Test: Geography Of India - 2 - UPSC MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Geography Of India - 2
When you travel in Himalayas, you will see the following:
1. Deep gorges
2. U-turn river courses
3. Parallel mountain ranges
4. Steep gradients causing land-sliding
Which of the above can be said to be the evidences for Himalayas being young fold mountains?
[2012]
1. Deep gorges
2. U-turn river courses
3. Parallel mountain ranges
4. Steep gradients causing land-sliding
With reference to the wetlands of India, consider the following statements:
1. The country’s total geographical ar ea under the category of wetlands is recorded more in Gujarat as compared to other States.
2. In India, the total geographical area of coastal wetlands is larger than that of inland wetlands.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
[2012]
1. The country’s total geographical ar ea under the category of wetlands is recorded more in Gujarat as compared to other States.
2. In India, the total geographical area of coastal wetlands is larger than that of inland wetlands.
A particular State in India has the following characteristics :
1. It is located on the same latitude which passes through northern Rajasthan.
2. It has over 80% of its area under forest cover.
3. Over 12% of forest cover constitutes Protected Area Network in this State.
Which one among the following States has all the above characteristics?
[2012]
1. It is located on the same latitude which passes through northern Rajasthan.
2. It has over 80% of its area under forest cover.
3. Over 12% of forest cover constitutes Protected Area Network in this State.
A state in India has the following characteristics:
1. Its northern part is arid and semi-arid.
2. Its central part produces cotton.
3. Cultivation of cash crops is predominant over food crops.
Which one of the following states has all of the above characteristics?
[2011]
The Brahmaputra, Irrawady and Mekong rivers originate in Tibet and flow though narrow and parallel mountain ranges in their upper reaches. Of these rivers, Brahmaputra makes a “U” turn in its course to flow into India. This “U” turn is due to
[2011]
Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’?
[2014]
The lower Gangetic plain is characterised by humid climate with high temperature throughout the year. Which one among the following pairs of crops is most suitable for this region?
[2011]
Between India and East Asia, the navigation-time and distance can be greatly reduced by which of the following ?
1. Deepening the Malacca straits between Malaysia and Indonesia.
2. Opening a new canal across the Kra Isthmus between the Gulf of Siam and Andaman Sea.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
[2011]
The approximate representation of land use classification in India is:
[ 2010]
The latitudes that pass through Sikkim also pass through:
[2010]
If there were no Himalayan ranges, what would have been the most likely geographical impact on India?
1. Much of the country would experience the cold waves from Siberia.
2. Indo-gangetic plain would be devoid of such extensive alluvial soils.
3. The pattern of monsoon would be different from what it is at present.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
[2010]
Which one of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
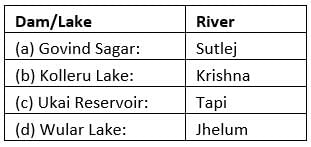
[2010]
Which one of the following is the appropriate reason to considering the Gondwana rocks as most important of rock systems of India?
[2010]
When you travel in certain parts of India, you will notice red soil. What is the main reason for this colour?
[2010]
Rivers that pass through Himachal Pradesh are:
[2010]
With reference to, the river Luni, which one of the following statements is correct?
[2010]
In India, which type of forest among the following occupies the largest area?
[2010]
Consider the following pairs:
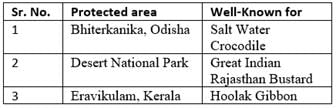
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
[2010]
With reference to the mineral resources of India, consider the following pairs:
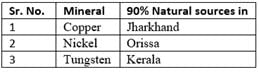
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
[2010]
Following are the characteristics of an area in India:
1. Hot and humid climate
2. Annual rainfall 200 cm
3. Hill slopes up to an altitude of 1100 metres
4. Annual range of temperature 15°C to 30°C.
Which one among the following crops are you most likely to find in the area described above?
[2010]



















