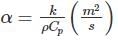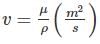Full Test 5 - EKT Mechanical - AFCAT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Full Test 5 - EKT Mechanical
The angle between two vectors a = i + 2j – k and b = 2i + j + k is
Given P(A) = 1/4, P(B) = 1/3 and P(AUB) = 1/2. Value of P(A/B) is
Force of buoyancy on a floating body equals ________.
A car of mass 1000 kg travelling at 32 ms-1 dashes into the rear of a truck of mass 8000 kg moving in the same direction with a velocity of 4 ms-1. After the collision, the car bounces back with a velocity of 8 ms-1. What is the velocity of the truck after the impact?
If the errors involved in the measurement of a side and mass of a cube are 3% and 4% respectively. What is the maximum permissible error in the density of the material?
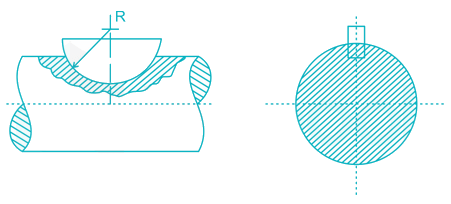
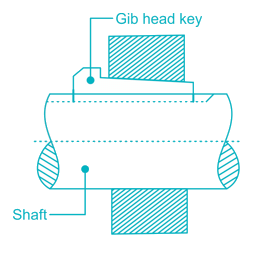
A key made from a cylindrical disc having segmental cross-section, is known as
If the tearing efficiency of a riveted joint is 60%, then ratio of rivet hole diameter to the pitch of rivets is _____.
The difference between tensions on the tight and slack slides of a belt drive is 3000 N. If the belt speed is 15 m/sec, the transmitted power, in kW, is
If two equal forces of magnitude P acts at an angle θ, their resultant will be
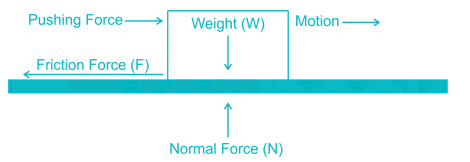
A body of weight 30 N rests on a horizontal floor. A gradually increasing horizontal force is applied to the body which just starts moving when the force is 9 N. The coefficient of friction between the body and the floor will be
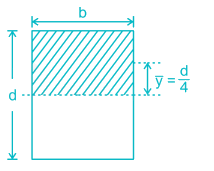
Maximum shear stress in a beam of rectangular cross section is ________ times the average shear stress.
A bar of length ‘L’ cm extends by ‘I’ mm under a tensile force of ‘P’. Then, the strain produced in the bar is
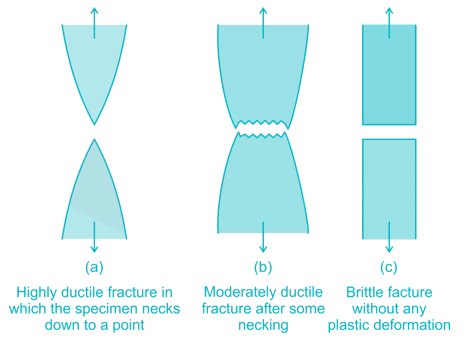
A tensile test is performed on a round bar. After fracture, it has been found that the diameter remains approximately same at fracture. The material under test was
The maximum distortion energy theory of failure is suitable to predict the failure of which one of the following types of materials?
A sample of 200 g of water is slowly heated from 27°C to 97°C. Calculate the change in entropy of the water. Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/kgK
In the Van der Waal’s gas equation 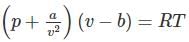 the constant ‘a’ is introduced to compensate for
the constant ‘a’ is introduced to compensate for
Efficiency of a Carnot engine is 75%. If the cycle direction is reverse, COP of the heat pump working on reversed Carnot cycle will be
The product of diameteral pitch and circular pitch is
The barometric pressure at the base of a mountain is 750 mm Hg and at the top 600 mm Hg. if the average air density is 1 kg/m3, the height of the mountain (in m) is approximately
The expression 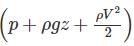 commonly used to express Bernoulli’s equation, has units of total energy per unit
commonly used to express Bernoulli’s equation, has units of total energy per unit



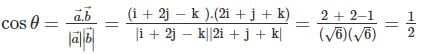

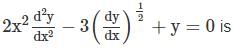
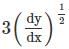 to the right side and square both sides to remove the radical.
to the right side and square both sides to remove the radical.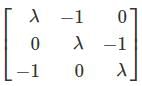 is 2 then λ is
is 2 then λ is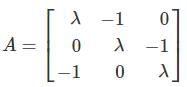
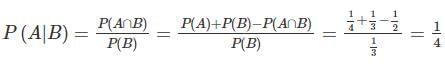
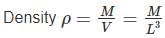
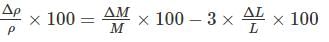
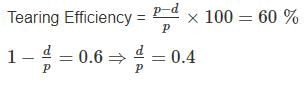
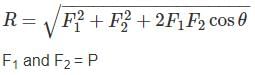
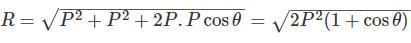
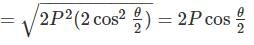
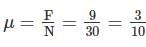
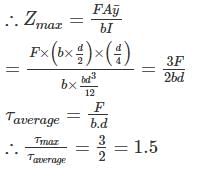
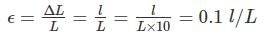
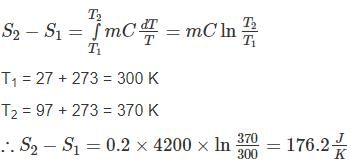
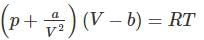
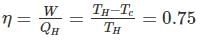
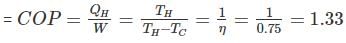

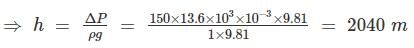
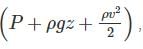 has units of total energy per unit volume.
has units of total energy per unit volume.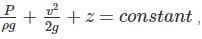 , then it is energy per unit weight.
, then it is energy per unit weight.