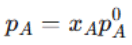|
Card: 2 / 38 |
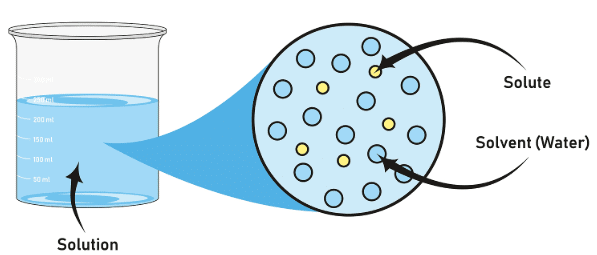
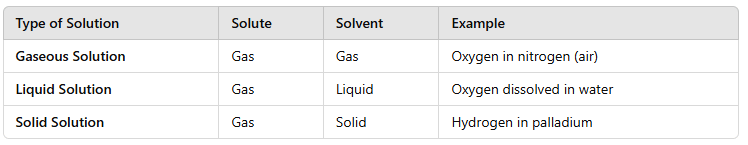
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. The solvent is present in a larger amount and dissolves the solute. |
|
Card: 6 / 38 |
Concentration is the amount of solute present in a given amount of solvent or solution. |
|
Card: 10 / 38 |
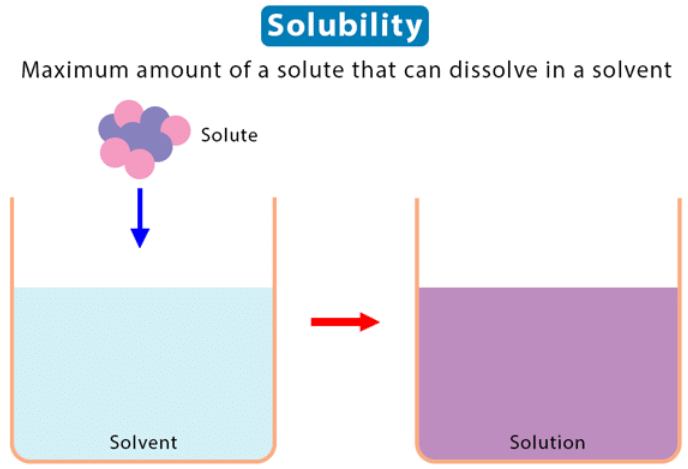
Solubility is the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent at a specific temperature and pressure. |
|
Card: 12 / 38 |
|
|
Card: 14 / 38 |
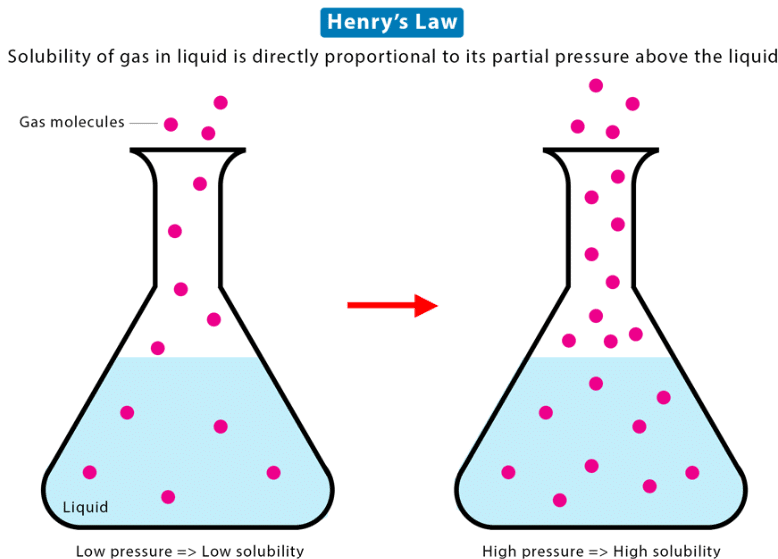
Henry’s Law states that at constant temperature, the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas above the liquid. |
|
Card: 16 / 38 |
p=KHx where:
|
|
Card: 18 / 38 |
Used to increase CO2 solubility in soft drinks by applying high pressure. Scuba divers experience decompression sickness (bends) due to nitrogen gas bubbles forming in blood at low pressures. |
|
Card: 20 / 38 |
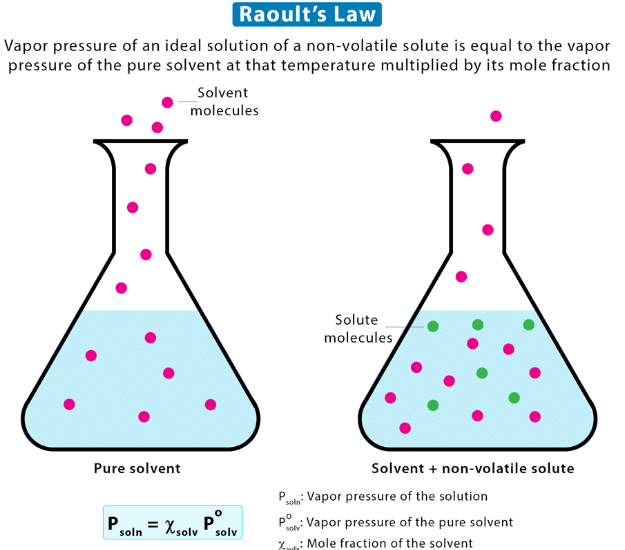
Raoult’s Law states that the partial vapor pressure of a volatile component in a solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction in the solution. |
|
Card: 22 / 38 |
pA = Partial vapor pressure of component A, xA = Mole fraction of A, pA0 = Vapor pressure of pure A. |
|
Card: 24 / 38 |
Raoult’s Law is a special case of Henry’s Law when the proportionality constant (KH) = vapor pressure of pure solvent. |
|
Card: 26 / 38 |
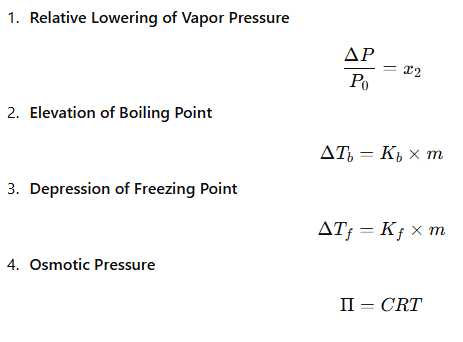
Colligative properties are properties of solutions that depend only on the number of solute particles, not their nature. |
|
Card: 30 / 38 |
The van’t Hoff factor (i) accounts for dissociation or association of solutes in solutions. |
|
Card: 34 / 38 |
i > 1 for solutes that dissociate (e.g., NaCl → Na⁺ + Cl⁻, i = 2). i < 1 for solutes that associate (e.g., Acetic acid dimerizes in benzene). |
|
Card: 36 / 38 |
Reverse osmosis (RO) is the process of forcing solvent molecules through a semi-permeable membrane by applying pressure greater than the osmotic pressure. |
|
Card: 38 / 38 |
|
 Completed! Keep practicing to master all of them. |