|
The widespread use of iron in eastern Uttar Pradesh and western Bihar from the sixth century B.C. led to the formation of ___ states. |
Card: 1 / 40 |
|
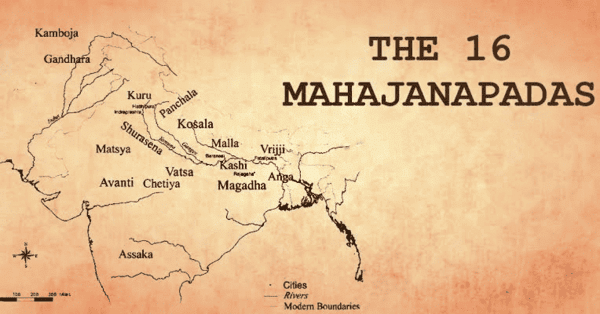
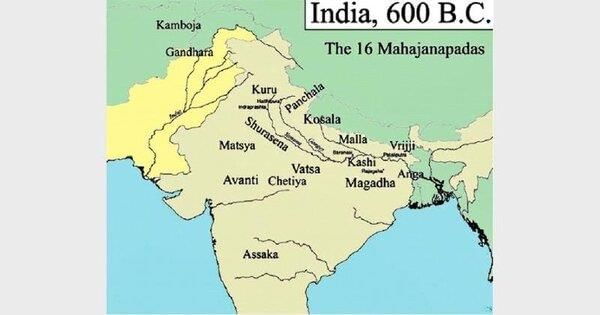
True or False: The Mahajanapadas included 16 large states during the Buddha's age, primarily located north of the Vindhyas. |
Card: 3 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The powerful state that emerged as the leading Mahajanapada was ___, which included districts like Patna and Gaya. |
Card: 5 / 40 |
|
True or False: The capital of the Malla kingdom was Kushinara, which is known as the place of Gautama Buddha's passing away. |
Card: 9 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The capital of the Vatsa kingdom was ___, located along the bank of the Yamuna. |
Card: 13 / 40 |
|
True or False: The Kurus and Panchalas were emerging states of great political importance during the time of the Mahajanapadas. |
Card: 15 / 40 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
True or False: Ajatashatru was successful in his conflicts with both Kashi and Koshala. |
Card: 21 / 40 |
|
Ajatashatru used advanced war tactics including a ___ and a ___ attached chariot. |
Card: 23 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The fertile alluvial soil in Magadha supported the cultivation of various crops, particularly ___. |
Card: 31 / 40 |
|
Economic prosperity, driven by the rise of towns and the use of coins, enabled the Magadhan princes to levy tolls on trade, accumulating wealth for maintaining their armies.  |
Card: 34 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: Magadha pioneered the use of ___ on a large scale in warfare, which was crucial for storming fortresses. |
Card: 35 / 40 |
|
True or False: The social structure of Magadha was homogenous and did not include groups looked down upon by orthodox society. |
Card: 37 / 40 |
|
False. The social structure was unorthodox, including groups like the Kiratas and Magadhas, who were initially marginalized.  |
Card: 38 / 40 |
|
Agricultural fertility was critical as it provided the necessary resources to support a large population and army, enabling sustained military campaigns and economic stability. |
Card: 40 / 40 |