Test: Refraction through Spherical Lense - Class 10 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Science Class 10 - Test: Refraction through Spherical Lense
If a lens has a focal length, F = +12 cm, then it is a
If a lens has a focal length, f = -12 cm. then it is a
Which lens always forms a virtual image ?
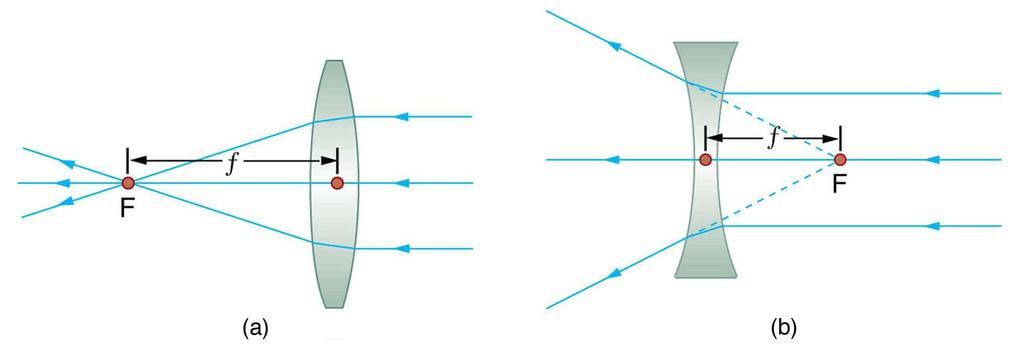
In a convex lens, where is the image formed, when an object is placed at 2F ?
What happens to the image formed by a convex lens if its lower part is blackened ?
Which lens always forms diminished and erect image ?
A ray of light incident on the optical centre of a spherical lens, after refraction passes through:
Four students A, B, C and D did their experiment on finding the focal length of convex lens by obtaining the image of a distant object as follows:
Student A used the window grill in the laboratory as the object and a white paper sheet held in hand, as the screen.
Student B used a distant tree in absence of sunlight as the object, and a white thick board held on a stand, as the screen.
Student C used a well illuminated laboratory window grill as the object and a white paper sheet held on a stand as the screen.
Student D used a well illuminated distant tree as the object and a white thick board held on a stand, as the screen.
Arrange these techniques in order of decreasing accuracy in measurement.
Is the optical centre always at the centre of lens ?
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object ?
The minimum distance between an object and its real image in a convex lens is (f = focal length of the lens)
The image formed by a convex lens is virtual when
A lens which forms a virtual and enlarged image is
To determine the focal length of convex lens by obtaining a sharp image of a distant object we generally follow the following steps which are not in proper sequence.
(a) Hold the lens between the object and the screen
(b) Measure the distance between the lens and the screen
(c) Select a well lit distant object
(d) Adjust the position of the lens to form a sharp image
The correct sequence will be:
The image formed by a convex lens is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Then the position of the object should be
The lens which is used to correct myopia (shortsightedness) is
|
80 videos|512 docs|74 tests
|