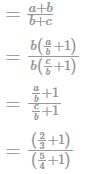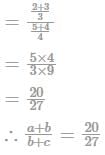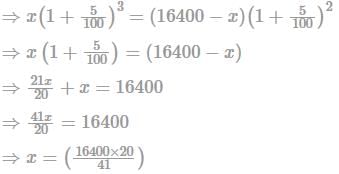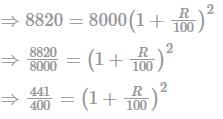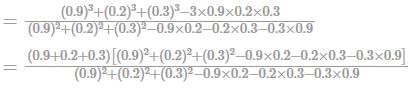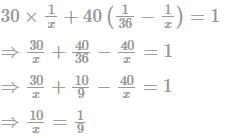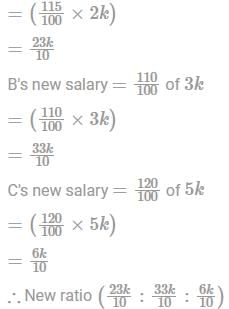Practice Test for SLAT - 4 - CLAT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Practice Test for SLAT - 4
All disputes arising in connection with the election of the President of India are required to be decided by the _______________.
Legal Principle - A contract is not voidable because it was caused as to mistake as to any law in force in India.
Factual Situation -Raghav had borrowed a sum of amount from Mohit which he was unable to pay. Raghav and Mohit entered into a contract grounded on the erroneous belief that a particular debt is barred by the Indian law of limitation. By this contract Mohit agreed to take only half of the sum due from Raghav. When Mohit found out that the debt was not barred by law of limitation, he sought to cancel the contract and sued Raghav for the entire amount due from him.
Will Mohit succeed?
In which case it was held that it is the obligation of a Muslim husband to pay maintenance to his divorced wife even beyond iddat period:
Legal Principle: Article -14 Equality before law - The State shall not deny to any person equality before the law or the equal protection of the laws within the territory of India.
Practical Situation: The executive council of the 'P' University announced the reservation of a certain number of seats to the employees to the graduate law program. Whether the same is justifiable in terms of Article 14?
Legal Principle - A contract that is caused by coercion is voidable at the option of the person whose consent is so caused. Coercion is committing or threatening to commit any act forbidden by Indian Penal Code, 1860.
Factual Situation - Gopal threatened Suresh that if Suresh does not sell his land to him, he will torture his sister who is Gopal's wife. Suresh sold the land to Gopal for a meager sum of amount. After few days his sister (copal's wife) died of natural death. Suresh sued Gopal for the recovery of land.
Will Suresh succeed?
As per the Factories Act "Adult" means a person who has completed ___ year of age.
In terms of Parliamentary terminology, What do we call a rule of legislative procedure under which a further debate on a motion can be stopped?
What is the meaning of the term "Ubi jus ibi remedium?"
Under the provisions of the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973, confessions:
Given that 100.48 = x, 100.70 = y and xz = y2, then the value of z is close to?
The length, breadth, and height of a room in the shape of a cuboid are increased by 10%,20% and 50% respectively. Find the percentage change in the volume of the cuboid.
If a/b = 2/3 and b/c = 4/5, then the ratio a+b/b+c equal to:
The population of a city is 35000. On an increase of 6% in the number of men and an increase of 4% in the number of women, the population would become 36760. What was the number of women initially?
A father left a will of Rs. 16400 for his two sons aged 17 and 18 years. They must get an equal amount when they are 20 years, at 5% compound interest. Find the present share of the younger son.
A sum of Rs. 8000 will amount to Rs. 8820 in 2 years if the interest is calculated every year. The rate of compound interest is:
Find the average increase rate, if the increase in the population in the first year is 30% and that in the second year is 40%.
A tank can be filled with water by two pipes A and B together in 36 minutes. If pipe B was stopped after 30 minutes, the tank is filled in 40 minutes. The pipe B can alone fill the tank in:
The marked price of a shirt and trousers are in the ratio 1:2. The shopkeeper gives a 40% discount on the shirt. If the total discount in the set of the shirt and trousers is 30%, the discount offered on the trousers is:
The salaries A, B, C are in the ratio 2 : 3 : 5. If the increments of 15%, 10%, and 20% are allowed respectively in their salaries, then what will be the new ratio of their salaries?
Find the least number which will leave the remainder 5 when divided by 8, 12, 16, and 20.
The product of two numbers is 2028 and their H.C.F. is 13. The number of such pairs is: