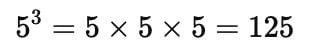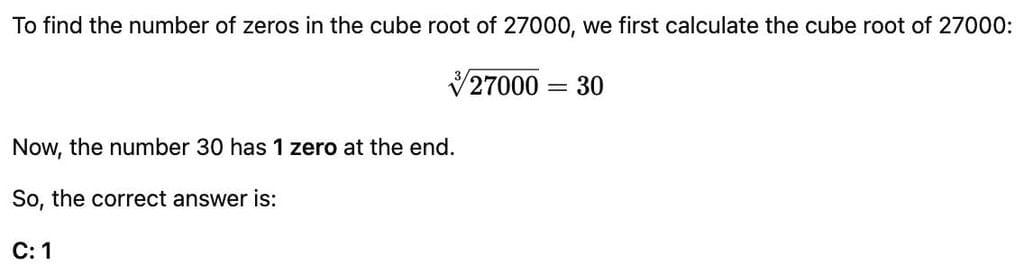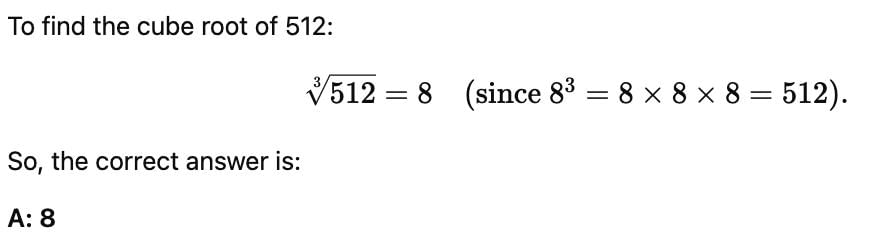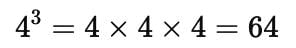Test: Cubes And Cube Roots- 2 - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test CSAT Preparation - Test: Cubes And Cube Roots- 2
What will be the unit digit of the cube of a number ending with 6 ?
Each prime factor appears _________ times in its cube.
What will be the unit digit of the cube of a number ending with 2 ?
The number of digits in the cube root of a 6-digit number is _______.
What will be the unit digit of the cube root of a number ends with 3?
The smallest natural number by which 135 must be divided to obtain a perfect cube is
How many zeros will be there in the cube root of 800?
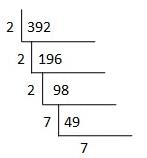
By which smallest natural number 392 must be multiplied so as to make the product a perfect cube ?
The smallest natural number by which 243 must be multiplied to make the product a perfect cube is __________.
How many zeros will be there in the cube root of 27000?
What will be the unit digit of the cube of a number ending with 4 ?
For a number ending with 7, the unit digit of its cube is equal to:
The smallest natural number by which 704 must be divided to obtain a perfect cube is
What will be the unit digit of the cube root of a number ends with 2?
|
208 videos|138 docs|138 tests
|