Test: Geography- 5 - UPSC MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Geography- 5
With reference to the interior structure of the earth, consider the following statements:
1. Molten iron in the core is responsible for Earth's magnetic field.
2. Earth's magnetic field is gradually becoming weaker with time.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
1. Molten iron in the core is responsible for Earth's magnetic field.
2. Earth's magnetic field is gradually becoming weaker with time.
Consider the following statements:
1. India ranks fourth in the world in terms of wind energy installed capacity.
2. The state of Tamil Nadu leads in the production of wind energy in India.
3. Under Paris Agreement, India has pledged a target of 100 GW of wind energy generation by 2022.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
1. India ranks fourth in the world in terms of wind energy installed capacity.
2. The state of Tamil Nadu leads in the production of wind energy in India.
3. Under Paris Agreement, India has pledged a target of 100 GW of wind energy generation by 2022.
Consider the following statements related to the locust infestation:
1. They originate in Rajasthan as Deserts provide the perfect bare ground for laying eggs.
2. The rainfall in these regions will produce enough green vegetation to enable both egg-laying and hopper development.
3. In India Ministry of Earth Sciences is responsible for monitoring, survey, and control of Desert Locust.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
1. They originate in Rajasthan as Deserts provide the perfect bare ground for laying eggs.
2. The rainfall in these regions will produce enough green vegetation to enable both egg-laying and hopper development.
3. In India Ministry of Earth Sciences is responsible for monitoring, survey, and control of Desert Locust.
Which of the following are marine protected areas in India?
1. Wildlife Sanctuary Pitti
2. Wildlife Sanctuary Coringa
3. Wildlife Sanctuary Gahirmatha
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Which of the following forces can disturb the equilibrium?
1. Mountain building
2. Glaciation
3. Volcanism
4. Sedimentation
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
With reference to the International Criminal Court (ICC), consider the following statements:
1. It is the world’s first permanent international criminal court.
2. It is a non-UN organization.
3. Its judgments can be appealed against.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to the occurrence of minerals across India, consider the following pairs: Mineral Mine
1. Copper : Khetri
2. Aluminum : Balaghat
3. Iron Ore : Gurumahisani
4. Manganese : Panchpatmali Hills
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
These are immature soils which overlie the Vindhyan sandstones and Ladakh shales. Their color ranges from light yellow to deep brown with a thickness of 7 to 15 cm. These soils contain 35 per cent or more, by volume, of rock fragments, cobbles, gravel, and laterite concretions or ironstones within shallow depths.
Which of the following soils is best described by the above passage?
With reference to India's biodiversity, Eriocaulon parvicephalum, Eriocaulon karaavalense, Ardisia ramaswami recently seen in the news are species of
In the context of environmental protection, the Waigani Convention deals with
Confederation of Indian Industry's Green Building Congress 2020 was recently inaugurated. In this context, consider the following statements regarding green buildings rating systems in India:
1. Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment (GRIHA) is the only rating tool for green buildings in India.
2. The Indian Green Building Council develops new green building rating programmes.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Arrange the following commodities in increasing order of their share in India's export basket:
1. Petroleum Products
2. Precious and Semi-precious stones
3. Iron and Steel
4. Drug formulations
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Arrange the following rock system in the correct chronological order.
1. Gondwana
2. Dharwar
3. Cuddapah
4. Dravidian
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
ADMM-Plus sometimes seen in the news is a platform to strengthen security and defense cooperation for peace, stability, and development of?
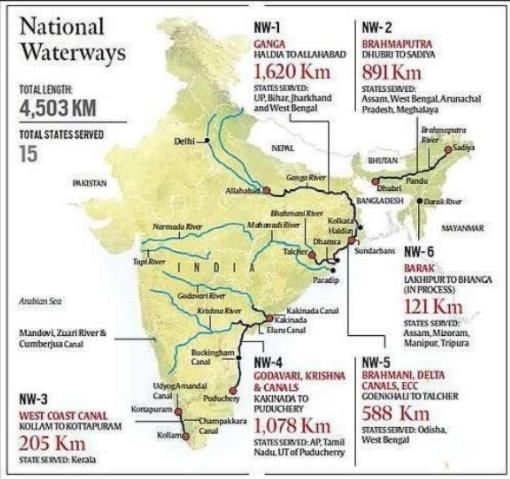
Consider the following statements regarding India's national inland waterways:
1. The National Waterway 4 connecting Kakinada to Puducherry is the shortest Inland water of India.
2. The National Waterway 5 connects Lakhipur and Bhanga of the Barak River in North-East India.
3. National Waterway 3 is the only waterway of India that serves five states.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
Which of the following rivers in India pass through the cities where the Kumbh Mela is observed?
1. Ganga
2. Godavari
3. Kaveri
4. Shipra
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
With reference to the common occurrence of various drainage patterns across different regions, consider the following pairs: Drainage Pattern Region
1. Rectangular Drainage : Chotanagpur Plateau
2. Radial Pattern : Amarkantak Mountain
3. Dendritic Drainage : Indo-Gangetic Plains
4. Trellis Drainage : Vindhyan Mountains
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
With reference to the 'TEEB India Initiative', consider the following statements:
1. It highlights the economic consequences of the loss of biological diversity.
2. It has been developed by India and France as a part of their Paris Climate Change commitments.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following factors can affect the rotational speed of Earth?
1. Tides
2. Mean sea level
3. Wind patterns
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
With reference to the phenomenon of Lake Effect Snow, consider the following statements:
1. It is the snowfall caused by a cold airmass moving over relatively warm lake waters.
2. It is commonly observed in the Great Lakes region of North America.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding Jet Streams:
1. Jet streams are stronger in winters for both the northern and southern hemispheres.
2. Speed of jet streams gradually increases from its central core towards the outer boundary.
3. Jet streams move along with the apparent latitudinal movement of the sun.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
With reference to Pangong Tso Lake, consider the following statements:
1. It is a part of the Indus river basin area.
2. It is a narrow deep endorheic (landlocked) lake situated in Ladakh Himalayas.
3. It does not freeze in winter due to high salinity.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following pairs: Panch Prayag River Confluence
1. Vishnuprayag : Alaknanda and Dhauli Ganga
2. Nandpragay : Alaknanda and Nandakini
3. Karnaprayag : Alaknanda and Mandakini
4. Rudraprayag : Alaknanda and Pinder
5. Devprayag : Bhagirathi and Alaknanda
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
Consider the following pairs: Hill Ranges State
1. Palkonda Range : Andhra Pradesh
2. Kaimur Range : Maharashtra
3. Maikal Range : Jharkhand
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
With reference to different types of Shipping Ports, consider the following pairs: Type of Port Port
1. Dry Port : Kolkata
2. Inland Port : Riyadh
3. Warm Water Port : Kushiro
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?