Test: PU LLB Mock Test - 5 (New Pattern) - CLAT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: PU LLB Mock Test - 5 (New Pattern)
Which period is called the Golden period for Ancient India?
What is the name of the condition that prevents blood from clotting?
Which of the following Viceroys withdrew Doctrine of Lapse?
Where is the International Court of Justice located?
Which schedules lists the 22 languages recognized by the constitution?
What defines a statistical estimation based on extending a known sequence of values/facts beyond the area that is already known?
The United Nations has how many principal organs to carry out its functions?
What was a significant reason for the Karnataka government's rejection of the Kasturirangan Committee report?
After 44th Constitutional Amendment Act, 1978 when the Proclamation of Emergency is made under Article 352(1)
In which year were the Indian states recognized on a linguistic basis:
Which of the following provisions came into force immediately after adoption of the Indian Constitution
Rules
A. The fundamental right to freedom of association includes the right to form an association as well as not join an association.
B. The fundamental right to freedom of association also includes the freedom to decide with whom to associate.
C. The fundamental right to freedom of association does not extend to the right to realize the objectives of forming the association.
D. Fundamental rights are applicable only to laws made by or administrative actions of the State and do not apply to actions of private persons.
E. Any law in contravention of fundamental rights is unconstitutional and therefore cannot bind any person.
Facts
Gajodhar Pharmaceuticals, a private company, offered an employment contract of two years to Syed Monirul Alam. One of the clauses in the employment contract provided that Syed Monirul Alam must join Gajodhar Mazdoor Singh (GMS), one of the trade unions active in Gajodhar Pharmaceuticals.
Q. If Parliament enacts is law that requires a trade union to open its membership to all the employees, then
The 42nd Amendment added the following words to the Preamble of the Indian Constitution:
Right to Property as a Fundamental Right from the list of Fundamental Rights was removed by virtue of
Under Article 143 the Supreme Court enjoys
Which one of the following is not a method of by which an Indian individual may loose his/her citizenship
Principle: Acceptance must be given only by the person to whom the offer has been made
Facts: A sold his to his manager B without disclosing the fact to his customers. C, a customer, who had a running account with A, sent an order for the supply of goods to A by name. B received the order and executed the same, C refused to pay the price. Is C liable to pay B?
Assertion: In the event of violation of any legal right the aggrieved party is entitled to recover unliquidated damages
Reason: The object of awarding damages to the aggrieved party is to put him in the same position in which he would have been if the wrong would not have been committed. Damages are therefore assessed on that basis.
The railway authorities allowed a train to be overcrowded. In consequence, a legitimate passenger Mr. X got his pocket picked. Choose the appropriate answer:
In the questions given below, choose the word opposite in meaning to the given word.
Permit
Improve the bracketed part of the sentence.
At harvest the corn was cut high on the stalk with short sickles and (put up in sheafs), after which it was carried to the threshing-floor and trodden out by the hoofs of oxen.
In the following questions, four words are given in each question, out of which only one word is correctly spelled. Find the correctly spelt word.
In the following questions, one part of the sentence may have an error. Find out which part of the sentence has an error and mark the option corresponding to it. If the sentence is free from error, mark the No Error option.
The library members were asked to return the books to the library.
Directions: In making decisions about important questions, it is desirable to be able to distinguish between `strong` arguments and `weak` arguments.
`Strong` arguments are those which are both important and directly related to the question. `Weak` arguments are those which are of minor importance and they are directly related to the question or may be related to a trivial aspect of the question.
The question below is followed by two arguments numbered I and II. You have to decide which of the given arguments is a `strong` argument.
Question: Should all the non-performing employees in the public sector be compulsorily retrenched from service?
Arguments:
I. No, this will give an unjust handle to the management and they may use it indiscriminately.
II. Yes, this will help in increasing the efficiency of these organisations and these organisations will become more profitable establishments as a result.
Direction: Read the given information carefully and answer the question that follows.
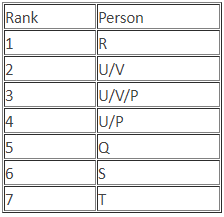
(i) Seven students P, Q, R, S, T, U and V take a series of tests.
(ii) No two students score the same marks.
(iii) V always scores more than P.
(iv) P always scores more than Q.
(v) Each time, either R scores the highest and T scores the least or S scores the highest and U or Q scores the least.
Q. If S is ranked sixth and Q is ranked fifth, then which of the following statements can be true?
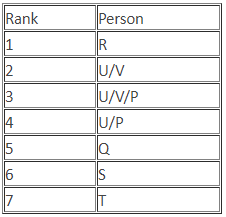
Direction: Read the given information carefully and answer the question that follows.
(i) Seven students P, Q, R, S, T, U and V take a series of tests.
(ii) No two students score the same marks.
(iii) V always scores more than P.
(iv) P always scores more than Q.
(v) Each time, either R scores the highest and T scores the least or S scores the highest and U or Q scores the least.
Q. If V is ranked fifth, then which of the following statements must be true?
Direction: Read the given information carefully and answer the question that follows.
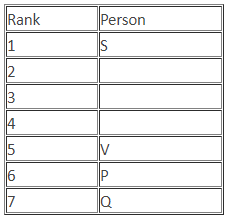
(i) Seven students P, Q, R, S, T, U and V take a series of tests.
(ii) No two students score the same marks.
(iii) V always scores more than P.
(iv) P always scores more than Q.
(v) Each time, either R scores the highest and T scores the least or S scores the highest and U or Q scores the least.
Q. If S is ranked second, then which of the following statements can be true?
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below.
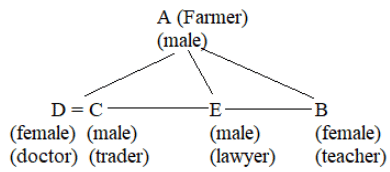
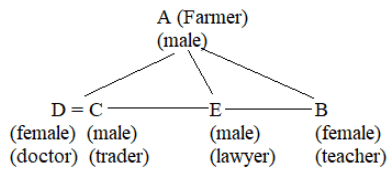
(i) There is a family of 5 persons – A, B, C, D and E.
(ii) They have different professions: Doctor, Teacher, Trader, Lawyer, and Farmer.
(iii) B, an unmarried teacher, is the daughter of A.
(iv) E, a lawyer, is the brother of C.
(v) C is the husband in the only married couple of the family.
(vi) A, a farmer, is a father of two sons and an unmarried daughter.
(vii) Daughter–in–law of A is a doctor.
Q. Which among the following is a group of female members of the family?
Direction: Read the following information carefully and answer the question given below.
(i) There is a family of 5 persons – A, B, C, D and E.
(ii) They have different professions: Doctor, Teacher, Trader, Lawyer, and Farmer.
(iii) B, an unmarried teacher, is the daughter of A.
(iv) E, a lawyer, is the brother of C.
(v) C is the husband in the only married couple of the family.
(vi) A, a farmer, is a father of two sons and an unmarried daughter.
(vii) Daughter–in–law of A is a doctor.
Q. Who is the trader in the family?
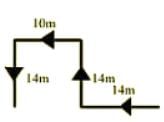
Namratha walks 14 metres towards west, then turns to her right and walks 14 meters and then turns to her left and walks 10 metres. Again turning to her left she walks 14 metres. What is the shortest distance (in metres) between her starting point and her present position?