Test: Market Equilibrium - 2 - UPSC MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Market Equilibrium - 2
The factor that causes a change in quantity demanded is
The factor that causes a change in quantity supplied is
A rise in the price of the complementary good leads to
A fall in the price of the good for a seller leads to
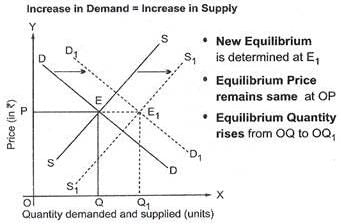
Market for a good is in equilibrium. An increase in demand for the good will
Market for a good is in equilibrium. A decrease in demand for the good will
Market for a good is in equilibrium. An increase in supply for the good will
Market for a good is in equilibrium. A decrease in supply for the good will
Market for a good is in equilibrium. An increase in demand for the good will
Market for a good is in equilibrium. An increase in supply for the good will
Market for a good is in equilibrium. An increase in the price of the good will
Market for a good is in equilibrium. A decrease in price for the good will