|
The Treaty of Tordesillas in 1494 divided the non-Christian world between which two countries? |
Card: 1 / 40 |
|
True or False: The fall of Constantinople in 1453 allowed for increased trade routes between Europe and India. |
Card: 3 / 40 |
|
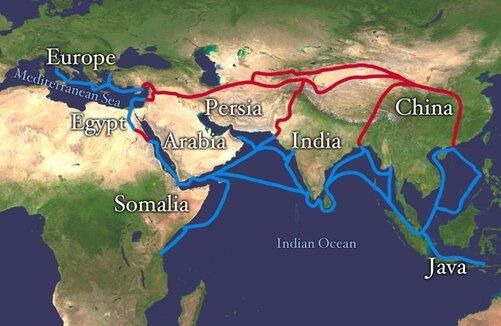
False. The fall of Constantinople led to a decline in direct contact and made the Red Sea trade route a lucrative monopoly for Islamic rulers.  |
Card: 4 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Portuguese exploration was significantly promoted by ___, known as the 'Navigator.' |
Card: 5 / 40 |
|
The Blue Water Policy advocated for the establishment of a territorial empire in India. True or False? |
Card: 7 / 40 |
|
False. The Blue Water Policy opposed the establishment of a territorial empire in India, favoring maritime supremacy and commercial activities. |
Card: 8 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: King Ferdinand I of Portugal appointed a governor in India for a duration of ___ years. |
Card: 9 / 40 |
|
What was the primary goal of Francisco de Almeida's appointment as governor in India? |
Card: 11 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: Upon arrival at Cochin, Almeida discovered that Portuguese traders at Quilon had been ___. |
Card: 13 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: Only ___ ships left when Francisco de Almeida arrived at Cochin. |
Card: 15 / 40 |
|
True or False: Goa was initially under the control of the Portuguese before it became their main settlement in India. |
Card: 19 / 40 |
|
False. Goa was taken from the Sultan of Bijapur by Francisco de Almeida in 1510. 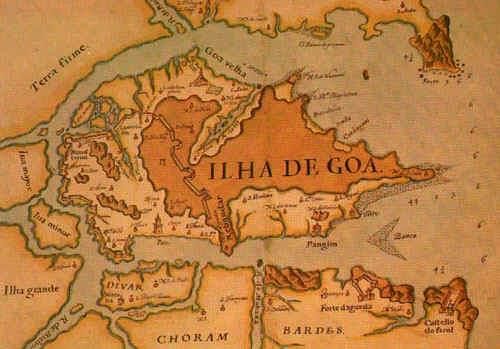 |
Card: 20 / 40 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
The Portuguese established a factory at Calicut in ___ after negotiations with local rulers. |
Card: 21 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Portuguese aimed to destroy Muslim trade by targeting key locations such as ___ and ___. |
Card: 25 / 40 |
|
True or False: The Portuguese maintained a tolerant religious policy towards Muslims in India. |
Card: 27 / 40 |
|
False. The Portuguese were intolerant toward Muslims and had a zeal to promote Christianity.  |
Card: 28 / 40 |
|
Fill in the blank: The Portuguese lost their monopoly on trade in India largely due to the rise of the ___ and ___ as significant commercial powers. |
Card: 29 / 40 |
|
What role did Captain William Hawkins play in the decline of Portuguese influence in India? |
Card: 31 / 40 |
|
He was appointed as a mansabdar by Jahangir, which signified a shift in political alliances away from the Portuguese.  |
Card: 32 / 40 |
|
True or False: The Dutch founded their first factory in India in 1605 at Masulipatnam. |
Card: 35 / 40 |
|
The Dutch established their principal factories in India at Surat, Bimlipatam, and ___. |
Card: 37 / 40 |
|
True or False: The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824 AD resulted in the Dutch retaining control of their possessions in India. |
Card: 39 / 40 |
|
False. The treaty required the Dutch to ensure the transfer of their properties to the British, leading to the loss of all commercial sites in India by 1825. 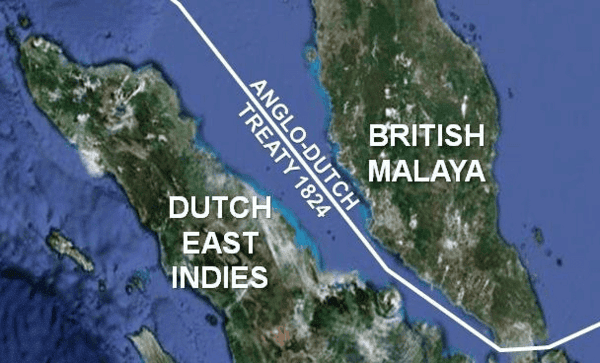 |
Card: 40 / 40 |