Test: Motion- 2 - UPSC MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Science & Technology for UPSC CSE - Test: Motion- 2
For a body starting from rest and moving with a constant acceleration, if it acquires a velocity of 4 m/s in 2 seconds, what is the displacement in 10 seconds?
On a velocity-time graph, a horizontal straight line corresponds to motion at_______.
DIRECTION: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R).
Assertion: The speedometer of an automobile measures the average time taken to travel a distance by an automobile.
Reason: Average velocity is equal to total displacement per total time taken.
Assertion: Acceleration of a moving body is always positive.
Reason: Acceleration of a moving body is the rate of change of velocity
Assertion: The displacement of a body may be zero when distance travelled by it is not zero.
Reason: The displacement is the longer distance between the initial and final positions.
Assertion (A): An object moving with uniform acceleration follows a parabolic trajectory on a velocity-time graph.
Reason (R): The distance-time graph for uniform acceleration is a straight line, indicating constant acceleration.
|
114 videos|428 docs|209 tests
|



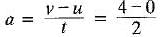 = 2m/s2
= 2m/s2