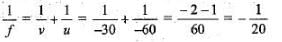Light: Reflection & Refraction - 1 - Grade 9 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Light: Reflection & Refraction - 1
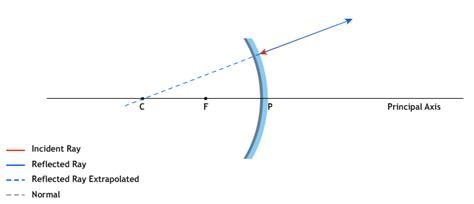
A concave mirror is used to form an image of the sun on a white screen. If the lower half of the mirror is covered with a black paper, the effect on the image formed on the screen would be:
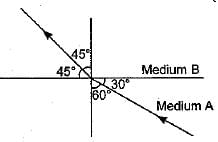
Figure shows a ray of light as it travels from medium A to medium B. Refractive index of the medium B relative to medium A is

A full length image of a distant tall building can definitely be seen by using:
The angle of incidence of any light ray passing through the centre of curvature of a spherical mirror is:
A 10 mm long awl pin is placed vertically in front of a concave mirror. A 5 mm long image of the awl pin is formed at 30 cm in front of the mirror. The focal length of this mirror is:
In case of a real and inverted image the magnification of a mirror is:
Rays from sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of the image is exactly equal to the size of the object ?
A magnified real image is formed by a convex lens when the object is at:
A virtual, erect and magnified image of an object is to be produced with a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm. Object may be placed at a distance of: