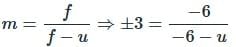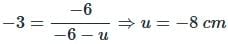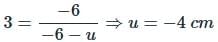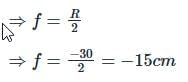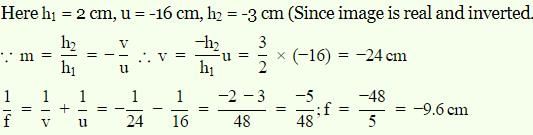Test: Mirror Formulae - UPSC MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Science & Technology for UPSC CSE - Test: Mirror Formulae
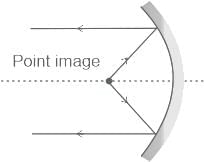
If the magnification has a negative sign, the image formed by the concave mirror must be
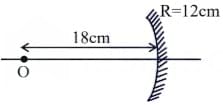
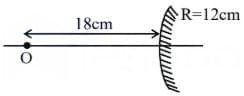
Two identical objects are placed in front of convex mirror and concave mirror having same radii of curvature of 12 cm, at same distance of 18 cm from the respective mirrors. The ratio of sizes of the images formed by convex mirror and by concave mirror is:
Image formed by a concave mirror of focal length 6 cm, is 3 times of the object, then the distance of object from mirror is
The radius of curvature of a concave mirror is 30 cm. Following Cartesian Sign Convention, its focal length is expressed as ________.
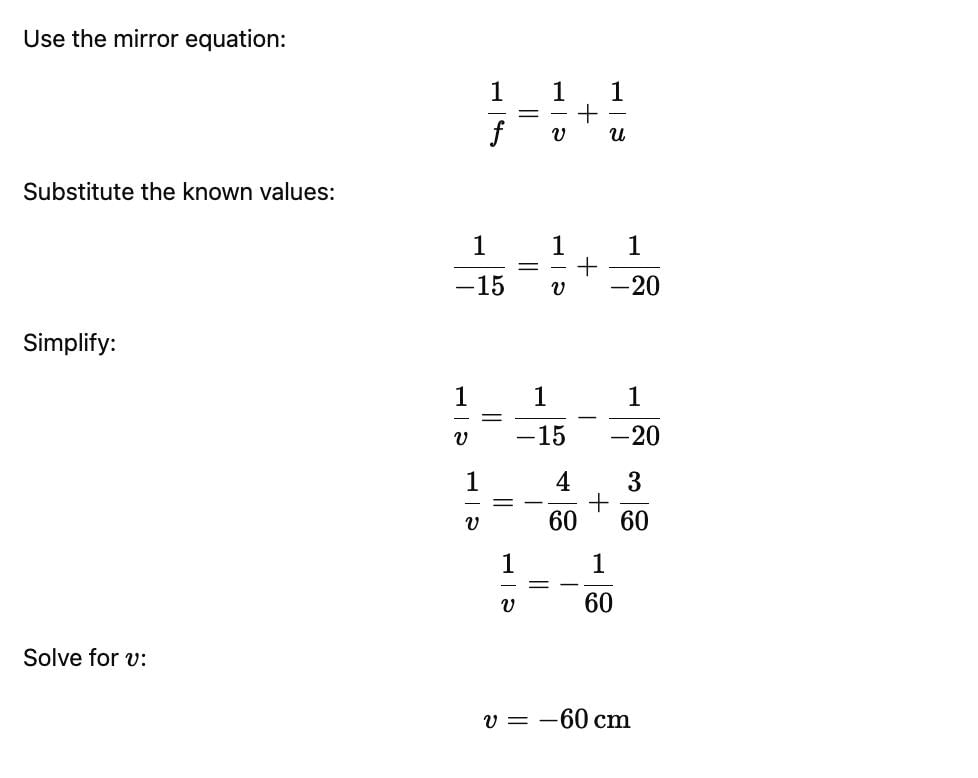
An object is placed 20 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. The image formed will be:
The focal length of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is 30 cm will be:
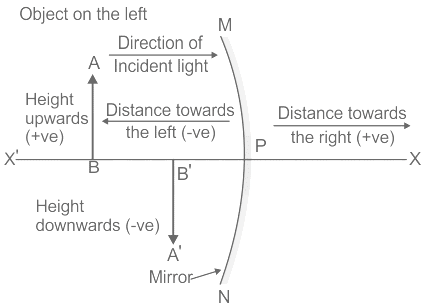
Which one is correct as the new cartesian sign conventions ?
An object 2 cm high is placed at a distance of 16 cm from a concave mirror, which produces a real image 3 cm high. What is the focal length of the mirror ?
|
91 videos|516 docs|212 tests
|