Test: Geomorphology - 2 - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Geomorphology - 2
Fold mountains are formed due to large- scale movements in the Earth’s surface when stresses are set up in the Earth’s crust. What is/are the possible reason(s) for this?
1. Increased load of overlying rocks
2. Flow movements in the mantle
3. Magmatic intrusions in the crust
Choose the correct answer using the codes below:
Regarding fold mountains, consider the following statements:
1. Alpine mountain building phase is the recent phase to which the Himalayan mountains belong to.
2. The Ural Mountains were formed during Alpine orogeny (mountain building phase) too.
Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
Why a very large thickness of sedimentary rocks is found in the Fold Mountains?
Which of the following are examples of FOLD mountains?
1. Himalayas
2. Alps - Europe
3. Appalachians - North America
4. Ural-Russia
5. Aravalli - India
Which of the above is/are correct?
Which of the following are the salient features of fold Mountains?
1. They are least likely to have conical peaks.
2. They are created when large areas are broken and displaced vertically.
3. They must be associated with volcanism either from the mountain core or its vicinity.
Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
Tectonic plateaus are formed due to Earth movements that cause uplifts. Consider the following statements:
1. Meseta of Central Iberia
2. Harz of Germany
3. Bolivian plateau found between two ranges of Andes
Which of the following are tectonic plateaus found on Earth?
In humid highlands, several dissected plateaus like the Scottish Highlands are found. Which of the forces are responsible for the formation of such dissected plateaus?
1. Stream action
2. Cuts done due to glaciation
3. Abrasion by wind
Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
Which of the following evidence supports the theory of continental drift?
1. Jigsaw fit of shorelines of Africa and South America
2. Occurrence of gold deposits in Ghana coast but the absence of any source rocks there
3. All the east South American and Wes African coasts are good natural harbours
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
The belt of ancient rocks of 2,000 million years from the Brazil coast matches those from western Africa. Also, the earliest marine deposits along the coastline of South America and Africa are of the Jurassic age. What are we talking about?
Regarding Plate tectonics, consider the following statements:
1. It is the theory that Earth’s outer shell is divided into several plates that glide over the mantle.
2. It is another name for the theory of continental drift.
3. It discards the conventional geological view that there is the conventional current flowing in the mantle.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
Which of the following about the tectonic ‘Indian Plate’ is not correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. The northward movement of the Indian plate continues to date.
2. A part of the Western peninsular region of India is submerged beneath the sea.
3. The river valleys in the Peninsular region are deep with high gradients.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
Consider the following statements about seafloor spreading concept:
1. Constant eruptions at the crest of oceanic ridges cause the rupture of the oceanic crust and the new lava wedges into it, pushing the oceanic crust on either side. The ocean floor thus spreads.
2. The ocean floor that gets pushed due to volcanic eruptions at the crest sinks at the oceanic trenches and gets consumed.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Which of the following evidence supports the hypothesis of ‘seafloor spreading’?
1. Rocks on either side of mid-oceanic ridges have remarkable similarities.
2. Earthquake foci at mid-oceanic ridges are shallower than oceanic trenches.
3. Oceanic crust rocks arc younger than continental rock crust.
Choose the correct answer using the codes below:
Which of the following oceanic regions is the primary site of generation of new crust, hosting mineral resources and supporting unique ecosystems?
The action of the endogenic forces is not uniform and thus the tectonically controlled original crustal surface is uneven. This can be attributed to factors like
1. Variation in crustal thickness
2. Variation in geothermal gradients
3. Volcanism in the lithosphere
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
Which of the following is responsible for bringing changes on the surface of the Earth?
1. Gravitational force
2. Tectonic forces
3. Electromagnetic radiation
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
Which of the following factors contributes to the evolution of landforms on Earth?
1. Movement of magma within the Earth
2. Growth and decay of vegetation
3. Erosion and deposition
4. Frost action
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
Geological folds are undulations or waves of the stratified rocks of the Earth’s crust. Consider the following statements in the context of mechanisms contributing to geological folding:
1. Hydrostatic and pore pressure
2. Temperature gradient on the surface of the Earth
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
Consider the following statements about rock formation:
1. Magnetically susceptible minerals get aligned to the Earth’s magnetic field during the period of rock formation.
2. Foliated metamorphic rocks are formed within the Earth’s interior under extremely high pressures that arc unequal in different directions.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
Consider the following statements:
1. Rocks from which minerals are mined are known as ores.
2. Kalgoorlie and Coolgardie areas of western Australia have the largest deposits of gold.
3. The Katanga Plateau located in the Democratic Republic of Congo(DRC) is known for rich deposits of Copper.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
The oldest rocks in the world can be found in which of these regions?
Consider the following statements:
1. Granite is mainly made up of quartz, feldspar and mica.
2. Quartz is more quickly weathered than feldspar.
3. Regolith is the mineral remains of the decomposed rocks which form the basis of soil.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are incorrect?
What is/are the difference(s) between extrusive and intrusive rocks?
1. Extrusive rocks are formed from magma, whereas intrusive rocks are formed from lava.
2. Extrusive rocks arc fine-grained, whereas intrusive rocks arc coarse-grained.
3. Extrusive rocks form over a much longer duration of time compared to intrusive rocks.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
Consider the following statements:
1. Generally metallic minerals are found in igneous and metamorphic rock formations that form large plateaus.
2. Sedimentary rock formations of plains and young fold mountains contain non-metallic minerals.
3. Sedimentary rocks can be formed organically also.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
Consider the following statements about rocks:
1. Igneous rocks arc also called as primary rocks.
2. Igneous and sedimentary rocks can change into metamorphic rocks under great heat and pressure.
3. Sandstone is a metamorphic rock.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Which of these rocks make up for large portions of the crust of Earth?
1. Granitic rocks
2. Basaltic rocks
3. Pumice rocks
4. Obsidian rocks
Choose the correct answer from the following codes:
Consider the following statements about igneous rocks:
1. They are generally crystalline.
2. They occur in layers and often contain fossils.
3. Igneous rocks are always acidic.
Choose the correct answer using the codes below:
Consider the following pairs:
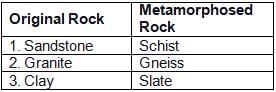
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?














