145 kJ/kmol K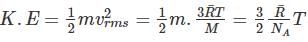
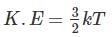
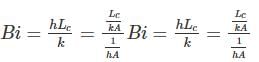
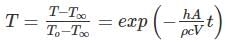
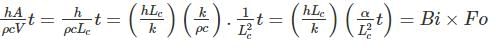
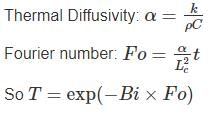
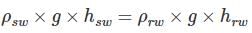
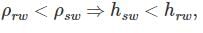 where h is the depth of ship into the water
where h is the depth of ship into the water










