Test: Heating Effect of Electric Current - Class 10 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Heating Effect of Electric Current
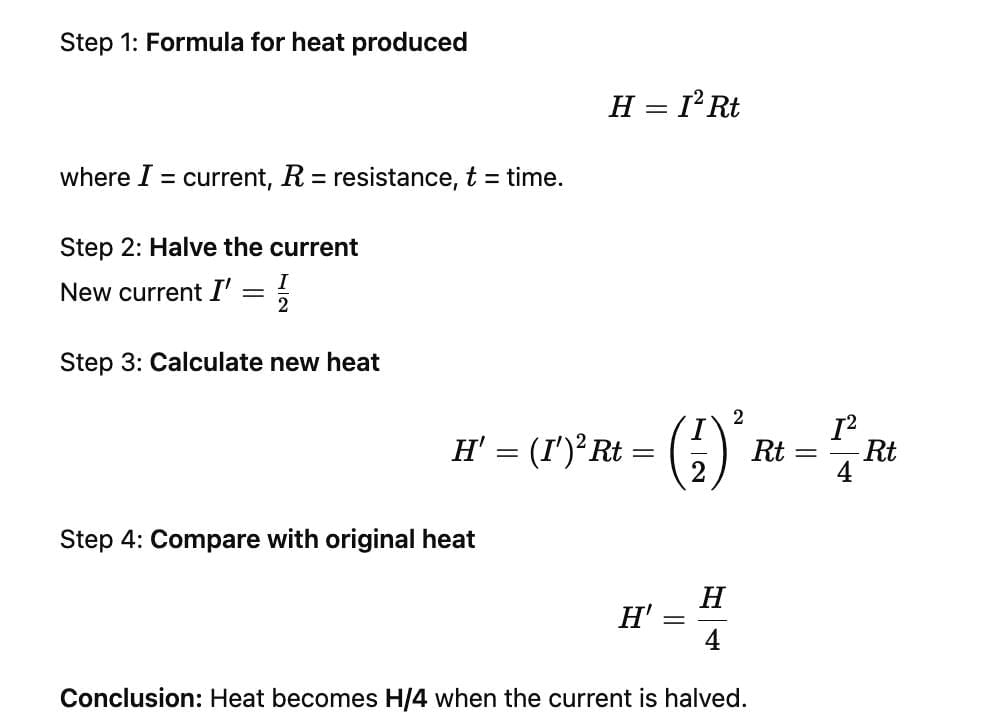
If the current passing through a heater is halved, then the heat produced by it becomes
An electric bulb is marked 18watt-240 volt. If it is used across 240 V power line for one hour daily, calculate the number of days to consume 1 unit of electric energy.
Two bulbs marked 200 watt-250 volts and 100 watt-250 volts are joined in series to 250 volts supply. Power consumed in circuit is
Which of the following terms does not represent electrical power in a circuit ?
The resistance of a conductor increases with-
I: Increase in length
II: Increase in volume
III: Decrease in area
How much heat energy is produced in 10 second in an electric iron having resistance 440 Ω, when a potential difference of 220 volt is applied across it?
An electric refrigerator rated 500 W operates 10 hr per day. What is the cost of the energy to operate it for 30 days at Rs. 4.00 per kWh ?
Which property of the electricity is responsible for use of Fuse wire in household wiring?
Two light bulbs P and Q are identical in all respects, except that P’s filament is thicker than Q’s. If the same potential difference is applied to each, then
Find the potential difference across the resistor, when 125 J of heat is produced each second in a 5 ohm resistor.
A bulb is rated as 270V, 0.5 A. Its power is
How much energy is transferred when 10 A current flows through a resistor of 5 ohm for 30 minutes ?
Two light bulbs are marked 230 V; 75 W and 230 V; 150 W. If the first bulb has a resistance R, then the resistance of the second is;
A certain wire has a resistance R. The resistance of another wire identical with the first and having twice its diameter is;