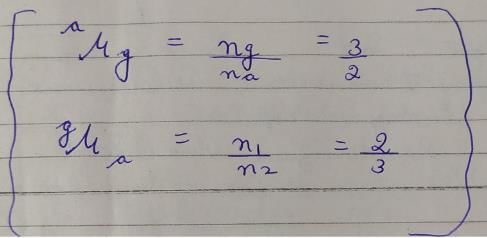Test: Ray Optics - 2 - Class 10 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Science Class 10 - Test: Ray Optics - 2
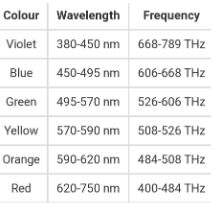
When white light passes through a prism, it splits into its component colours. This phenomenon is called
The wavelengths corresponding to violet, yellow and red lights are λv , λy and λr respectively.
In a museum a child walks towards a large concave mirror. He will see that
The magnification of an object placed 10 cm from a convex mirror of radius of curvature 20 cm will be
The angle of incidence for a light ray incident on a plane mirror is 30 degrees. What will be the angle of reflection?
A concave mirror of focal length 10 cm produces an image five times as large as the object. If the image is in front of the mirror, the distance of the object from the mirror will be
1. Which of the following statements is true regarding reflection of light?
To form an image twice the size of the object, using a convex lens of focal length 20 cm, the object distance must be –
Refractive index of glass w.r.t. air is 3/2. What is the refractie index of air w.r.t glass ?
Which of the following conditions are necessary for total internal reflection to take place at the boundary of two optical media?
I. Light is passing from optically denser medium to optically rarer medium.
II. Light is passing from optically rarer medium to optically denser medium.
III. Angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle.
IV. Angle of incidence is less than the critical angle.
The speed of light in vacuum is 3.0 × 108 m/s. If the refractive index of a transparent liquid is 4/3, then the speed of light in the liquid is
The refractive indices of water and glass are 4/3 and 3/2 respectively. The refractive index of water with respect to glass is
Which of the following can be used to form a virtual image of an object?
I. convex lens
II. concave lens
III. concave mirror
|
83 videos|437 docs|74 tests
|